一:基础认识
1.Git 三种状态
- Working Directory :本地工作目录,工作区
- Staging Area:添加文件,用于commit前,暂存区
- .git directory(Repository):本地仓库,存储commit数据,版本库

2. 基本概念
- Committed 表示数据已经安全存储到本地数据库中(本质是标记版本号git commit -m "版本号")
- Modified 表示已经修改的文件,但没有进行Commit
- Staged 表示已经标记一个修改过的文件当前版本,下次commite上传(本质就是git add 文件名)
3. Git基本工作流程
- 在working tree中修改文件
- Committed 表示数据已经安全存储到本地数据库中
- Modified 表示已经修改的文件,但没有进行Commit
- Staged 表示已经标记一个修改过的文件当前版本,下次commite使用
4. Git配置文件
- Git可以更改config文件,自定义化主题。Git配置文件可能存储到三个位置:
- /etc/gitconfig file: 全局配置文件
- ~/.gitconfig or ~/.config/git/config file:本地存储个人账号
- .git/config:本地git仓库路径中的文件,包含初始化,上传,下载的配置
二:相关命令
1.新建代码库
bash
# 在当前目录新建一个Git代码库
$ git init
# 新建一个目录,将其初始化为Git代码库
$ git init [project-name]
# 下载一个项目和它的整个代码历史
$ git clone [url]2.配置
bash
# 显示当前的Git配置
$ git config --list
# 编辑Git配置文件
$ git config -e [--global]
# 设置提交代码时的用户信息
$ git config [--global] user.name "[name]"
$ git config [--global] user.email "[email address]"3.增加/删除文件
bash
# 添加指定文件到暂存区
$ git add [file1] [file2] ...
# 添加指定目录到暂存区,包括子目录
$ git add [dir]
# 添加当前目录的所有文件到暂存区
$ git add .
# 添加每个变化前,都会要求确认
# 对于同一个文件的多处变化,可以实现分次提交
$ git add -p
# 删除工作区文件,并且将这次删除放入暂存区
$ git rm [file1] [file2] ...
# 停止追踪指定文件,但该文件会保留在工作区
$ git rm --cached [file]
# 改名文件,并且将这个改名放入暂存区
$ git mv [file-original] [file-renamed]4.代码提交
bash
# 提交暂存区到仓库区
$ git commit -m [message]
# 提交暂存区的指定文件到仓库区
$ git commit [file1] [file2] ... -m [message]
# 提交工作区自上次commit之后的变化,直接到仓库区
$ git commit -a
# 提交时显示所有diff信息
$ git commit -v
# 使用一次新的commit,替代上一次提交
# 如果代码没有任何新变化,则用来改写上一次commit的提交信息
$ git commit --amend -m [message]
# 重做上一次commit,并包括指定文件的新变化
$ git commit --amend [file1] [file2] ...5.分支
bash
# 列出所有本地分支
$ git branch
# 列出所有远程分支
$ git branch -r
# 列出所有本地分支和远程分支
$ git branch -a
# 新建一个分支,但依然停留在当前分支
$ git branch [branch-name]
# 新建一个分支,并切换到该分支
$ git checkout -b [branch]
# 新建一个分支,指向指定commit
$ git branch [branch] [commit]
# 新建一个分支,与指定的远程分支建立追踪关系
$ git branch --track [branch] [remote-branch]
# 切换到指定分支,并更新工作区
$ git checkout [branch-name]
# 切换到上一个分支
$ git checkout -
# 建立追踪关系,在现有分支与指定的远程分支之间
$ git branch --set-upstream [branch] [remote-branch]
# 合并指定分支到当前分支
$ git merge [branch]
# 选择一个commit,合并进当前分支
$ git cherry-pick [commit]
# 删除分支
$ git branch -d [branch-name]
# 删除远程分支
$ git push origin --delete [branch-name]
$ git branch -dr [remote/branch]
# 本地存在一个分支,名称叫:
develop_test
,但远程没有怎么办?
