一:背景
1. 讲故事
前面几篇我们说完了 harmony 的几个注入点,这篇我们聚焦注入点可接收的几类参数的解读,非常有意思,在.NET高级调试 视角下也是非常重要的,到底是哪些参数,用一张表格整理如下:
| 参数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
__instance |
访问非静态方法的实例(类似 this)。 |
__result |
获取/修改返回值,要想修改用 ref。 |
__resultRef |
修改返回引用(方法返回是 ref 返回 )。 |
__state |
在前缀和后缀间传递自定义数据 。 |
___fields |
读写私有字段(三下划线开头,修改需加 ref)。 |
__args |
以 object[] 形式访问所有参数(修改数组即修改参数)。 |
方法参数同名 |
直接映射原参数。 |
__n |
__n 表示直接访问第 n 个参数,从 0 开始)。 |
__originalMethod |
获取原方法的 MethodBase。 |
__runOriginal |
判断原方法是否被执行。 |
大体上有10类参数,接下来开始介绍吧。
二:补丁参数解读
1. __instance
我们都知道 new Thread() 出来的线程默认都是 前台线程,而这种线程会阻塞程序的退出,所以需求就来了,能不能让 new Thread() 出来的线程自动变为后台线程呢?哈哈,这就需要借助 __instance 啦,我们对有参Start 方法进行注入, 参考代码如下:
C#
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.threadhook");
harmony.PatchAll();
var thread = new Thread((object obj) =>
{
var currentThread = Thread.CurrentThread;
Console.WriteLine($"3. tid={currentThread.ManagedThreadId}, 线程内容为: {obj}, 是否为后台线程:{Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground}");
});
Console.WriteLine($"1. new Thread() 完毕,当前是否为后台线程:{thread.IsBackground}");
thread.Start("hello world!");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(Thread), "Start", new Type[] { typeof(object) })]
public class ThreadStartHook
{
public static void Prefix(Thread __instance)
{
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
Console.WriteLine($"2. 即将 Thread.Start: 线程tid={__instance.ManagedThreadId}");
Console.WriteLine("----------------------------");
// 将默认的 前台线程 改为 后台线程
__instance.IsBackground = true;
}
}
从卦中来看,非常完美,现在 Thread 再也不会阻塞程序的退出啦。。。
2. __state
有时候我们有这样的一个场景,想测量一个某个底层sdk方法的执行时间,更具体一点就是测量某个线程的执行时间,做法的话通常有两种。
- 在类中定义私有字段。
有些朋友可能知道 harmony 有这么一条规定,那就是xxxhook中的注入方法必须是 static,所以我们只能定义 static 类型的Dictionary字段来记录,有点尴尬,参考代码如下:
C#
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.threadhook");
harmony.PatchAll();
var thread = new Thread((object obj) =>
{
Thread.Sleep(new Random().Next(1000, 3000));
var currentThread = Thread.CurrentThread;
Console.WriteLine($"tid={currentThread.ManagedThreadId}, 线程内容为: {obj}");
});
thread.Start("hello world!");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(Thread), "StartCallback")]
public class ThreadStartHook
{
public static ConcurrentDictionary<int, Stopwatch> tidThreadTimeDict = new ConcurrentDictionary<int, Stopwatch>();
public static void Prefix(Thread __instance)
{
Console.WriteLine($"1. 正在测量线程的执行时间...");
var watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Start();
tidThreadTimeDict.TryAdd(__instance.ManagedThreadId, watch);
}
public static void Postfix(Thread __instance)
{
var watch = tidThreadTimeDict[__instance.ManagedThreadId];
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"2. 线程执行结束,耗费时间:{watch.Elapsed.ToString()}");
}
}
从卦中可以看到当前线程执行了 1.58s,有点意思吧,针对上面的代码,有些朋友可能会挑毛病了。
- 实现过于繁琐。
确实有点繁琐,这时候就可以借助 __state 来充当 Perfix 和 Postfix 之间的临时变量,同时要知道 __state 可以定义成任何类型。
- 我要看到方法,而不是线程
从卦中的输出看,确实我们要监控方法名,而不是线程,否则在真实场景中就会很乱,方法名我们从 Thread 下的 _startHelper 字段提取,这是一个匿名类,修改后的代码如下:
C#
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(Thread), "StartCallback")]
public class ThreadStartCallbackHook
{
public static void Prefix(Thread __instance, out (Stopwatch, string) __state)
{
object startHelper = Traverse.Create(__instance).Field("_startHelper").GetValue();
string methodName = Traverse.Create(startHelper).Field<Delegate>("_start").Value.Method.Name;
object startArg = Traverse.Create(startHelper).Field("_startArg").GetValue();
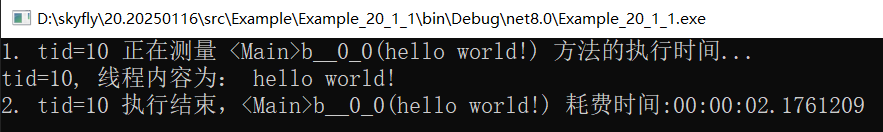
Console.WriteLine($"1. 正在测量 {methodName}({startArg}) 方法的执行时间...");
var stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
__state = (stopwatch, $"{methodName}({startArg})");
}
public static void Postfix(Thread __instance, (Stopwatch, string) __state)
{
var (stopwatch, methodName) = __state;
Console.WriteLine($"2. 线程执行结束,{methodName} 耗费时间:{stopwatch.Elapsed.ToString()}");
}
}
哈哈,修改后的代码相比第一版是不是爽了很多。。。
3. __originalMethod
这个参数也是蛮重要的,通过它可以让你知道当前 patch 正骑在哪个原方法上,起到了过滤识别的作用,参考代码如下:
C#
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var harmony = new Harmony("com.example.threadhook");
harmony.PatchAll();
var max = Math.Max(10, 20);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
[HarmonyPatch(typeof(Math), "Max", new Type[] { typeof(int), typeof(int) })]
public class ThreadStartCallbackHook
{
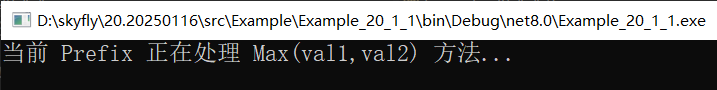
public static void Prefix(Thread __instance, MethodBase __originalMethod)
{
var parameters = string.Join(",", __originalMethod.GetParameters().Select(i => i.Name));
Console.WriteLine($"当前 Prefix 正在处理 {__originalMethod.Name}({parameters}) 方法...");
}
}
三:总结
灵活运用这些奇奇怪怪的参数,相信你对 harmony 的使用有了一个全新的认识,大家可以开开心心的投放生产吧,去解决那些 Windows,Linux 上的 .NET程序的疑难杂症。
