1. 虚拟列表基础
首先,让我简单介绍一下虚拟列表的概念。虚拟列表(Virtual List)是一种优化长列表渲染性能的技术,它只渲染可视区域内的元素,而不是渲染整个列表。这样可以大大减少DOM节点数量,提高渲染性能。
虚拟列表的基本原理:
- 计算可视区域的高度和可以显示的元素数量
- 根据滚动位置确定应该渲染哪些元素
- 只渲染这些元素,并在它们周围添加适当的空白(padding)来保持滚动条的正确性
2. 渲染抖动问题
渲染抖动(Rendering Jitter)是指在滚动虚拟列表时,列表元素出现闪烁、跳动或不稳定的现象。这通常是由以下几个原因造成的:
2.1 渲染抖动的原因
- 滚动事件处理延迟:滚动事件触发频繁,如果处理逻辑复杂,可能导致渲染延迟。
- 高度计算不准确:如果元素的高度计算不准确,会导致滚动位置与实际渲染不匹配。
- DOM更新与滚动不同步:React的渲染机制可能导致DOM更新与滚动不同步。
- 浏览器重排/重绘:频繁的DOM操作可能导致浏览器重排/重绘,引起视觉抖动。
2.2 渲染抖动的解决方案
2.2.1 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualList = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [isScrolling, setIsScrolling] = useState(false);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const rafId = useRef(null);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
setScrollTop(scrollRef.current.scrollTop);
setIsScrolling(true);
// 滚动结束后重置状态
clearTimeout(rafId.current);
rafId.current = setTimeout(() => {
setIsScrolling(false);
}, 150);
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
clearTimeout(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + visibleCount, data.length - 1);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight;
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex - 1) * itemHeight;
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px`, paddingBottom: `${paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => (
<div
key={startIndex + index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${(startIndex + index) * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
transition: isScrolling ? 'none' : 'all 0.2s ease',
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualList;2.2.2 使用Intersection Observer优化渲染
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithIntersectionObserver = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [visibleItems, setVisibleItems] = useState(new Set());
const containerRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
// 创建Intersection Observer
useEffect(() => {
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(
(entries) => {
const newVisibleItems = new Set(visibleItems);
entries.forEach(entry => {
const index = parseInt(entry.target.dataset.index);
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
newVisibleItems.add(index);
} else {
newVisibleItems.delete(index);
}
});
setVisibleItems(newVisibleItems);
},
{
root: containerRef.current,
threshold: 0.1,
}
);
// 观察所有项目
itemRefs.current.forEach(item => {
if (item) observer.observe(item);
});
return () => {
itemRefs.current.forEach(item => {
if (item) observer.unobserve(item);
});
};
}, [visibleItems]);
// 计算需要渲染的项目
const itemsToRender = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (visibleItems.has(i)) {
itemsToRender.push(i);
}
}
// 如果没有可见项目,初始化渲染前几个项目
if (itemsToRender.length === 0) {
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(visibleCount, data.length); i++) {
itemsToRender.push(i);
}
}
return (
<div
ref={containerRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ height: `${data.length * itemHeight}px`, position: 'relative' }}>
{itemsToRender.map(index => (
<div
key={index}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[index] = el}
data-index={index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${index * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
{data[index].content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithIntersectionObserver;3. 滚动锚点优化
滚动锚点(Scroll Anchoring)是指在滚动过程中保持用户关注的元素在视口中的位置相对稳定。在虚拟列表中,由于元素是动态渲染和销毁的,如果没有适当的锚点处理,用户在滚动时可能会感到迷失或不适。
3.1 滚动锚点问题的原因
- 动态内容加载:当新内容加载时,如果没有保持滚动位置,用户可能会突然跳转到列表的其他位置。
- 元素高度变化:如果列表项的高度是动态的,当高度变化时,滚动位置可能会发生偏移。
- 元素插入/删除:在列表中间插入或删除元素时,滚动位置可能会不正确。
3.2 滚动锚点优化方案
3.2.1 保存和恢复滚动位置
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithScrollAnchor = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [lastVisibleItem, setLastVisibleItem] = useState(null);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
// 计算当前可见的最后一个项目
const lastVisibleIndex = Math.floor((currentScrollTop + visibleCount * itemHeight) / itemHeight) - 1;
setLastVisibleItem(lastVisibleIndex);
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [itemHeight, visibleCount]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItem !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem * itemHeight - (visibleCount * itemHeight - itemHeight);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [data, lastVisibleItem, itemHeight, visibleCount]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + visibleCount, data.length - 1);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight;
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex - 1) * itemHeight;
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px`, paddingBottom: `${paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => (
<div
