C++ 模拟实现 map 和 set:掌握核心数据结构
文章目录
- [C++ 模拟实现 map 和 set:掌握核心数据结构](#C++ 模拟实现 map 和 set:掌握核心数据结构)
- [一、set 和 map 的结构](#一、set 和 map 的结构)
-
- [1.1 set的结构](#1.1 set的结构)
- [1.2 map的结构](#1.2 map的结构)
- 二、对红黑树的改造
-
- [2.1 改造红黑树的节点](#2.1 改造红黑树的节点)
- [2.2 改造红黑树](#2.2 改造红黑树)
-
- [2.2.1 仿函数的使用](#2.2.1 仿函数的使用)
- [2.2.2 插入函数的改造](#2.2.2 插入函数的改造)
- [2.2.3 删除函数的改造](#2.2.3 删除函数的改造)
- 三、对迭代器的改造
-
- [3.1 *、->、!=、==](#3.1 *、->、!=、==)
- [3.2 begin和end](#3.2 begin和end)
- [3.3 ++ 和 --](#3.3 ++ 和 --)
- [3.4 const迭代器](#3.4 const迭代器)
- [3.5 复用红黑树接口实现set/map中的成员函数](#3.5 复用红黑树接口实现set/map中的成员函数)
-
- [3.5.1 set成员函数](#3.5.1 set成员函数)
- [3.5.2 map成员函数](#3.5.2 map成员函数)
- 四、源代码总结
-
- [4.1 Myset.h](#4.1 Myset.h)
- [4.2 Mymap.h](#4.2 Mymap.h)
- [4.3 RBTree.h](#4.3 RBTree.h)
一、set 和 map 的结构
STL中set和map底层是一颗红黑树,模拟set和map需要一颗红黑树作为我们的成员变量
点击这里了解红黑树
1.1 set的结构
set结构就是 K模型,所以set容器对红黑树的封装如下:
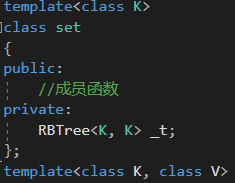
1.2 map的结构
map结构就是 KV模型,所以map容器对红黑树的封装如下
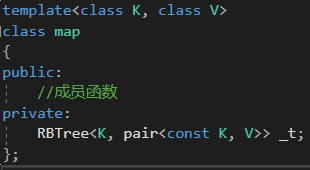
二、对红黑树的改造

2.1 改造红黑树的节点
其中红黑树的节点类型就是模版参数T
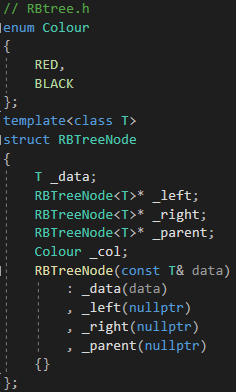
2.2 改造红黑树
2.2.1 仿函数的使用

