710,反射快速入门

代码:
先创建一个 re.properties 文件:
classfullpath=com.hspedu.Cat
method=hiCat.java
package com.hspedu;
public class Cat {
private String name = "招财猫";
public void hi() { //常用方法
System.out.println("hi " + name);
}
}ReflectionQuestion.javapackage com.hspedu.reflection.question;
import com.hspedu.Cat;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Properties;
//反射问题的引入
public class ReflectionQuestion {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
//根据配置文件 re.properties 指定信息, 创建 Cat 对象并调用方法 hi
//传统的方式 new 对象 -》 调用方法
// Cat cat = new Cat();
// cat.hi();
//我们尝试做一做 -> 明白反射
//1. 使用 Properties 类, 可以读写配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\re.properties"));
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath").toString();//"com.hspedu.Cat"
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method").toString();
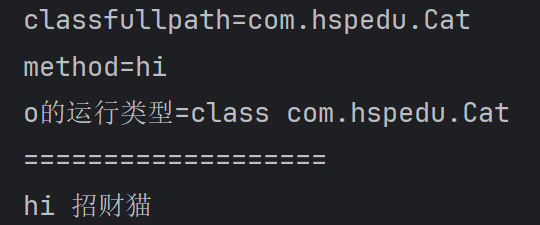
System.out.println("classfullpath=" + classfullpath);
System.out.println("method=" + methodName);
//2. 创建对象 , 传统的方法, 行不通 =》 反射机制
// Cat cat1 = new com.hspedu.Cat();
// new classfullpath();//这个是String,不是类名
//3. 使用反射机制解决
//(1) 加载类, 返回 Class 类型的对象 cls
Class cls = Class.forName(classfullpath);
//(2) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 com.hspedu.Cat 的对象实例
Object o = cls.newInstance();
System.out.println("o的运行类型=" + o.getClass());//运行类型
//(3) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 com.hspedu.Cat 的 methodName"hi" 的方法对象
// 即: 在反射中, 可以把方法视为对象(万物皆对象)
Method method1 = cls.getMethod(methodName);
System.out.println("===================");
//(4) 通过 method1 调用方法: 即通过方法对象来实现调用方法
method1.invoke(o);//传统方法 对象.方法() , 反射机制 方法.invoke(对象)
}
}运行结果:
713,反射相关类


代码:
re.properties 代码不变。
Cat.java
package com.hspedu;
public class Cat {
private String name = "招财猫";
public int age = 10;
public Cat() {} //无参构造器
public Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hi() { //常用方法
System.out.println("hi " + name);
}
}Reflection01.java
package com.hspedu.reflection;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Reflection01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 使用 Properties 类, 可以读写配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileInputStream("src\\re.properties"));
String classfullpath = properties.getProperty("classfullpath").toString();//"com.hspedu.Cat"
String methodName = properties.getProperty("method").toString();
//3. 使用反射机制解决
//(1) 加载类, 返回 Class 类型的对象 cls
Class cls = Class.forName(classfullpath);
//(2) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 com.hspedu.Cat 的对象实例
Object o = cls.newInstance();
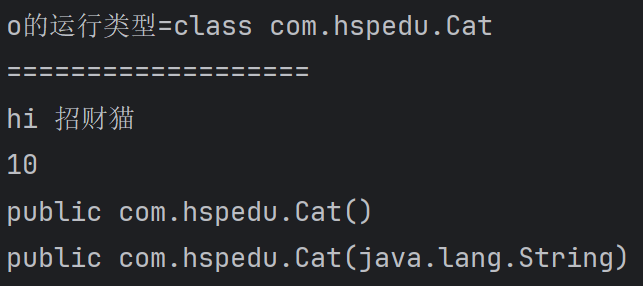
System.out.println("o的运行类型=" + o.getClass());//运行类型
//(3) 通过 cls 得到你加载的类 com.hspedu.Cat 的 methodName"hi" 的方法对象
// 即: 在反射中, 可以把方法视为对象(万物皆对象)
Method method1 = cls.getMethod(methodName);
System.out.println("===================");
//(4) 通过 method1 调用方法: 即通过方法对象来实现调用方法
method1.invoke(o);//传统方法 对象.方法() , 反射机制 方法.invoke(对象)
//java.lang.reflect.Field: 代表类的成员变量, Field 对象表示某个类的成员变量
//得到 name 字段
//getField 不能得到私有的属性,name是private,age是public
Field nameField = cls.getField("age");
System.out.println(nameField.get(o));// 传统写法 对象.成员变量 , 反射 : 成员变量对象.get(对象)
//java.lang.reflect.Constructor: 代表类的构造方法, Constructor 对象表示构造器
//()中可以指定构造器参数类型, 返回无参构造器
Constructor constructor = cls.getConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor);
//这里老师传入的 String.class 就是 String 类的Class 对象
Constructor constructor2 = cls.getConstructor(String.class);
System.out.println(constructor2);
}
}运行结果:
714,反射调用优化