key={startIndex + index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${(startIndex + index) * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithScrollAnchor;3.2.2 使用CSS scroll-anchor属性
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithCSSScrollAnchor = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const rafId = useRef(null);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
setScrollTop(scrollRef.current.scrollTop);
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + visibleCount, data.length - 1);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight;
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex - 1) * itemHeight;
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
// 使用CSS scroll-anchor属性
scrollAnchor: 'auto',
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px`, paddingBottom: `${paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => (
<div
key={startIndex + index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${(startIndex + index) * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
// 为每个项目设置scroll-anchor
scrollAnchor: 'auto',
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithCSSScrollAnchor;3.2.3 动态高度列表的滚动锚点优化
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithDynamicHeight = ({ data, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [itemHeights, setItemHeights] = useState({});
const [totalHeight, setTotalHeight] = useState(0);
const [positions, setPositions] = useState([]);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
const lastVisibleItemRef = useRef(null);
// 初始化位置和高度
useEffect(() => {
const newPositions = [];
let currentPosition = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const height = itemHeights[i] || 50; // 默认高度50px
newPositions.push({
index: i,
top: currentPosition,
height: height,
});
currentPosition += height;
}
setPositions(newPositions);
setTotalHeight(currentPosition);
}, [data, itemHeights]);
// 更新项目高度
const updateItemHeight = useCallback((index, height) => {
setItemHeights(prev => ({
...prev,
[index]: height,
}));
}, []);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
// 找到当前可见的最后一个项目
let lastVisibleIndex = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= currentScrollTop + visibleCount * 100) { // 假设平均高度100px
lastVisibleIndex = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
lastVisibleItemRef.current = lastVisibleIndex;
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [positions, visibleCount]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据或高度变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItemRef.current !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 找到之前可见的最后一个项目的新位置
const lastVisibleItem = positions.find(p => p.index === lastVisibleItemRef.current);
if (lastVisibleItem) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem.top - (visibleCount * 100 - lastVisibleItem.height);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [positions, visibleCount]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
let startIndex = 0;
let endIndex = Math.min(visibleCount, data.length - 1);
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= scrollTop) {
startIndex = i;
}
if (positions[i].top + positions[i].height <= scrollTop + visibleCount * 100) {
endIndex = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = positions[startIndex]?.top || 0;
const paddingBottom = totalHeight - (positions[endIndex]?.top || 0) - (positions[endIndex]?.height || 0);
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * 100, // 假设平均高度100px
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px`, paddingBottom: `${paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => {
const actualIndex = startIndex + index;
const position = positions.find(p => p.index === actualIndex);
return (
<div
key={actualIndex}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[actualIndex] = el}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: `${position?.top || 0}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
<div
ref={el => {
if (el && !itemHeights[actualIndex]) {
// 测量实际高度
const height = el.getBoundingClientRect().height;
updateItemHeight(actualIndex, height);
}
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithDynamicHeight;4. 综合优化方案
现在,我将结合上述技术,提供一个综合优化方案,同时解决渲染抖动和滚动锚点问题。
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
const OptimizedVirtualList = ({
data,
estimatedItemHeight = 50,
visibleCount,
overscanCount = 3,
onScroll,
onItemsRendered
}) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [isScrolling, setIsScrolling] = useState(false);
const [itemHeights, setItemHeights] = useState({});
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const scrollTimeoutId = useRef(null);
const lastVisibleItemRef = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
// 计算每个项目的位置和总高度
const { positions, totalHeight } = useMemo(() => {
