文章目录
FSOP
介绍:
-
FSOP 是 File Stream Oriented Programming 的缩写,根据前面对 FILE 的介绍得知进程内所有的 _ IO_FILE 结构会使用 _ chain 域相互连接形成一个链表,这个链表的头部由_IO_list_all 维护。
-
FSOP 的核心思想就是劫持_IO_list_all 的值 来伪造链表和其中的_IO_FILE 项,但是单纯的伪造只是构造了数据还需要某种方法进行触发。FSOP 选择的触发方法 是调用_IO_flush_all_lockp ,这个函数会刷新_IO_list_all 链表 中所有项的文件流,相当于对每个 FILE 调用 fflush,也对应着会调用_IO_FILE_plus.vtable 中的_IO_overflow。
-
关键函数**_IO_flush_all_lockp**:
cint _IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock) { ... fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all; while (fp != NULL) { ... if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)) && _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF) { result = EOF; } ... } }
FOSP链执行流程:
malloc中unsorted bin出错会调用malloc_printerr 输出错误:
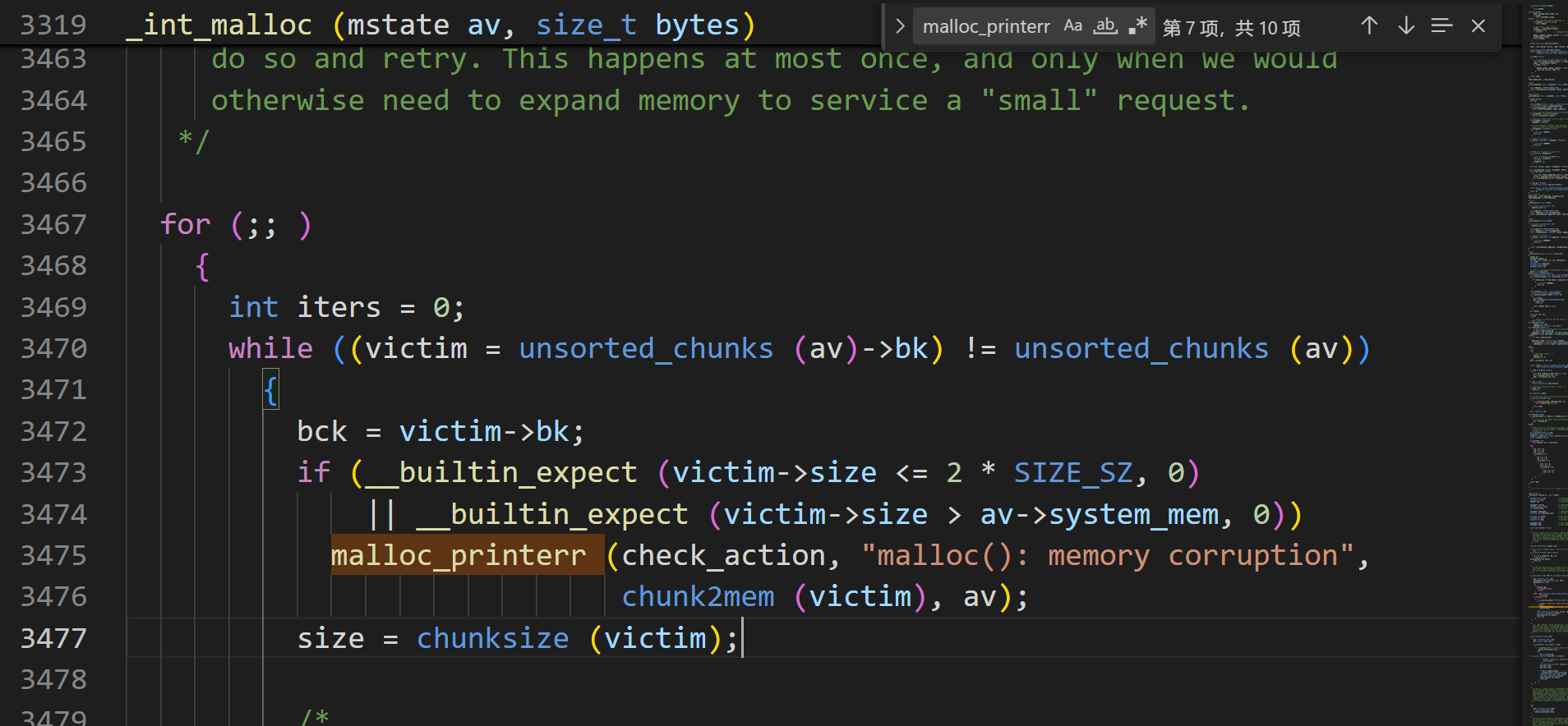
malloc_printerr 函数:

跟进__libc_message函数,最后也调用了abort函数:
c
/* Abort with an error message. */
void
__libc_message (int do_abort, const char *fmt, ...)
{
va_list ap;
int fd = -1;
va_start (ap, fmt);
#ifdef FATAL_PREPARE
FATAL_PREPARE;
#endif
/* Open a descriptor for /dev/tty unless the user explicitly
requests errors on standard error. */
const char *on_2 = __libc_secure_getenv ("LIBC_FATAL_STDERR_");
if (on_2 == NULL || *on_2 == '\0')
