哈希表
1哈希算法
将数据通过哈希算法映射成一个键值,存取都在同一个位置实现数据的高效存储和查找,将时间复杂度尽可能降低至O(1)
2哈希碰撞
多个数据通过哈希算法得到的键值相同,成为产生哈希碰撞
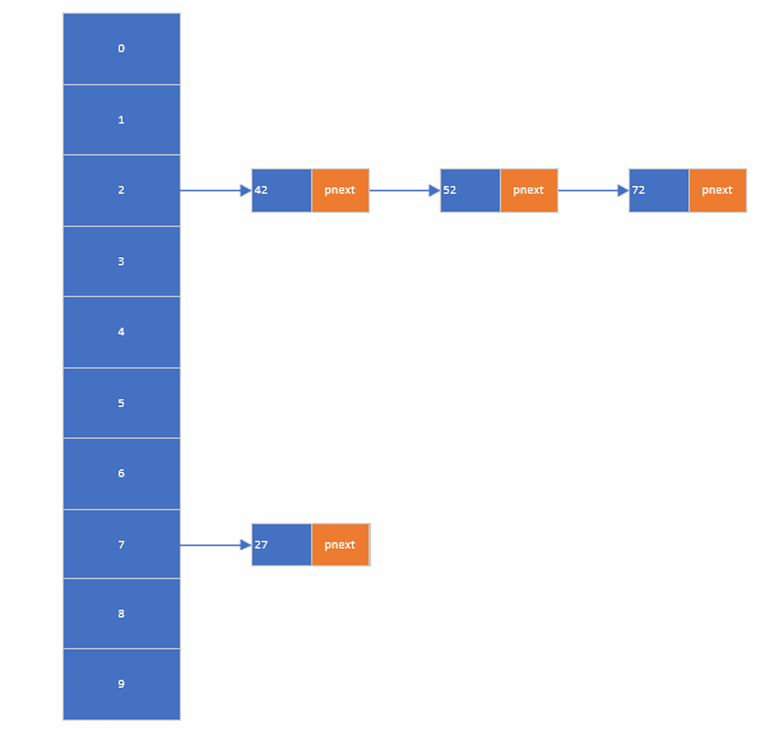
3哈希表:
- 构建哈希表存放0-100之间的数据
- 哈希算法选择:
- 将0-100之间的数据的各位作为键值
4. 哈希表的实现
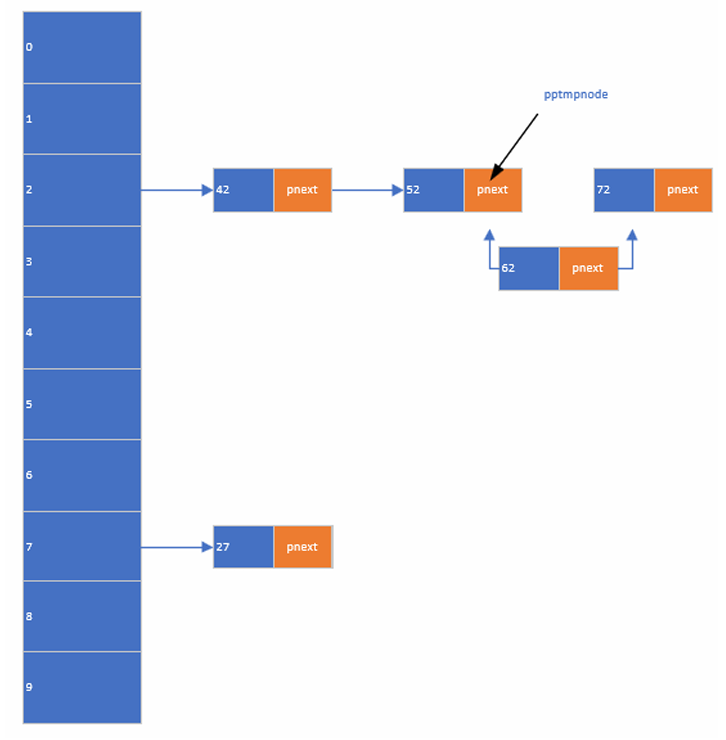
1. 哈希表插入
cpp
linknode *phashtable[INDEX];
// 一个名为phashtable的指针型数组,一共INDEX个元素 每个元素的值都是linknode*型 指向链表的头节点指针
// phashtable是二级指针哦 指向数组头元素的地址常量(数组内元素都为地址 指向指针的指针则是二级指针)
int insert_hashtable(int tmpdata)
{
int key = 0;
linknode **pptmpnode = NULL;
linknode *pnewnode = NULL;
key = tmpdata % INDEX;
//*pptmpnode != NULL说明哈希表当前这个元素后面有链表
// 注意:你要操作循环的是 存放哈希表的元素指针值(这里变化的i是 二级指针)
// pptmpnode等于哈希表里存的元素的地址
// 先1 若2 再3(把指针往后挪一个)若2 再3 直到找到存放大于输入的数据的链表位置退出循环
for (pptmpnode = &phashtable[key]; *pptmpnode != NULL && (*pptmpnode)->data < tmpdata; pptmpnode = &((*pptmpnode)->pnext))
{
}
// 新建链式空间
pnewnode = malloc(sizeof(linknode));
if (pnewnode == NULL)
{
perror("fail to malloc");
return -1;
}
pnewnode->data = tmpdata;
pnewnode->pnext = *pptmpnode; // 若你插入的数字是62 *pptmpnode则是指向72节点的地址
*pptmpnode = pnewnode; //**ptmpnode 同时也是指向52节点里面pnext的值 改这个值
return 0;
}- 哈希表遍历
cpp
int show_hashtable(void)
{
int i = 0;
linknode *ptmpnode = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < INDEX; i++)
{
printf("%d:", i);
ptmpnode = phashtable[i];
while (ptmpnode != NULL)
{
printf("%2d ", ptmpnode->data);
ptmpnode = ptmpnode->pnext;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}排序和查找算法:
1.冒泡排序
-
- 时间复杂度为O(
)
- 时间复杂度为O(
-
- 稳定的排序算法
-
- 排序方法:
- 相邻的两个元素比较,大的向后走,小的向前走
- 循环找len-1个大的值
cpp
int bubble_sort(int *parray, int len)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int tmp = 0;
for (j = 0; j < len-1; j++)
{
for (i = 0; i < len-1-j; i++)
{
if (parray[i] > parray[i+1])
{
tmp = parray[i];
parray[i] = parray[i+1];
parray[i+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
return 0;
}- 选择排序
-
- 时间复杂度O(
)
- 时间复杂度O(
-
- 不稳定排序算法
-
- 排序方法:
- 从前到后找最小值与前面的元素交换
- 找到len-1个最小值吗,最后一个最大值即排序完成
cpp
int select_sort(int *parray, int len)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int tmp = 0;
int min = 0;
for (j = 0; j < len-1; j++)
{
min = j;
for (i = j+1; i < len; i++)