const newPositions = [];
let currentPosition = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const height = itemHeights[i] || estimatedItemHeight;
newPositions.push({
index: i,
top: currentPosition,
height: height,
bottom: currentPosition + height
});
currentPosition += height;
}
return {
positions: newPositions,
totalHeight: currentPosition
};
}, [data, itemHeights, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 更新项目高度
const updateItemHeight = useCallback((index, height) => {
setItemHeights(prev => {
if (prev[index] === height) return prev;
return { ...prev, [index]: height };
});
}, []);
// 处理滚动事件,使用requestAnimationFrame优化
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
setIsScrolling(true);
// 清除之前的超时
if (scrollTimeoutId.current) {
clearTimeout(scrollTimeoutId.current);
}
// 设置新的超时,标记滚动结束
scrollTimeoutId.current = setTimeout(() => {
setIsScrolling(false);
}, 150);
// 找到当前可见的最后一个项目
let lastVisibleIndex = 0;
const viewportBottom = currentScrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
lastVisibleIndex = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
lastVisibleItemRef.current = lastVisibleIndex;
// 调用外部回调
if (onScroll) {
onScroll({ scrollTop: currentScrollTop });
}
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight, onScroll]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll, { passive: true });
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
if (scrollTimeoutId.current) {
clearTimeout(scrollTimeoutId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据或高度变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItemRef.current !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 找到之前可见的最后一个项目的新位置
const lastVisibleItem = positions.find(p => p.index === lastVisibleItemRef.current);
if (lastVisibleItem) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const viewportHeight = visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem.top - (viewportHeight - lastVisibleItem.height);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const { startIndex, endIndex } = useMemo(() => {
const viewportBottom = scrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
let start = 0;
let end = Math.min(data.length - 1, visibleCount - 1);
// 使用二分查找优化起始索引的查找
let low = 0;
let high = positions.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (positions[mid].bottom <= scrollTop) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (positions[mid].top >= scrollTop) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
start = mid;
break;
}
}
if (low > high) {
start = low;
}
// 查找结束索引
for (let i = start; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
end = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 添加额外的渲染项(overscan)
start = Math.max(0, start - overscanCount);
end = Math.min(data.length - 1, end + overscanCount);
return { startIndex: start, endIndex: end };
}, [scrollTop, positions, data.length, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight, overscanCount]);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const { paddingTop, paddingBottom } = useMemo(() => {
const paddingTop = positions[startIndex]?.top || 0;
const paddingBottom = totalHeight - (positions[endIndex]?.bottom || 0);
return { paddingTop, paddingBottom };
}, [positions, startIndex, endIndex, totalHeight]);
// 调用外部回调
useEffect(() => {
if (onItemsRendered) {
onItemsRendered({
visibleStartIndex: startIndex + overscanCount,
visibleEndIndex: endIndex - overscanCount,
overscanStartIndex: startIndex,
overscanEndIndex: endIndex
});
}
}, [startIndex, endIndex, overscanCount, onItemsRendered]);
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
willChange: 'transform', // 优化滚动性能
}}
>
<div style={{ height: `${totalHeight}px`, position: 'relative' }}>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `${paddingTop}px`, paddingBottom: `${paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => {
const actualIndex = startIndex + index;
const position = positions.find(p => p.index === actualIndex);
return (
<div
key={actualIndex}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[actualIndex] = el}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: `${position?.top || 0}px`,
width: '100%',
// 在滚动时禁用过渡效果,减少抖动
transition: isScrolling ? 'none' : 'all 0.2s ease',
}}
>
<div
ref={el => {
if (el && !itemHeights[actualIndex]) {
// 测量实际高度
const height = el.getBoundingClientRect().height;
updateItemHeight(actualIndex, height);
}
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default OptimizedVirtualList;5. 图表和图文解释
5.1 虚拟列表工作原理图
+------------------------------------------+
| |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | 可视区域 (Viewport) | |
| | | |
| | +----------------------------+ | |
| | | | | |
| | | 渲染的项目 | | |
| | | | | |
| | +----------------------------+ | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| |
