python
复制代码
import time
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
from scipy.special import comb
def linear_interpolation(route, num_points):
# 1. 线性插值
# 将经纬度分开
lons = np.array([point[0] for point in route])
lats = np.array([point[1] for point in route])
# 创建插值函数
distance = np.cumsum(np.sqrt(np.ediff1d(lons, to_begin=0) ** 2 + np.ediff1d(lats, to_begin=0) ** 2))
distance /= distance[-1]
# 创建插值函数
lon_interp = interp1d(distance, lons, kind='linear')
lat_interp = interp1d(distance, lats, kind='linear')
# 生成新的距离点
new_distance = np.linspace(0, 1, num_points)
# 插值
new_lons = lon_interp(new_distance)
new_lats = lat_interp(new_distance)
return list(zip(new_lons, new_lats))
def cubic_spline_interpolation(route, num_points):
# 2. 三次样条插值
lons = np.array([point[0] for point in route])
lats = np.array([point[1] for point in route])
distance = np.cumsum(np.sqrt(np.ediff1d(lons, to_begin=0) ** 2 + np.ediff1d(lats, to_begin=0) ** 2))
distance /= distance[-1]
lon_interp = interp1d(distance, lons, kind='cubic')
lat_interp = interp1d(distance, lats, kind='cubic')
new_distance = np.linspace(0, 1, num_points)
new_lons = lon_interp(new_distance)
new_lats = lat_interp(new_distance)
return list(zip(new_lons, new_lats))
def bernstein_poly(i, n, t):
return comb(n, i) * (t ** i) * ((1 - t) ** (n - i))
def bezier_curve(route, num_points=100):
# 3. 贝塞尔曲线插值
n = len(route) - 1
t = np.linspace(0, 1, num_points)
lons = np.array([point[0] for point in route])
lats = np.array([point[1] for point in route])
new_lons = np.zeros(num_points)
new_lats = np.zeros(num_points)
for i in range(n + 1):
new_lons += bernstein_poly(i, n, t) * lons[i]
new_lats += bernstein_poly(i, n, t) * lats[i]
return list(zip(new_lons, new_lats))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
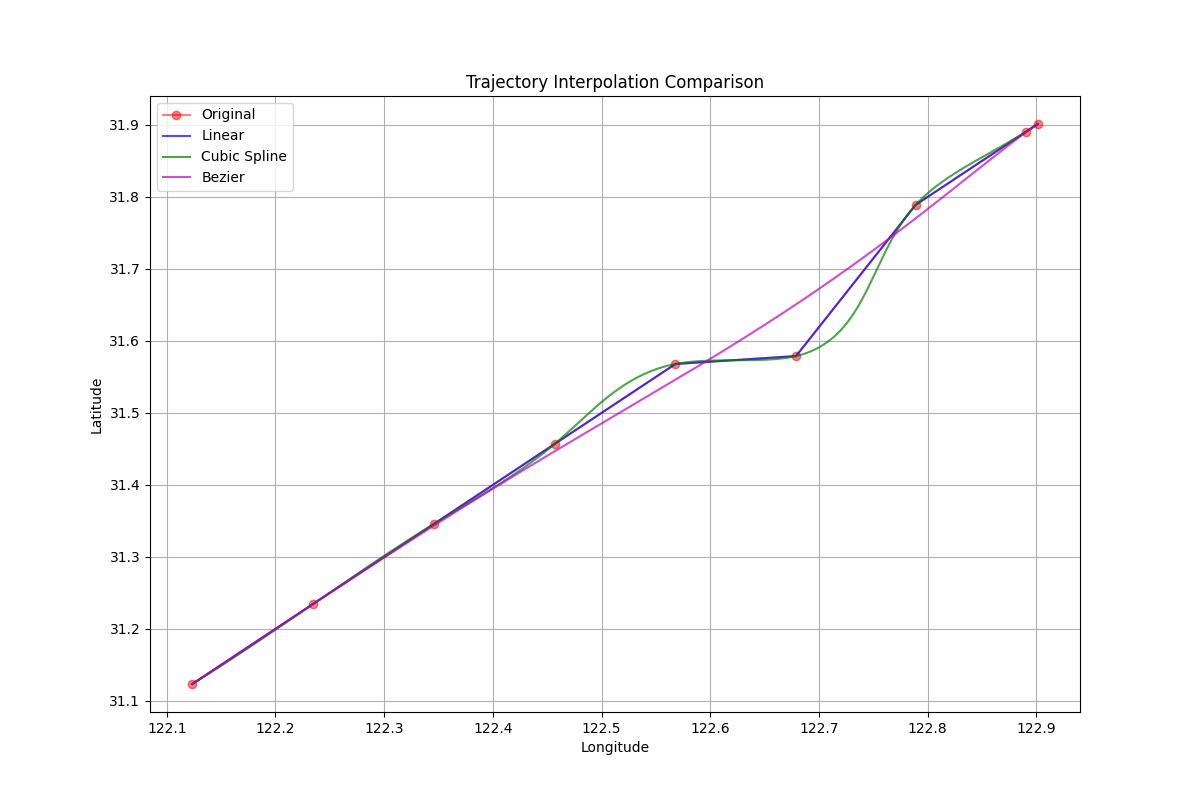
def plot_routes(original, linear, cubic, bezier):
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
# 原始轨迹
orig_lons, orig_lats = zip(*original)
plt.plot(orig_lons, orig_lats, 'ro-', label='Original', alpha=0.5)
# 线性插值
lin_lons, lin_lats = zip(*linear)
plt.plot(lin_lons, lin_lats, 'b-', label='Linear', alpha=0.7)
# 三次样条插值
cub_lons, cub_lats = zip(*cubic)
plt.plot(cub_lons, cub_lats, 'g-', label='Cubic Spline', alpha=0.7)
# 贝塞尔曲线
bez_lons, bez_lats = zip(*bezier)
plt.plot(bez_lons, bez_lats, 'm-', label='Bezier', alpha=0.7)
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('Longitude')
plt.ylabel('Latitude')
plt.title('Trajectory Interpolation Comparison')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 原始轨迹数据
route = [
[122.123456, 31.123456],
[122.234567, 31.234567],
[122.345678, 31.345678],
[122.456789, 31.456789],
[122.567890, 31.567890],
[122.678901, 31.578901],
[122.789012, 31.789012],
[122.890123, 31.890123],
[122.901234, 31.901234],
]
start_time = time.time()
# 线性插值
linear_route = linear_interpolation(route, 1000)
print("线性插值结果 (前5个点):", linear_route[:5])
print("线性插值用时:", time.time() - start_time, "秒")
start_time = time.time()
# 三次样条插值
cubic_route = cubic_spline_interpolation(route, 1000)
print("三次样条插值结果 (前5个点):", cubic_route[:5])
print("三次样条插值用时:", time.time() - start_time, "秒")
start_time = time.time()
# 贝塞尔曲线插值
bezier_route = bezier_curve(route, 1000)
print("贝塞尔曲线插值结果 (前5个点):", bezier_route[:5])
print("贝塞尔曲线插值用时:", time.time() - start_time, "秒")
# 绘制比较图
plot_routes(route, linear_route, cubic_route, bezier_route)
python
复制代码
# 4、拉格朗日插值算法
import time
from scipy.interpolate import lagrange
import numpy as np
def lagrange_interp(x, y, x_new):
"""
Lagrange interpolation
:param x: x coordinates of data points
:param y: y coordinates of data points
:param x_new: x coordinates of new interpolated points
:return: y coordinates of new interpolated points
"""
f = lagrange(x, y)
y_new = f(x_new)
return y_new
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 原始数据
route = [
[122.123456, 31.123456],
[122.234567, 31.234567],
[122.345678, 31.345678],
[122.456789, 31.456789],
[122.567890, 31.567890],
[122.678901, 31.678901],
[122.789012, 31.789012],
[122.890123, 31.890123],
[122.901234, 31.901234],
]
x_list = [i[0] for i in route]
y_list = [i[1] for i in route]
# 新数据
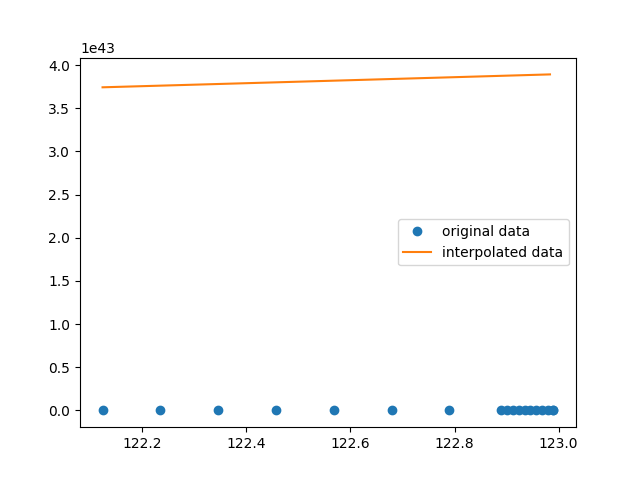
x_new = np.arange(122.123456, 122.990123, 0.01)
y_new = lagrange_interp(x_list, y_list, x_new)
# 绘图
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(x_list, y_list, 'o', label='original data')
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, label='interpolated data')
plt.legend()
plt.show()