git push origin develop_test
这样就在远程建立一个和本地一样的分支
git branch --set-upstream-to=origin/develop develop 本地分支和远程分支简历跟踪关系6.标签
bash
# 列出所有tag
$ git tag
# 新建一个tag在当前commit
$ git tag [tag]
# 新建一个tag在指定commit
$ git tag [tag] [commit]
# 删除本地tag
$ git tag -d [tag]
# 删除远程tag
$ git push origin :refs/tags/[tagName]
# 查看tag信息
$ git show [tag]
# 提交指定tag
$ git push [remote] [tag]
# 提交所有tag
$ git push [remote] --tags
# 新建一个分支,指向某个tag
$ git checkout -b [branch] [tag]7.查看信息
bash
# 显示有变更的文件
$ git status
# 显示当前分支的版本历史
$ git log
# 显示commit历史,以及每次commit发生变更的文件
$ git log --stat
# 搜索提交历史,根据关键词
$ git log -S [keyword]
# 显示某个commit之后的所有变动,每个commit占据一行
$ git log [tag] HEAD --pretty=format:%s
# 显示某个commit之后的所有变动,其"提交说明"必须符合搜索条件
$ git log [tag] HEAD --grep feature
# 显示某个文件的版本历史,包括文件改名
$ git log --follow [file]
$ git whatchanged [file]
# 显示指定文件相关的每一次diff
$ git log -p [file]
# 显示过去5次提交
$ git log -5 --pretty --oneline
# 显示所有提交过的用户,按提交次数排序
$ git shortlog -sn
# 显示指定文件是什么人在什么时间修改过
$ git blame [file]
# 显示暂存区和工作区的代码差异
$ git diff
# 显示暂存区和上一个commit的差异
$ git diff --cached [file]
# 显示工作区与当前分支最新commit之间的差异
$ git diff HEAD
# 显示两次提交之间的差异
$ git diff [first-branch]...[second-branch]
# 显示今天你写了多少行代码
$ git diff --shortstat "@{0 day ago}"
# 显示某次提交的元数据和内容变化
$ git show [commit]
# 显示某次提交发生变化的文件
$ git show --name-only [commit]
# 显示某次提交时,某个文件的内容
$ git show [commit]:[filename]
# 显示当前分支的最近几次提交
$ git reflog
# 从本地master拉取代码更新当前分支:branch 一般为master
$ git rebase [branch]8.远程同步
bash
$ git remote update --更新远程仓储
# 下载远程仓库的所有变动
$ git fetch [remote]
# 显示所有远程仓库
$ git remote -v
# 显示某个远程仓库的信息
$ git remote show [remote]
# 增加一个新的远程仓库,并命名
$ git remote add [shortname] [url]
# 取回远程仓库的变化,并与本地分支合并
$ git pull [remote] [branch]
# 上传本地指定分支到远程仓库
$ git push [remote] [branch]
# 强行推送当前分支到远程仓库,即使有冲突
$ git push [remote] --force
# 推送所有分支到远程仓库
$ git push [remote] --all9.撤销
bash
# 恢复暂存区的指定文件到工作区
$ git checkout [file]
# 恢复某个commit的指定文件到暂存区和工作区
$ git checkout [commit] [file]
# 恢复暂存区的所有文件到工作区
$ git checkout .
# 重置暂存区的指定文件,与上一次commit保持一致,但工作区不变
$ git reset [file]
# 重置暂存区与工作区,与上一次commit保持一致
$ git reset --hard
# 重置当前分支的指针为指定commit,同时重置暂存区,但工作区不变
$ git reset [commit]
# 重置当前分支的HEAD为指定commit,同时重置暂存区和工作区,与指定commit一致
$ git reset --hard [commit]
# 重置当前HEAD为指定commit,但保持暂存区和工作区不变
$ git reset --keep [commit]
# 新建一个commit,用来撤销指定commit
# 后者的所有变化都将被前者抵消,并且应用到当前分支
$ git revert [commit]
# 暂时将未提交的变化移除,稍后再移入
$ git stash
$ git stash pop三:其他
1.常见报错及处理
1. git push错误failed to push some refs to的解决
bash
这个问题是因为远程库与本地库不一致造成的,那么我们把远程库同步到本地库就可以了。
git pull --rebase origin master这条指令的意思是把远程库中的更新合并到本地库中,--rebase的作用是取消掉本地库中刚刚的commit,并把他们接到更新后的版本库之中。
2. 报错2
# 原因:本地与托管平台数据不一致,常是由在托管平台删除导致
! [rejected] master -> master (non-fast-forward)
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://gitee.com/***/***.git'
hint: Updates were rejected because the tip of your current branch is behind
hint: its remote counterpart. Integrate the remote changes (e.g.
hint: 'git pull ...') before pushing again.
hint: See the 'Note about fast-forwards' in 'git push --help' for details.
