Vite的底层工作原理,关键点:
- 原生ES模块(ESM)支持 :利用
现代浏览器原生支持的ES模块系统,无需打包 - 按需编译 :只
编译当前页面需要的文件,而非整个应用 - 预构建依赖 :对node_modules中的依赖进行
预构建 - 即时服务 :基于ESM的
即时服务器启动,毫秒级热更新
手写简易Vite实现
做个简化版 的 Vite服务器:
node服务器,处理浏览器加载各种资源的请求
- index.html
- js
- vue
目录结构如下:
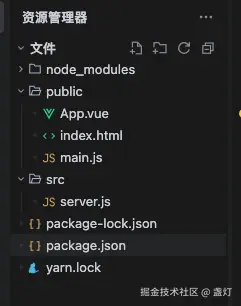
1. 基础服务器搭建
- 基础服务器搭建
javascript
const Koa = require("koa");
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
const app = new Koa(); // 创建Koa应用实例
// 裸模块路径重写函数(稍后定义)
function rewriteImport(content) { /*...*/ }
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log("KVite Server running at 3001");
});这部分初始化了一个Koa服务器,设置了3001端口监听,并预留了核心的rewriteImport函数位置。
- 主请求处理中间件
javascript
app.use(async (ctx) => {
const { url } = ctx.request; // 获取请求路径
// 路由分发处理(下面分四个部分详细说明)
if (url === "/") { /* 处理首页 */ }
else if (url.endsWith(".js")) { /* 处理JS文件 */ }
else if (url.startsWith("/@modules/")) { /* 处理npm模块 */ }
else if (url.indexOf(".vue") > -1) { /* 处理Vue单文件组件 */ }
});这是核心中间件,根据不同的URL路径分发到对应的处理逻辑。
- 首页请求处理
javascript
if (url === "/") {
ctx.type = "text/html";
let content = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, "..", "public", "index.html"), "utf-8");
// 重写HTML内联模块脚本中的导入路径
content = content.replace(
/<script type="module">([\s\S]*?)<\/script>/g,
(match, scriptContent) => {
const rewrittenScript = rewriteImport(scriptContent);
return `<script type="module">${rewrittenScript}</script>`;
}
);
ctx.body = content;
}处理根路径请求,读取index.html并重写其中的模块导入路径。
- 普通JS文件处理
javascript
else if (url.endsWith(".js")) {
const p = path.join(__dirname, "..", "public", url);
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
const content = fs.readFileSync(p, "utf-8");
ctx.body = rewriteImport(content); // 重写JS文件中的导入路径
}处理.js文件请求,读取文件内容并重写其中的模块导入路径。
- NPM模块请求处理
javascript
else if (url.startsWith("/@modules/")) {
const moduleName = ctx.request.url.replace("/@modules/", "");
// 特殊处理vue模块
if (moduleName === "vue") {
const vuePath = path.join(__dirname, "..", "node_modules", "vue", "dist", "vue.esm-browser.js");
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
ctx.body = rewriteImport(fs.readFileSync(vuePath, "utf-8"));
}
// 处理@vue/开头的作用域包
else if (moduleName.startsWith("@vue/")) {
const [scope, packageName] = moduleName.split("/");
const modulePath = path.join(__dirname, "..", "node_modules", scope, packageName);
// 通过package.json找到入口文件
const modulePkg = require(path.join(modulePath, "package.json"));
const entryPath = path.join(modulePath, modulePkg.module || modulePkg.main || "index.js");