{
if (parray[i] < parray[min])
{
min = i;
}
}
if (min != j)
{
tmp = parray[min];
parray[min] = parray[j];
parray[j] = tmp;
}
}
return 0;
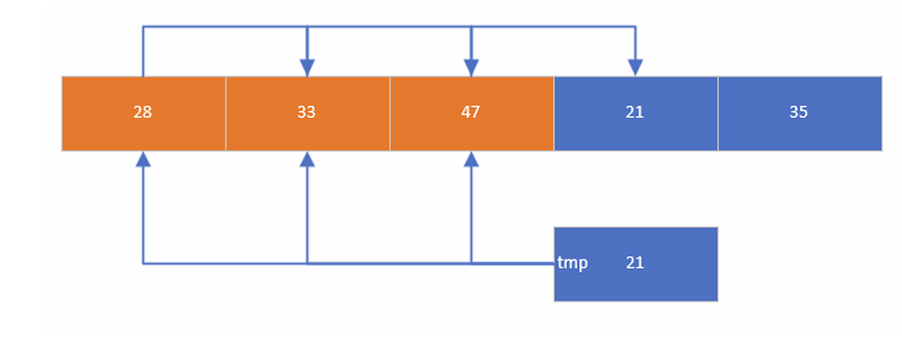
}3.插入排序
-
- 时间复杂度O(
),如果是组有序时间复杂度降低至O(n)
- 时间复杂度O(
-
- 稳定的排序算法
-
- 排序方法:
- 将数组中的每个元素插入到有序数列中
- 先将要插入的元素取出O(
)
- 依次和前面元素比较,比元素大的向后走,直到前一个元素比要插入的元素小,或者到 达有序数列开头停止
- 插入元素即可
cpp
int insert_sort(int *parray, int len)
{
int tmp = 0;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (j = 1; j < len; j++)
{
tmp = parray[j];
for (i = j; i > 0 && tmp < parray[i-1]; i--)
{
parray[i] = parray[i-1];
}
parray[i] = tmp;
}
return 0;
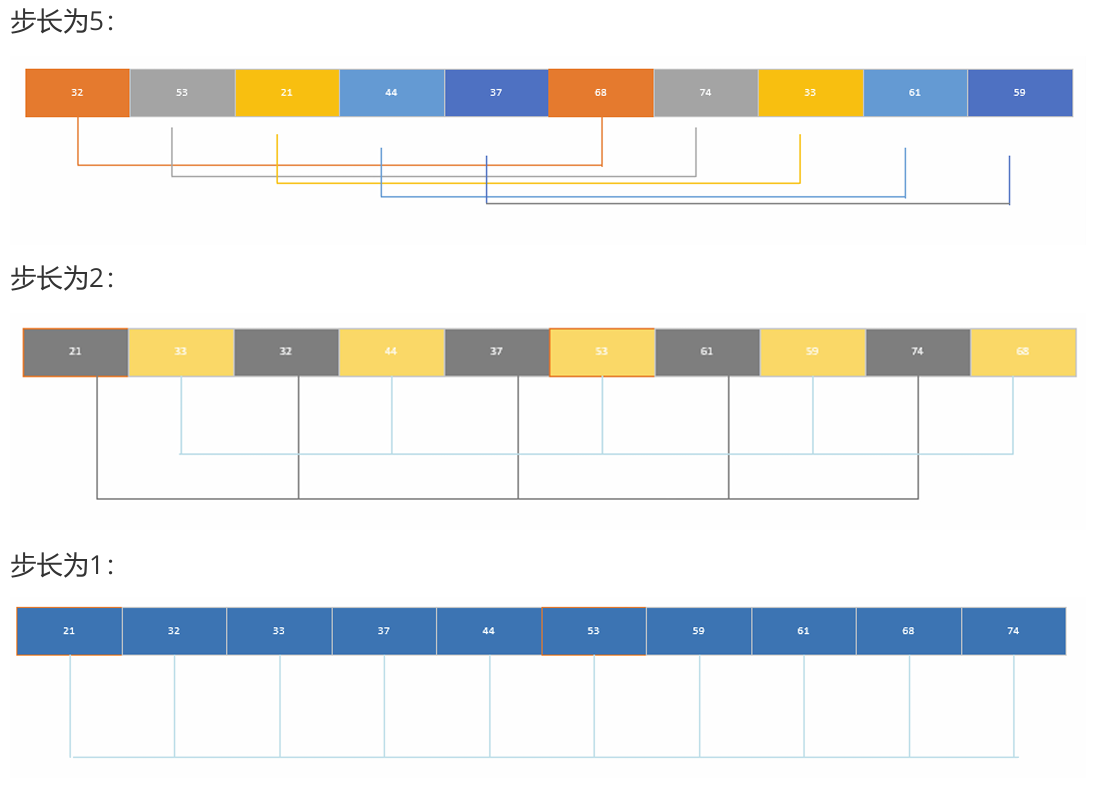
}4.希尔排序
- 时间复杂度O(nlogn)
- 不稳定的排序算法
- 通过选择不同的步长,将数组拆分成若干个小的数组实现插入排序
- 若干个小的数组称为有序数列后,使得数组中的数据大致有序
- 最后再对整体完成一个插入排序
cpp
/* 耗时: 5 - 10ms*/
int shell_sort(int *parray, int len)
{
int step = 0;
int j = 0;
int i = 0;
int tmp = 0;
for (step = len/2; step > 0; step /= 2)
{
for (j = step; j < len; j++)
{
tmp = parray[j];
for (i = j; i >= step && tmp < parray[i-step]; i -=
step)
{
parray[i] = parray[i-step];
}