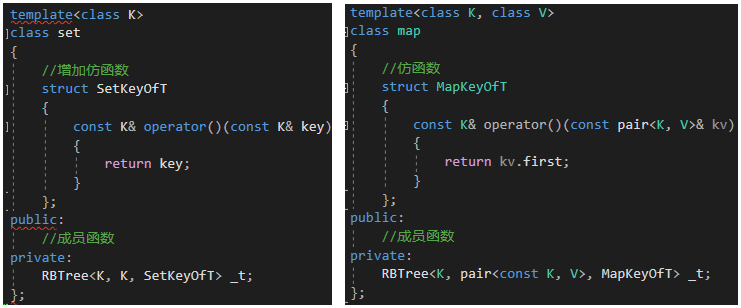
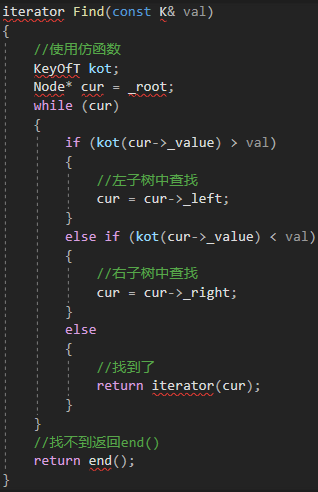
然后我们将所有需要比较key的函数利用仿函数进行替换,我们以Find为例
2.2.2 插入函数的改造
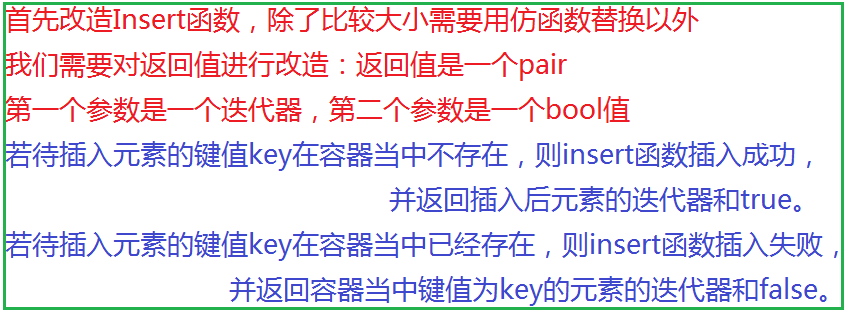
代码如下(示例):
c
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
{
//情况一:如果是根节点
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(_root),true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_value) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_value) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(iterator(cur), false);
}
}
//找到插入位置
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
if (kot(parent->_value) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
//情况三:如果叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//情况四:叔叔不存在/存在且为黑,且cur在parent的左侧
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//情况五:叔叔不存在 / 存在且为黑,cur在parent的右侧
{
// g
// p u
// c
RotateLR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
//这时该子树的根节点变为黑色,不需要继续调整
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
//情况三:如果叔叔存在且为红
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续调整
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
//情况四:叔叔不存在/存在且为黑,且cur在parent的左侧
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else // 情况五:叔叔不存在 / 存在且为黑,cur在parent的右侧
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateRL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
//这时该子树的根节点变为黑色,不需要继续调整
break;
}
}
}
//防止情况三改到根节点变为红色
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true);
}
2.2.3 删除函数的改造

代码如下(示例):
c
else //待删除结点的左右子树均不为空
{
//替换法删除
//寻找待删除结点右子树当中key值最小的结点作为实际删除结点
Node* minParent = cur;
Node* minRight = cur->_right;
while (minRight->_left)
{
minParent = minRight;
minRight = minRight->_left;
}
// 原本直接可以赋值
// cur->_value = minRight->_value
//将待删除结点的键值改为minRight的键值
Node* newnode = new Node(minRight->_value,cur->_col);
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//重新链接祖父孙三代节点关系
cur->_left->_parent = newnode;
cur->_right->_parent = newnode;
if (parent)
{
if (parent->_left == cur)
{
parent->_left = newnode;
}
else
{
parent->_right = newnode;
}
}
else
{
//如果是根节点
_root = newnode;
}
newnode->_parent = parent;
newnode->_left = cur->_left;
newnode->_right = cur->_right;
//如果minParent是cur
if (minParent == cur)
{
minParent = newnode;
}
delete cur;
delParent = minParent; //标记实际删除的父节点
delCur = minRight; //标记实际删除的结点
}三、对迭代器的改造
3.1 *、->、!=、==

代码如下(示例):
c
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
//构造
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_value;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_value;
}
//判断两个正向迭代器是否不同
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
//判断两个正向迭代器是否相同
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
Node* getNode()
{
return _node;
}
};3.2 begin和end

代码如下(示例):
c
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;//普通迭代器
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;//const迭代器
//最左节点
iterator begin()
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return iterator(cur);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
//const版本begin和end
const_iterator begin()const
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur && cur->_left)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
return const_iterator(cur);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}3.3 ++ 和 --