| 上方内边距 (未渲染的项目) |
| |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | 未渲染的项目 | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| |
| 下方内边距 (未渲染的项目) |
| |
+------------------------------------------+5.2 渲染抖动问题示意图
正常滚动:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
渲染抖动:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | (空白) | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
|
v
+-----------------+
| Item 11 |
+-----------------+5.3 滚动锚点优化示意图
数据加载前:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
数据加载后 (无锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 8 | -> | Item 9 | -> | Item 10 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
数据加载后 (有锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+5.4 动态高度列表的滚动锚点优化
高度变化前:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 (50px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) | -> | Item 12 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
高度变化后 (无锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 (100px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) | -> | Item 12 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
高度变化后 (有锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 9 | -> | Item 10 (100px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+6. 性能优化建议
- 使用React.memo:对于列表项组件,使用React.memo避免不必要的重新渲染。
- 避免内联函数:将事件处理函数提取到组件外部或使用useCallback。
- 使用key属性:确保每个列表项有稳定且唯一的key。
- 避免在渲染中计算:将复杂的计算移到useMemo中。
- 使用CSS will-change:对于滚动容器,使用will-change: transform优化性能。
- 使用passive事件监听器:对于滚动事件,使用{ passive: true }选项。
- 避免同步布局:避免在滚动事件处理程序中读取DOM属性,如offsetHeight。
- 使用虚拟化库:考虑使用成熟的虚拟化库,如react-window或react-virtualized。
7. 完整示例
下面是一个完整的示例,展示了如何使用优化后的虚拟列表组件:
import React, { useState, useEffect, useCallback } from 'react';
import OptimizedVirtualList from './OptimizedVirtualList';
// 生成测试数据
const generateData = (count) => {
return Array.from({ length: count }, (_, index) => ({
id: index,
content: `Item ${index}`,
// 随机高度,模拟动态高度列表
height: 30 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 70)
}));
};
const App = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
// 初始化数据
useEffect(() => {
setData(generateData(100));
}, []);
// 加载更多数据
const loadMoreData = useCallback(() => {
if (loading) return;
setLoading(true);
// 模拟异步加载
setTimeout(() => {
setData(prevData => [
...prevData,
...generateData(20)
]);
setLoading(false);
}, 1000);
}, [loading]);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(({ scrollTop }) => {
// 当滚动到底部时加载更多数据
const container = document.querySelector('.virtual-list-container');
if (container) {
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight, clientHeight } = container;
if (scrollHeight - scrollTop <= clientHeight * 1.5) {
loadMoreData();
}
}
}, [loadMoreData]);
// 处理项目渲染
const handleItemsRendered = useCallback(({ visibleStartIndex, visibleEndIndex }) => {
console.log(`Rendering items from ${visibleStartIndex} to${visibleEndIndex}`);
}, []);
// 渲染项目
const renderItem = useCallback((item) => {
return (
<div style={{
padding: '10px',
borderBottom: '1px solid #eee',
backgroundColor: '#fff',
boxSizing: 'border-box'
}}>
<h3>{item.content}</h3>
<p>This is item {item.id} with dynamic height.</p>
</div>
);
}, []);
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>Optimized Virtual List Demo</h1>
<div className="virtual-list-container">
<OptimizedVirtualList
data={data}
estimatedItemHeight={50}
visibleCount={10}
overscanCount={3}
onScroll={handleScroll}
onItemsRendered={handleItemsRendered}
renderItem={renderItem}
/>
</div>
{loading && <div className="loading">Loading more items...</div>}
</div>
);
};
export default App;8. 总结
在React虚拟列表实现中,渲染抖动和滚动锚点是两个常见但关键的问题。通过以下技术可以有效解决这些问题:
解决渲染抖动的技术:
- 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理:将滚动事件处理放在requestAnimationFrame中,确保与浏览器的渲染周期同步。
- 使用Intersection Observer:利用Intersection Observer API来确定哪些元素在可视区域内,而不是依赖滚动事件。
- 禁用滚动时的过渡效果:在滚动过程中禁用CSS过渡效果,减少视觉抖动。
- 使用passive事件监听器:对于滚动事件,使用{ passive: true }选项,提高滚动性能。
解决滚动锚点问题的技术:
- 保存和恢复滚动位置:在数据变化时,保存最后一个可见项目的索引,并在数据更新后恢复滚动位置。
- 使用CSS scroll-anchor属性:利用CSS的scroll-anchor属性,让浏览器自动处理滚动锚点。
- 动态高度列表的锚点优化:对于动态高度的列表,需要更精确地计算每个项目的位置,并在高度变化时调整滚动位置。
综合优化:
- 使用二分查找优化索引计算:对于长列表,使用二分查找来快速确定可视区域的起始和结束索引。
- 添加额外的渲染项(overscan):在可视区域之外额外渲染一些项目,减少滚动时的空白区域。
- 使用React.memo和useCallback:避免不必要的重新渲染和函数创建。
- 使用CSS will-change:对于滚动容器,使用will-change: transform优化性能。
通过综合应用这些技术,可以创建一个高性能、流畅的虚拟列表组件,有效解决渲染抖动和滚动锚点问题。
React虚拟列表实现中的渲染抖动问题与滚动锚点优化方案
虚拟列表是处理大量数据渲染的关键技术,但在实现过程中常会遇到渲染抖动和滚动锚点问题。本文将深入探讨这些问题并提供优化方案。
一、虚拟列表基础与渲染抖动问题
1. 虚拟列表工作原理
虚拟列表通过只渲染可视区域内的元素来优化性能,基本原理如下:
+------------------------------------------+
| |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | 可视区域 (Viewport) | |
| | | |
| | +----------------------------+ | |
| | | | | |
| | | 渲染的项目 | | |
| | | | | |
| | +----------------------------+ | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| |