代码:
re.properties 文件内容不变
cat.java
package com.hspedu;
public class Cat {
private String name = "招财猫";
public int age = 10;
public Cat() {} //无参构造器
public Cat(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void hi() { //常用方法
//System.out.println("hi " + name);
}
}Reflection02.java
package com.hspedu.reflection;
import com.hspedu.Cat;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//测试反射调用的性能, 和优化方案
public class Reflection02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
m1();
m2();
m3();
}
//传统方法来调用 hi
public static void m1() {
Cat cat = new Cat();
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 90000000; i++) {
cat.hi();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("传统方法调用hi 耗时=" + (end - start));
}
//反射机制调用方法 hi
public static void m2() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class cls = Class.forName("com.hspedu.Cat");//参数直接给了全类名(来自re.properties文件里)
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi = cls.getMethod("hi");//参数直接给了方法名(来自re.properties文件里)
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 90000000; i++) {
hi.invoke(o);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("m2() 耗时=" + (end - start));
}
//反射机制调用方法 hi
public static void m3() throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException {
Class cls = Class.forName("com.hspedu.Cat");//参数直接给了全类名(来自re.properties文件里)
Object o = cls.newInstance();
Method hi = cls.getMethod("hi");//参数直接给了方法名(来自re.properties文件里)
hi.setAccessible(true);//在反射调用方法时, 取消访问检查
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 90000000; i++) {
hi.invoke(o);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("m3() 耗时=" + (end - start));
}
}运行结果:

716,Class常用方法
代码:
Car.java
package com.hspedu;
public class Car {
public String brand = "宝马";
public int price = 500000;
public String color = "白色";
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", color='" + color + '\'' +
'}';
}
}Class02.java
package com.hspedu.reflection.class_;
import com.hspedu.Car;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Class02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
//1 . 获取到 Car 类 对应的 Class 对象
//<?> 表示不确定的 Java 类型
String classAllPath = "com.hspedu.Car";
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(classAllPath);
//2. 输出 cls
//显示 cls 对象, 是哪个类的 Class 对象 com.hspedu.Car
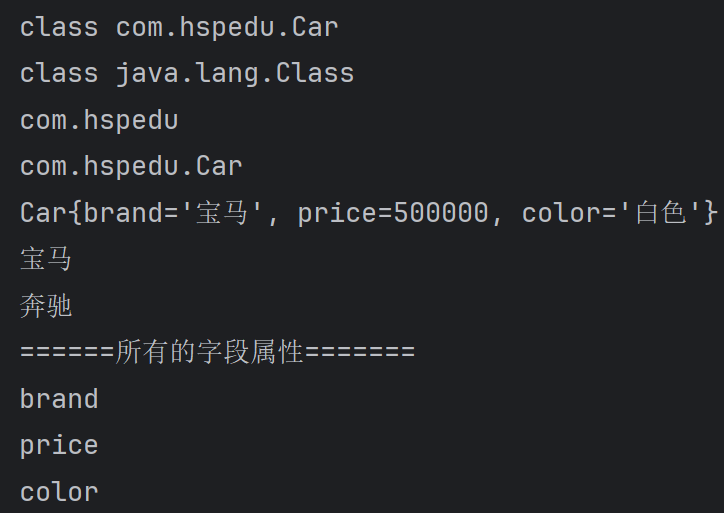
System.out.println(cls);
//输出 cls 运行类型 java.lang.Class
System.out.println(cls.getClass());
//3. 得到包名
System.out.println(cls.getPackage().getName());
//4. 得到全类名
System.out.println(cls.getName());
//5. 通过 cls 创建对象实例
Car car = (Car)cls.newInstance();
System.out.println(car);//car.toString()
//6. 通过反射获取属性 brand
Field brand = cls.getField("brand");
System.out.println(brand.get(car));
//7. 通过反射给属性赋值
brand.set(car, "奔驰");
System.out.println(brand.get(car));
//8 我希望大家可以得到所有的属性(字段)
System.out.println("======所有的字段属性=======");
Field[] fields = cls.getFields();
for (Field f : fields) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
}运行结果:
717,获取Class对象六种方式

