概述:在linux内核中,存在OOM(Out of memory)内存保护机制,即当系统内存资源严重不足时,通过终止部分进程来释放内存资源,防止系统崩溃,下面是我对OOM机制的初步研究。
现象:我们在使用linux系统的过程中,可能存在某些进程被后台杀死的情况,在linux系统日志中(dmesg、kernel、messages、syslog等)会出现killed process或out of memory或oom等事件日志。
触发条件:系统内存资源严重不足时导致,遇到触发的实际场景有:①物理内存资源不足;②部分进程存在内存泄露,导致内存资源浪费,长时间会导致内存资源不足。
影响:系统内存资源不足时会影响机器性能,设备卡顿,严重时会导致关键进程被杀死,影响业务和使用。
OOM机制介绍
OOM机制的执行者是OOM Killer,它会在触发OOM机制时,选择oom_score分数最高的进程杀死,下面我们来展开看看OOM Killer是如何选择目标进程的。
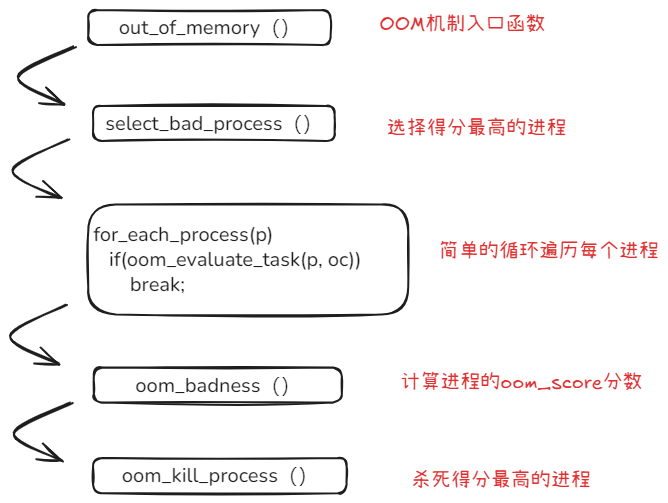
从上诉流程可以看到杀死的进程是通过oom_score分数值决定,分数即在/proc/[pid]/oom_score文件中,下图举例,这个分数越高,则越优先被杀死。
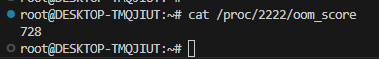
深入代码
在内核代码mm/oom_kill.c中,可以看到由oom_badness()函数来完成
/**
* oom_badness - heuristic function to determine which candidate task to kill
* @p: task struct of which task we should calculate
* @totalpages: total present RAM allowed for page allocation
* @memcg: task's memory controller, if constrained
* @nodemask: nodemask passed to page allocator for mempolicy ooms
*
* The heuristic for determining which task to kill is made to be as simple and
* predictable as possible. The goal is to return the highest value for the
* task consuming the most memory to avoid subsequent oom failures.
*/
unsigned long oom_badness(struct task_struct *p, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
const nodemask_t *nodemask, unsigned long totalpages)
{
long points;
long adj;
if (oom_unkillable_task(p, memcg, nodemask))
return 0;
p = find_lock_task_mm(p);
if (!p)
return 0;
/*
* Do not even consider tasks which are explicitly marked oom
* unkillable or have been already oom reaped or the are in
* the middle of vfork
*/
adj = (long)p->signal->oom_score_adj;
if (adj == OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN ||
test_bit(MMF_OOM_SKIP, &p->mm->flags) ||
in_vfork(p)) {
task_unlock(p);
return 0;
}
/*
* The baseline for the badness score is the proportion of RAM that each
* task's rss, pagetable and swap space use.
*/
points = get_mm_rss(p->mm) + get_mm_counter(p->mm, MM_SWAPENTS) +
mm_pgtables_bytes(p->mm) / PAGE_SIZE;
task_unlock(p);
/* Normalize to oom_score_adj units */
adj *= totalpages / 1000;
points += adj;
/*
* Never return 0 for an eligible task regardless of the root bonus and
* oom_score_adj (oom_score_adj can't be OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN here).
*/
return points > 0 ? points : 1;
}分段进行代码解读
if (oom_unkillable_task(p, memcg, nodemask))
return 0;免疫进程检查:若进程属于以下类型,直接返回 0(不会被杀死)
1、内核线程(无用户空间内存)。
2、Init 进程(PID=1)。
3、受内存控制组(cgroup)限制且无法终止的进程
p = find_lock_task_mm(p);
if (!p)
return 0;锁定进程内存描述符:
1、锁定进程的 task_struct 和 mm_struct,确保内存状态一致。
2、若进程无活跃内存(如僵尸进程),跳过计算
adj = (long)p->signal->oom_score_adj;
if (adj == OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN || test_bit(MMF_OOM_SKIP, &p->mm->flags) || in_vfork(p)) {
task_unlock(p);
return 0;
}三种保护情况:
1、oom_score_adj = -1000:用户显式标记"永不杀死"(如 SSH 守护进程)
2、MMF_OOM_SKIP 标志:内核标记跳过 OOM(如关键驱动)。
3、in_vfork():进程处于 vfork() 状态(父子进程共享内存,杀死可能破坏状态)
points = get_mm_rss(p->mm) + get_mm_counter(p->mm, MM_SWAPENTS) +
mm_pgtables_bytes(p->mm) / PAGE_SIZE;基础内存占用计算:计算进程的三部分内存开销:
1、RSS(常驻物理内存):get_mm_rss(p->mm)
2、Swap 占用:get_mm_counter(p->mm, MM_SWAPENTS)
3、页表内存:mm_pgtables_bytes(p->mm) / PAGE_SIZE(转换为页面数)
adj *= totalpages / 1000;
points += adj;oom_score_adj 的作用:用户可通过 /proc//oom_score_adj 调整分数(范围 -1000 到 1000)
return points > 0 ? points : 1;确保返回值 ≥1,避免免疫进程外的任务得 0 分(即使分数为负也返回 1)
总结:权重优先级
1、内存占用主导:RSS + Swap + 页表内存是基础分,占比最大。
2、用户控制权:oom_score_adj 允许精准调控进程生死(如保护数据库,牺牲日志服务)权重优先级。