| 上方内边距 (未渲染的项目) |
| |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| | | |
| | 未渲染的项目 | |
| | | |
| +------------------------------------+ |
| |
| 下方内边距 (未渲染的项目) |
| |
+------------------------------------------+2. 渲染抖动问题及原因
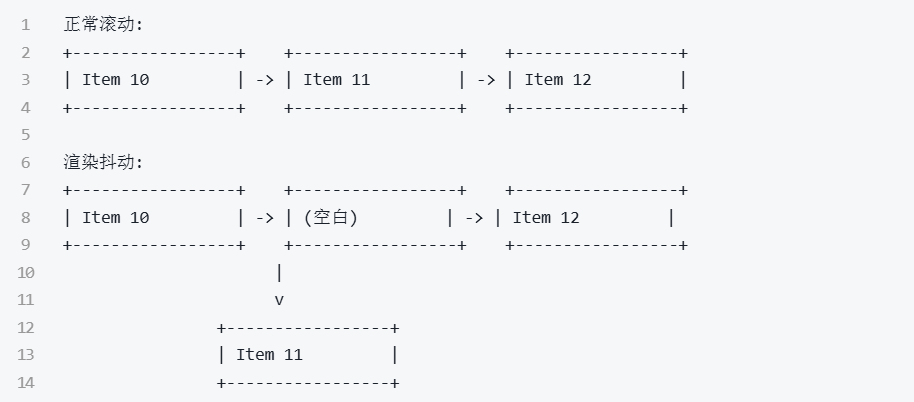
渲染抖动是指在滚动虚拟列表时,列表元素出现闪烁、跳动或不稳定的现象。
正常滚动 vs 渲染抖动对比图:
正常滚动:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
渲染抖动:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | (空白) | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
|
v
+-----------------+
| Item 11 |
+-----------------+
主要原因:
- 滚动事件处理延迟
- 高度计算不准确
- DOM更新与滚动不同步
- 浏览器重排/重绘
二、渲染抖动优化方案
1. 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualList = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [isScrolling, setIsScrolling] = useState(false);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const rafId = useRef(null);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
setScrollTop(scrollRef.current.scrollTop);
setIsScrolling(true);
// 滚动结束后重置状态
clearTimeout(rafId.current);
rafId.current = setTimeout(() => {
setIsScrolling(false);
}, 150);
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
clearTimeout(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + visibleCount, data.length - 1);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight;
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex - 1) * itemHeight;
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
willChange: 'transform', // 优化滚动性能
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `{paddingTop}px\`, paddingBottom: \`{paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => (
<div
key={startIndex + index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${(startIndex + index) * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
// 在滚动时禁用过渡效果,减少抖动
transition: isScrolling ? 'none' : 'all 0.2s ease',
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualList;
JSX代码
2. 使用Intersection Observer优化渲染
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithIntersectionObserver = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [visibleItems, setVisibleItems] = useState(new Set());
const containerRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
// 创建Intersection Observer
useEffect(() => {
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(
(entries) => {
const newVisibleItems = new Set(visibleItems);
entries.forEach(entry => {
const index = parseInt(entry.target.dataset.index);
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
newVisibleItems.add(index);
} else {
newVisibleItems.delete(index);
}
});
setVisibleItems(newVisibleItems);
},
{
root: containerRef.current,
threshold: 0.1,
}
);
// 观察所有项目
itemRefs.current.forEach(item => {
if (item) observer.observe(item);
});
return () => {
itemRefs.current.forEach(item => {
if (item) observer.unobserve(item);
});
};
}, [visibleItems]);
// 计算需要渲染的项目
const itemsToRender = [];
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (visibleItems.has(i)) {
itemsToRender.push(i);
}
}
// 如果没有可见项目,初始化渲染前几个项目
if (itemsToRender.length === 0) {
for (let i = 0; i < Math.min(visibleCount, data.length); i++) {
itemsToRender.push(i);
}
}
return (
<div
ref={containerRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ height: `${data.length * itemHeight}px`, position: 'relative' }}>
{itemsToRender.map(index => (
<div
key={index}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[index] = el}
data-index={index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${index * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
{data[index].content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithIntersectionObserver;
JSX代码
三、滚动锚点问题与优化方案
1. 滚动锚点问题及原因
滚动锚点是指在滚动过程中保持用户关注的元素在视口中的位置相对稳定。在虚拟列表中,由于元素是动态渲染和销毁的,可能导致滚动位置不稳定。
数据加载前后对比图:
数据加载前:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
数据加载后 (无锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 8 | -> | Item 9 | -> | Item 10 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
数据加载后 (有锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 | -> | Item 11 | -> | Item 12 |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+主要原因:
- 动态内容加载
- 元素高度变化
- 元素插入/删除
2. 保存和恢复滚动位置
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithScrollAnchor = ({ data, itemHeight, visibleCount }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [lastVisibleItem, setLastVisibleItem] = useState(null);
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
// 计算当前可见的最后一个项目
const lastVisibleIndex = Math.floor((currentScrollTop + visibleCount * itemHeight) / itemHeight) - 1;
setLastVisibleItem(lastVisibleIndex);