代码:
package com.hspedu.reflection.class_;
import com.hspedu.Car;
public class GetClass_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1. Class.forName
//通过读取配置文件获取
String classAllPath = "com.hspedu.Car";
Class<?> cls1 = Class.forName(classAllPath);
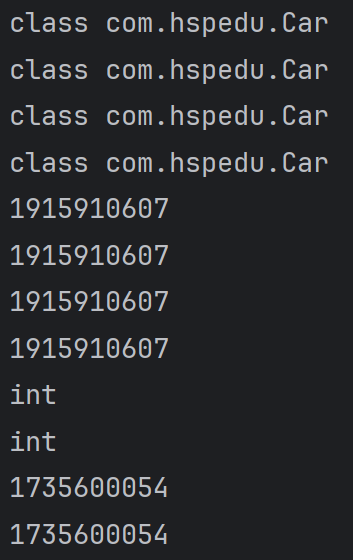
System.out.println(cls1);
//2. 类名.class , 应用场景: 用于参数传递
Class cls2 = Car.class;
System.out.println(cls2);
//3. 对象.getClass(), 应用场景, 有对象实例
Car car = new Car();
Class cls3 = car.getClass();
System.out.println(cls3);
//4. 通过类加载器【4 种】 来获取到类的 Class 对象
//(1)先得到类加载器 classLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = car.getClass().getClassLoader();
//(2)通过类加载器得到 Class 对象
Class cls4 = classLoader.loadClass(classAllPath);
System.out.println(cls4);
//cls1 , cls2 , cls3 , cls4 其实是同一个对象
System.out.println(cls1.hashCode());
System.out.println(cls2.hashCode());
System.out.println(cls3.hashCode());
System.out.println(cls4.hashCode());
//5. 基本数据(int, char,boolean,float,double,byte,long,short) 按如下方式得到 Class 类对象
Class<Integer> integerClass = int.class;
Class<Character> characterClass = char.class;
Class<Boolean> booleanClass = boolean.class;
System.out.println(integerClass);//int
//6. 基本数据类型对应的包装类, 可以通过 .TYPE 得到 Class 类对象
Class<Integer> type1 = Integer.TYPE;
Class<Character> type2 = Character.TYPE;
System.out.println(type1);
System.out.println(integerClass.hashCode());
System.out.println(type1.hashCode());
}
}运行结果:
718,哪些类型有Class对象

代码:
package com.hspedu.reflection.class_;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class AllTypeClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<String> cls1 = String.class;//外部类
Class<Serializable> cls2 = Serializable.class;//接口
Class<Integer[]> cls3 = Integer[].class;//数组
Class<float[][]> cls4 = float[][].class;//二维数组
Class<Deprecated> cls5 = Deprecated.class;//注解
Class<Thread.State> cls6 = Thread.State.class;//枚举
Class<Long> cls7 = long.class;//基本数据类型
Class<Void> cls8 = void.class;//void 数据类型
Class<Class> cls9 = Class.class;
System.out.println(cls1);
System.out.println(cls2);
System.out.println(cls3);
System.out.println(cls4);
System.out.println(cls5);
System.out.println(cls6);
System.out.println(cls7);
System.out.println(cls8);
System.out.println(cls9);
}
}运行结果:

725,反射暴破创建实例

代码:
package com.hspedu.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
public class ReflecCreateInstance {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
//1. 先获取到 User 类的 Class 对象
Class<?> userClass = Class.forName("com.hspedu.reflection.User");
//2. 通过 public 的无参构造器创建实例
Object o = userClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(o);
//3. 通过 public 的有参构造器创建实例
//3.1 先得到对应构造器
Constructor<?> constructor = userClass.getConstructor(String.class);
//3.2 创建实例, 并传入实参
Object hsp = constructor.newInstance("hsp");
System.out.println("hsp=" + hsp);
//4. 通过非 public 的有参构造器创建实例
//4.1 得到 private 的构造器对象
Constructor<?> constructor1 = userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class);
//4.2 创建实例
//暴破【暴力破解】 , 使用反射可以访问 private 构造器/方法/属性, 反射面前, 都是纸老虎
constructor1.setAccessible(true);
Object user2 = constructor1.newInstance(100, "张三丰");
System.out.println("user2=" + user2);
}
}
class User { //User 类
private int age = 10;
private String name = "韩顺平教育";
public User() {//无参 public
}
public User(String name) {//public 的有参构造器
this.name = name;
}
private User(int age, String name) {//private 有参构造器
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}运行结果:

726,反射暴破操作属性

代码:
package com.hspedu.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ReflectAccessProperty {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
//1. 得到 Student 类对应的 Class 对象
Class<?> stuClass = Class.forName("com.hspedu.reflection.Student");
//2. 创建对象
Object o = stuClass.newInstance();
//o 的运行类型就是 Student
System.out.println(o.getClass());
//3. 使用反射得到 age 属性对象
Field age = stuClass.getField("age");
//通过反射来操作属性
age.set(o, 88);
System.out.println(o);
//返回 age 属性的值
System.out.println(age.get(o));
//4. 使用反射操作 name 属性
Field name = stuClass.getDeclaredField("name");
//对 name 进行暴破, 可以操作 private 属性
name.setAccessible(true);
//因为 name 是 static 属性, 因此 o 也可以写出 null, name.set(o, "老韩");
name.set(null, "老韩");
System.out.println(o);
System.out.println(name.get(o)); //获取属性值
System.out.println(name.get(null));//获取属性值, 要求 name 是 static
}
}
class Student {//类
public int age;
private static String name;
public Student() {//构造器
}
public String toString() {
return "Student [age=" + age + ", name=" + name + "]";
}
}运行结果:
727,反射暴破操作方法

代码:
package com.hspedu.reflection;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflecAccessMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException {
//1. 得到 Boss 类对应的 Class 对象
Class<?> bossCls = Class.forName("com.hspedu.reflection.Boss");
//2. 创建对象
Object o = bossCls.newInstance();
//3. 调用 public 的 hi 方法
//Method hi = bossCls.getMethod("hi", String.class);//OK
//3.1 得到 hi 方法对象
Method hi = bossCls.getDeclaredMethod("hi", String.class);
//3.2 调用
hi.invoke(o, "韩顺平教育");
//4. 调用 private static 方法
//4.1 得到 say 方法对象
Method say = bossCls.getDeclaredMethod("say", int.class, String.class, char.class);
//4.2 因为 say 方法是 private, 所以需要暴破, 原理和前面讲的构造器和属性一样
say.setAccessible(true);
System.out.println(say.invoke(o, 100, "张三", '男'));
//4.3 因为 say 方法是 static 的, 还可以这样调用 , 可以传入 null
System.out.println(say.invoke(null, 200, "李四", '女'));
//5. 在反射中, 如果方法有返回值, 统一返回 Object , 但是他运行类型和方法定义的返回类型一致
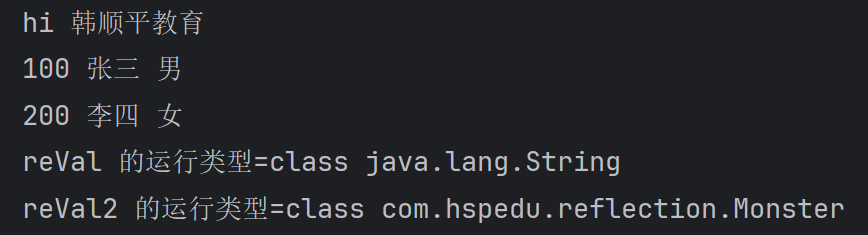
Object reVal = say.invoke(null, 300, "王五", '男');
System.out.println("reVal 的运行类型=" + reVal.getClass());//String
//在演示一个返回的案例
Method m1 = bossCls.getDeclaredMethod("m1");
Object reVal2 = m1.invoke(o);
System.out.println("reVal2 的运行类型=" + reVal2.getClass());//Monster
}
}
class Monster {}
class Boss {//类
public int age;
private static String name;
public Boss() {//构造器
}
public Monster m1() {
return new Monster();
}
private static String say(int n, String s, char c) {//静态方法
return n + " " + s + " " + c;
}
public void hi(String s) {//普通 public 方法
System.out.println("hi " + s);
}
}运行结果: