一、力扣
1、缺失的第一个正数

java
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]<=0){
nums[i]=n+1;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int target=Math.abs(nums[i]);
if(target<=n){
nums[target-1]=-Math.abs(nums[target-1]);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]>0){
return i+1;
}
}
return n+1;
}
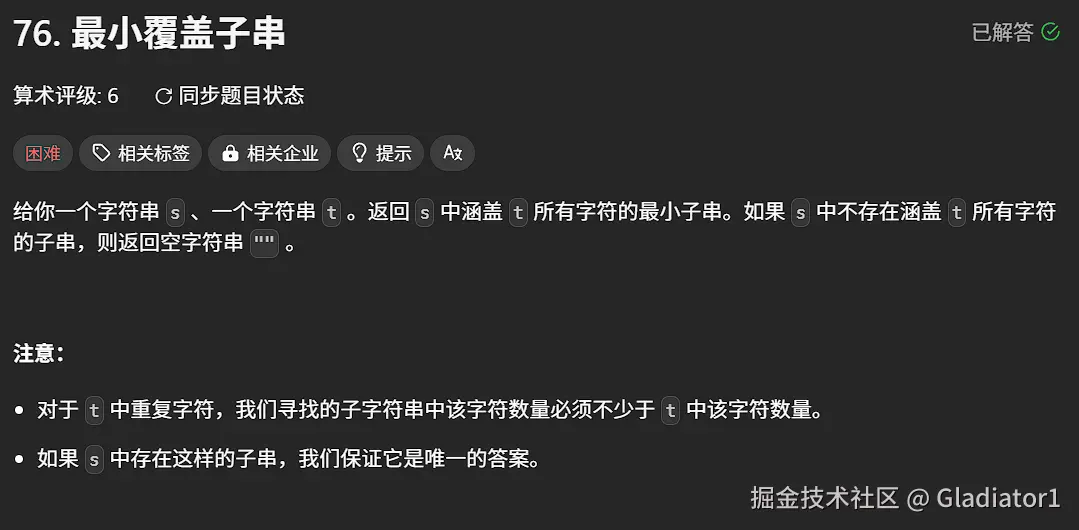
}2、最小覆盖子串
java
class Solution {
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
int[] target=new int[128];
for(var e:t.toCharArray()){
target[e]++;
}
int[] count=new int[128];
int left=0,right=0;
int n=s.length();
int resleft=0,resright=Integer.MAX_VALUE/2;
while(right<n){
count[s.charAt(right)]++;
while(check(count,target)){
if(right-left<resright-resleft){
resright=right;
resleft=left;
}
count[s.charAt(left++)]--;
}
right++;
}
return resright==Integer.MAX_VALUE/2?"":s.substring(resleft,resright+1);
}
public boolean check(int[] count,int[] target){
for(int i=0;i<128;i++){
if(count[i]<target[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}3、字符串相乘

java
class Solution {
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1.equals("0") || num2.equals("0")) {
return "0";
}
String ans = "0";
int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length();
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
StringBuffer curr = new StringBuffer();
int add = 0;
for (int j = n - 1; j > i; j--) {
curr.append(0);
}
int y = num2.charAt(i) - '0';
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int x = num1.charAt(j) - '0';
int product = x * y + add;
curr.append(product % 10);
add = product / 10;
}
if (add != 0) {
curr.append(add);
}
ans = addStrings(ans, curr.reverse().toString());
}
return ans;
}
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
int i = num1.length() - 1, j = num2.length() - 1, add = 0;
StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer();
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0) {
int x = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0;
int y = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0;
int result = x + y + add;
ans.append(result % 10);
add = result / 10;
i--;
j--;
}
ans.reverse();
return ans.toString();
}
}4、二叉搜索树中的插入操作

迭代法:
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(val);
if (root == null) {
return node;
}
TreeNode cur = root;
while (true) {
if (cur.val > val) {
if (cur.left == null) {
cur.left = node;
break;
}
cur = cur.left;
} else {
if (cur.right == null) {
cur.right = node;
break;
}
cur = cur.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}递归写法:
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) {
return new TreeNode(val);
}
if (root.val < val) {
root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
} else {
root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
}
return root;
}
}5、删除二叉搜索树中的节点

java
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
// 1. 递归终止条件:当前节点为空,直接返回null
if (root == null) return null;
// 2. 查找待删除节点
if (root.val == key) {
// 情况1:左子树为空,直接返回右子树作为新的子树根
if (root.left == null) return root.right;
// 情况2:右子树为空,直接返回左子树作为新的子树根
if (root.right == null) return root.left;
// 情况3:左右子树均存在
// 找到左子树中的最大节点(最右节点)
TreeNode t = root.left;
while (t.right != null) t = t.right;
// 将原右子树挂到左子树最大节点的右子树
t.right = root.right;
// 返回左子树作为新的根节点
return root.left;
} else if (root.val < key) {
// 递归在右子树中删除节点,并更新当前节点的右指针
root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key);
} else {
// 递归在左子树中删除节点,并更新当前节点的左指针
root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key);
}
// 返回处理后的当前节点(可能已被修改)
return root;
}
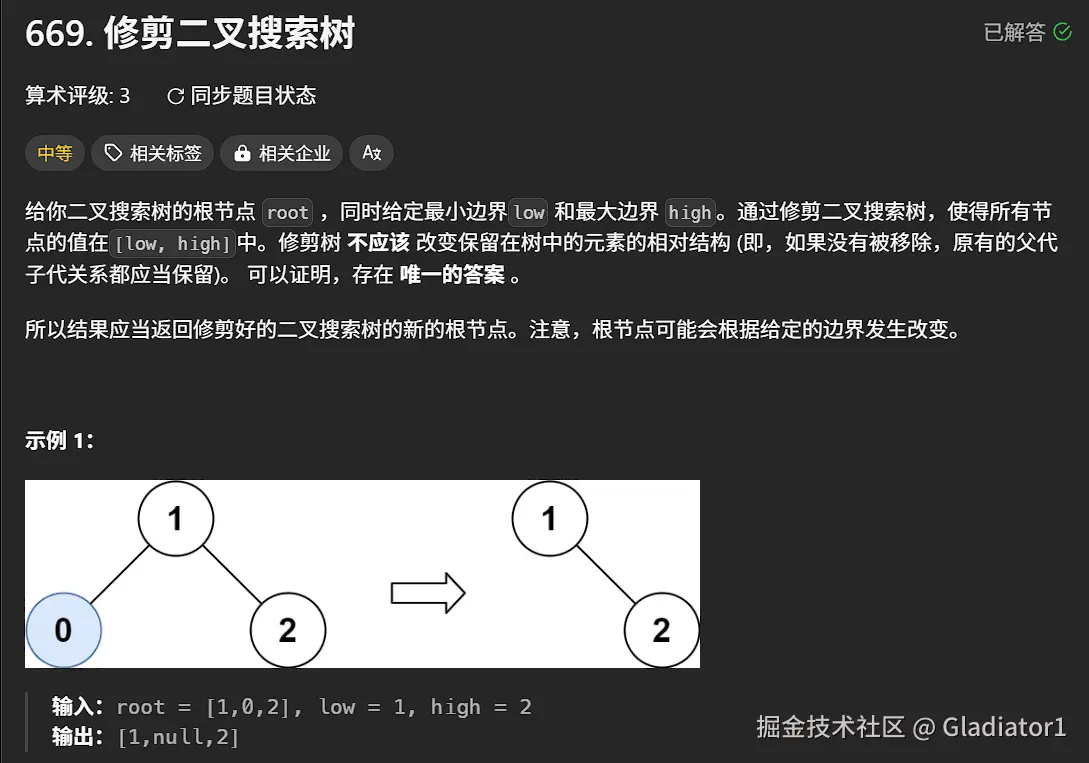
}6、修剪二叉搜索树
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
// 递归终止条件:当前节点为空,直接返回null
if (root == null) return null;
// 当前节点值小于下界:说明当前节点及其左子树都不符合要求
// 根据BST性质,左子树所有节点值都更小,因此只需递归处理右子树
if (root.val < low) {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
}
// 当前节点值大于上界:说明当前节点及其右子树都不符合要求
// 根据BST性质,右子树所有节点值都更大,因此只需递归处理左子树
else if (root.val > high) {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
}
// 当前节点值在范围内,递归修剪左右子树
// 注意:需要将修剪后的子树重新赋值给当前节点的左右指针
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); // 修剪左子树
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); // 修剪右子树
// 返回当前已修剪的节点(作为父节点的子节点)
return root;
}
}二、语雀-编程题
1、如何用队列实现一个栈?
- 将新元素添加到inque队尾
- 将outque中的全部元素依次转移到inque中
- 交换两个队列的引用,使得outque始终保存最新栈状态
java
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
class MyStack {
// 使用两个双端队列模拟栈的操作
// inque 用于入栈时的临时存储
// outque 用于出栈操作,保持栈顶元素在队首
ArrayDeque<Integer> inque = new ArrayDeque<>();
ArrayDeque<Integer> outque = new ArrayDeque<>();
public MyStack() {
// 构造函数无需特殊初始化
}
/**
* 入栈操作
* @param x 待压入栈的元素
* 实现思路:
* 1. 将新元素添加到inque队尾
* 2. 将outque中的全部元素依次转移到inque中(反转原有顺序)
* 3. 交换两个队列的引用,使得outque始终保存最新栈状态
* 此操作确保新元素始终位于outque队首,符合栈的后进先出特性
*/
public void push(int x) {
inque.offerLast(x); // 将新元素加入inque队尾
while (!outque.isEmpty()) { // 将outque现有元素全部转移到inque
inque.offer(outque.poll());
}
// 交换队列引用,使outque始终持有当前栈内容
ArrayDeque<Integer> temp = inque;
inque = outque;
outque = temp;
}
/** 弹出栈顶元素 */
public int pop() {
return outque.poll(); // 直接移除并返回outque队首元素(即栈顶)
}
/** 获取栈顶元素但不弹出 */
public int top() {
return outque.peek(); // 查看outque队首元素
}
/** 判断栈是否为空 */
public boolean empty() {
return inque.isEmpty() && outque.isEmpty(); // 两队列均为空时栈为空
}
}2、如何用栈实现一个队列
将一个栈当作输入栈,用于压入 push 传入的数据;另一个栈当作输出栈,用于 pop 和 peek 操作。
每次 pop 或 peek 时,若输出栈为空则将输入栈的全部数据依次弹出并压入输出栈,这样输出栈从栈顶往栈底的顺序就是队列从队首往队尾的顺序。
java
class MyQueue {
ArrayDeque<Integer> stack1=new ArrayDeque<>();
ArrayDeque<Integer> stack2=new ArrayDeque<>();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.isEmpty()&&stack2.isEmpty();
}
}3、快速排序

java
class Solution {
Random random=new Random();
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
quicksort(nums,0,nums.length-1);
return nums;
}
public void quicksort(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return;
int partiton=left+random.nextInt(right-left+1);
swap(nums,partiton,left);
int i=left+1,j=right;
while(true){
while(i<=j&&nums[i]<nums[left]) i++;
while(i<=j&&nums[j]>nums[left]) j--;
if(i>=j) break;
swap(nums,i,j);
i++;
j--;
}
swap(nums,left,j);
quicksort(nums,left,j-1);
quicksort(nums,j+1,right);
}
public void swap(int[] nums,int left,int right){
int temp=nums[left];
nums[left]=nums[right];
nums[right]=temp;
}
}4、有一个包含N个整数的数组,请编写一个算法,找到其中的两个元素,使它们之差最小。时间复杂度必须为O(n)。
✅有一个包含N个整数的数组,请编写一个算法,找到其中的两个元素,使它们之差最小。时间复杂度必须为O(n)。

- 该算法时间复杂度为O(n + k)(k为数值范围),适用于整数数组且数值范围可控的场景
- 当前桶宽度设置为1(每个桶对应一个具体数值),可根据实际需求调整桶宽以优化性能
在元素均匀分布且桶内元素数量较小时,时间复杂度接近线性;否则可能退化为O(n log n)
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MinDiff {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {3, 1, 4, 5, 9, 2, 6, 8, 7};
int minDiff = findMinDiff(arr);
System.out.println("最小差为:" + minDiff);
}
public static int findMinDiff(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
if (n < 2) {
return -1; // 数组元素不足,无法计算差值
}
// 步骤1:查找数组中的最小值和最大值
int minVal = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxVal = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
minval=Math.min(minVal,arr[i]);
maxval=Math.max(maxVal,arr[i]);
}
// 步骤2:初始化桶结构
int bucketCount = maxVal - minVal + 1; // 桶的数量等于数值范围的大小
int[][] buckets = new int[bucketCount][n]; // 存储各桶元素
int[] bucketSizes = new int[bucketCount]; // 记录各桶实际元素个数
// 步骤3:将元素分配到对应的桶中
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int index = arr[i] - minVal; // 计算元素所属桶的索引
buckets[index][bucketSizes[index]++] = arr[i]; // 将元素放入桶中
}
// 步骤4:对每个非空桶进行排序
for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) {
if (bucketSizes[i] > 0) {
// 仅对桶内实际存在的元素进行排序
Arrays.sort(buckets[i], 0, bucketSizes[i]);
}
}
// 步骤5:计算相邻非空桶之间的最小差值
int minDiff = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int prevMax = buckets[0][bucketSizes[0] - 1]; // 初始化为第一个桶的最大值(已排序)
for (int i = 1; i < bucketCount; i++) {
if (bucketSizes[i] == 0) {
continue; // 跳过空桶
}
int currMin = buckets[i][0]; // 当前桶的最小值(已排序)
int diff = currMin - prevMax; // 计算相邻桶差值
if (diff < minDiff) {
minDiff = diff; // 更新最小差值
}
prevMax = buckets[i][bucketSizes[i] - 1]; // 更新prevMax为当前桶的最大值
}
return minDiff;
}
}5、实现一个LRU缓存淘汰策略,支持get和put操作
java
class LRUCache {
class ListNode{
int key,val;
ListNode prev,next;
public ListNode(){};
public ListNode(int key,int val){
this.key=key;
this.val=val;
}
}
ListNode dummy;
Map<Integer,ListNode> map;
int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity=capacity;
dummy=new ListNode();
dummy.next=dummy;
dummy.prev=dummy;
map=new HashMap<>();
}
public int get(int key) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){
ListNode target=map.get(key);
remove(target);
pushFirst(target);
return target.val;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){
ListNode target=map.get(key);
target.val=value;
remove(target);
pushFirst(target);
}else{
ListNode target=new ListNode(key,value);
map.put(key,target);
pushFirst(target);
if(map.size()>capacity){
ListNode last=dummy.prev;
remove(last);
map.remove(last.key);
}
}
}
public void remove(ListNode target){
target.prev.next=target.next;
target.next.prev=target.prev;
}
public void pushFirst(ListNode target){
dummy.next.prev=target;
target.next=dummy.next;
target.prev=dummy;
dummy.next=target;
}
}6、判断101-200之间有多少个质数,并输出所有质数
java
public class PrimeNumbers {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0; // 统计质数的数量
for (int i = 101; i <= 200; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
System.out.println(i); // 输出质数
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("Total prime numbers between 101 and 200: " + count);
}
public static boolean isPrime(int n) {
// 处理小于等于1的非质数情况
if (n <= 1) {
return false;
}
// 检查从2到n的平方根是否存在因子
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
return false; // 发现因子,非质数
}
}
// 无因子,确认是质数
return true;
}
}7、请分别写出一个Java堆、栈、元空间溢出的代码
1. Java堆溢出
java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HeapOverflow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Object> objects = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
objects.add(new Object()); // 不断创建对象并保留引用
}
}
}2. Java 栈溢出
java
public class StackOverflow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
recursiveMethod(1); // 递归调用,没有终止条件
}
private static void recursiveMethod(int i) {
recursiveMethod(i);
}
}3. 元空间溢出
java
import javassist.ClassPool;
public class MetaspaceOverflow {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPool classPool = ClassPool.getDefault();
for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
classPool.makeClass("Class" + i).toClass(); // 动态创建大量的类
}
}
}8、给定一个二叉搜索树,请找出其中第k小的元素
java
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
}
public class Solution {
private int count = 0; // 用于计数已遍历的节点
private int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 存储第k小的元素
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
inOrderTraverse(root, k);
return result;
}
private void inOrderTraverse(TreeNode node, int k) {
if (node == null) return;
// 先遍历左子树
inOrderTraverse(node.left, k);
// 访问节点
count++;
if (count == k) {
result = node.val;
return; // 找到第k小的元素后返回
}
// 遍历右子树
inOrderTraverse(node.right, k);
}
}9、两个线程,一个打印奇数,一个打印偶数,然后顺序打印出1-100
✅两个线程,一个打印奇数,一个打印偶数,然后顺序打印出1-100
java
public class AlternatePrinting {
private static int count = 1;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程A负责打印奇数
Thread threadA = new Thread(() -> {
while (count <= 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (count % 2 == 1) { // 打印奇数
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + count++);
lock.notify(); // 唤醒线程B
} else {
try {
lock.wait(); // 让出锁并等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}, "Thread-A");
// 线程B负责打印偶数
Thread threadB = new Thread(() -> {
while (count <= 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (count % 2 == 0) { // 打印偶数
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + count++);
lock.notify(); // 唤醒线程A
} else {
try {
lock.wait(); // 让出锁并等待
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}, "Thread-B");
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
}
}10、两个线程,一个打印123,一个打印ABC,交替输出1A2B3C
✅两个线程,一个打印123,一个打印ABC,交替输出1A2B3C
java
public class PrintingWithWaitNotify {
private static final Object lock = new Object();
private static boolean printNumber = true;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread numberThread = new Thread(new NumberPrinter());
Thread letterThread = new Thread(new LetterPrinter());
numberThread.start();
letterThread.start();
}
static class NumberPrinter implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
while (!printNumber) {
lock.wait();
}
System.out.print(i);
printNumber = false;
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
static class LetterPrinter implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock) {
try {
for (char c = 'A'; c <= 'C'; c++) {
while (printNumber) {
lock.wait();
}
System.out.print(c);
printNumber = true;
lock.notify();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}11、10个线程模拟赛马,所有马就绪后才能开跑,所有马到达终点后裁判宣布赛马成绩
✅10个线程模拟赛马,所有马就绪后才能开跑,所有马到达终点后裁判宣布赛马成绩
要实现这个功能,可以使用 CountDownLatch 来确保所有马都就绪后再开始比赛,并使用 CyclicBarrier 来确保所有马到达终点后裁判再宣布成绩。

java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
public class HorseRace {
// 用于存储赛马成绩
private static List<String> results = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 用于控制所有马同时开跑
private static CountDownLatch startLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// 用于确保所有马到达终点后再宣布成绩
private static CyclicBarrier finishBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(10, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 裁判宣布成绩
System.out.println("Race finished! Announcing results:");
for (String result : results) {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Horse("Horse " + i)).start();
}
// 所有马就绪后开跑
try {
System.out.println("All horses ready. Race starts now!");
startLatch.countDown(); // 马开跑
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class Horse implements Runnable {
private String name;
public Horse(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 马就绪,等待开跑信号
startLatch.await();
// 马开始跑
long raceTime = (long) (Math.random() * 10000); // 模拟跑的时间
Thread.sleep(raceTime);
// 马到达终点
results.add(name + " finished in " + raceTime + " ms");
// 等待其他马到达终点
finishBarrier.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
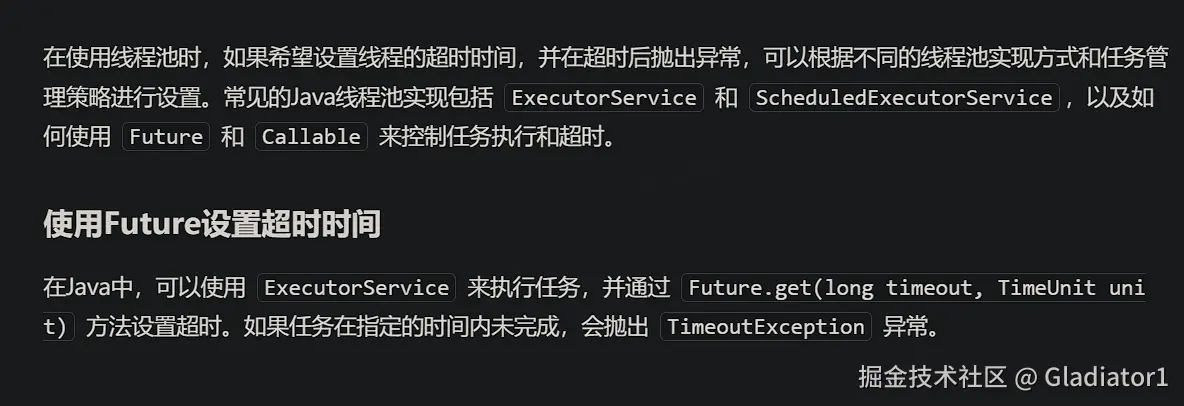
}12、线程池中怎么设置超时时间?一个线程如果要运行10s,怎么在1s就抛出异常
✅线程池中怎么设置超时时间?一个线程如果要运行10s,怎么在1s就抛出异常
java
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class ThreadPoolTimeoutExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 创建一个Callable任务
Callable<String> task = () -> {
// 模拟执行10秒的任务
Thread.sleep(10000);
return "Task completed";
};
// 提交任务并获取Future对象
Future<String> future = executor.submit(task);
try {
// 设置任务的超时时间为1秒
String result = future.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 1秒超时
System.out.println(result);
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
System.out.println("Task timed out!");
future.cancel(true); // 取消任务
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
}