parray[i] = tmp;
}
}
return 0;
}5.快速排序
-
时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
-
不稳定的排序算法
-
选择左边的作为键值,从后面找一个比键值小的放前面,从前面找一个比键值大的放后面,键 值放中间
-
左右两边有元素则递归调用快速排序
cpp
int quick_sort(int *parray, int low, int high)
{
int key = 0;
int j = 0;
int i = 0;
key = parray[low];
j = high;
i = low;
while (i < j)
{
while (i < j && parray[j] >= key)
{
j--;
}
if (i < j)
{
parray[i] = parray[j];
}
while (i < j && parray[i] <= key)
{
i++;
}
if (i < j)
{
parray[j] = parray[i];
}
}
parray[i] = key;
if (i-1 > low)
{
quick_sort(parray, low, i-1);
}
if (i+1 < high)
{
quick_sort(parray, i+1, high);
}
return 0;
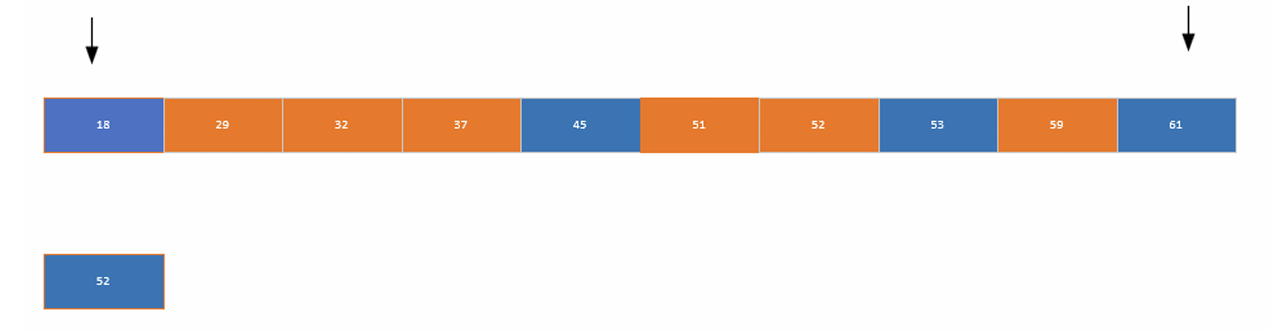
}6.折半查找(二分查找)
时间复杂度O(logn)
cpp
int mid_search(int *parray, int low, int high, int tmpdata)
{
int mid = 0;
if (low > high)
{
return -1;
}
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (tmpdata == parray[mid])
{
return mid;
}
else if (tmpdata > parray[mid])
{
return mid_search(parray, mid+1, high, tmpdata);
}
else if (tmpdata < parray[mid])
{
return mid_search(parray, low, mid-1, tmpdata);
}
}7顺序查找
时间复杂度为O(n)