
扫描二维码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长
发现1000+提升效率与开发的AI工具和实用程序:https://tools.cmdragon.cn/
FastAPI BackgroundTasks 进阶指南
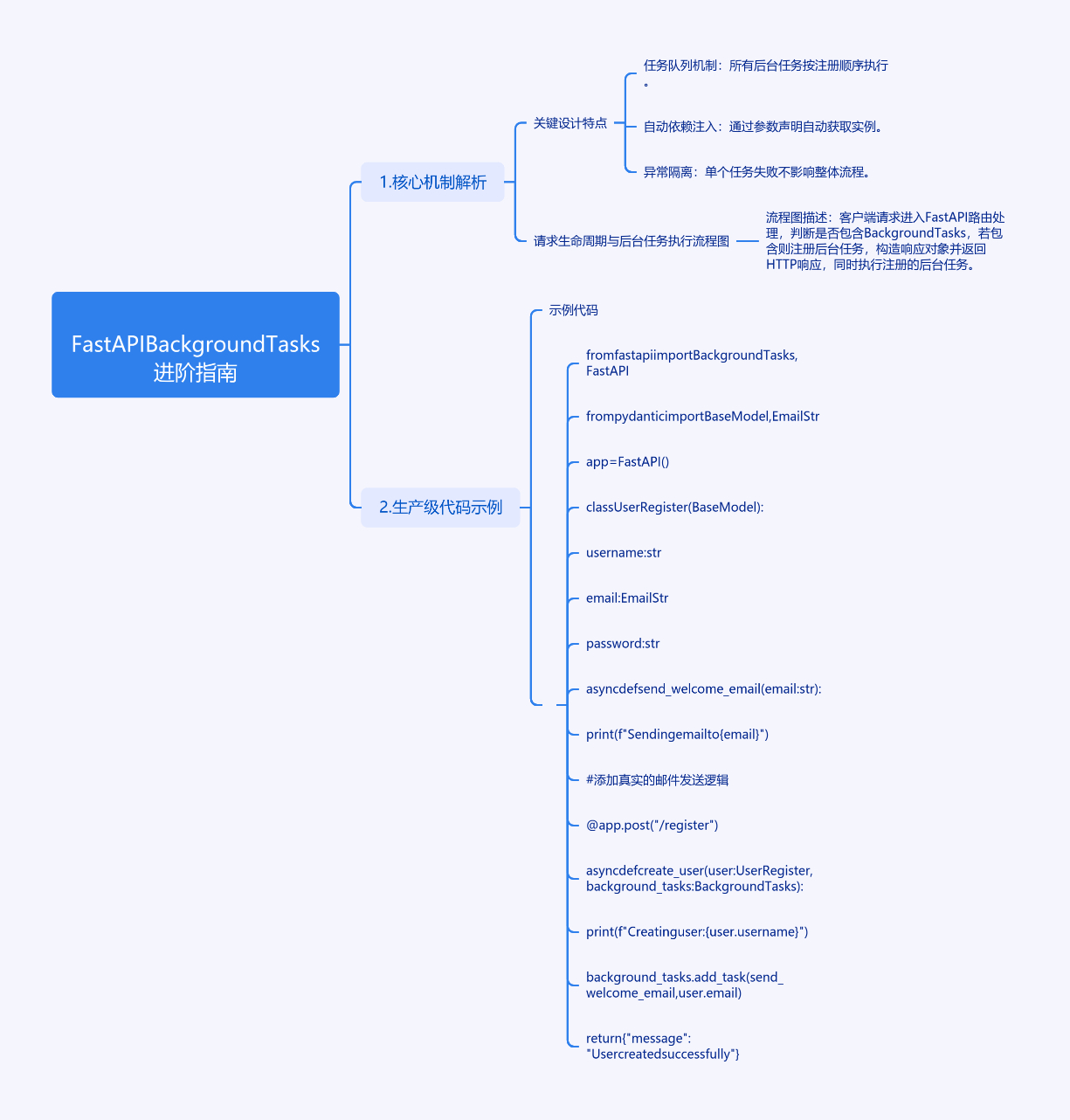
1. 核心机制解析
graph TD A[客户端请求] --> B[FastAPI路由处理] B --> C{是否包含BackgroundTasks} C -->|是| D[注册后台任务] C -->|否| E[直接返回响应] D --> F[构造响应对象] F --> G[返回HTTP响应] G --> H[执行注册的后台任务]
关键设计特点:
- 任务队列机制:所有后台任务按注册顺序执行
- 自动依赖注入:通过参数声明自动获取实例
- 异常隔离:单个任务失败不影响整体流程
2. 生产级代码示例
python
# requirements.txt
fastapi==0.103.2
pydantic==2.5.3
uvicorn==0.23.2
python
from fastapi import BackgroundTasks, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, EmailStr
app = FastAPI()
class UserRegister(BaseModel):
username: str
email: EmailStr
password: str
async def send_welcome_email(email: str):
"""模拟邮件发送(实际应使用SMTP库)"""
print(f"Sending email to {email}")
# 这里可以添加真正的邮件发送逻辑
@app.post("/register", status_code=201)
async def create_user(
user: UserRegister,
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
"""用户注册接口"""
# 主逻辑处理
print(f"Creating user: {user.username}")
# 添加后台任务
background_tasks.add_task(
send_welcome_email,
user.email
)
return {"message": "User created successfully"}3. 高级应用场景
3.1 数据库事务补偿
python
async def cleanup_failed_registration(user_id: int):
"""注册失败后的数据回滚"""
async with AsyncSessionLocal() as session:
await session.execute(
delete(User).where(User.id == user_id)
)
await session.commit()
@app.post("/register")
async def register_user(
user: UserRegister,
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
try:
# 数据库操作...
except Exception as e:
background_tasks.add_task(
cleanup_failed_registration,
new_user.id
)
raise HTTPException(...)3.2 任务编排模式
python
def task_wrapper(func):
"""任务执行监控装饰器"""
async def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
try:
print(f"Starting task {func.__name__}")
await func(*args, **kwargs)
print(f"Task {func.__name__} completed")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Task failed: {str(e)}")
# 可添加重试逻辑
return wrapper
@app.post("/batch-process")
async def batch_processing(
background_tasks: BackgroundTasks
):
background_tasks.add_task(
task_wrapper(process_data)
)
background_tasks.add_task(
task_wrapper(generate_reports)
)4. 性能优化策略
- 任务分片:将大任务拆分为多个子任务
- 资源限制:通过信号量控制并发量
- 超时设置:为长时间任务添加执行时限
python
from fastapi.concurrency import run_in_threadpool
async def resource_intensive_task():
# CPU密集型任务示例
await run_in_threadpool(
lambda: heavy_computation()
)5. 课后 Quiz
Q1: 当后台任务需要访问数据库时,应该如何正确处理数据库会话?
A) 直接使用主请求的会话
B) 每个任务创建独立会话
C) 使用全局共享会话
正确答案:B
解析:每个后台任务应该创建独立的数据库会话,因为主请求的会话在响应返回后可能已关闭。推荐在任务内部使用上下文管理器创建新会话。
6. 典型报错处理
报错现象:
RuntimeError: No response returned.
原因分析:
在后台任务中直接返回了响应对象
解决方案:
- 确保后台任务函数不返回任何值
- 将响应处理逻辑移到主请求流程
- 使用独立的路由处理异步任务结果
预防建议:
- 严格区分请求处理与后台任务职责
- 使用类型检查工具验证函数返回值
- 在任务函数中添加返回值检测逻辑
余下文章内容请点击跳转至 个人博客页面 或者 扫码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长,阅读完整的文章:FastAPI后台任务:是时候让你的代码飞起来了吗?
往期文章归档:
- FastAPI后台任务为何能让邮件发送如此丝滑? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI的请求-响应周期为何需要后台任务分离? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中让后台任务既高效又不会让你的应用崩溃? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI后台任务:异步魔法还是同步噩梦? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中玩转Schema版本管理和灰度发布? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI的查询白名单和安全沙箱机制如何确保你的API坚不可摧? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在 FastAPI 中玩转 GraphQL 性能监控与 APM 集成? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在 FastAPI 中玩转 GraphQL 和 WebSocket 的实时数据推送魔法? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中玩转GraphQL联邦架构,让数据源手拉手跳探戈? - cmdragon's Blog
- GraphQL批量查询优化:DataLoader如何让数据库访问速度飞起来? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中整合GraphQL的复杂度与限流? - cmdragon's Blog
- GraphQL错误处理为何让你又爱又恨?FastAPI中间件能否成为你的救星? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI遇上GraphQL:异步解析器如何让API性能飙升? - cmdragon's Blog
- GraphQL的N+1问题如何被DataLoader巧妙化解? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI与GraphQL的完美邂逅:如何打造高效API? - cmdragon's Blog
- GraphQL类型系统如何让FastAPI开发更高效? - cmdragon's Blog
- REST和GraphQL究竟谁才是API设计的终极赢家? - cmdragon's Blog
- IoT设备的OTA升级是如何通过MQTT协议实现无缝对接的? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中玩转STOMP协议升级,让你的消息传递更高效? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何用WebSocket打造毫秒级实时协作系统? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何用WebSocket打造毫秒级实时协作系统? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何让你的WebSocket连接既安全又高效?
- 如何让多客户端会话管理不再成为你的技术噩梦? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中玩转WebSocket消息处理?
- 如何在FastAPI中玩转WebSocket,让实时通信不再烦恼? - cmdragon's Blog
- WebSocket与HTTP协议究竟有何不同?FastAPI如何让长连接变得如此简单? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI如何玩转安全防护,让黑客望而却步?
- 如何用三层防护体系打造坚不可摧的 API 安全堡垒? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI安全加固:密钥轮换、限流策略与安全头部如何实现三重防护? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中巧妙玩转数据脱敏,让敏感信息安全无忧? - cmdragon's Blog
- RBAC权限模型如何让API访问控制既安全又灵活? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI中的敏感数据如何在不泄露的情况下翩翩起舞?
- FastAPI安全认证的终极秘籍:OAuth2与JWT如何完美融合? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何在FastAPI中打造坚不可摧的Web安全防线? - cmdragon's Blog
- 如何用 FastAPI 和 RBAC 打造坚不可摧的安全堡垒? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI权限配置:你的系统真的安全吗? - cmdragon's Blog
- FastAPI权限缓存:你的性能瓶颈是否藏在这只"看不见的手"里? | cmdragon's Blog
免费好用的热门在线工具
- ASCII字符画生成器 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- JSON Web Tokens 工具 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- Bcrypt 密码工具 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- GIF 合成器 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- GIF 分解器 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- 文本隐写术 - 应用商店 | By cmdragon
- CMDragon 在线工具 - 高级AI工具箱与开发者套件 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 应用商店 - 发现1000+提升效率与开发的AI工具和实用程序 | 免费好用的在线工具
- CMDragon 更新日志 - 最新更新、功能与改进 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 支持我们 - 成为赞助者 | 免费好用的在线工具
- AI文本生成图像 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 临时邮箱 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 二维码解析器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 文本转思维导图 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 正则表达式可视化工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 文件隐写工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- IPTV 频道探索器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 快传 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 随机抽奖工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 动漫场景查找器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 时间工具箱 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 网速测试 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- AI 智能抠图工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 背景替换工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 艺术二维码生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- Open Graph 元标签生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 图像对比工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 图片压缩专业版 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 密码生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- SVG优化器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 调色板生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 在线节拍器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- IP归属地查询 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- CSS网格布局生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 邮箱验证工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 书法练习字帖 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 金融计算器套件 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 中国亲戚关系计算器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- Protocol Buffer 工具箱 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- IP归属地查询 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 图片无损放大 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 文本比较工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- IP批量查询工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 域名查询工具 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- DNS工具箱 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- 网站图标生成器 - 应用商店 | 免费好用的在线工具
- XML Sitemap