十五、管道符
复制代码
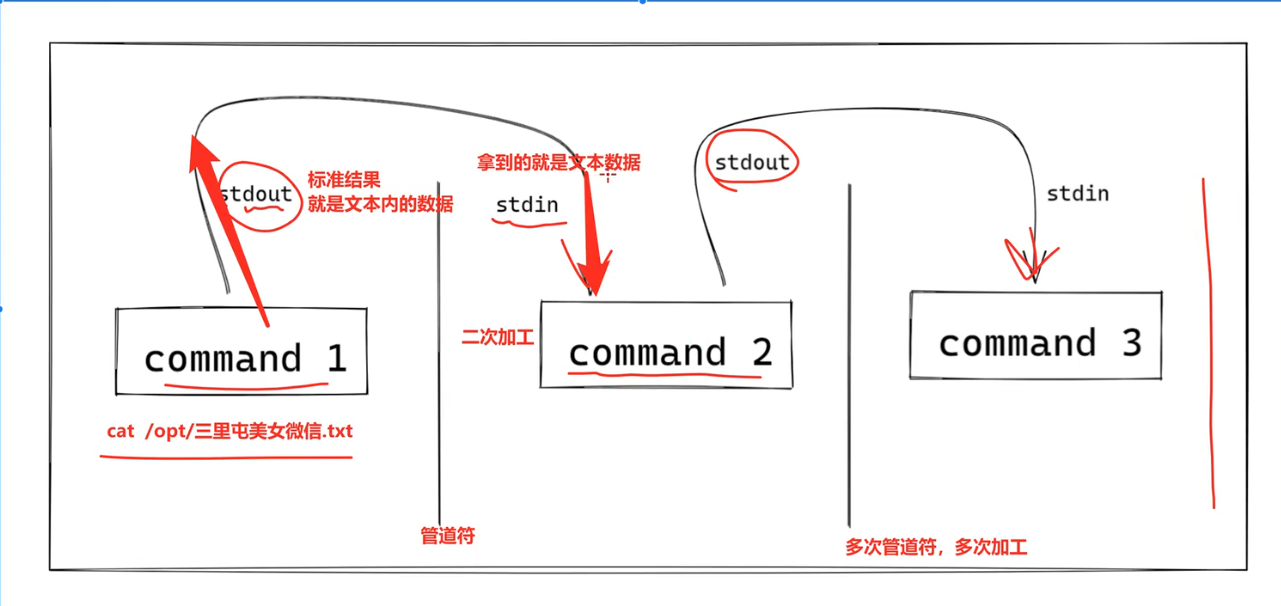
管道符和grep命令结合的是最多的
管道符的标准定义:
管道是一种通信机制,常用语进程之间的通信。它表现出来的形式:将前一个的标准输出(stdout)作为后面命令的标准输入(stdin)
复制代码
利用grep和管道符来查看用户信息
用户信息存储在 /etc/passwd中
我们自己创建的用户的ID号从1000开始
zwj:x:1002:1003::/home/zwj:/bin/bash
通过grep命令可以确定用户是不是存在
grep username /etc/passwd
比方说我想要查找xuruizhao用户的信息
有两种方法
1、不用管道符
grep username /etc/passwd
2、用管道符
[root@bogon ~]# cat /etc/passwd | grep 'xuruizhao'
xuruizhao:x:1001:1001::/home/xuruizhao:/bin/bash
管道符结合find命令搜索信息
找出系统中所有的.txt的文件,找到在/home目录下的文件
[root@bogon ~]# find / -name '*.txt' ### 找到根目录下所有的txt文件
[root@bogon ~]# find / -name '*.txt' | grep '/home' ### 在、home目录下有哪些txt的文件
有一个问题:我们通过find命令找到的仅仅是一行行的文本,并不是把文件筛选出来了,也可以理解为是筛选出了文件名,并不是文件,我们不可以通过find命令找到的文件名去对对应的文件进行文件操作
[root@bogon opt]# find / -name '*.txt' | grep 'apple' ## 这个命令是过滤出文件名中含有apple的.txt文件,并不是文件内容中含有apple的文件,因为我们不可以对通过find命令查找出的文件名对文件进行操作,我们只可以对find所找到的文本(文件名)进行操作
那么我们如何可以通过find命令去对文件的内容进行过滤,我们需要使用到xargs命令
grep的参数
1、-n 显示对应内容存在的行号
[root@localhost opt]# grep -n 'apple' ./a*
./a1:4:apple
./a2:1:apple
./a3:1:apple
2、-i 在查找内容时忽略大小写
[root@localhost opt]# grep -n -i 'apple' ./a*
./a1:2:APple
./a1:4:apple
./a2:1:apple
./a3:1:apple
【1】使用管道符来查看进程
复制代码
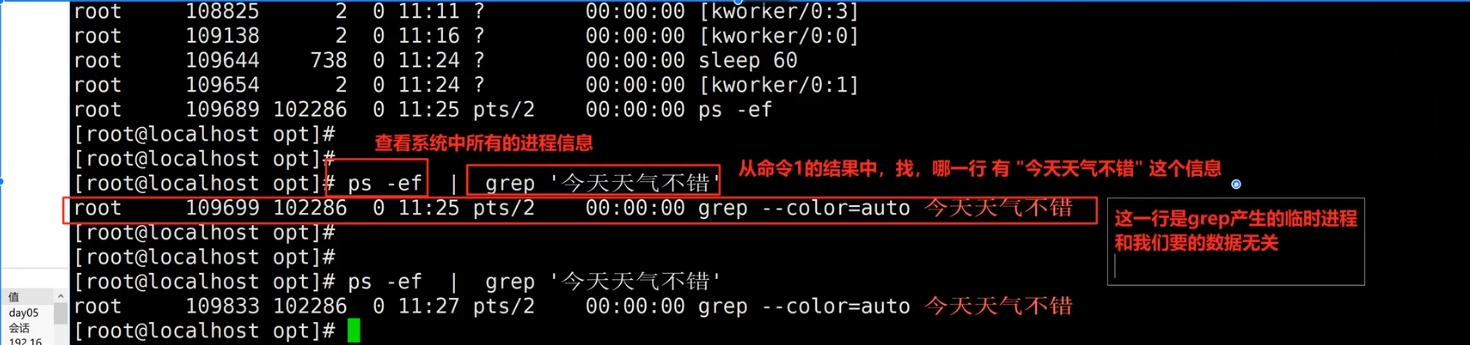
ps -ef 是查看系统中所有的进程,我们可以将得到的所有的进程写入一个新文件中,再去通过grep和管道符进行筛选
如果系统中不存在这个进程,使用
ps -ef | grep 所需要查的进程 命令,如下图的结果,这并不是对应程序的进程,而是grep在使用时产生的临时进程,输出结果的第二个数字是进程的ID号,临时进程的ID号在每一次建立时是会不断发生变化的,由此可以判断出这是一个临时进程。
[root@localhost opt]# cat new.txt | grep -n 'root'
这样即可查看出想要查询的程序了
【2】查看系统的端口
复制代码
需要学习查看系统端口的命令,和ps -ef 一样,都是查看某一种系统资源的
netstat -tunlp ### 这个组合参数是查看系统上所有的端口信息
[root@localhost opt]# netstat -tunlp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1490/master
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1351/sshd: root@pts
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 634/rpcbind
tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1581/dnsmasq
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1126/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1128/cupsd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1490/master
tcp6 0 0 ::1:6010 :::* LISTEN 1351/sshd: root@pts
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 634/rpcbind
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 1126/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 1128/cupsd
。。。。。
【3】检查文件个数
复制代码
比如检查/var/log 中log文件的个数
[root@localhost opt]# find /var/log -name '*.log' | wc -l
40
判断出系统中用多少个txt文件
[root@localhost opt]# find / -name '*.txt' | wc -l
1207
统计系统的统计用户数量
[root@localhost opt]# cat /etc/passwd | wc -l
46
【4】、管道符和xargs结合使用
sh
复制代码
将前一个命令得到结果通过管道符传递给xargs命令进行二次加工,xargs的二次加工是真正意义上的二次加工,而不是对前一个命令得到的结果的文本进行处理,而是对文本所对行的文件进行处理。
xargs可以与find命令、ls命令等进行搭配使用。
-i 参数:可以使用{}来表示前一个命令得到的结果(文件)
1、通过xargs对文件进行批量备份
sh
复制代码
我们对/opt目录下的.txt文件进行备份
[root@bogon opt]# find /opt -name '*.txt' | xargs -i cp {} {}.apk
### 将find得到的结果传递给xargs 进行重命名操作,{}代表find得到的文件内容
[root@bogon opt]# ll
total 60
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 159 Nov 9 14:52 1
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 10.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 10.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 1.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 1.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 2.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 2.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 3.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 3.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 4.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 4.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 5.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 5.txt.apk
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:14 6.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:16 6.txt.apk
。。。
2、通过xargs对文件进行重命名
复制代码
将/opt目录下的。txt文件改为.log文件
[root@bogon opt]# find /opt -name '*.txt' | xargs rename .txt .log {}
[root@bogon opt]# ll
total 8
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 10.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 1.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 2.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 3.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 4.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 5.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 6.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 7.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 8.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 Nov 27 14:37 9.log
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 91 Nov 17 22:44 gushishi
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 51 Nov 27 14:38 he
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 269 Nov 9 17:09 practice.tar.gz
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 6 Sep 10 16:18 rh
rename命令是重命名命令,
语法:rename 原字符串 新字符串 作用对象
3、查找系统中的txt文件中哪些存在apple内容
复制代码
[root@bogon opt]# find / -type f -name '*.txt' | xargs -i grep -l 'apple' {}
grep的-l参数:显示出这个内容在哪一个文件中
【5】、grep命令 1、grep 关键字 filename
sh
复制代码
[root@bogon opt]# grep '有' gushi.txt
借问酒家何处有
2、-n
sh
复制代码
显示行号
[root@bogon opt]# grep -n '有' gushi.txt ### 显示行号
5:借问酒家何处有
grep 不仅仅可以从文件中搜索数据,只要是文本他就可以进行搜索
3、grep从多个文件中搜索过滤
sh
复制代码
[root@bogon opt]# grep 'apple' ./* ### grep是不可查目录的
./a:apple
./a1:apple
./a2:apple
./a3:apple
grep: ./abc: Is a directory
grep: ./he: Is a directory
grep: ./rh: Is a directory
4、 -i
sh
复制代码
[root@bogon opt]# grep -i 'apple' ./*
./a:apple
./a1:APple
./a2:apple
./a3:apple
grep: ./abc: Is a directory
grep: ./he: Is a directory
grep: ./rh: Is a directory
5、-R
sh
复制代码
递归查找
[root@bogon opt]# grep -Rn 'passwd' /var/log
6、-v参数
sh
复制代码
反向过滤
[root@bogon opt]# df -Th | grep -v tmp
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/mapper/rhel-root xfs 37G 20G 18G 52% /
/dev/mapper/rhel-home xfs 19G 162M 18G 1% /home
/dev/nvme0n2p2 xfs 495M 29M 466M 6% /mnt/xfs
/dev/sr0 iso9660 13G 13G 0 100% /mnt/cdrom
/dev/nvme0n2p1 ext4 189M 14K 175M 1% /mnt/ext
/dev/nvme0n1p1 xfs 1014M 198M 817M 20% /boot
7、grep和正则结合使用
复制代码
*表示以什么开头
$表示以什么结尾
^$表示空行