代码如下(示例):
c
//前置++
Self& operator++()
{
//如果右子树不为空
if (_node->_right)
{
//寻找该结点右子树当中的最左结点
Node* left = _node->_right;
while (left->_left)
{
left = left->_left;
}
_node = left;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
//寻找孩子不在右的祖先
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
//前置--
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left) //结点的左子树不为空
{
//寻找该结点左子树当中的最右结点
Node* right = _node->_left;
while (right->_right)
{
right = right->_right;
}
_node = right;
}
else
{
//寻找孩子不在父亲左的祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
3.4 const迭代器

代码如下(示例):
c
//普通迭代器构造const迭代器
__RBTreeIterator(const __RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*>& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}3.5 复用红黑树接口实现set/map中的成员函数
3.5.1 set成员函数
代码如下(示例):
c
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
//typename声明是一个类型而不是静态变量
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
//成员函数
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
//删除函数
void erase(const K& key)
{
_t.Erase(key);
}
//查找函数
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};3.5.2 map成员函数
代码如下(示例):
c
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
//仿函数
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//typename声明是一个类型而不是静态变量
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
//成员函数
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.end();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K,V>& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
//删除函数
void erase(const K& key)
{
_t.Erase(key);
}
//查找函数
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
//[]运算符重载
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.Insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
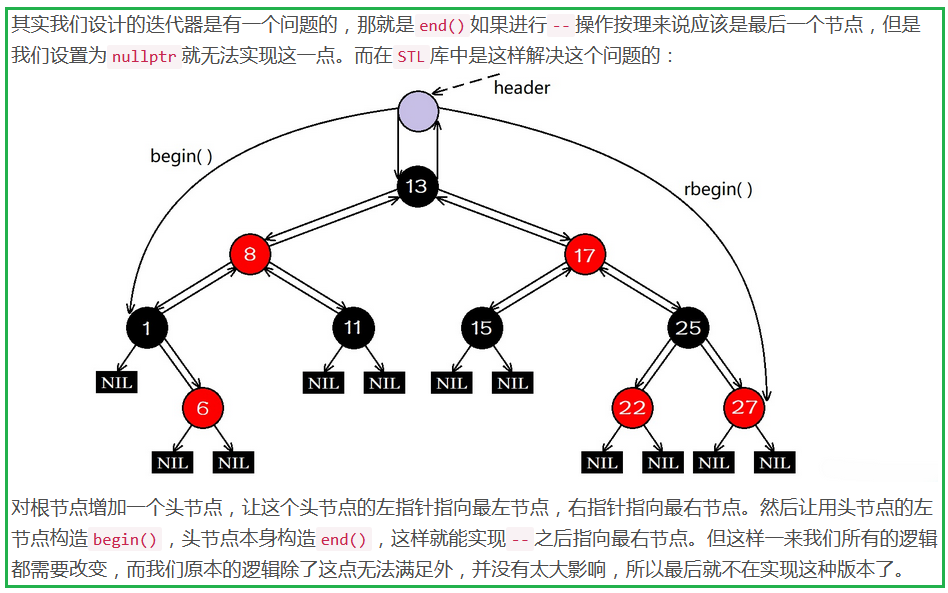
};
四、源代码总结
4.1 Myset.h
代码如下(示例):
c
#pragma once
// Myset.h
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace bit
{
template<class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::Iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::ConstIterator
const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
return _t.Insert(key);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
private:
RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void Print(const set<int>& s)
{
set<int>::const_iterator it = s.end();
while (it != s.begin())
{
--it;
// 不⽀持修改
//*it += 2;
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
Print(s);
}
}4.2 Mymap.h
代码如下(示例):
c
#pragma once
#include"RBTree.h"
namespace bit
{
template<class K, class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::Iterator
iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::ConstIterator
const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.Begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.End();
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _t.Begin();
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _t.End();
}
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
iterator find(const K& key)
{
return _t.Find(key);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test_map()
{
map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert({ "sort", "排序" });
dict.insert({ "left", "左边" });
dict.insert({ "right", "右边" });
dict["left"] = "左边,剩余";
dict["insert"] = "插⼊";
dict["string"];
map<string, string>::iterator it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
// 不能修改first,可以修改second
//it->first += 'x';
it->second += 'x';
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}4.3 RBTree.h
代码如下(示例):
c
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// RBtree.h
enum Colour
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{
T _data;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
Colour _col;
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
: _data(data)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
Node* _root;
RBTreeIterator(Node* node, Node* root)
:_node(node)
, _root(root)
{}
Self& operator++()
{
if (_node->_right)
{
// 右不为空,右⼦树最左结点就是中序第⼀个
Node* leftMost = _node->_right;