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [itemHeight, visibleCount]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItem !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem * itemHeight - (visibleCount * itemHeight - itemHeight);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [data, lastVisibleItem, itemHeight, visibleCount]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
const endIndex = Math.min(startIndex + visibleCount, data.length - 1);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const paddingTop = startIndex * itemHeight;
const paddingBottom = (data.length - endIndex - 1) * itemHeight;
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * itemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
}}
>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `{paddingTop}px\`, paddingBottom: \`{paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => (
<div
key={startIndex + index}
style={{
height: `${itemHeight}px`,
position: 'absolute',
top: `${(startIndex + index) * itemHeight}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithScrollAnchor;
3. 动态高度列表的滚动锚点优化
对于动态高度的列表,需要更精确地计算每个项目的位置。
高度变化前后对比图:
高度变化前:
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 (50px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) | -> | Item 12 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
高度变化后 (无锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 10 (100px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) | -> | Item 12 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
高度变化后 (有锚点优化):
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+
| Item 9 | -> | Item 10 (100px) | -> | Item 11 (50px) |
+-----------------+ +-----------------+ +-----------------+import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
const VirtualListWithDynamicHeight = ({ data, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight = 50 }) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [itemHeights, setItemHeights] = useState({});
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const lastVisibleItemRef = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
// 计算每个项目的位置和总高度
const { positions, totalHeight } = useMemo(() => {
const newPositions = [];
let currentPosition = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const height = itemHeights[i] || estimatedItemHeight;
newPositions.push({
index: i,
top: currentPosition,
height: height,
bottom: currentPosition + height
});
currentPosition += height;
}
return {
positions: newPositions,
totalHeight: currentPosition
};
}, [data, itemHeights, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 更新项目高度
const updateItemHeight = useCallback((index, height) => {
setItemHeights(prev => {
if (prev[index] === height) return prev;
return { ...prev, [index]: height };
});
}, []);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
// 找到当前可见的最后一个项目
let lastVisibleIndex = 0;
const viewportBottom = currentScrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
lastVisibleIndex = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
lastVisibleItemRef.current = lastVisibleIndex;
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll, { passive: true });
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据或高度变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItemRef.current !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 找到之前可见的最后一个项目的新位置
const lastVisibleItem = positions.find(p => p.index === lastVisibleItemRef.current);
if (lastVisibleItem) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const viewportHeight = visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem.top - (viewportHeight - lastVisibleItem.height);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const { startIndex, endIndex } = useMemo(() => {
const viewportBottom = scrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
let start = 0;
let end = Math.min(data.length - 1, visibleCount - 1);
// 使用二分查找优化起始索引的查找
let low = 0;
let high = positions.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (positions[mid].bottom <= scrollTop) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (positions[mid].top >= scrollTop) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
start = mid;
break;
}
}
if (low > high) {
start = low;
}
// 查找结束索引
for (let i = start; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
end = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
return { startIndex: start, endIndex: end };
}, [scrollTop, positions, data.length, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const { paddingTop, paddingBottom } = useMemo(() => {
const paddingTop = positions[startIndex]?.top || 0;
const paddingBottom = totalHeight - (positions[endIndex]?.bottom || 0);
return { paddingTop, paddingBottom };
}, [positions, startIndex, endIndex, totalHeight]);
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
willChange: 'transform',
}}
>