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
ctx.body = rewriteImport(fs.readFileSync(entryPath, "utf-8"));
}
// 处理普通npm包
else {
const modulePath = path.join(__dirname, "..", "node_modules", moduleName);
// 同上,通过package.json找到入口文件
const modulePkg = require(path.join(modulePath, "package.json"));
const entryPath = path.join(modulePath, modulePkg.module || modulePkg.main || "index.js");
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
ctx.body = rewriteImport(fs.readFileSync(entryPath, "utf-8"));
}
}处理被重写为/@modules/开头的npm模块请求,根据package.json找到正确的入口文件。
- Vue单文件组件处理
javascript
else if (url.indexOf(".vue") > -1) {
const p = path.join(__dirname, "..", "public", url.split("?")[0]);
const file = fs.readFileSync(p, "utf-8");
// 使用Vue官方编译器解析SFC
const { parse, compileTemplate } = require("@vue/compiler-sfc");
const { descriptor } = parse(file);
// 首次请求(不带type参数)
if (!ctx.request.query.type) {
let scriptContent = descriptor.script.content.replace("export default", "const __script =");
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
ctx.body = `
${rewriteImport(scriptContent)}
import { render as __render } from "${url}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`;
}
// 模板部分请求
else if (ctx.request.query.type === "template") {
const { code } = compileTemplate({ source: descriptor.template.content });
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
ctx.body = rewriteImport(code);
}
}处理.vue文件请求,将单文件组件拆分为脚本和模板两部分分别处理。
- 路径重写函数
javascript
function rewriteImport(content) {
return content.replace(/from ['"](.*)['"]/g, (s1, s2) => {
// 保留相对路径和绝对路径
if (s2.startsWith("./") || s2.startsWith("../") || s2.startsWith("/")) {
return s1;
}
// 重写裸模块为/@modules/路径
else {
return `from '/@modules/${s2}'`;
}
});
}将代码中的裸模块导入(如import vue from 'vue')重写为浏览器可识别的路径格式(import vue from '/@modules/vue')。
index.html
js
// 1. 返回宿主页
if (url === "/") {
ctx.type = "text/html";
let content = fs.readFileSync(path.join(__dirname, "..", "public", "index.html"), "utf-8");
// 处理HTML中的内联模块脚本
content = content.replace(
/<script type="module">([\s\S]*?)<\/script>/g,
(match, scriptContent) => {
const rewrittenScript = rewriteImport(scriptContent);
return `<script type="module">${rewrittenScript}</script>`;
}
);
ctx.body = content;
}这段代码在服务器返回HTML页面时,会自动查找并重写其中的<script type="module">内容,将裸模块导入(如import vue from 'vue')转换为浏览器可识别的路径格式(如/@modules/vue),使得浏览器能够正确加载Node模块。


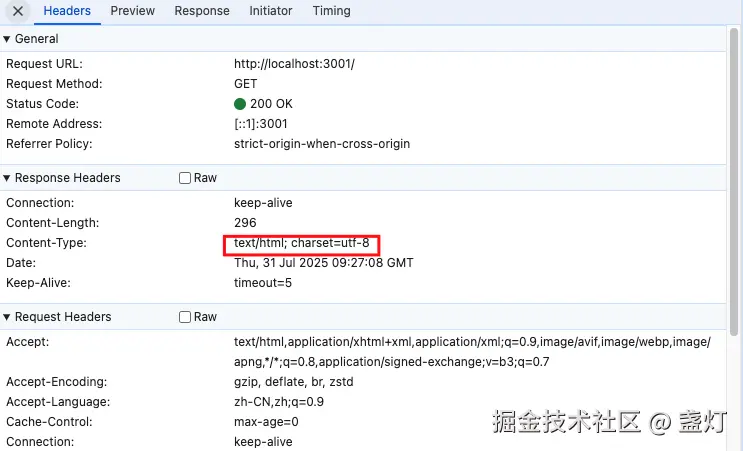
js
js
// 2. 处理JS文件请求
else if (url.endsWith(".js")) {