while (leftMost->_left)
{
leftMost = leftMost->_left;
}
_node = leftMost;
}
else
{
// 孩⼦是⽗亲左的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node == nullptr) // end()
{
// --end(),特殊处理,⾛到中序最后⼀个结点,整棵树的最右结点
Node* rightMost = _root;
while (rightMost && rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else if (_node->_left)
{
// 左⼦树不为空,中序左⼦树最后⼀个
Node* rightMost = _node->_left;
while (rightMost->_right)
{
rightMost = rightMost->_right;
}
_node = rightMost;
}
else
{
// 孩⼦是⽗亲右的那个祖先
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
bool operator!= (const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator== (const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
typedef RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> ConstIterator;
Iterator Begin()
{
Node* leftMost = _root;
while (leftMost && leftMost->_left)
{
leftMost = leftMost->_left;
}
return Iterator(leftMost, _root);
}
Iterator End()
{
return Iterator(nullptr, _root);
}
ConstIterator Begin() const
{
Node* leftMost = _root;
while (leftMost && leftMost->_left)
{
leftMost = leftMost->_left;
}
return ConstIterator(leftMost, _root);
}
ConstIterator End() const
{
return ConstIterator(nullptr, _root);
}
RBTree() = default;
~RBTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
_root = nullptr;
}
pair<Iterator, bool> Insert(const T & data)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(Iterator(_root, _root), true);
}
KeyOfT kot;
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return make_pair(Iterator(cur, _root), false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newnode = cur;
// 新增结点。颜⾊红⾊给红⾊
cur->_col = RED;
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
}
cur->_parent = parent;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
// g
// p u
if (parent == grandfather->_left)
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
// u存在且为红 -》变⾊再继续往上处理
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
// u存在且为⿊或不存在 -》旋转+变⾊
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
// g
// p u
//c
//单旋
RotateR(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// p u
// c
//双旋
RotateL(parent);
RotateR(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else
{
// g
// u p
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
// 叔叔存在且为红,-》变⾊即可
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
// 继续往上处理
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为⿊
{
// 情况⼆:叔叔不存在或者存在且为⿊
// 旋转+变⾊
// g
// u p
// c
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
RotateL(grandfather);
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else
{
// g
// u p
// c
RotateR(parent);
RotateL(grandfather);
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(Iterator(newnode, _root), true);
}
Iterator Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_kv.first > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return Iterator(cur, _root);
}
}
return End();
}
private:
void RotateL(Node* parent)
{
Node* subR = parent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
parent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
subR->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subR;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subR;
subR->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == parentParent->_left)
{
parentParent->_left = subR;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subR;
}
subR->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
void RotateR(Node* parent)
{
Node* subL = parent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
parent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = parent;
Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;
subL->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subL;
if (parentParent == nullptr)
{
_root = subL;
subL->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (parent == parentParent->_left)
{
parentParent->_left = subL;
}
else
{
parentParent->_right = subL;
}
subL->_parent = parentParent;
}
}
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};