<div style={{ height: `${totalHeight}px`, position: 'relative' }}>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `{paddingTop}px\`, paddingBottom: \`{paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => {
const actualIndex = startIndex + index;
const position = positions.find(p => p.index === actualIndex);
return (
<div
key={actualIndex}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[actualIndex] = el}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: `${position?.top || 0}px`,
width: '100%',
}}
>
<div
ref={el => {
if (el && !itemHeights[actualIndex]) {
// 测量实际高度
const height = el.getBoundingClientRect().height;
updateItemHeight(actualIndex, height);
}
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default VirtualListWithDynamicHeight;
JSX代码
四、综合优化方案
下面是一个综合优化方案,同时解决渲染抖动和滚动锚点问题:
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
const OptimizedVirtualList = ({
data,
estimatedItemHeight = 50,
visibleCount,
overscanCount = 3,
onScroll,
onItemsRendered
}) => {
const [scrollTop, setScrollTop] = useState(0);
const [isScrolling, setIsScrolling] = useState(false);
const [itemHeights, setItemHeights] = useState({});
const scrollRef = useRef(null);
const itemRefs = useRef([]);
const rafId = useRef(null);
const scrollTimeoutId = useRef(null);
const lastVisibleItemRef = useRef(null);
const isDataChangeRef = useRef(false);
// 计算每个项目的位置和总高度
const { positions, totalHeight } = useMemo(() => {
const newPositions = [];
let currentPosition = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const height = itemHeights[i] || estimatedItemHeight;
newPositions.push({
index: i,
top: currentPosition,
height: height,
bottom: currentPosition + height
});
currentPosition += height;
}
return {
positions: newPositions,
totalHeight: currentPosition
};
}, [data, itemHeights, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 更新项目高度
const updateItemHeight = useCallback((index, height) => {
setItemHeights(prev => {
if (prev[index] === height) return prev;
return { ...prev, [index]: height };
});
}, []);
// 处理滚动事件,使用requestAnimationFrame优化
const handleScroll = useCallback(() => {
if (rafId.current !== null) {
return;
}
rafId.current = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
const currentScrollTop = scrollRef.current.scrollTop;
setScrollTop(currentScrollTop);
setIsScrolling(true);
// 清除之前的超时
if (scrollTimeoutId.current) {
clearTimeout(scrollTimeoutId.current);
}
// 设置新的超时,标记滚动结束
scrollTimeoutId.current = setTimeout(() => {
setIsScrolling(false);
}, 150);
// 找到当前可见的最后一个项目
let lastVisibleIndex = 0;
const viewportBottom = currentScrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
for (let i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
lastVisibleIndex = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
lastVisibleItemRef.current = lastVisibleIndex;
// 调用外部回调
if (onScroll) {
onScroll({ scrollTop: currentScrollTop });
}
}
rafId.current = null;
});
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight, onScroll]);
useEffect(() => {
const scrollElement = scrollRef.current;
if (scrollElement) {
scrollElement.addEventListener('scroll', handleScroll, { passive: true });
return () => {
scrollElement.removeEventListener('scroll', handleScroll);
if (rafId.current) {
cancelAnimationFrame(rafId.current);
}
if (scrollTimeoutId.current) {
clearTimeout(scrollTimeoutId.current);
}
};
}
}, [handleScroll]);
// 当数据或高度变化时,尝试保持滚动位置
useEffect(() => {
if (isDataChangeRef.current && lastVisibleItemRef.current !== null && scrollRef.current) {
// 找到之前可见的最后一个项目的新位置
const lastVisibleItem = positions.find(p => p.index === lastVisibleItemRef.current);
if (lastVisibleItem) {
// 计算新的滚动位置,使最后一个可见的项目保持在相同位置
const viewportHeight = visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
const newScrollTop = lastVisibleItem.top - (viewportHeight - lastVisibleItem.height);
// 使用requestAnimationFrame确保在下一帧应用滚动位置
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
if (scrollRef.current) {
scrollRef.current.scrollTop = newScrollTop;
setScrollTop(newScrollTop);
}
});
}
}
isDataChangeRef.current = true;
}, [positions, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight]);
// 计算可视区域的起始索引和结束索引
const { startIndex, endIndex } = useMemo(() => {
const viewportBottom = scrollTop + visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight;
let start = 0;
let end = Math.min(data.length - 1, visibleCount - 1);
// 使用二分查找优化起始索引的查找
let low = 0;
let high = positions.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (positions[mid].bottom <= scrollTop) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (positions[mid].top >= scrollTop) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
start = mid;
break;
}
}
if (low > high) {
start = low;
}
// 查找结束索引
for (let i = start; i < positions.length; i++) {
if (positions[i].top <= viewportBottom) {
end = i;
} else {
break;
}
}
// 添加额外的渲染项(overscan)
start = Math.max(0, start - overscanCount);
