经过长途跋涉,我们从开始一无所有,到现在终于集齐了南慕容北乔峰,呸!集齐了视频和音频!但是音频和视频在之前的章节中,都是独立存在的,既然它们集齐了,就让我们开启最终章节--最后一战:音视频合封!
等等等等,不要误会,最后一战是说USB摄像头的部分的。理论上来说如果电脑挂一个USB摄像头,然后执行我们这一部分的代码,是基本能够实现运动相机的功能的。但是就一个小缺点:有一点点大。。。
序章--MP4搭起舞台
两大高手集在一起,总要搭起戏台子。什么戏台子最合适呢?那就是MP4!MP4可以让我们的音视频合在一起,唱一出好戏。
1、MP4简介
MP4(文件扩展名通常是 .mp4)是目前应用最广泛、最通用的数字多媒体容器格式 之一。它的核心功能是封装 或容纳多种不同类型的数据流(主要是视频流、音频流),并辅以元数据(如标题、作者、字幕、章节信息等),将它们组合成一个单一的文件。
核心概念和特点:
-
容器格式 (Container Format):
- 这是 MP4 的本质。它本身不定义视频或音频的编码方式(压缩算法)。
- 它像一个"盒子"或"包裹",可以把用不同编码标准(如 H.264, H.265/HEVC, AAC, MP3)压缩的视频和音频轨道、字幕、图片等"装"在一起。
- 与之相对的是编码格式(如 H.264, AAC),它们负责具体的音视频数据压缩和解压缩。
-
基于 ISO 基础媒体文件格式 (ISO Base Media File Format):
- 这种结构使用"盒子"来组织文件内容。每个
box(或atom)包含特定类型的数据,并具有明确的长度和类型标识符。 - 常见的盒子包括:
ftyp:文件类型标识(表明这是一个 MP4 文件及其兼容性)。moov:电影元数据盒子(Movie Box)。这是最关键的盒子之一,包含了关于整个文件的结构信息:有多少条轨道(视频、音频、字幕等)、每条轨道的编码格式、时长、分辨率、采样率、时间戳映射关系等。mdat:媒体数据盒子(Media Data Box)。这是文件的主体部分,实际存储着压缩后的视频帧、音频帧等媒体数据。free:空闲空间盒子。
- 这种结构使用"盒子"来组织文件内容。每个
-
MP4 vs .m4a, .m4v, .m4p:
这些本质上都是 MP4 容器格式的文件。
.m4a:通常表示只包含音频(通常是 AAC)的 MP4 文件。.m4v:通常表示包含视频(通常是 H.264)的 MP4 文件。Apple 有时用它来区分包含特定功能(如 DRM 或章节)的视频。.m4p:Apple iTunes 使用的受 DRM 保护的音频文件(也是 MP4 容器)。.mp4:最通用的扩展名,可以包含音视频、纯音频或纯视频(较少见)。注:这里提到的DRM是Digital Rights Management(数字版权管理),而非Linux系统中的Direct Rendering Manager(直接渲染管理器)
2、MP4文件结构
网络上有很多优秀的解析MP4的文章,我就不在重复造轮子了,推荐这篇文章可以看一下,实在弄不清楚也没关系,反正这些活都是交给FFmpeg去做的,推荐了解但并不会对我们的进程造成影响,因为FFmpeg已经帮我们做好了,比如生成mp4的文件头,使用函数avformat_write_header就能帮我们搞定,其他的部分也类似。
下面是解析mp4文件特别详细的一张图,原来我把这张图贴在了我的卧室,想着天天看,给他背下来。但是现在想想多少有点冒傻气,谁会拿着一本字典天天背呢。没错,这张图就是一本关于mp4的字典,哪里不会看哪里(但是大概率是不会用到的)。
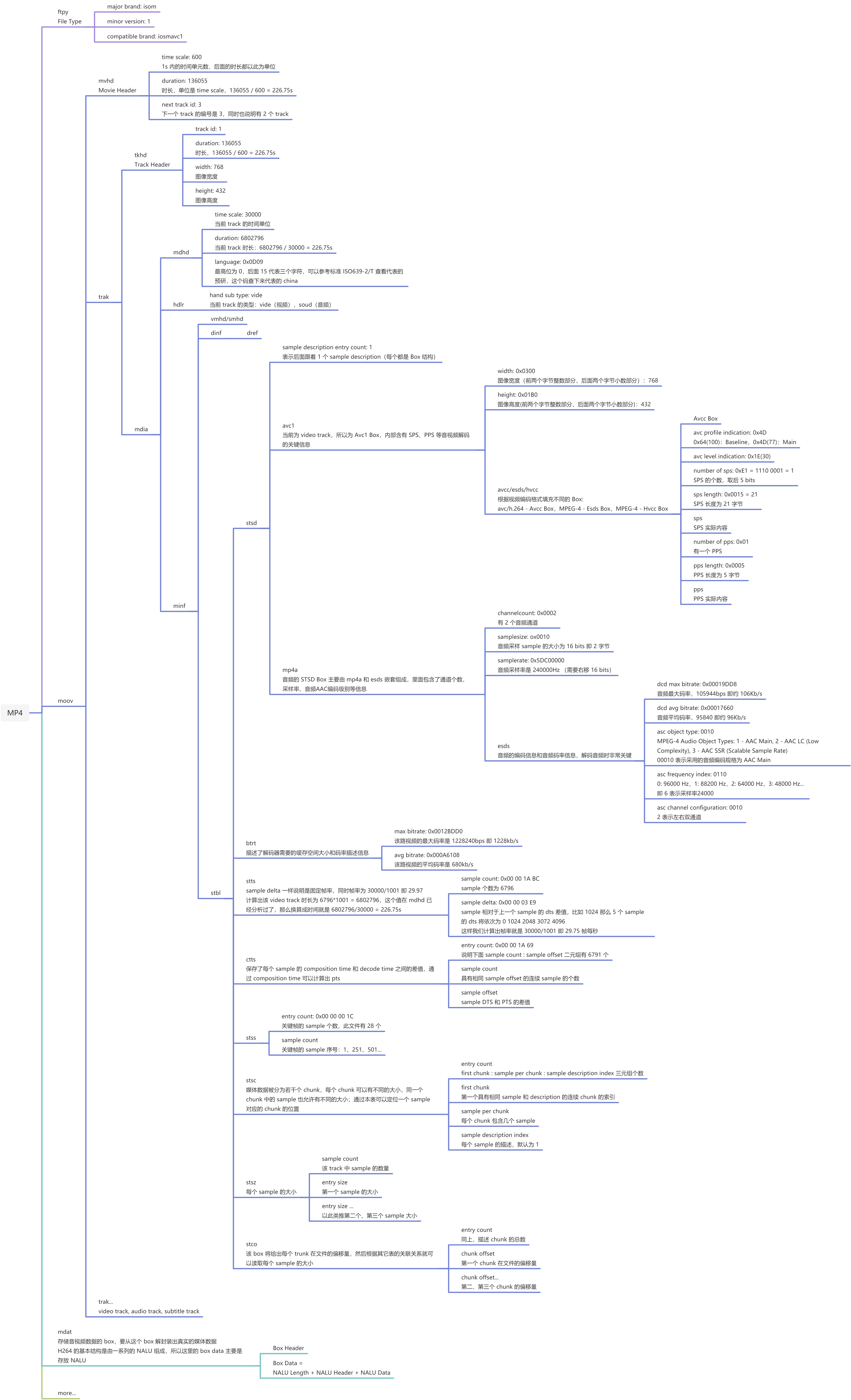
3、将我们之前的内容稍作梳理
我们在第7章,讨论了如何进行实时录像:
7:实时录像、延时摄影、水印--基于FFmpeg(下)_如何把ffmpeg.c封装成动态库-CSDN博客
并在第8章讨论了如何从摄像头获取音频流:
8:从USB摄像头把声音拿出来--ALSA大佬登场!-CSDN博客
这两章内容一个为纯视频,一个为纯音频。笔者打算在第7章的最终代码上进行修改,把第8章的代码加进去,合封到一起。
进入正戏--兵合一处、将打一家
我们先定个目标:我们通过USB摄像头,使用V4L2将视频获取出来,使用ALSA将音频取出来,并使用FFmpeg将视频编码成h264,将音频编码成aac,并通过FFmpeg将音视频封装进mp4文件。
1、代码结构
由于这次的代码比较复杂,不能再以单个的文件进行编写和变异了,所以这次将代码分成了以下几个部分:
audio_capture:主要负责的是音频的初始化、采集、清理等工作。需要注意以下几点:
1)初始化完毕后,就要启动。否则如果超过一定的时间后(本人时长大约500ms),USB摄像头可能会进入休眠的状态,导致无法正常启动。
2)USB摄像头传输的PCM数据格式为S16的,但是FFmpeg需要的是浮点型,所以需要经过转换,否则音频编码会出现问题,导致声音无法正常编码和播放。
3)AAC编码器启动等因素,会导致音频出现一个200ms左右的固定延迟,如果音视频同步要求没那么高,也可以不处理,但是本人看着很难受,所以将音频的PTS(稍后讨论)固定提前200ms。
4)USB摄像头的音频数据周期大小为512,但是FFmpeg编码需要的周期大小为1024,所以需要进行拼包后再放入FFmpeg进行AAC编码。
video_capture:主要负责的是视频的初始化、采集、清理等工作。视频方面反而比音频注意的地方少,只需要注意初始化完毕后,要及时启动,否则可能摄像头会进入休眠模式,导致启动和捕获失败。
encoder :主要负责编码器的初始化、视频编码、音频编码以及容器封装的工作。由于我们之前已经有了单独视频和单独音频的编码经验,这里无非就是将AAC和H264两个编码器的工作内容进行了合并。里面最主要的功能之一就是音视频同步的技术,我们会在后面一节专门介绍。
main:主要负责的是音视频设备的初始化、编码器的初始化、循环处理音视频数据等工作。在大循环中,处理完视频后,再处理音频,实际上这样是不合理的。最合理的方式应该是开启两个独立的线程分别处理。但是因为我的最终目标并非PC端,所以没再深入进行优化,有兴趣的道友可以自行尝试。
Makefile:由于之前的代码都是单个的,所以直接使用gcc即可完成编译,但是随着文件的增多以及功能越来越负责,只靠手动gcc越来越繁重,所以我们引入Makefile,这个工具可以将我们需要编译的文件、链接的库、编译选项等统统的管理起来。编译的时候只需要执行"make"就可以对工程进行编译。(WOW,又是个新鲜玩意,嵌入式真是个学无止境的领域......)
以下为全部源码。
main.c:
cpp
#include "common.h"
#include "video_capture.h"
#include "audio_capture.h"
#include "encoder.h"
#include <signal.h>
// 全局退出标志
static volatile int should_exit = 0;
// 信号处理函数
void signal_handler(int sig) {
printf("\nReceived signal %d, stopping recording...\n", sig);
should_exit = 1;
}
// 主函数
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
struct recording_config config;
struct video_capture_ctx video_ctx;
struct audio_capture_ctx audio_ctx;
struct encoder_ctx encoder_ctx;
uint8_t *video_data;
size_t video_size;
int64_t video_timestamp;
int16_t audio_buffer[AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE];
int audio_frames;
// 初始化默认配置
init_default_config(&config);
if (argc > 1) {
config.recording_time = atoi(argv[1]);
}
printf("=== USB Camera Recorder ===\n");
printf("Recording time: %d seconds\n", config.recording_time);
printf("Output file: %s\n", config.output_file);
// 设置信号处理
signal(SIGINT, signal_handler); // Ctrl+C
signal(SIGTERM, signal_handler); // 终止信号
// 初始化视频捕获
if (video_capture_init(&video_ctx, VIDEO_DEVICE) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize video capture\n");
goto cleanup;
}
// 初始化音频捕获(与原始代码顺序一致,在编码器之前)
// 先用临时帧大小初始化,后面会根据编码器要求调整
if (audio_capture_init(&audio_ctx, AUDIO_DEVICE, AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize audio capture\n");
goto cleanup;
}
// 初始化编码器(最后初始化)
if (encoder_init(&encoder_ctx, &config) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize encoder\n");
goto cleanup;
}
// 更新音频帧大小(在编码器初始化后)
audio_ctx.frame_size = encoder_ctx.audio_codec_ctx->frame_size;
// 重新分配音频累积缓冲区以匹配实际帧大小
if (audio_ctx.accumulate_buffer) {
free(audio_ctx.accumulate_buffer);
}
audio_ctx.accumulate_buffer = (int16_t*)malloc(audio_ctx.frame_size * sizeof(int16_t));
if (!audio_ctx.accumulate_buffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to reallocate audio accumulation buffer\n");
goto cleanup;
}
printf("Starting recording...\n");
printf("Video: %dx%d @ %dfps, NV12 -> H.264\n", config.video_width, config.video_height, config.video_fps);
printf("Audio: %dHz, %d samples/period, %d channels, S16 -> AAC\n",
config.audio_sample_rate, AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE, config.audio_channels);
printf("Codec frame size: %d samples\n", encoder_ctx.audio_codec_ctx->frame_size);
printf("Time base: 1/%d\n", AV_TIME_BASE);
// 记录录制开始的精确时间
struct timespec recording_start_time;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &recording_start_time);
// 计算录制结束的目标时间(微秒精度)
int64_t target_duration_us = (int64_t)config.recording_time * 1000000LL;
// 主录制循环
int loop_count = 0;
int64_t video_frame_count = 0;
while (1) {
loop_count++;
// 检查是否收到退出信号
if (should_exit) {
printf("Exit signal received, stopping recording...\n");
break;
}
// 检查是否达到录制时长(使用微秒精度)
struct timespec current_time;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, ¤t_time);
int64_t elapsed_us = (current_time.tv_sec - recording_start_time.tv_sec) * 1000000LL +
(current_time.tv_nsec - recording_start_time.tv_nsec) / 1000LL;