const p = path.join(__dirname, "..", "public", url);
ctx.type = "application/javascript";
const content = fs.readFileSync(p, "utf-8");
ctx.body = rewriteImport(content);
}这段代码处理.js文件请求,读取文件内容后通过rewriteImport函数转换模块导入路径(如将'vue'转成'/@modules/vue'),确保浏览器能正确解析依赖。
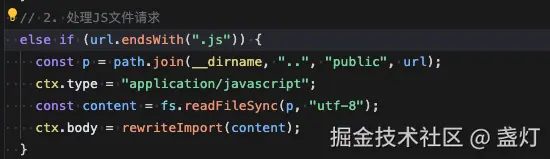
vue
专门处理/@modules/开头的请求,根据模块名(如vue、@vue/runtime-dom或其他npm包)从node_modules中读取对应的ES模块文件,并通过rewriteImport转换内部依赖路径后返回给浏览器。
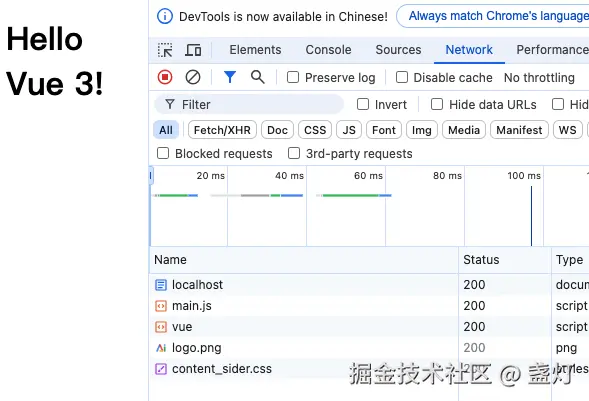
2. 添加Vue SFC文件支持
处理.vue单文件组件请求:首次请求返回脚本逻辑并注入模板导入,带?type=template的二次请求则编译模板为渲染函数,最终组合成完整的Vue组件返回给浏览器。
javascript
// 在中间件中添加SFC文件处理逻辑
else if (url.indexOf('.vue') > -1) {
const p = path.join(__dirname, url.split('?')[0])
const file = fs.readFileSync(p, 'utf-8')
// 解析SFC
const { parse } = require('@vue/compiler-sfc')
const { descriptor } = parse(file)
// 处理不带查询参数的请求
if (!ctx.request.query.type) {
// 处理script部分
let scriptContent = descriptor.script.content
scriptContent = scriptContent.replace('export default', 'const __script =')
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
ctx.body = `
${rewriteImport(scriptContent)}
import { render as __render } from "${url}?type=template"
__script.render = __render
export default __script
`
}
// 处理template部分请求
else if (ctx.request.query.type === 'template') {
// 编译模板为渲染函数
const { compileTemplate } = require('@vue/compiler-dom')
const template = descriptor.template.content
const { code } = compileTemplate({ source: template })
ctx.type = 'application/javascript'
ctx.body = rewriteImport(code)
}
}
3. 客户端HTML示例
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<script type="module">
// 浏览器环境变量hack
window.process = { env: { NODE_ENV: 'development' } }
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App).mount('#app')
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>完整工作流程
- 浏览器请求index.html
- HTML中加载main.js (
type=module) - 处理main.js中的裸模块导入 (如
vue)- 重写为
/@modules/vue - 服务器返回预构建的vue模块
- 重写为
- 处理.vue文件请求
- 解析SFC为描述对象
- 分别处理script和template部分
- 动态生成组件代码
- 浏览器执行生成的代码,渲染应用
总结
当然,有的小伙伴说还欠其他的文件兼容,比如css,比如图片,比如json,最后还有热更,和预构建:
- CSS处理 :支持
<style>块解析 - 静态资源处理 :
图片、JSON等资源导入 - 热更新(HMR) :通过
WebSocket实现 - 预构建优化 :使用
esbuild预构建依赖
当面试官问:
为什么 Vite 速度比 Webpack 快?,这时候我们知道怎么回答了吧。
1. 组成结构
- 开发服务器:基于原生ES模块,支持极速HMR
- 生产构建:使用Rollup预配置优化打包
2. 核心特性
- ⚡ 毫秒级冷启动(无打包)
- 🔥 即时模块热更新
- 🎯 真正的按需编译
3. 核心优势
| 对比维度 | Webpack | Vite |
|---|---|---|
| 启动 | 需构建依赖图 | 直接启动 |
| HMR | 全依赖链重编译 | 单模块更新 |
| 编译 | 全量预编译 | 动态按需编译 |
4. 工作原理
浏览器 → 请求ES模块 → 服务端动态编译 → 返回编译结果这个简易实现展示了
Vite的核心思想:利用浏览器原生ES模块系统,按需编译,实现快速开发体验。