end = Math.min(data.length - 1, end + overscanCount);
return { startIndex: start, endIndex: end };
}, [scrollTop, positions, data.length, visibleCount, estimatedItemHeight, overscanCount]);
// 计算内边距,保持滚动条的正确性
const { paddingTop, paddingBottom } = useMemo(() => {
const paddingTop = positions[startIndex]?.top || 0;
const paddingBottom = totalHeight - (positions[endIndex]?.bottom || 0);
return { paddingTop, paddingBottom };
}, [positions, startIndex, endIndex, totalHeight]);
// 调用外部回调
useEffect(() => {
if (onItemsRendered) {
onItemsRendered({
visibleStartIndex: startIndex + overscanCount,
visibleEndIndex: endIndex - overscanCount,
overscanStartIndex: startIndex,
overscanEndIndex: endIndex
});
}
}, [startIndex, endIndex, overscanCount, onItemsRendered]);
return (
<div
ref={scrollRef}
style={{
height: visibleCount * estimatedItemHeight,
overflow: 'auto',
position: 'relative',
willChange: 'transform', // 优化滚动性能
}}
>
<div style={{ height: `${totalHeight}px`, position: 'relative' }}>
<div style={{ paddingTop: `{paddingTop}px\`, paddingBottom: \`{paddingBottom}px` }}>
{data.slice(startIndex, endIndex + 1).map((item, index) => {
const actualIndex = startIndex + index;
const position = positions.find(p => p.index === actualIndex);
return (
<div
key={actualIndex}
ref={el => itemRefs.current[actualIndex] = el}
style={{
position: 'absolute',
top: `${position?.top || 0}px`,
width: '100%',
// 在滚动时禁用过渡效果,减少抖动
transition: isScrolling ? 'none' : 'all 0.2s ease',
}}
>
<div
ref={el => {
if (el && !itemHeights[actualIndex]) {
// 测量实际高度
const height = el.getBoundingClientRect().height;
updateItemHeight(actualIndex, height);
}
}}
>
{item.content}
</div>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default OptimizedVirtualList;
JSX代码
五、性能优化建议
- 使用React.memo:对于列表项组件,使用React.memo避免不必要的重新渲染。
- 避免内联函数:将事件处理函数提取到组件外部或使用useCallback。
- 使用key属性:确保每个列表项有稳定且唯一的key。
- 避免在渲染中计算:将复杂的计算移到useMemo中。
- 使用CSS will-change:对于滚动容器,使用will-change: transform优化性能。
- 使用passive事件监听器:对于滚动事件,使用{ passive: true }选项。
- 避免同步布局:避免在滚动事件处理程序中读取DOM属性,如offsetHeight。
- 使用虚拟化库:考虑使用成熟的虚拟化库,如react-window或react-virtualized。
六、完整示例
import React, { useState, useEffect, useCallback } from 'react';
import OptimizedVirtualList from './OptimizedVirtualList';
// 生成测试数据
const generateData = (count) => {
return Array.from({ length: count }, (_, index) => ({
id: index,
content: `Item ${index}`,
// 随机高度,模拟动态高度列表
height: 30 + Math.floor(Math.random() * 70)
}));
};
const App = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([]);
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(false);
// 初始化数据
useEffect(() => {
setData(generateData(100));
}, []);
// 加载更多数据
const loadMoreData = useCallback(() => {
if (loading) return;
setLoading(true);
// 模拟异步加载
setTimeout(() => {
setData(prevData => [
...prevData,
...generateData(20)
]);
setLoading(false);
}, 1000);
}, [loading]);
// 处理滚动事件
const handleScroll = useCallback(({ scrollTop }) => {
// 当滚动到底部时加载更多数据
const container = document.querySelector('.virtual-list-container');
if (container) {
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight, clientHeight } = container;
if (scrollHeight - scrollTop <= clientHeight * 1.5) {
loadMoreData();
}
}
}, [loadMoreData]);
// 处理项目渲染
const handleItemsRendered = useCallback(({ visibleStartIndex, visibleEndIndex }) => {
console.log(`Rendering items from {visibleStartIndex} to {visibleEndIndex}`);
}, []);
// 渲染项目
const renderItem = useCallback((item) => {
return (
<div style={{
padding: '10px',
borderBottom: '1px solid #eee',
backgroundColor: '#fff',
boxSizing: 'border-box'
}}>
<h3>{item.content}</h3>
<p>This is item {item.id} with dynamic height.</p>
</div>
);
}, []);
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>Optimized Virtual List Demo</h1>
<div className="virtual-list-container">
<OptimizedVirtualList
data={data}
estimatedItemHeight={50}
visibleCount={10}
overscanCount={3}
onScroll={handleScroll}
onItemsRendered={handleItemsRendered}
renderItem={renderItem}
/>
</div>
{loading && <div className="loading">Loading more items...</div>}
</div>
);
};
export default App;
JSX代码
七、总结
在React虚拟列表实现中,渲染抖动和滚动锚点是两个常见但关键的问题。通过以下技术可以有效解决这些问题:
解决渲染抖动的技术:
- 使用requestAnimationFrame优化滚动事件处理:将滚动事件处理放在requestAnimationFrame中,确保与浏览器的渲染周期同步。
- 使用Intersection Observer:利用Intersection Observer API来确定哪些元素在可视区域内,而不是依赖滚动事件。
- 禁用滚动时的过渡效果:在滚动过程中禁用CSS过渡效果,减少视觉抖动。
- 使用passive事件监听器:对于滚动事件,使用{ passive: true }选项,提高滚动性能。
解决滚动锚点问题的技术:
- 保存和恢复滚动位置:在数据变化时,保存最后一个可见项目的索引,并在数据更新后恢复滚动位置。
- 使用CSS scroll-anchor属性:利用CSS的scroll-anchor属性,让浏览器自动处理滚动锚点。
- 动态高度列表的锚点优化:对于动态高度的列表,需要更精确地计算每个项目的位置,并在高度变化时调整滚动位置。
综合优化:
- 使用二分查找优化索引计算:对于长列表,使用二分查找来快速确定可视区域的起始和结束索引。
- 添加额外的渲染项(overscan):在可视区域之外额外渲染一些项目,减少滚动时的空白区域。
- 使用React.memo和useCallback:避免不必要的重新渲染和函数创建。
- 使用CSS will-change:对于滚动容器,使用will-change: transform优化性能。
通过综合应用这些技术,可以创建一个高性能、流畅的虚拟列表组件,有效解决渲染抖动和滚动锚点问题。