if (elapsed_us >= target_duration_us) {
printf("Recording time reached: %.3fs\n", (double)elapsed_us / 1000000.0);
break;
}
if (loop_count % 25 == 1) { // 每25次循环显示一次进度
printf("Loop %d, elapsed: %.3fs\n", loop_count, (double)elapsed_us / 1000000.0);
}
// 捕获视频帧
if (loop_count % 100 == 1) { // 每100次循环显示调试信息
printf("DEBUG: About to capture video frame (loop %d)\n", loop_count);
}
int video_ret = video_capture_frame(&video_ctx, &video_data, &video_size, &video_timestamp);
if (video_ret > 0) {
// 使用已获取的当前时间计算视频时间戳
int64_t video_pts = elapsed_us;
printf("Video frame: count=%ld, elapsed=%.3fs, pts=%ld\n",
video_frame_count, (double)elapsed_us / 1000000.0, video_pts);
if (loop_count % 100 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: About to encode video frame\n");
}
int encode_ret = encoder_encode_video_frame(&encoder_ctx, video_data, video_pts);
if (encode_ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to encode video frame\n");
break;
}
video_frame_count++;
if (loop_count % 100 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: Video frame encoded successfully\n");
}
} else if (video_ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Video capture error: %d\n", video_ret);
break;
} else if (loop_count <= 10) { // 前10次循环显示详细信息
printf("Video capture returned 0 (no data available)\n");
}
// 捕获音频数据
if (loop_count % 200 == 1) { // 每200次循环显示调试信息
printf("DEBUG: About to capture audio data (loop %d)\n", loop_count);
}
audio_frames = audio_capture_data(&audio_ctx, audio_buffer, AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE);
if (audio_frames > 0) {
// 更新实际接收的样本总数(与原始代码一致)
audio_ctx.total_samples_received += audio_frames;
// 累积音频样本,当达到编码器要求帧大小时自动编码
// 关键修复:传递与视频相同的实时时间戳,确保音视频完全同步
if (audio_capture_accumulate_and_encode(&audio_ctx, &encoder_ctx, audio_buffer, audio_frames, elapsed_us) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to accumulate and encode audio\n");
break;
}
} else if (audio_frames < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Audio capture error: %d\n", audio_frames);
break;
} else {
// 音频无数据的情况
static int no_audio_count = 0;
no_audio_count++;
if (no_audio_count % 1000 == 0) { // 每1000次无数据时警告
printf("Warning: No audio data for %d loops (%.3fs)\n",
no_audio_count, (double)elapsed_us / 1000000.0);
}
// 如果音频长时间无数据,尝试重新准备设备
if (no_audio_count > 5000) { // 5000次循环后重置
printf("Attempting to reset audio device...\n");
snd_pcm_prepare(audio_ctx.handle);
no_audio_count = 0;
}
}
// 短暂休眠以避免过度占用CPU
// 如果前几次都没有数据,给摄像头更多时间启动
if (loop_count < 100) {
usleep(10000); // 10ms,给USB摄像头更多启动时间
} else {
usleep(1000); // 1ms,正常运行时的休眠
}
if (loop_count <= 10) {
printf("End of loop %d\n", loop_count);
}
}
printf("Recording finished\n");
// 显示最终统计信息
printf("Final statistics:\n");
printf("- Video frames: %ld\n", video_frame_count);
printf("- Audio samples: %ld (%.3fs)\n",
audio_ctx.total_samples_received,
(double)audio_ctx.total_samples_received / AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE);
printf("- Expected duration: %d seconds\n", config.recording_time);
// 处理剩余的音频数据
if (audio_ctx.accumulated_samples > 0) {
// 获取最终的实时时间戳
struct timespec final_time;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &final_time);
int64_t final_elapsed_us = (final_time.tv_sec - recording_start_time.tv_sec) * 1000000LL +
(final_time.tv_nsec - recording_start_time.tv_nsec) / 1000LL;
// 应用相同的AAC编码器延迟补偿
int64_t compensated_timestamp = final_elapsed_us - AAC_ENCODER_DELAY_US;
if (compensated_timestamp < 0) {
compensated_timestamp = 0;
}
encoder_finalize_remaining_audio(&encoder_ctx, audio_ctx.accumulate_buffer,
audio_ctx.accumulated_samples, compensated_timestamp);
}
cleanup:
// 停止视频捕获
video_capture_stop(&video_ctx);
// 清理所有资源
video_capture_cleanup(&video_ctx);
audio_capture_cleanup(&audio_ctx);
encoder_cleanup(&encoder_ctx);
printf("=== Recording Complete ===\n");
return 0;
}audio_capture.c和.h
cpp
#include "audio_capture.h"
#include "encoder.h" // 需要encoder_ctx结构体定义
// 初始化音频捕获设备
int audio_capture_init(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, const char *device, int frame_size) {
snd_pcm_hw_params_t *hw_params;
int err;
// 初始化上下文
memset(ctx, 0, sizeof(*ctx));
ctx->frame_size = frame_size;
if ((err = snd_pcm_open(&ctx->handle, device, SND_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open audio device %s: %s\n", device, snd_strerror(err));
return -1;
}
// 分配硬件参数结构
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_malloc(&hw_params)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate hw params: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 初始化硬件参数
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_any(ctx->handle, hw_params)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize hw params: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置访问类型
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access(ctx->handle, hw_params, SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set access type: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置采样格式
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format(ctx->handle, hw_params, SND_PCM_FORMAT_S16_LE)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set audio format: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置采样率
unsigned int sample_rate = AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE;
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near(ctx->handle, hw_params, &sample_rate, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set sample rate: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置通道数
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels(ctx->handle, hw_params, AUDIO_CHANNELS)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set channels: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置周期大小
snd_pcm_uframes_t period_size = AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE;
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_size_near(ctx->handle, hw_params, &period_size, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set period size: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 设置周期数
unsigned int periods = AUDIO_PERIODS;
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params_set_periods_near(ctx->handle, hw_params, &periods, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set periods: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 应用硬件参数
if ((err = snd_pcm_hw_params(ctx->handle, hw_params)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set hw params: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
snd_pcm_hw_params_free(hw_params);
// 准备PCM
if ((err = snd_pcm_prepare(ctx->handle)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to prepare audio: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 分配累积缓冲区
ctx->accumulate_buffer = (int16_t*)malloc(frame_size * sizeof(int16_t));
if (!ctx->accumulate_buffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate audio accumulation buffer\n");
audio_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->accumulated_samples = 0;
ctx->total_samples_received = 0;
printf("Audio device initialized successfully\n");
return 0;
}
// 捕获音频数据
int audio_capture_data(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, int16_t *buffer, int buffer_size) {
snd_pcm_sframes_t err;
// 添加debug输出,与原始代码一致
static int debug_count = 0;
if (debug_count < 5) { // 只显示前5次
printf("audio_handle: %p\n", ctx->handle);
}
// 检查PCM状态
snd_pcm_state_t state = snd_pcm_state(ctx->handle);
if (state != SND_PCM_STATE_RUNNING && state != SND_PCM_STATE_PREPARED) {
printf("Audio PCM state: %s, attempting recovery...\n", snd_pcm_state_name(state));
if (state == SND_PCM_STATE_XRUN) {
// 处理欠载/溢出
if (snd_pcm_prepare(ctx->handle) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to recover from XRUN\n");
return -1;
}
} else if (state == SND_PCM_STATE_SUSPENDED) {
// 处理设备暂停
int res;
while ((res = snd_pcm_resume(ctx->handle)) == -EAGAIN) {
usleep(1000); // 等待1ms
}
if (res < 0) {
if (snd_pcm_prepare(ctx->handle) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to recover from SUSPEND\n");
return -1;
}
}
}
}
err = snd_pcm_readi(ctx->handle, buffer, buffer_size);
if (debug_count < 5) { // 只显示前5次
printf("err: %ld\n", err);
debug_count++;
}
if (err == -EAGAIN) {
// 非阻塞模式下没有数据可用,正常情况
return 0;
} else if (err == -EPIPE) {
// 缓冲区欠载,恢复
printf("Audio underrun occurred, recovering...\n");
snd_pcm_prepare(ctx->handle);
return 0;
} else if (err == -ESTRPIPE) {
// 设备暂停,恢复
printf("Audio device suspended, recovering...\n");
int res;
while ((res = snd_pcm_resume(ctx->handle)) == -EAGAIN) {
usleep(1000);
}
if (res < 0) {
snd_pcm_prepare(ctx->handle);
}
return 0;
} else if (err < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to read audio: %s\n", snd_strerror(err));
return -1;
}
// 仅每10次采集显示一次,避免输出过多
if (ctx->total_samples_received % (AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE * 10) == 0) {
printf("Audio: total=%ld samples (%.3fs)\n",
ctx->total_samples_received,
(double)ctx->total_samples_received / AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE);
}
return err; // 返回实际读取的帧数
}
// 累积音频样本并在需要时编码(使用实时时间戳确保与视频同步)
int audio_capture_accumulate_and_encode(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, struct encoder_ctx *encoder, int16_t *audio_data, int samples, int64_t current_timestamp_us) {
// 计算还需要多少样本才能填满一个编码帧
int samples_needed = ctx->frame_size - ctx->accumulated_samples;
int samples_to_copy = (samples < samples_needed) ? samples : samples_needed;
// 将新样本拷贝到累积缓冲区
memcpy(ctx->accumulate_buffer + ctx->accumulated_samples,
audio_data, samples_to_copy * sizeof(int16_t));
ctx->accumulated_samples += samples_to_copy;
// 如果累积够了一个完整帧,进行编码
if (ctx->accumulated_samples >= ctx->frame_size) {
// 关键修复:补偿AAC编码器的200ms固有延迟
// 通过将音频时间戳提前200ms来实现音视频同步
int64_t audio_pts = current_timestamp_us - AAC_ENCODER_DELAY_US;
// 如果补偿后为负,使用原始时间戳但添加警告
if (audio_pts < 0) {
static int warning_count = 0;
if (warning_count < 3) { // 只警告前3次
printf("WARNING: Audio timestamp compensation resulted in negative value, using 0 (warning %d/3)\n", warning_count + 1);
warning_count++;
}
audio_pts = 0;
}
if (encoder_encode_audio_frame(encoder, ctx->accumulate_buffer, audio_pts) < 0) {
return -1;
}
ctx->accumulated_samples = 0;
// 如果还有剩余样本,递归处理,更新时间戳避免重复
int remaining_samples = samples - samples_to_copy;
if (remaining_samples > 0) {
// 为下一帧计算新的时间戳,基于帧大小推进时间
int64_t frame_duration_us = (int64_t)ctx->frame_size * 1000000LL / AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE;
int64_t next_timestamp = current_timestamp_us + frame_duration_us;
return audio_capture_accumulate_and_encode(ctx, encoder, audio_data + samples_to_copy, remaining_samples, next_timestamp);
}
}
return 0;
}
// 清理音频捕获资源
void audio_capture_cleanup(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx) {
if (ctx->accumulate_buffer) {
free(ctx->accumulate_buffer);
ctx->accumulate_buffer = NULL;
}
if (ctx->handle) {
snd_pcm_close(ctx->handle);
ctx->handle = NULL;
}
ctx->accumulated_samples = 0;
ctx->total_samples_received = 0;
}
cpp
#ifndef AUDIO_CAPTURE_H
#define AUDIO_CAPTURE_H
#include "common.h"
struct encoder_ctx;
// 音频捕获上下文结构
struct audio_capture_ctx {
snd_pcm_t *handle;
int16_t *accumulate_buffer;
int accumulated_samples;
int64_t total_samples_received;
int frame_size; // AAC编码器要求的帧大小
};
int audio_capture_init(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, const char *device, int frame_size);
int audio_capture_data(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, int16_t *buffer, int buffer_size);
int audio_capture_accumulate_and_encode(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx, struct encoder_ctx *encoder, int16_t *audio_data, int samples, int64_t current_timestamp_us);
void audio_capture_cleanup(struct audio_capture_ctx *ctx);
#endif // AUDIO_CAPTURE_H video_capture.c和.h
cpp
#include "video_capture.h"
// 初始化视频捕获设备
int video_capture_init(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx, const char *device) {
struct v4l2_format fmt;
struct v4l2_requestbuffers req;
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
// 初始化上下文
memset(ctx, 0, sizeof(*ctx));
ctx->fd = -1;
// 打开视频设备
ctx->fd = open(device, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK, 0);
if (ctx->fd == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open video device %s: %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// 设置视频格式
memset(&fmt, 0, sizeof(fmt));
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
fmt.fmt.pix.width = VIDEO_WIDTH;
fmt.fmt.pix.height = VIDEO_HEIGHT;
fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = VIDEO_FORMAT;
fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_S_FMT, &fmt) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to set video format: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 请求缓冲区
memset(&req, 0, sizeof(req));
req.count = 4;
req.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
req.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_REQBUFS, &req) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to request video buffers: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->buffer_count = req.count;
ctx->buffers = calloc(req.count, sizeof(*ctx->buffers));
if (!ctx->buffers) {
fprintf(stderr, "Out of memory\n");
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 映射缓冲区
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < req.count; ++i) {
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_QUERYBUF, &buf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to query video buffer: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->buffers[i].length = buf.length;
ctx->buffers[i].start = mmap(NULL, buf.length,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
ctx->fd, buf.m.offset);
if (ctx->buffers[i].start == MAP_FAILED) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to mmap video buffer: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
}
printf("Video device initialized successfully\n");
// 将缓冲区入队并启动视频流(与原始代码一致)
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < ctx->buffer_count; ++i) {
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to queue video buffer: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
}
// 开始视频捕获(在初始化时就启动,与原始代码一致)
enum v4l2_buf_type type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_STREAMON, &type) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to start video stream: %s\n", strerror(errno));
video_capture_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 记录开始时间
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ctx->start_time);
ctx->frame_count = 0;
return 0;
}
// 捕获视频帧
int video_capture_frame(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx, uint8_t **frame_data,
size_t *frame_size, int64_t *timestamp) {
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
memset(&buf, 0, sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_DQBUF, &buf) == -1) {
if (errno == EAGAIN) {
return 0; // 没有数据可用
}
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to dequeue video buffer: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
// 首次捕获成功时显示信息
if (ctx->frame_count == 0) {
printf("First video frame captured! Size: %u bytes\n", buf.bytesused);
}
*frame_data = (uint8_t*)ctx->buffers[buf.index].start;
*frame_size = buf.bytesused;
// 不在这里计算时间戳,由调用者计算
*timestamp = 0; // 占位,主循环会重新设置
ctx->frame_count++;
// 重新入队缓冲区
if (ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_QBUF, &buf) == -1) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to queue video buffer: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
return 1; // 成功捕获帧
}
// 停止视频捕获
void video_capture_stop(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx) {
if (ctx->fd != -1) {
enum v4l2_buf_type type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
ioctl(ctx->fd, VIDIOC_STREAMOFF, &type);
}
}
// 清理视频捕获资源
void video_capture_cleanup(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx) {
if (ctx->buffers) {
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < ctx->buffer_count; ++i) {
if (ctx->buffers[i].start != MAP_FAILED && ctx->buffers[i].start != NULL) {
munmap(ctx->buffers[i].start, ctx->buffers[i].length);
}
}
free(ctx->buffers);
ctx->buffers = NULL;
}
if (ctx->fd != -1) {
close(ctx->fd);
ctx->fd = -1;
}
ctx->buffer_count = 0;
}
cpp
#ifndef VIDEO_CAPTURE_H
#define VIDEO_CAPTURE_H
#include "common.h"
// 视频捕获上下文结构
struct video_capture_ctx {
int fd;
struct video_buffer *buffers;
unsigned int buffer_count;
struct timespec start_time;
int64_t frame_count;
};
// 函数声明
int video_capture_init(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx, const char *device);
int video_capture_frame(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx, uint8_t **frame_data,
size_t *frame_size, int64_t *timestamp);
void video_capture_stop(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx);
void video_capture_cleanup(struct video_capture_ctx *ctx);
#endif // VIDEO_CAPTURE_H encoder.c和.h
cpp
#include "encoder.h"
// 内部函数:编码完整的音频帧
static int encode_audio_frame_internal(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, int16_t *input_data, int64_t pts) {
int ret;
// 重采样音频数据:从S16整数格式转换为FLTP浮点格式
// 使用传入的input_data作为输入,避免与输出缓冲区冲突
const uint8_t *in[] = {(uint8_t*)input_data};
uint8_t **out = ctx->audio_frame->data;
ret = swr_convert(ctx->swr_ctx, out, ctx->audio_frame->nb_samples, in, ctx->audio_frame->nb_samples);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to resample audio (S16->FLTP): %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_frame->pts = pts;
// 编码帧
ret = avcodec_send_frame(ctx->audio_codec_ctx, ctx->audio_frame);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to send audio frame: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
while (ret >= 0) {
ret = avcodec_receive_packet(ctx->audio_codec_ctx, ctx->pkt);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)
break;
else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to receive audio packet: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
av_packet_rescale_ts(ctx->pkt, ctx->audio_codec_ctx->time_base, ctx->audio_stream->time_base);
ctx->pkt->stream_index = ctx->audio_stream->index;
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(ctx->fmt_ctx, ctx->pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to write audio packet: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
av_packet_unref(ctx->pkt);
}
return 0;
}
// 初始化编码器
int encoder_init(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, const struct recording_config *config) {
int ret;
// 初始化上下文
memset(ctx, 0, sizeof(*ctx));
// 分配输出上下文
ret = avformat_alloc_output_context2(&ctx->fmt_ctx, NULL, NULL, config->output_file);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate output context: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
// 初始化视频编码器
const AVCodec *video_codec = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if (!video_codec) {
fprintf(stderr, "H.264 encoder not found\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->video_stream = avformat_new_stream(ctx->fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (!ctx->video_stream) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create video stream\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->video_codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(video_codec);
if (!ctx->video_codec_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate video codec context\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->video_codec_ctx->bit_rate = config->video_bitrate;
ctx->video_codec_ctx->width = config->video_width;
ctx->video_codec_ctx->height = config->video_height;
ctx->video_codec_ctx->time_base = (AVRational){1, AV_TIME_BASE};
ctx->video_codec_ctx->framerate = (AVRational){config->video_fps, 1};
ctx->video_codec_ctx->gop_size = 12;
ctx->video_codec_ctx->max_b_frames = 0; // 去掉B帧,避免编码延迟
ctx->video_codec_ctx->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_NV12;
if (ctx->fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)
ctx->video_codec_ctx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
ret = avcodec_open2(ctx->video_codec_ctx, video_codec, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open video codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ret = avcodec_parameters_from_context(ctx->video_stream->codecpar, ctx->video_codec_ctx);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to copy video codec parameters: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->video_stream->time_base = ctx->video_codec_ctx->time_base;
// 初始化音频编码器
const AVCodec *audio_codec = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_AAC);
if (!audio_codec) {
fprintf(stderr, "AAC encoder not found\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_stream = avformat_new_stream(ctx->fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (!ctx->audio_stream) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to create audio stream\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_codec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(audio_codec);
if (!ctx->audio_codec_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate audio codec context\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->bit_rate = config->audio_bitrate;
// AAC编码器要求浮点数格式(FLTP = Float, Planar)
// 这能提供更好的音质和动态范围
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_fmt = AV_SAMPLE_FMT_FLTP;
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_rate = config->audio_sample_rate;
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->channels = config->audio_channels;
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->channel_layout = AV_CH_LAYOUT_MONO;
// 设置音频编码器时间基与AV_TIME_BASE统一
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->time_base = (AVRational){1, AV_TIME_BASE};
if (ctx->fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_GLOBALHEADER)
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->flags |= AV_CODEC_FLAG_GLOBAL_HEADER;
ret = avcodec_open2(ctx->audio_codec_ctx, audio_codec, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open audio codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ret = avcodec_parameters_from_context(ctx->audio_stream->codecpar, ctx->audio_codec_ctx);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to copy audio codec parameters: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_stream->time_base = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->time_base;
ctx->swr_ctx = swr_alloc_set_opts(NULL,
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->channel_layout, ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_fmt, ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_rate,
AV_CH_LAYOUT_MONO, AV_SAMPLE_FMT_S16, AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE,
0, NULL);
if (!ctx->swr_ctx) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate audio resampler\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ret = swr_init(ctx->swr_ctx);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize audio resampler: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 分配帧和包
ctx->video_frame = av_frame_alloc();
ctx->audio_frame = av_frame_alloc();
ctx->pkt = av_packet_alloc();
if (!ctx->video_frame || !ctx->audio_frame || !ctx->pkt) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate frames/packet\n");
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->video_frame->format = ctx->video_codec_ctx->pix_fmt;
ctx->video_frame->width = ctx->video_codec_ctx->width;
ctx->video_frame->height = ctx->video_codec_ctx->height;
ret = av_frame_get_buffer(ctx->video_frame, 32);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate video frame buffer: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
ctx->audio_frame->format = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_fmt;
ctx->audio_frame->channels = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->channels;
ctx->audio_frame->channel_layout = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->channel_layout;
ctx->audio_frame->sample_rate = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->sample_rate;
ctx->audio_frame->nb_samples = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->frame_size;
ret = av_frame_get_buffer(ctx->audio_frame, 0);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate audio frame buffer: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
// 打开输出文件
if (!(ctx->fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE)) {
ret = avio_open(&ctx->fmt_ctx->pb, config->output_file, AVIO_FLAG_WRITE);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open output file: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
}
// 写入文件头
ret = avformat_write_header(ctx->fmt_ctx, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to write header: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
encoder_cleanup(ctx);
return -1;
}
printf("FFmpeg encoders initialized successfully\n");
printf("Audio frame size: %d samples (accumulating from %d sample periods)\n",
ctx->audio_codec_ctx->frame_size, AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE);
return 0;
}
// 编码视频帧
int encoder_encode_video_frame(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *frame_data, int64_t timestamp) {
int ret;
static int frame_count = 0;
frame_count++;
if (frame_count % 25 == 1) { // 每25帧显示一次,减少输出
printf("Encoding video frame %d, timestamp: %ld\n", frame_count, timestamp);
}
// NV12格式:Y平面 + UV交错平面
memcpy(ctx->video_frame->data[0], frame_data, VIDEO_WIDTH * VIDEO_HEIGHT);
memcpy(ctx->video_frame->data[1], frame_data + VIDEO_WIDTH * VIDEO_HEIGHT, VIDEO_WIDTH * VIDEO_HEIGHT / 2);
ctx->video_frame->pts = timestamp;
// 编码帧
ret = avcodec_send_frame(ctx->video_codec_ctx, ctx->video_frame);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to send video frame: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
while (ret >= 0) {
ret = avcodec_receive_packet(ctx->video_codec_ctx, ctx->pkt);
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
break;
} else if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to receive video packet: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
// 直接使用帧的时间戳设置包的时间戳(修复INT64_MIN问题)
if (ctx->pkt->pts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
ctx->pkt->pts = ctx->video_frame->pts;
}
if (ctx->pkt->dts == AV_NOPTS_VALUE) {
ctx->pkt->dts = ctx->video_frame->pts;
}
av_packet_rescale_ts(ctx->pkt, ctx->video_codec_ctx->time_base, ctx->video_stream->time_base);
ctx->pkt->stream_index = ctx->video_stream->index;
// 添加写入前的调试信息
if (frame_count % 100 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: About to write video packet (size=%d)\n", ctx->pkt->size);
}
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(ctx->fmt_ctx, ctx->pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to write video packet: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
return -1;
}
if (frame_count % 100 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: Video packet written successfully\n");
}
// 只有当包有实际数据时才输出调试信息
if (frame_count % 25 == 1 && ctx->pkt->size > 0) {
printf("Video packet written: size=%d, pts=%ld, dts=%ld\n", ctx->pkt->size, ctx->pkt->pts, ctx->pkt->dts);
}
av_packet_unref(ctx->pkt);
}
return 0;
}
// 编码音频帧
int encoder_encode_audio_frame(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, int16_t *audio_data, int64_t timestamp) {
// 直接使用传入的audio_data,无需拷贝到audio_frame中
return encode_audio_frame_internal(ctx, audio_data, timestamp);
}
// 处理剩余的音频数据
int encoder_finalize_remaining_audio(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, int16_t *partial_frame,
int samples, int64_t timestamp) {
if (samples > 0) {
printf("Encoding remaining %d audio samples\n", samples);
// 创建临时缓冲区,填充剩余部分为静音
int16_t *temp_buffer = malloc(ctx->audio_codec_ctx->frame_size * sizeof(int16_t));
if (!temp_buffer) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to allocate temporary audio buffer\n");
return -1;
}
int remaining_samples = ctx->audio_codec_ctx->frame_size - samples;
memcpy(temp_buffer, partial_frame, samples * sizeof(int16_t));
memset(temp_buffer + samples, 0, remaining_samples * sizeof(int16_t));
int ret = encode_audio_frame_internal(ctx, temp_buffer, timestamp);
free(temp_buffer);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}
// 清理编码器资源
void encoder_cleanup(struct encoder_ctx *ctx) {
// 刷新视频编码器 - 发送NULL帧获取所有待编码的帧
if (ctx->video_codec_ctx && ctx->pkt) {
printf("Flushing video encoder...\n");
avcodec_send_frame(ctx->video_codec_ctx, NULL);
int ret;
int flushed_count = 0;
while ((ret = avcodec_receive_packet(ctx->video_codec_ctx, ctx->pkt)) >= 0) {
if (ctx->fmt_ctx) {
av_packet_rescale_ts(ctx->pkt, ctx->video_codec_ctx->time_base, ctx->video_stream->time_base);
ctx->pkt->stream_index = ctx->video_stream->index;
av_interleaved_write_frame(ctx->fmt_ctx, ctx->pkt);
// 只显示有效包的信息
if (ctx->pkt->size > 0) {
printf("Flushed video packet: size=%d, pts=%ld\n", ctx->pkt->size, ctx->pkt->pts);
flushed_count++;
}
}
av_packet_unref(ctx->pkt);
}
printf("Video encoder flushed %d packets\n", flushed_count);
}
// 刷新音频编码器
if (ctx->audio_codec_ctx && ctx->pkt) {
printf("Flushing audio encoder...\n");
avcodec_send_frame(ctx->audio_codec_ctx, NULL);
int ret;
int flushed_count = 0;
while ((ret = avcodec_receive_packet(ctx->audio_codec_ctx, ctx->pkt)) >= 0) {
if (ctx->fmt_ctx) {
av_packet_rescale_ts(ctx->pkt, ctx->audio_codec_ctx->time_base, ctx->audio_stream->time_base);
ctx->pkt->stream_index = ctx->audio_stream->index;
// 添加音频写入调试信息
static int audio_packet_count = 0;
audio_packet_count++;
if (audio_packet_count % 50 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: About to write audio packet (size=%d)\n", ctx->pkt->size);
}
ret = av_interleaved_write_frame(ctx->fmt_ctx, ctx->pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Failed to write audio packet: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));
break;
}
if (audio_packet_count % 50 == 1) {
printf("DEBUG: Audio packet written successfully\n");
}
// 只显示有效包的信息
if (ctx->pkt->size > 0) {
printf("Flushed audio packet: size=%d, pts=%ld\n", ctx->pkt->size, ctx->pkt->pts);
flushed_count++;
}
}
av_packet_unref(ctx->pkt);
}
printf("Audio encoder flushed %d packets\n", flushed_count);
}
// 写入文件尾
if (ctx->fmt_ctx) {
av_write_trailer(ctx->fmt_ctx);
}
// 清理FFmpeg资源
if (ctx->video_codec_ctx) {
avcodec_free_context(&ctx->video_codec_ctx);
}
if (ctx->audio_codec_ctx) {
avcodec_free_context(&ctx->audio_codec_ctx);
}
if (ctx->fmt_ctx) {
if (!(ctx->fmt_ctx->oformat->flags & AVFMT_NOFILE))
avio_closep(&ctx->fmt_ctx->pb);
avformat_free_context(ctx->fmt_ctx);
}
if (ctx->swr_ctx) {
swr_free(&ctx->swr_ctx);
}
if (ctx->video_frame) {
av_frame_free(&ctx->video_frame);
}
if (ctx->audio_frame) {
av_frame_free(&ctx->audio_frame);
}
if (ctx->pkt) {
av_packet_free(&ctx->pkt);
}
// 重置所有指针
memset(ctx, 0, sizeof(*ctx));
}
cpp
#ifndef ENCODER_H
#define ENCODER_H
#include "common.h"
// 编码器上下文结构
struct encoder_ctx {
// FFmpeg相关变量
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx;
AVCodecContext *video_codec_ctx;
AVCodecContext *audio_codec_ctx;
AVStream *video_stream;
AVStream *audio_stream;
struct SwsContext *sws_ctx; // 保留为NULL,因为直接使用NV12
SwrContext *swr_ctx;
AVFrame *video_frame;
AVFrame *audio_frame;
AVPacket *pkt;
};
// 函数声明
int encoder_init(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, const struct recording_config *config);
int encoder_encode_video_frame(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, uint8_t *frame_data, int64_t timestamp);
int encoder_encode_audio_frame(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, int16_t *audio_data, int64_t timestamp);
int encoder_finalize_remaining_audio(struct encoder_ctx *ctx, int16_t *partial_frame,
int samples, int64_t timestamp);
void encoder_cleanup(struct encoder_ctx *ctx);
#endif // ENCODER_H common.h
cpp
#ifndef COMMON_H
#define COMMON_H
// 定义功能特性宏
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#define _POSIX_C_SOURCE 200809L
// 标准C库
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
// FFmpeg头文件(在其他系统头文件之前包含)
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavformat/avformat.h>
#include <libavutil/opt.h>
#include <libavutil/imgutils.h>
#include <libswresample/swresample.h>
// V4L2和ALSA头文件(在FFmpeg之后包含)
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <alsa/asoundlib.h>
// 视频参数
#define VIDEO_DEVICE "/dev/video0"
#define VIDEO_WIDTH 640
#define VIDEO_HEIGHT 480
#define VIDEO_FPS 25
#define VIDEO_FORMAT V4L2_PIX_FMT_NV12
// 音频参数
#define AUDIO_DEVICE "plughw:1,0"
#define AUDIO_CHANNELS 1
#define AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE 22050
#define AUDIO_PERIOD_SIZE 256 // 减少到256以降低延迟 (约11.6ms @ 22050Hz)
#define AUDIO_PERIODS 5
// 编码参数
#define OUTPUT_FILE "output.mp4"
#define VIDEO_BITRATE 10000000
#define AUDIO_BITRATE 64000
// 音视频同步相关配置
#define AAC_ENCODER_DELAY_US 200000 // AAC编码器固有延迟(微秒)
#define SYNC_DEBUG_ENABLED 1 // 启用同步调试输出
#define MAX_TIMESTAMP_DRIFT_US 50000 // 最大允许时间戳漂移(50ms)
// 视频缓冲区结构
struct video_buffer {
void *start;
size_t length;
};
// 录制配置结构
struct recording_config {
int recording_time;
char output_file[256];
int video_width;
int video_height;
int video_fps;
int audio_sample_rate;
int audio_channels;
int video_bitrate;
int audio_bitrate;
};
// 错误字符串转换函数(仅在未定义时定义)
#ifndef av_err2str
static char error_buffer[AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE];
static const char* av_err2str_func(int errnum) {
av_strerror(errnum, error_buffer, AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE);
return error_buffer;
}
#define av_err2str(e) av_err2str_func(e)
#endif
// 初始化默认配置
static inline void init_default_config(struct recording_config *config) {
config->recording_time = 30;
strcpy(config->output_file, OUTPUT_FILE);
config->video_width = VIDEO_WIDTH;
config->video_height = VIDEO_HEIGHT;
config->video_fps = VIDEO_FPS;
config->audio_sample_rate = AUDIO_SAMPLE_RATE;
config->audio_channels = AUDIO_CHANNELS;
config->video_bitrate = VIDEO_BITRATE;
config->audio_bitrate = AUDIO_BITRATE;
}
#endif // COMMON_H Makefile:
bash
# USB Camera Recorder Makefile (Modular Version)
# 编译器设置
CC = gcc
CFLAGS = -Wall -Wextra -std=c99 -O2
# 程序名称
PROGRAM = usb_camera_recorder
# 源文件
SOURCES = main.c video_capture.c audio_capture.c encoder.c
# 目标文件
OBJECTS = $(SOURCES:.c=.o)
# 头文件
HEADERS = common.h video_capture.h audio_capture.h encoder.h
# 库文件链接
LIBS = -lavcodec -lavformat -lavutil -lswresample -lasound -lm
# PKG-CONFIG包
PKGS = libavcodec libavformat libavutil libswresample alsa
# 使用pkg-config获取编译和链接参数
CFLAGS += $(shell pkg-config --cflags $(PKGS))
LDFLAGS = $(shell pkg-config --libs $(PKGS))
# 默认目标
all: $(PROGRAM)
# 编译主程序
$(PROGRAM): $(OBJECTS)
$(CC) $(OBJECTS) -o $(PROGRAM) $(LDFLAGS) $(LIBS)
# 编译源文件(加入头文件依赖)
%.o: %.c $(HEADERS)
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
# 特定模块的依赖关系
main.o: main.c common.h video_capture.h audio_capture.h encoder.h
video_capture.o: video_capture.c video_capture.h common.h
audio_capture.o: audio_capture.c audio_capture.h common.h
encoder.o: encoder.c encoder.h common.h
# 清理编译文件
clean:
rm -f $(OBJECTS) $(PROGRAM)
# 深度清理(包括备份文件)
distclean: clean
rm -f *~ *.bak *.mp4
# 检查依赖
check-deps:
@echo "Checking dependencies..."
@pkg-config --exists $(PKGS) && echo "All dependencies found" || echo "Missing dependencies"
@which $(CC) > /dev/null && echo "Compiler found: $(CC)" || echo "Compiler not found: $(CC)"
# 显示项目结构
info:
@echo "=== USB Camera Recorder (Modular Version) ==="
@echo "Source files:"
@for src in $(SOURCES); do echo " $$src"; done
@echo "Header files:"
@for hdr in $(HEADERS); do echo " $$hdr"; done
@echo "Program: $(PROGRAM)"
@echo
# 伪目标声明
.PHONY: all clean distclean check-deps info 2、音视频同步
1)PTS是什么?
是英文Presentation Time Stamp首字母,直译为显示时间戳,比如视频的帧率为25fps,平均40ms产生一帧数据。
以下是针对 25fps 视频(帧间隔=40ms)的前5帧PTS与显示帧数的对照表:
| 帧序列 | 物理呈现时间 |
|---|---|
| 第0帧 | 0ms |
| 第1帧 | 40ms |
| 第2帧 | 80ms |
| 第3帧 | 120ms |
| 第4帧 | 160ms |
表1
当播放器运行到第0秒的时候,开始显示第0帧。运行到第40ms的时候,显示第1帧。以此类推,直到将所有的帧显示完毕。"物理呈现时间"就是显示时间戳,也就是PTS。
2)增加音频后,播放器应该如何显示?
假如音频的采样率为22050,音频的帧率为25,以下是0~160ms时间轴的事件:
| 事件发生时间(ms) | 事件类型 | 事件序号 | PTS(微秒) | 备注(实际对应的时间) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 视频帧 | 0 | 0 | 第0帧 |
| 0 | 音频包 | 0 | 0 | 第0个音频包 |
| 40 | 视频帧 | 1 | 40000 | 第1帧 |
| 46.44 | 音频包 | 1 | 46440 | 第1个音频包(起始) |
| 80 | 视频帧 | 2 | 80000 | 第2帧 |
| 92.88 | 音频包 | 2 | 92880 | 第2个音频包 |
| 120 | 视频帧 | 3 | 120000 | 第3帧 |
| 139.32 | 音频包 | 3 | 139320 | 第3个音频包 |
| 160 | 视频帧 | 4 | 160000 | 第4帧 |
表2
视频的播放这里就不再赘述,音频与视频的也是类似的,在92.88ms时,播放第2个音频包,这个音频包可以持续播放46.44ms,直到139.32ms到来后,播放第3个音频包。
3)音视频的PTS计算
音频和视频都有独立的PTS,我们记为pts_a和pts_v。依照上面的表格。
第0帧视频数据产生后,pts_v = 0(us),第1帧产生时,pts_v = 40000(us)。
第0包音频包产生后,pts_a = 0(us)。第1包产生时,pts_a = 46440(us)。
以此类推。
4)如果不做音视频同步会怎样?
依照前面三个小节的描述,pts就使用以下计算方式:
cpp
pts_v = 帧数 * (1 / 帧率)
pts_a = (包数 * 包周期) * (1 / 采样率)这样的计算方式有问题吗?
回答:在短时间内是没什么问题的(比如几十秒之内),但是录制时间久了会出现问题(比如一个小时)。
为什么录制时间久了会出现音视频不同步?
回答:第一、音频和视频的时钟都是独立的,又固定和波动偏差。第二、音频的计算有很多是除不尽的,导致数学计算后必须四舍五入。因为这两点原因,录制时间久了之后,会产生一个让人头大的问题:累积误差。
举个例子:假定录制一个小时,音频由于系统性误差为+10us,再加上除不尽的问题,那么1个小时后,累积误差将达到+0.8s左右,也就是音频比画面慢了将近1秒!基本上这个视频就没办法看了。(这个举例是很客气了,实际上音视频的累计误差比这个糟糕多了)
如果不做音视频同步会怎样?
回答:由于累计误差的问题,录制时间久了,会出现严重的声音画面不同步!
5)解决方案
其实核心思想很简单,就是加入一个第三方时钟,本次代码中采用的是单调递增时钟CLOCK_MONOTONIC作为时间基。每次产生一帧图像数据或者一包音频数据,将CLOCK_MONOTONIC生成的时间戳作为PTS写入即可。
示意图如下:
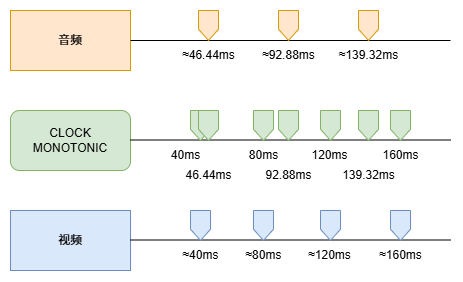
另外还有将音频时钟作为时间基,这种方式更加适合长时间的录制,此方式大家自己研究。
6)代码说明
该工程的代码是借助于前几章的代码合并而成的,无论是音频编码还是视频编码,都是较为简单的,无非就是初始化、采集数据、编码、写文件。但是如果要将音视频合并在一起,就需要实现"音视频同步",该代码中主要针对音频和视频的同步做了修改,采用CLOCK_MONOTONIC作为了PTS的时钟源。
这里面有两个概念有可能需要补充说明一下,那就是AV_TIME_BASE和CLOCK_MONOTONIC:
-
AV_TIME_BASE: 只是"单位标尺"(1秒=1,000,000),表示"用微秒记时"的时间基,不是时钟。
-
CLOCK_MONOTONIC: 是"时钟源",返回单调递增的当前时间。
二者关系:没有直接绑定。工程里常用"用CLOCK_MONOTONIC取时间",再"用AV_TIME_BASE把它表达为微秒",最后按各流的time_base做换算。
总结
音频和视频编码在之前的章节实现过,本章节将其合二为一,但是并非简单的合并,而是需要考虑"音视频同步",否则会造成画面和声音不同步的现象。
本章节使用AV_TIME_BASE作为时间基,将CLOCK_MONOTONIC作为时钟源,并且对音频做了一个固定时间偏执。笔者亲测该代码运行一个小时,音视频依然保持同步。
下一章节我们进入最终章的下半部分--音视频直播。