# 解决方案
git pull henry master # 强制把远端数据与本地数据同步
git push -u origin master # 重新推送即可
# 如果上述步骤不生效,还提示错误,可使用
git push origin master -f # -f 表示强制上传,不建议经常3. 本地仓库文件状态
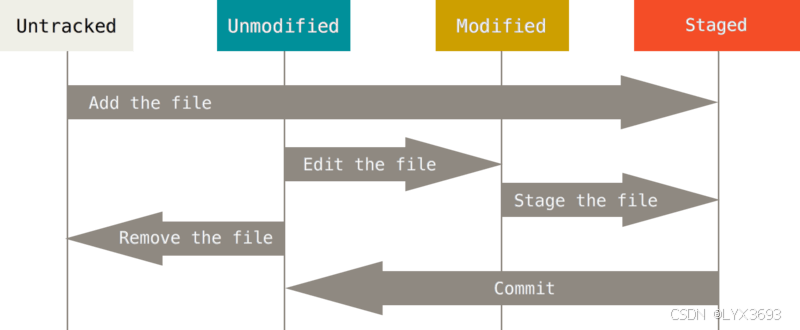
- 本地仓库中的任意文件只有两种状态:tracked (追踪)或者untracked(待追踪)。
- untracked的文件,git不会进行托管,只有tracked的文件才能push到remote(远端)。
- tracked文件可以有3种状态:unmodified(第一次clone后), modified(本地修改的文件)或者staged(add的文件)。
4. 删除remote端文件
- 先在Working Directory(本地),删除要删除的文件
bash
# 告知 git, 要删除的文件
git rm filename
# 查看文件状态
git status
# git 已经检测到用户删除的文件
bash
# 做标记
git commit -m 'test'
git push origin master
# commit历史阻止pull命令
git pull origin master --allow-unrelated-histories5. 强制同步(慎用)
bash
# 本步骤,主要针对于小白,无法解决远端和本地同步问题
1. git add .
2. git commit -m 'test'
3. git push origin master -f Note
- 第3步表示强制让remote端于local同步
- 这样会用local端刚push的数据完全覆盖remote 端
2.文件管理
1. 版本回滚
当我们本地文件误删或者更改后,想恢复之前的状态,如果已经进行commit,可以通过命令进行回滚
- 查看提交记录
- commit id 不用完全写完,git会自动寻找,但也不能太短,必须唯一
bash
# 可以查看到commit的id以及自己添加的标记
git log
# 数据进行回滚到指定的commit记录
git reset --hard commit的id号
HEAD is now at 83b0afe append GPL
# 查看操作记录
git reflog
# 回退版本后,想取消回滚操作
git reset --hard HEAD^2. 工作区和暂存区
- 工作区(Working Directory):当前git仓库的目录
- 版本库(Repository)
- 工作区有一个隐藏目录**.git**,这个不算工作区,而是Git的版本库。
- Git的版本库里存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是称为stage(或者叫index)的暂存区 ,还有Git为我们自动创建的第一个分支master ,以及指向maste的一个指针 叫HEAD。
bash
# 把要提交的所有修改放到暂存区(Stage)
git add 文件名/.
# 查看暂存区的状态
git status
# 一次性把暂存区的所有修改提交到分支。
git commit -m '标记'
# 推送到remote端
git push origin master- 查看工作区和版本库里面最新版本的区别
bash
git diff HEAD -- 文件名- 查看当前工作区状态
bash
git status- Git会告诉你,
git checkout -- file可以丢弃工作区修改
bash
# 在stage之前使用
git checkout -- 文件名
# -- 很重要,如果没加表示切换分支- 把暂存区的修改撤销掉(unstage),重新放回工作区
bash
# 在stage之后使用
git reset HEAD <file>- 删除文件
- git checkout其实是用版本库里的版本替换工作区的版本,无论工作区是修改还是删除,都可以"一键还原"。
bash
git rm test.txt
git commit -m 'del test'- 查看更改
bash
git diff3.合并代码
1. 创建切换分支
bash
git branch # 查看当前所有分支
git branch dev # 创建 dev 分支
git checkout dev # 切换到 dev 分支
git branch bug # 创建 bug 分支
git checkout bug # 切换 bug 分支,修复bugs2. 合并分支
-
需要切换到目标的分支后再合并
git checkout master
git merge bug # 合并 bug 分支,到 master 分支
git branch -d bug # 删除 bug 分支
3. 回到dev分支
-
冲突的解决
git checkout dev
git add .
git commit -m '开发完毕'
git checkout master # 切换到 master 分支准备合并dev
git merge dev # 此时会发生冲突,需要手动解决冲突
git add .
...