fd = open_not_cancel_2 (_PATH_TTY, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY);
if (fd == -1)
fd = STDERR_FILENO;
struct str_list *list = NULL;
int nlist = 0;
const char *cp = fmt;
while (*cp != '\0')
{
/* Find the next "%s" or the end of the string. */
const char *next = cp;
while (next[0] != '%' || next[1] != 's')
{
next = __strchrnul (next + 1, '%');
if (next[0] == '\0')
break;
}
/* Determine what to print. */
const char *str;
size_t len;
if (cp[0] == '%' && cp[1] == 's')
{
str = va_arg (ap, const char *);
len = strlen (str);
cp += 2;
}
else
{
str = cp;
len = next - cp;
cp = next;
}
struct str_list *newp = alloca (sizeof (struct str_list));
newp->str = str;
newp->len = len;
newp->next = list;
list = newp;
++nlist;
}
bool written = false;
if (nlist > 0)
{
struct iovec *iov = alloca (nlist * sizeof (struct iovec));
ssize_t total = 0;
for (int cnt = nlist - 1; cnt >= 0; --cnt)
{
iov[cnt].iov_base = (char *) list->str;
iov[cnt].iov_len = list->len;
total += list->len;
list = list->next;
}
written = WRITEV_FOR_FATAL (fd, iov, nlist, total);
if (do_abort)
{
total = ((total + 1 + GLRO(dl_pagesize) - 1)
& ~(GLRO(dl_pagesize) - 1));
struct abort_msg_s *buf = __mmap (NULL, total,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,
MAP_ANON | MAP_PRIVATE, -1, 0);
if (__glibc_likely (buf != MAP_FAILED))
{
buf->size = total;
char *wp = buf->msg;
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < nlist; ++cnt)
wp = mempcpy (wp, iov[cnt].iov_base, iov[cnt].iov_len);
*wp = '\0';
/* We have to free the old buffer since the application might
catch the SIGABRT signal. */
struct abort_msg_s *old = atomic_exchange_acq (&__abort_msg,
buf);
if (old != NULL)
__munmap (old, old->size);
}
}
}
va_end (ap);
if (do_abort)
{
BEFORE_ABORT (do_abort, written, fd);
/* Kill the application. */
abort ();
}
}跟进abort函数,其中调用了fflush函数:
c
/* Cause an abnormal program termination with core-dump. */
void
abort (void)
{
struct sigaction act;
sigset_t sigs;
/* First acquire the lock. */
__libc_lock_lock_recursive (lock);
/* Now it's for sure we are alone. But recursive calls are possible. */
/* Unlock SIGABRT. */
if (stage == 0)
{
++stage;
if (__sigemptyset (&sigs) == 0 &&
__sigaddset (&sigs, SIGABRT) == 0)
__sigprocmask (SIG_UNBLOCK, &sigs, (sigset_t *) NULL);
}
/* Flush all streams. We cannot close them now because the user
might have registered a handler for SIGABRT. */
if (stage == 1)
{
++stage;
fflush (NULL);
}
······
}跟进fflush函数,fflush是一个宏定义,调用了IO_fflush函数,且参数是NULL:

继续跟进IO_fflush(NULL),由于传入的参数为NULL,所以会调用_IO_flush_all函数:
c
int
_IO_fflush (_IO_FILE *fp)
{
if (fp == NULL)
return _IO_flush_all ();
else
{
int result;
CHECK_FILE (fp, EOF);
_IO_acquire_lock (fp);
result = _IO_SYNC (fp) ? EOF : 0;
_IO_release_lock (fp);
return result;
}
}跟进_IO_flush_all函数,_IO_flush_all_lockp调用了_IO_flush_all_lockp(1):
c
int
_IO_flush_all (void)
{
/* We want locking. */
return _IO_flush_all_lockp (1);
}跟进_IO_flush_all_lockp(1),而 _IO_flush_all_lockp就是这条FILE终点:
c
int
_IO_flush_all_lockp (int do_lock)
{
int result = 0;
struct _IO_FILE *fp;
int last_stamp;
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
__libc_cleanup_region_start (do_lock, flush_cleanup, NULL);
if (do_lock)
_IO_lock_lock (list_all_lock);
#endif
last_stamp = _IO_list_all_stamp;
fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all;//这里fp取到了_IO_list_all 这里fp直接指向了_IO_2_1_stderr_首地址
while (fp != NULL)//进入循环
{
run_fp = fp;
if (do_lock)
_IO_flockfile (fp);
if (((fp->_mode <= 0 && fp->_IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base)
#if defined _LIBC || defined _GLIBCPP_USE_WCHAR_T
|| (_IO_vtable_offset (fp) == 0
&& fp->_mode > 0 && (fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_ptr
> fp->_wide_data->_IO_write_base))
#endif
)
&& _IO_OVERFLOW (fp, EOF) == EOF)//这里经过前面的判断后调用了_IO_OVERFLOW(fp,EOF)
result = EOF;
if (do_lock)
_IO_funlockfile (fp);
run_fp = NULL;
if (last_stamp != _IO_list_all_stamp)
{
/* Something was added to the list. Start all over again. */
fp = (_IO_FILE *) _IO_list_all;
last_stamp = _IO_list_all_stamp;
}
else
fp = fp->_chain;//这里使用FILE结构中的_chain来更新fp,直到fp为空才退出循环,所以会刷新_IO_list_all 链表中所有项的文件流
}
#ifdef _IO_MTSAFE_IO
if (do_lock)
_IO_lock_unlock (list_all_lock);
__libc_cleanup_region_end (0);
#endif
return result;
}查看_IO_OVERFLOW(fp, EOF)定义,以及最后的:
c
//libc_2.23 的定义
define _IO_OVERFLOW(FP, CH) JUMP1 (__overflow, FP, CH)
define JUMP1(FUNC, THIS, X1) (_IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS)->FUNC) (THIS, X1)
define _IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS) (*(struct _IO_jump_t **) ((void *) &_IO_JUMPS_FILE_plus (THIS) + (THIS)->_vtable_offset))
//结合传入的参数转化后如下:相当于调用了fp的__overflow函数
define _IO_OVERFLOW(FP, CH) JUMP1 (__overflow, FP, CH)
define JUMP1(__overflow, FP, CH) (_IO_JUMPS_FUNC(FP)->__overflow) (FP, CH)
define _IO_JUMPS_FUNC(FP) (*(struct _IO_jump_t **) ((void *) &_IO_JUMPS_FILE_plus (FP) + (FP)->_vtable_offset))
//在libc_2.24后:_IO_JUMPS_FUNC的宏定义变化
define JUMP1(FUNC, THIS, X1) (_IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS)->FUNC) (THIS, X1)
define _IO_JUMPS_FUNC(THIS) (IO_validate_vtable (_IO_JUMPS_FILE_plus (THIS)))
/* Check if unknown vtable pointers are permitted; otherwise,
terminate the process. */
void _IO_vtable_check (void) attribute_hidden; //提前声明
/* Perform vtable pointer validation. If validation fails, terminate
the process. */
static inline const struct _IO_jump_t *
IO_validate_vtable (const struct _IO_jump_t *vtable)
{
/* Fast path: The vtable pointer is within the __libc_IO_vtables
section. */
uintptr_t section_length = __stop___libc_IO_vtables - __start___libc_IO_vtables;
const char *ptr = (const char *) vtable;
uintptr_t offset = ptr - __start___libc_IO_vtables;
if (__glibc_unlikely (offset >= section_length))
/* The vtable pointer is not in the expected section. Use the
slow path, which will terminate the process if necessary. */
_IO_vtable_check ();
return vtable;
}
void attribute_hidden _IO_vtable_check (void)
{
#ifdef SHARED
/* Honor the compatibility flag. */
void (*flag) (void) = atomic_load_relaxed (&IO_accept_foreign_vtables);
#ifdef PTR_DEMANGLE
PTR_DEMANGLE (flag);
#endif
if (flag == &_IO_vtable_check)
return;
/* In case this libc copy is in a non-default namespace, we always
need to accept foreign vtables because there is always a
possibility that FILE * objects are passed across the linking
boundary. */
{
Dl_info di;
struct link_map *l;
if (_dl_open_hook != NULL
|| (_dl_addr (_IO_vtable_check, &di, &l, NULL) != 0
&& l->l_ns != LM_ID_BASE))
return;
}
#else /* !SHARED */
/* We cannot perform vtable validation in the static dlopen case
because FILE * handles might be passed back and forth across the
boundary. Therefore, we disable checking in this case. */
if (__dlopen != NULL)
return;
#endif
__libc_fatal ("Fatal error: glibc detected an invalid stdio handle\n");
}
最后找函数地址时,使用了_vtable_offset 即 _IO_FILE 结构体的 vtable 指针,而vtable 指针指向的是一个虚表,所以相当于最后调用到了下面的_IO_file_overflow函数,并且传入的参数是fp指针,即文件的地址:
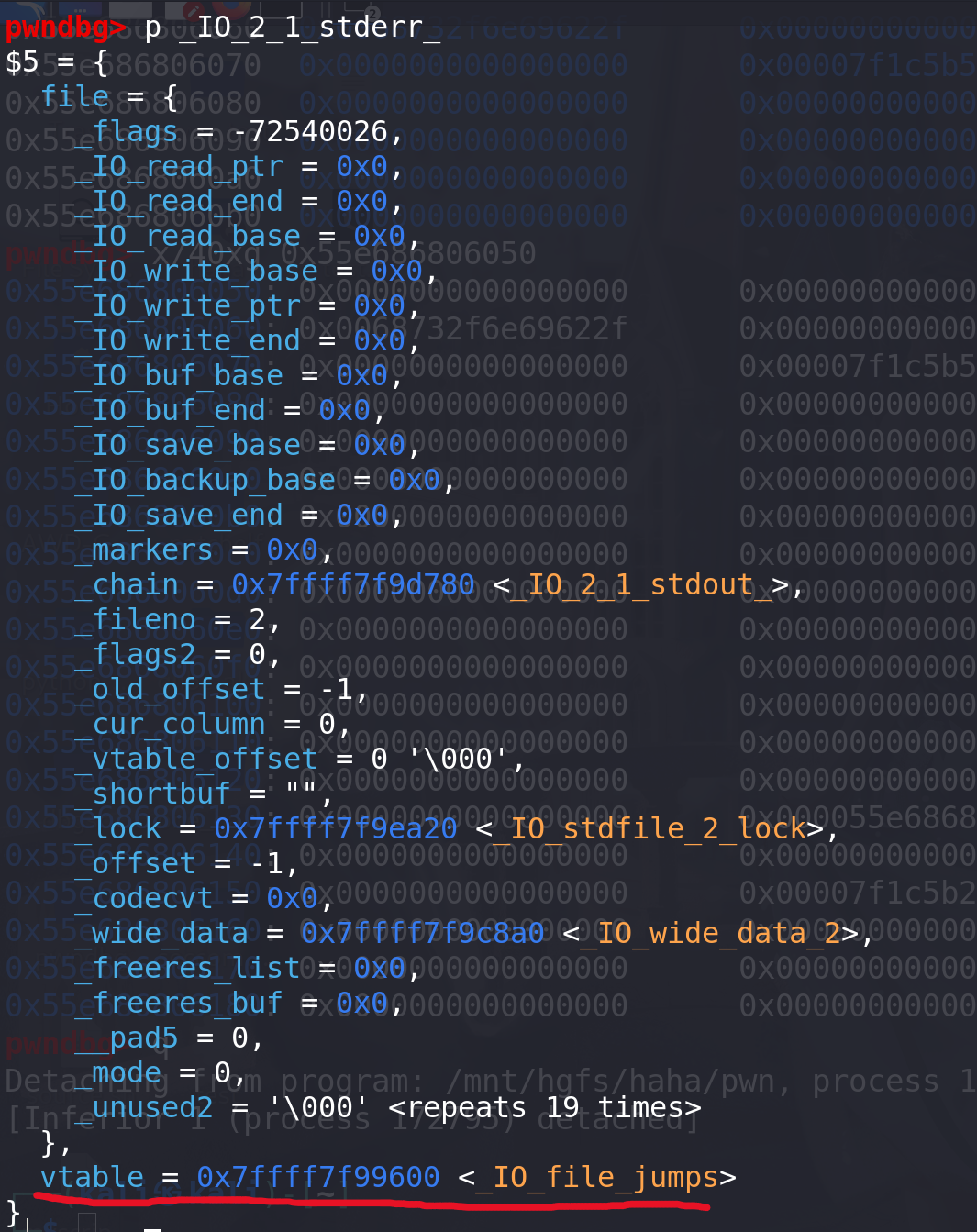

随意最后IO_FILE链为:malloc报错 ==> malloc_printerr ==> __libc_message ==> abort ==> fflush ==> IO_fflush ==> _IO_flush_all ==> _IO_flush_all_lockp ==> _IO_OVERFLOW(最后使用vtable 指向的虚表中的指针),
最后在_IO_flush_all_lockp中时有两个判断条件需要绕过,才能调用到_IO_OVERFLOW :
- fp->_mode <= 0
- fp-> _IO_write_ptr > fp->_IO_write_base
所以,在unsorted bin中构造的IO_FILE 要满足这两个条件即可,最后伪造虚表,并用system地址覆盖 掉_OVERFLOW指针,并在vtable位置伪造指针 ,指向这个虚表即可 。
源码调试过程
-
下面结合题目来调试这个过程,题目解析参考的这篇文章:House of Orange-CSDN博客,脚本和这篇文章完全一样,直接到最后一部调试malloc,直接断点到malloc:
-
此时堆上的布局如下,并且顺利进入malloc函数:
-
经过free_hook检查后进入到 _ int_malloc中分配chunk,传入的参数为main_arena地址,和申请的chunk大小:
-
进入 _int_malloc函数,先转化size的大小:
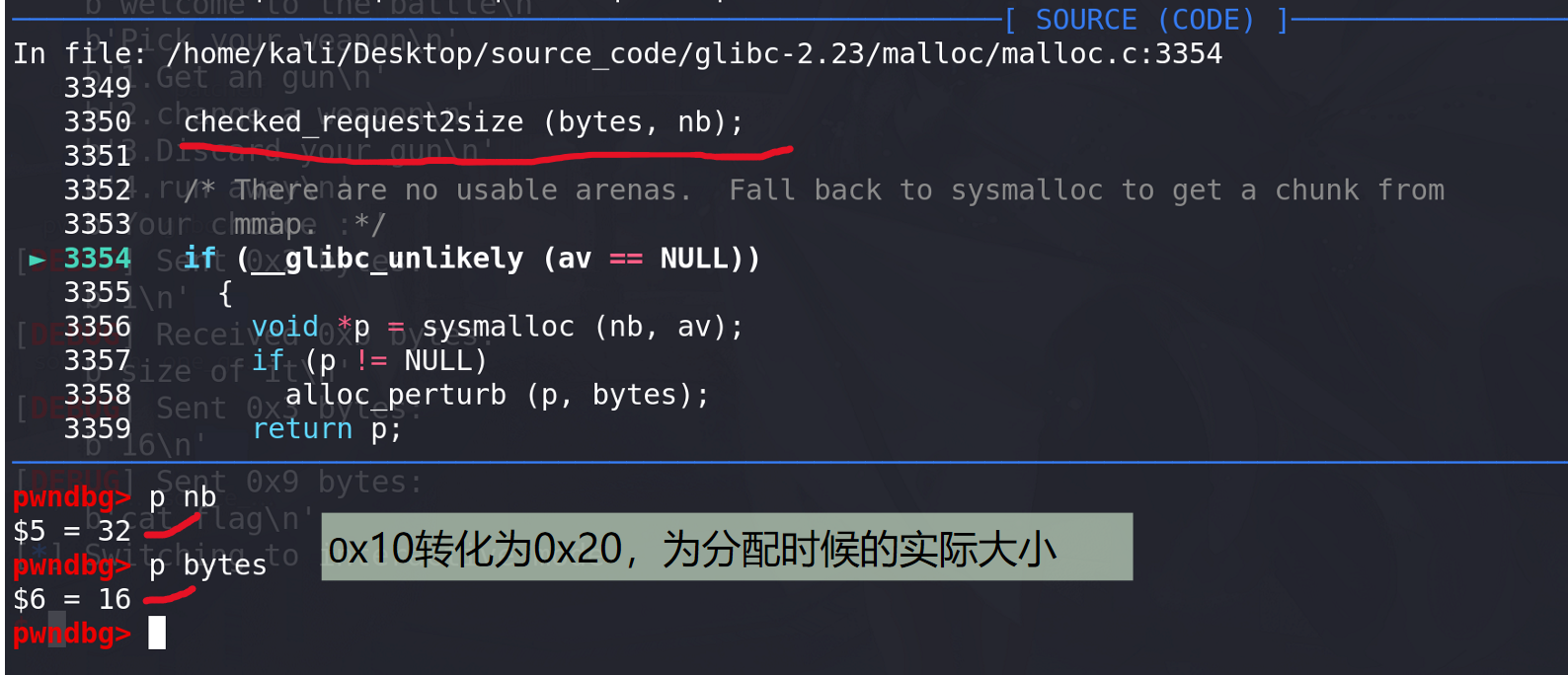
随后检查实际分配的大小与get_max_fast(0x80)比较,先访问fastbin:
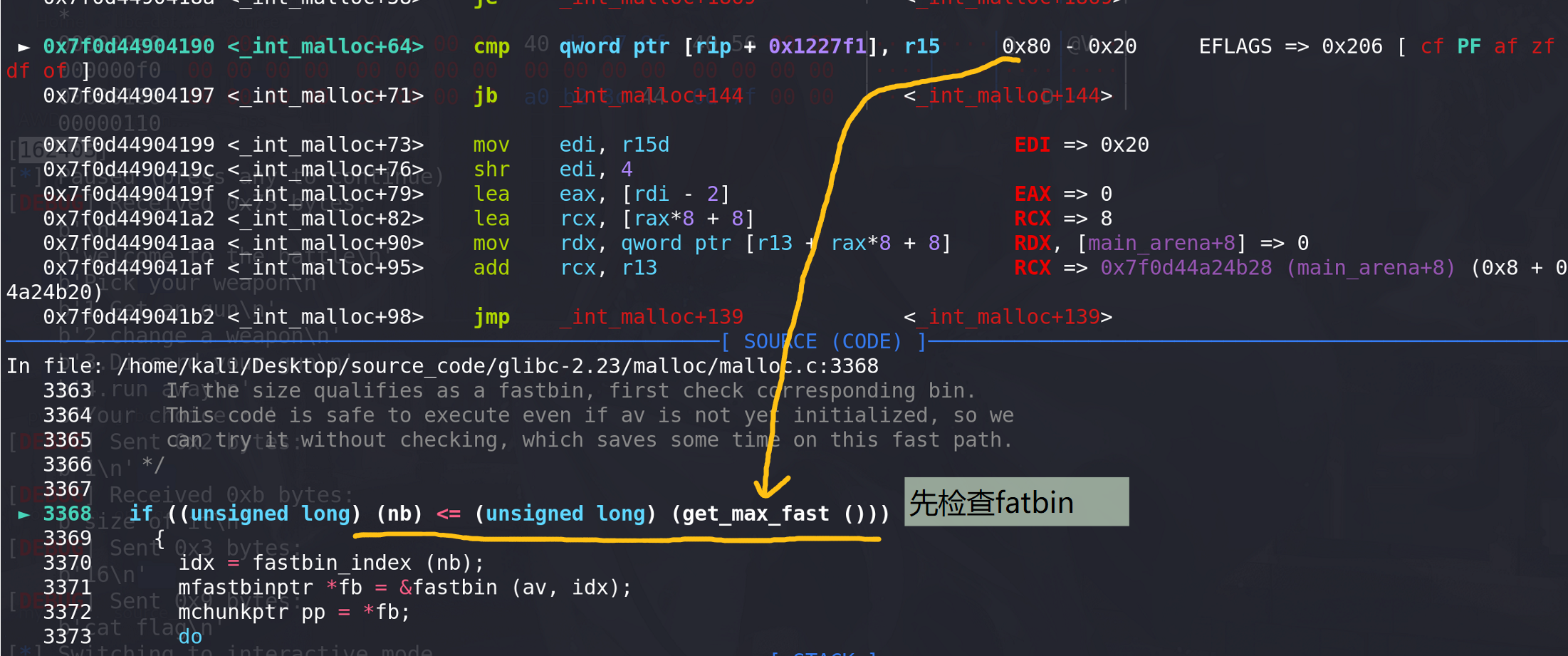
fatbin中没有剩余的chunk,接下来就访问small bin:
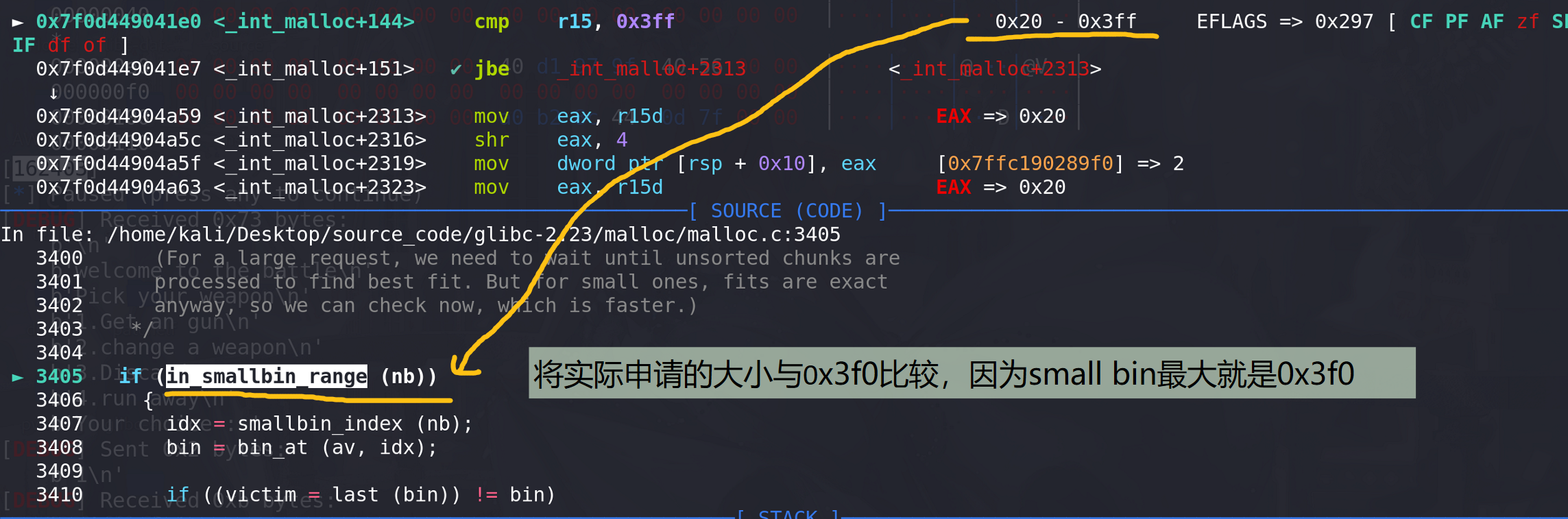
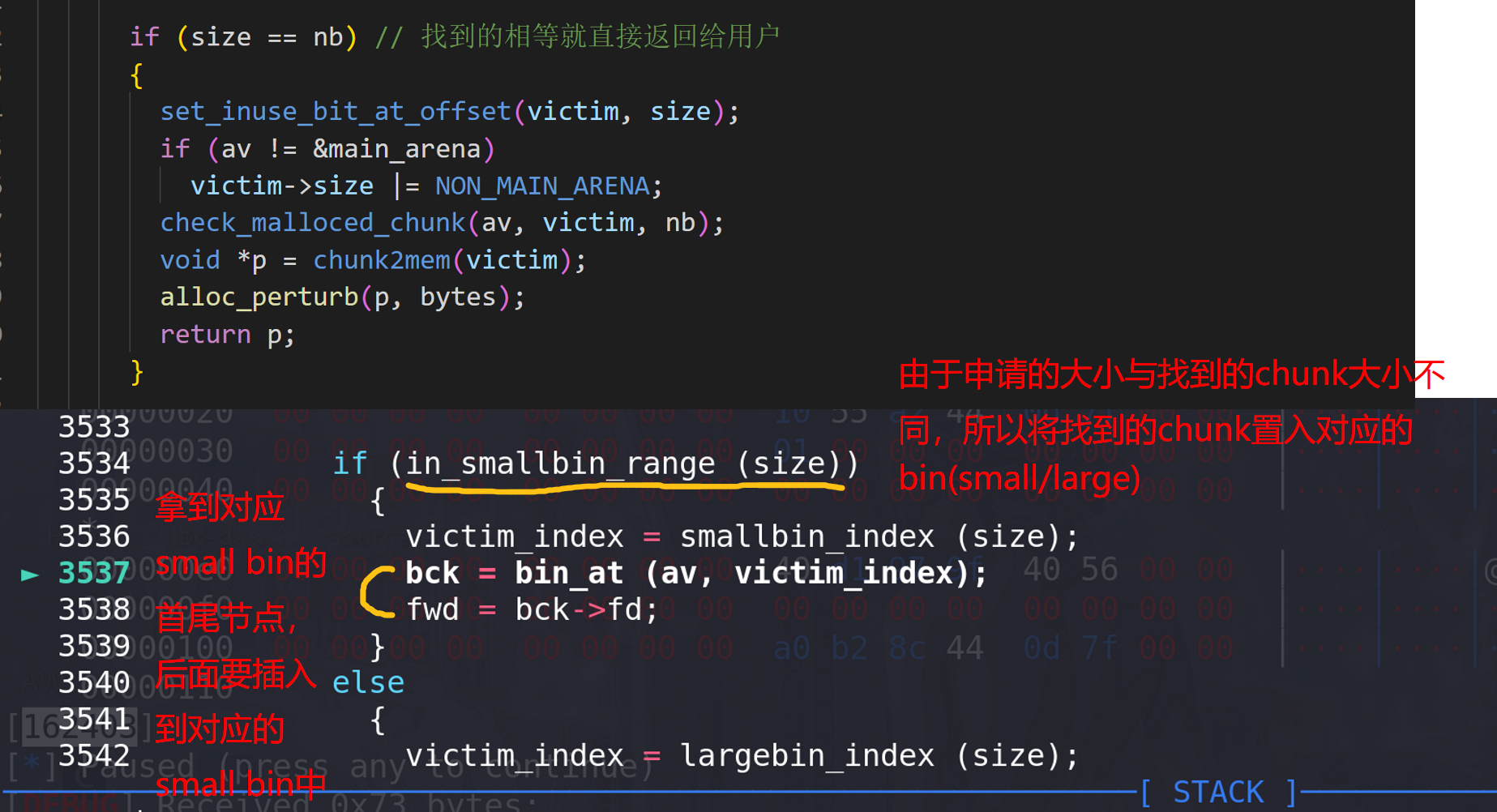
small bin中也没有剩余的chunk,下面进入到unsorted bin中查询:
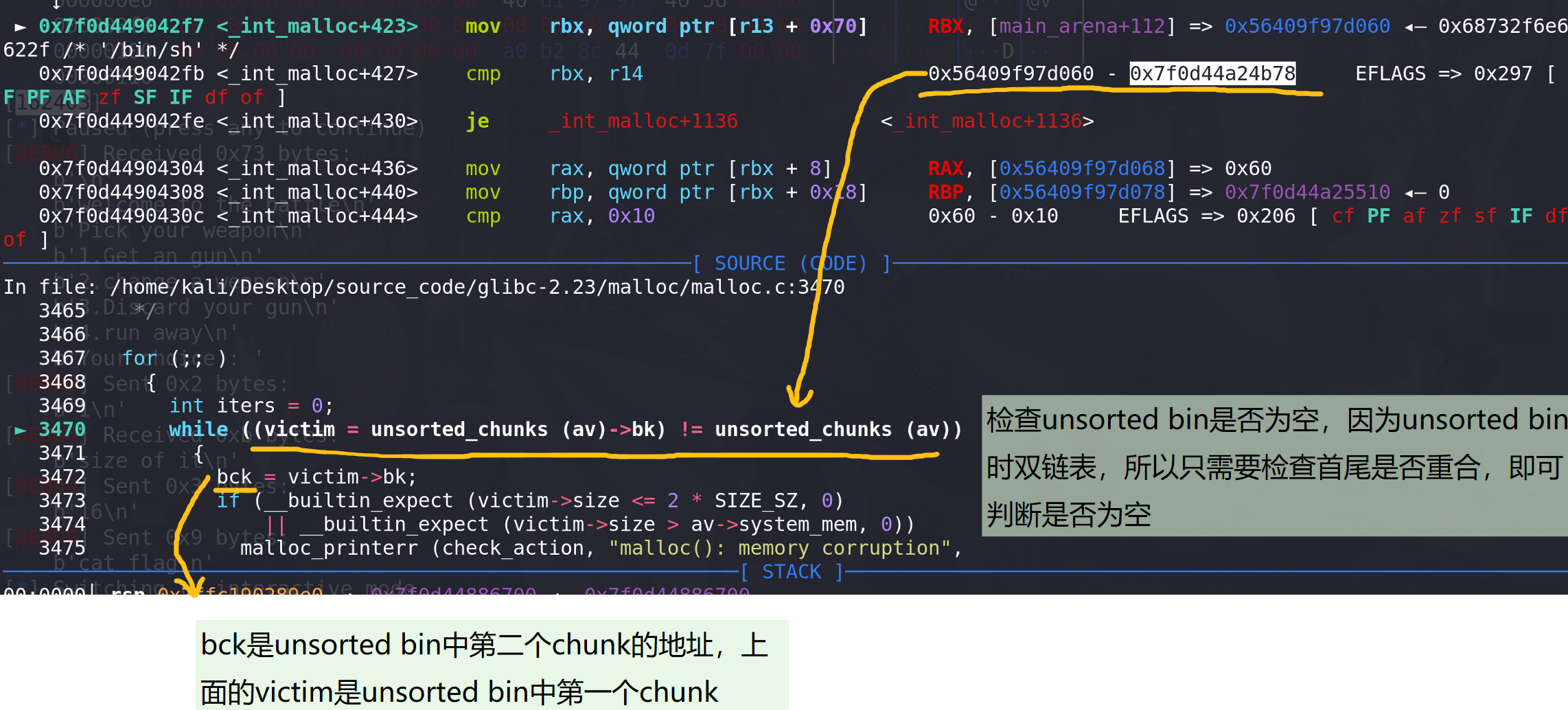
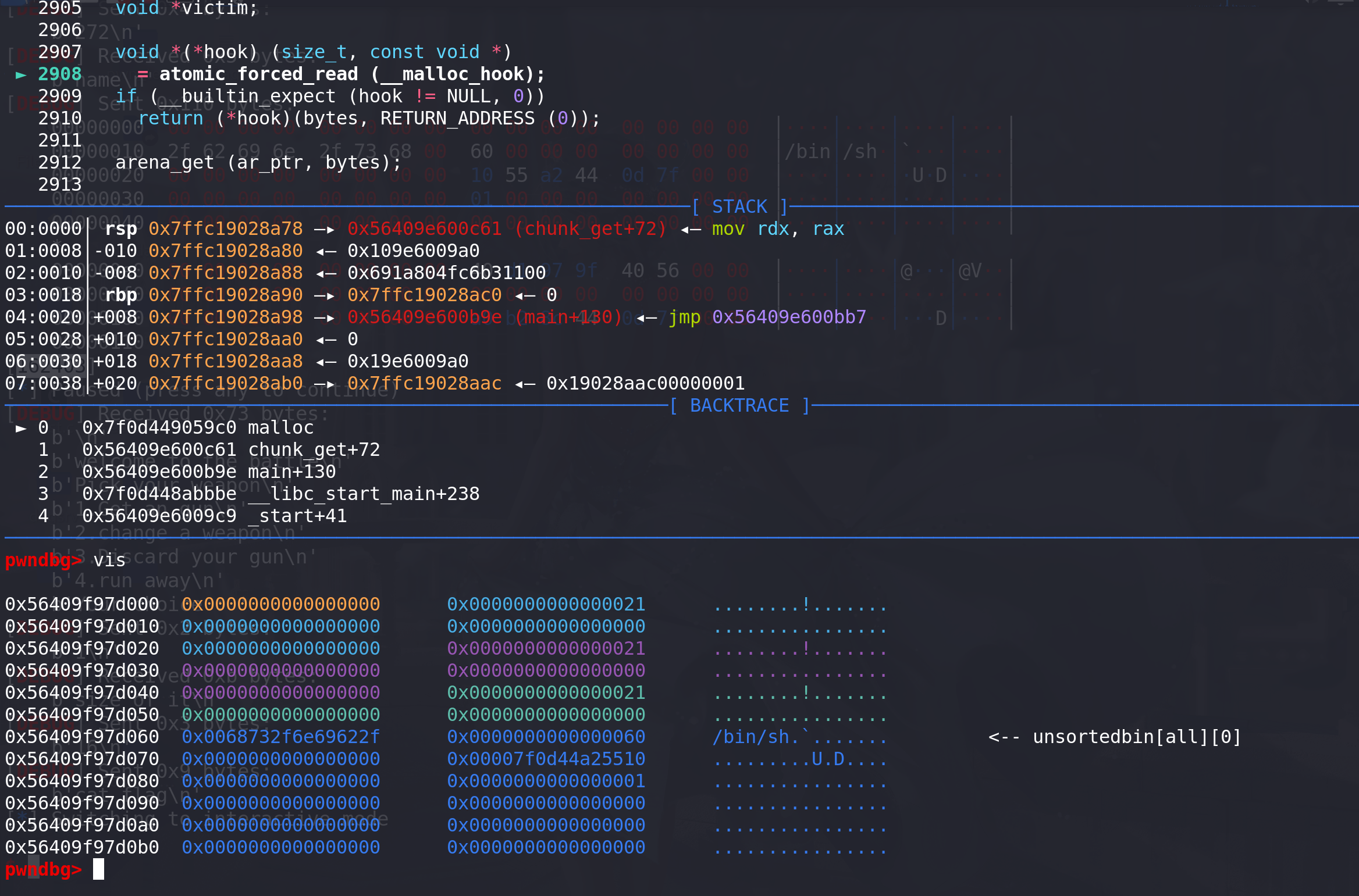
在unsorted bin中找到空闲chunk:
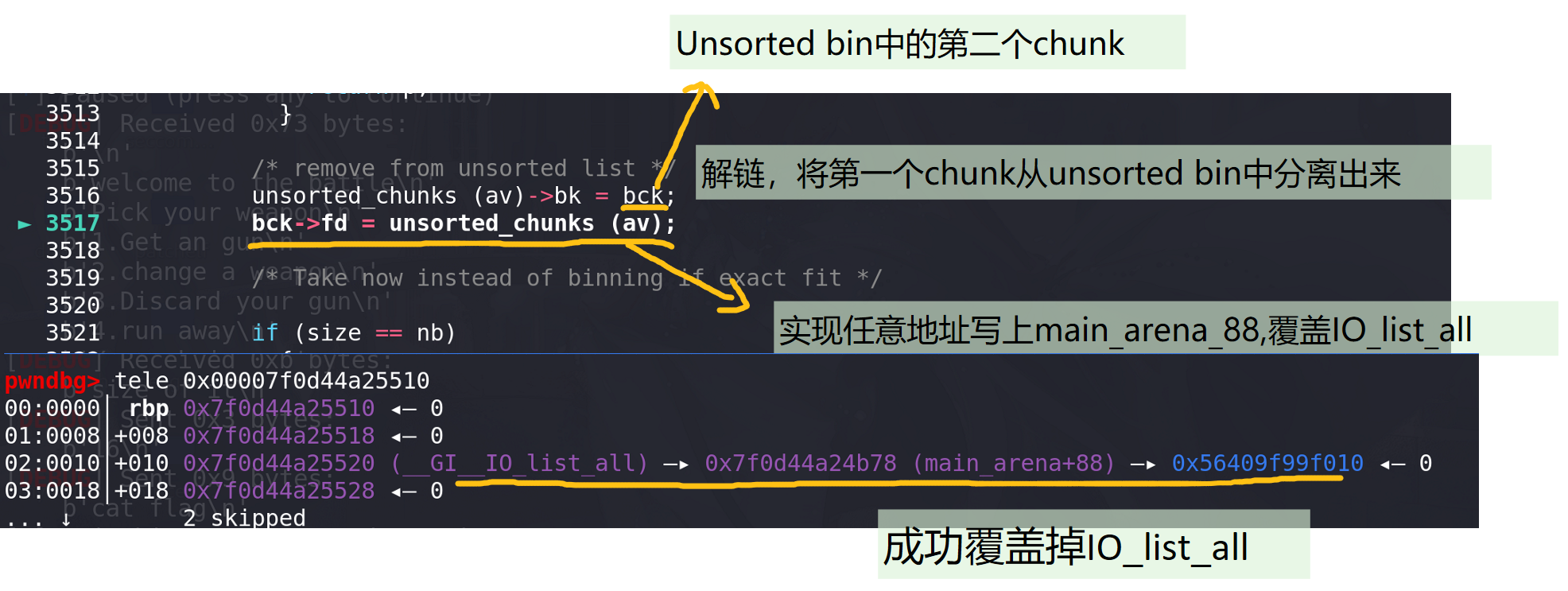
size != nb,所以先放入到small bin中:
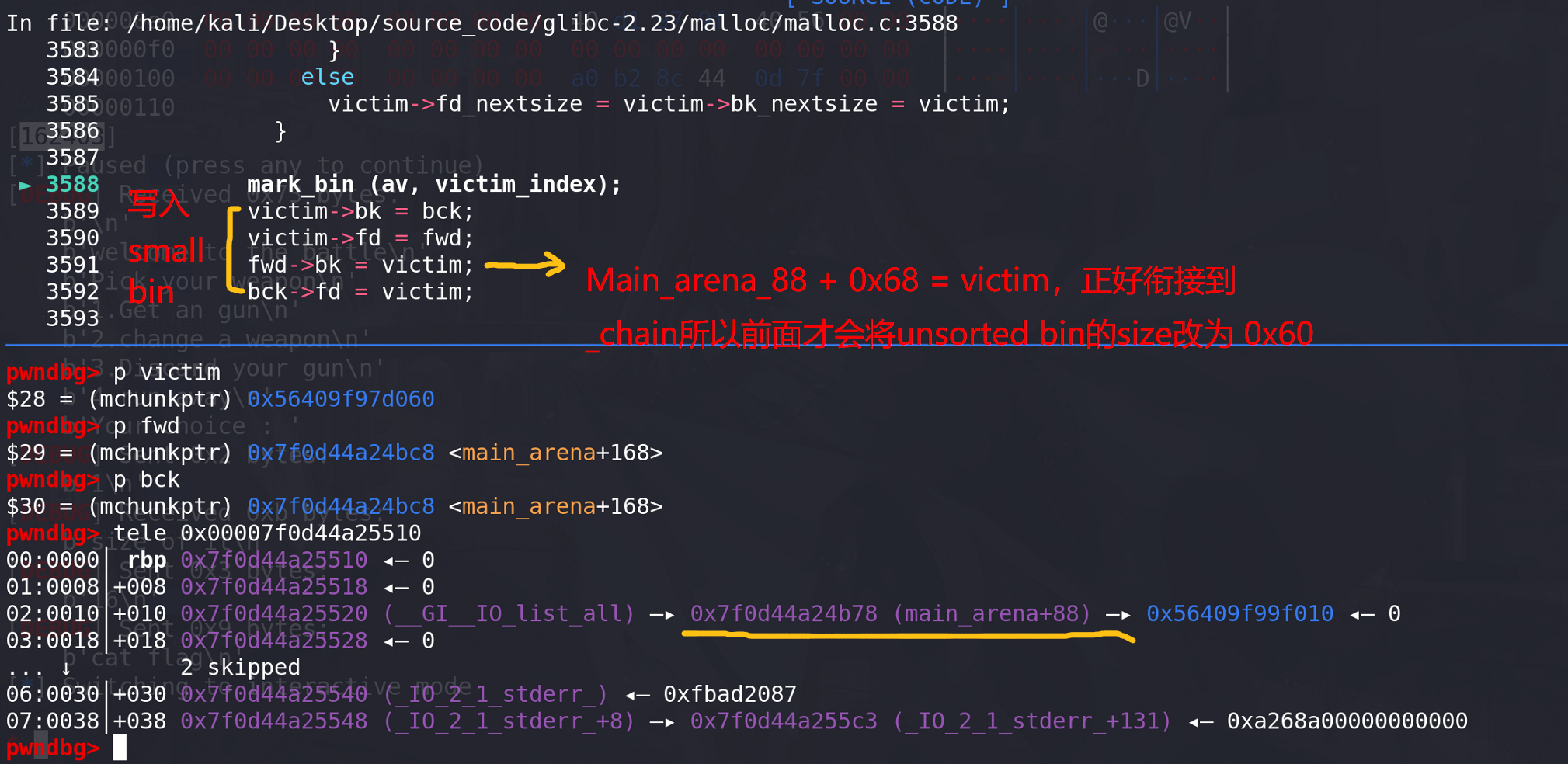
修改后的main_arena,覆盖的IO_list_all的file中的_chain正好衔接到fake_chunk:
查看到fake_chunk中伪造的file结构:
-
下面会因为unsorted bin的完整性报错 ,从而调用malloc_printerr函数:
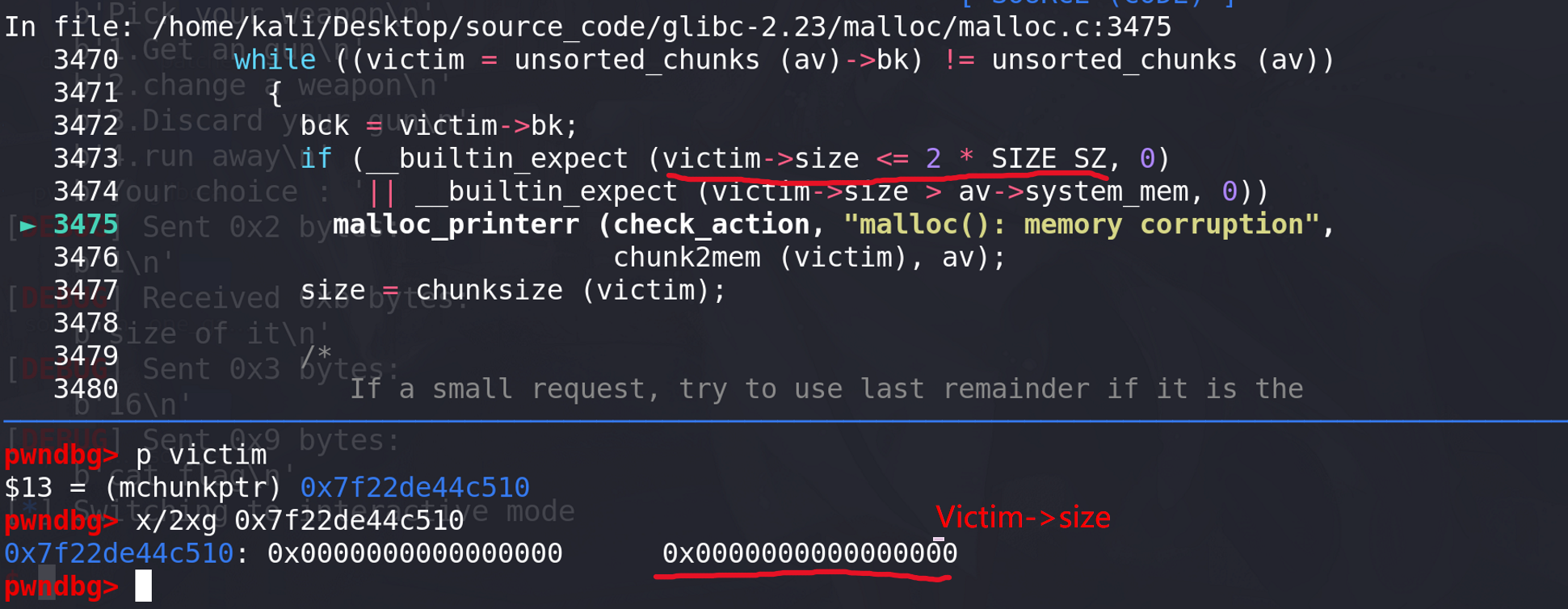
-
再调用**__libc_message**函数:
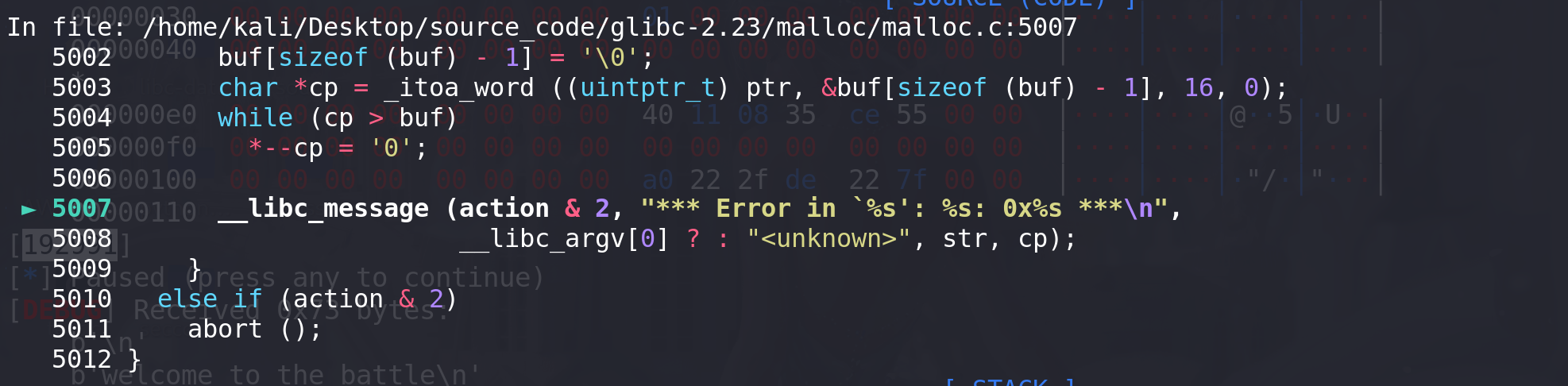
-
再调用abort函数:
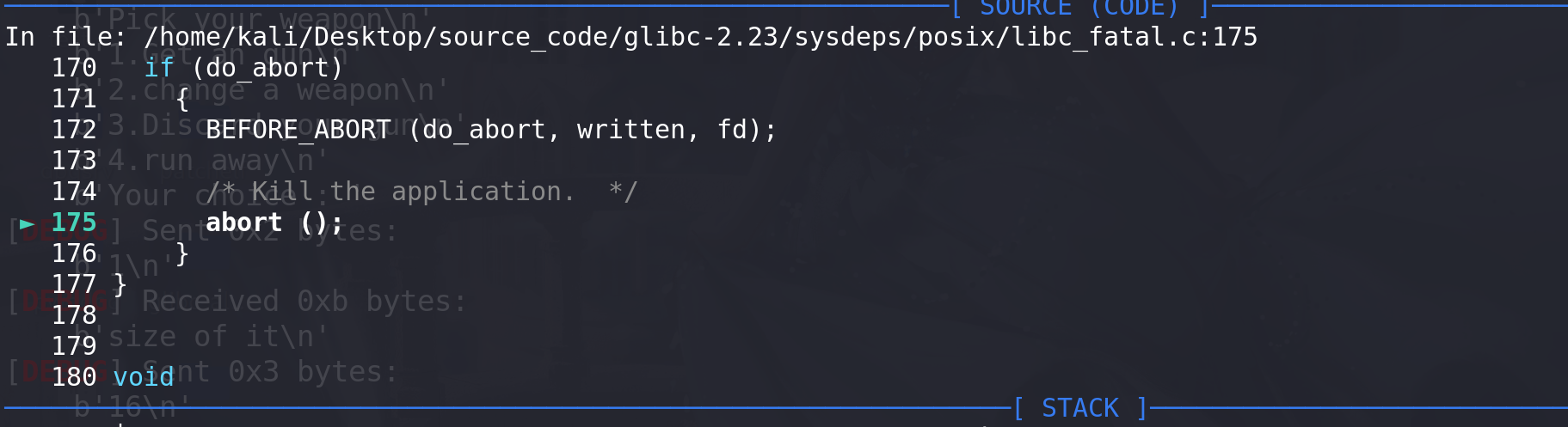
-
调用发flush(NULL),这里传入的参数是NULL:
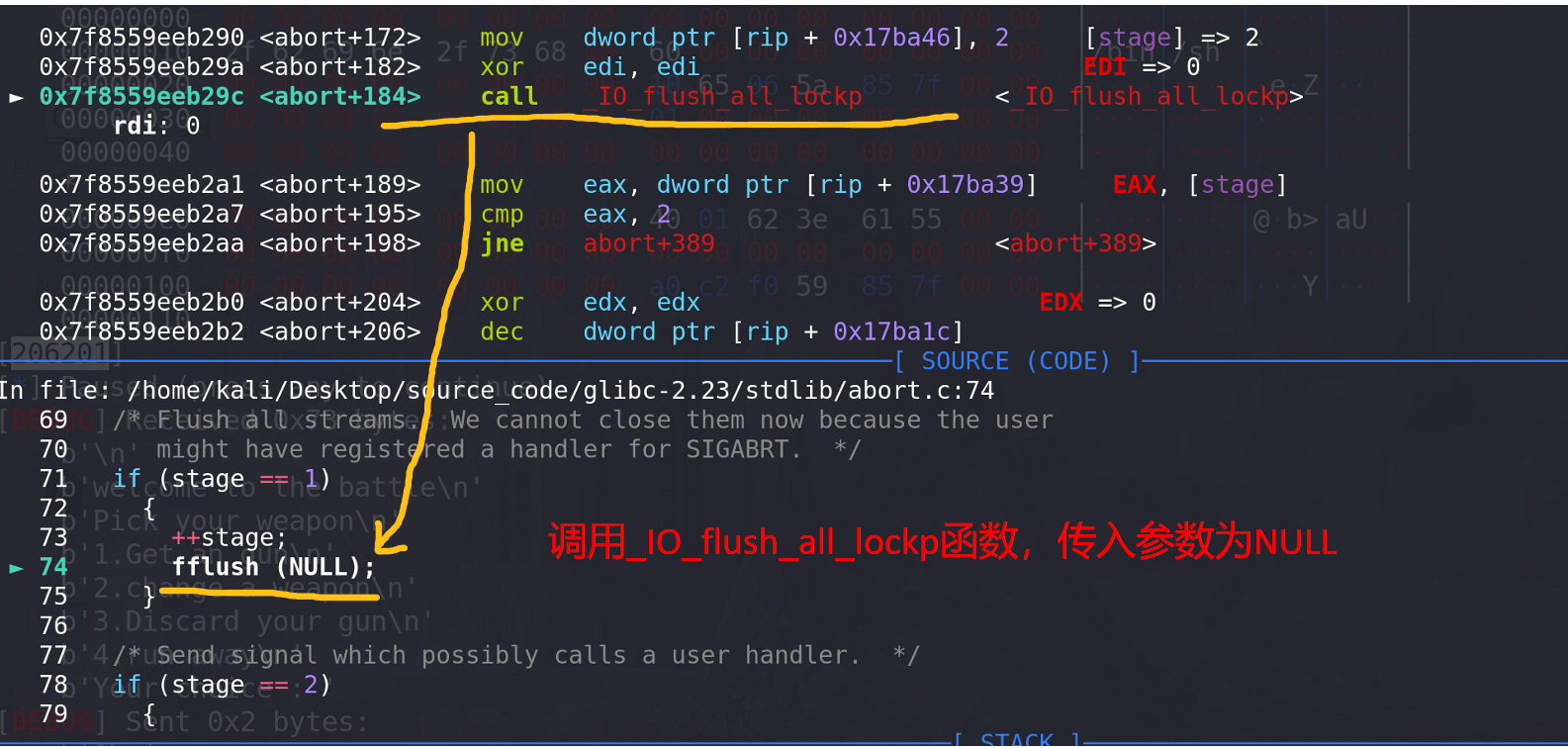
-
成功进入到_IO_flush_all_lockp函数,来刷新所有文件流:
第一个文件流,被我们覆盖掉IO_list_all后,移动到了main_arena_88:
通过_chain取到第二个文件,即为我们伪造的fake_chunk:
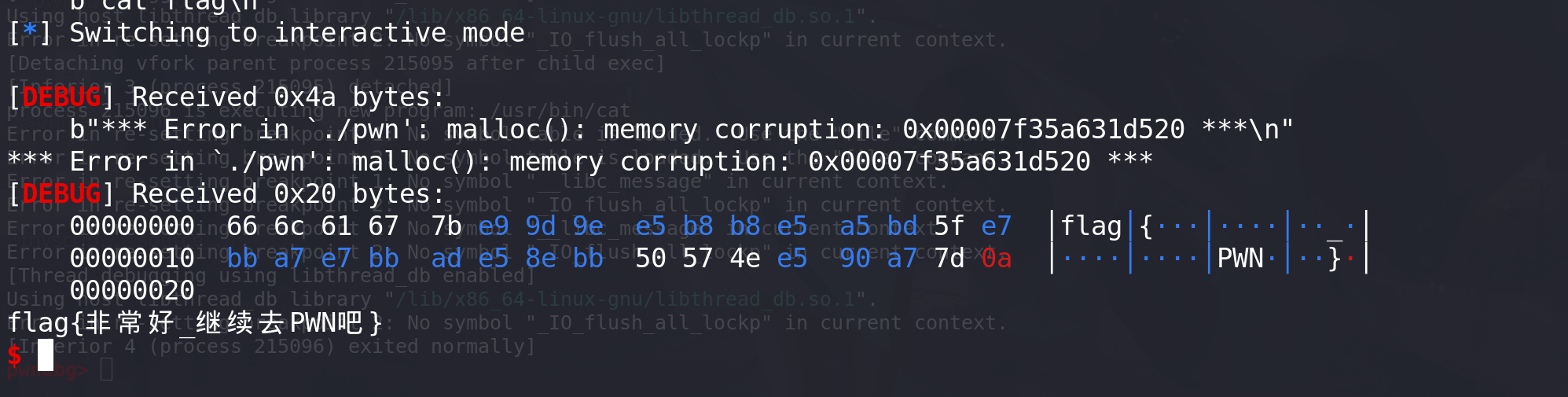
-
最后成功拿到flag: