作者:来自 Elastic Adrian Chen

PowerShell 日志完整上下文的存储减少示例。
数据保真度的高成本:当更多数据并不更好
在网络安全和可观测性领域,管理层面临一个长期的困境:对完全可见性的不可协商要求,与有限预算的严酷现实发生冲突。这种矛盾在 PowerShell 日志中表现得尤为明显。对于任何拥有大量 Windows 环境的现代企业来说,PowerShell 是管理和自动化的引擎。然而,它的强大和普及也让它成为对手的主要攻击目标,他们利用它进行无文件恶意软件执行、横向移动和凭证盗窃。
为应对这一威胁,安全框架要求全面记录日志,尤其是 PowerShell 脚本块日志(事件 ID 4104)。这些日志对威胁狩猎至关重要,因为它们捕获了攻击者运行的精确去混淆代码。然而,这一安全要求可能会引发数据管理危机。启用完整脚本块日志会生成大量事件,可能产生数 TB 的数据,从而导致显著的存储和索引成本。
这直接造成了安全需求与预算限制之间的冲突。本文介绍了一种更智能的策略,代表了处理日志数据方式的范式转变。假如可以保留每一条取证证据,而不必为其重复存储数百万次付费,会怎样?答案在于将日志视为高效、可搜索的笔记,而非冗长的日记 ------ 一种由 Elastic Stack 和革命性的 Elasticsearch Query Language (ES|QL) LOOKUP JOIN 命令驱动的策略。
潜力:大幅减少存储
让我们量化一下潜在的收益。考虑一个真实的企业场景:一个标准 9KB 的 PowerShell 健康检查脚本每 10 分钟在 10,000 台服务器上运行一次。这会每天生成 1,440,000 条事件。这种技术对存储消耗的影响是革命性的。
|-----------------------------|----------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------|---------------------------|
| Metric | Before optimization | After optimization | Impact |
| Script text storage/day | 12.96GB | 9KB | ~99.99% reduction |
| Total events logged | 1.44 million | 1.44 million (lean) + 1 (full) | No loss of event metadata |
| Analytic capability | Full script text available | Full script text available on demand | Zero loss of fidelity |
| Security rule coverage | Full | Full (with investigation via lookup index scanning) | Zero blind spots created |
注意:存储数据是在未应用任何索引级压缩前的数值。
策略:哈希、单次存储、按需查找
该解决方案的核心原则是智能数据去重。在任何大型企业中,用于健康检查、应用监控和管理任务的同一组 PowerShell 脚本每天会被执行数百万次。传统方法在每次执行时都会捕获这些脚本完整的多 KB 文本,导致大量数据冗余。
想象一下你的日常通勤。你不需要每次出行都准备一份新的详细地图;你只需要一条记录 "走了平常的路线"。我们的日志策略就是应用这一逻辑。与其每次都存储完整的 "地图"(脚本文本),不如只存储一次,然后在每次执行时简单记录一个轻量级的引用 ------ 哈希值。
这种架构基于 Elastic Stack 中的三个支柱:
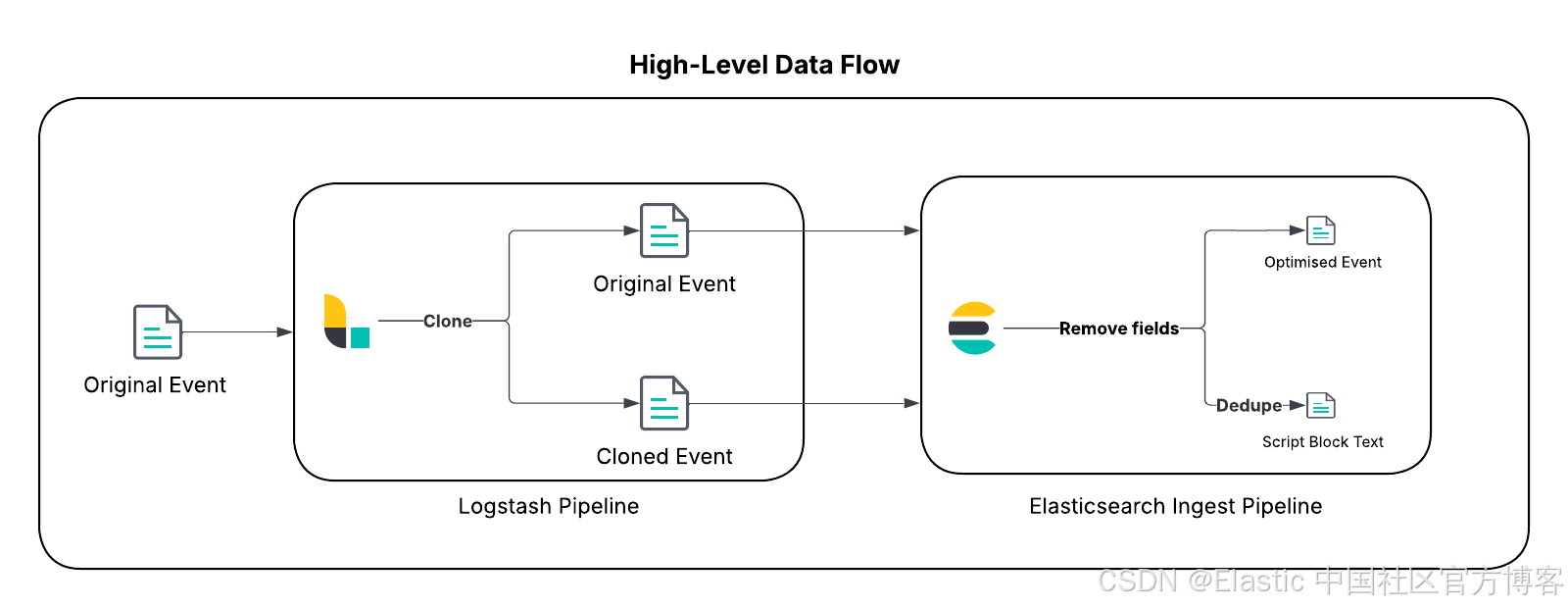
- 事件克隆(Logstash):作为一个多功能的服务端数据处理管道,Logstash 非常适合复杂路由。我们将使用其 clone 过滤器为每个 PowerShell 脚本块日志事件创建一个传输中的副本。
- 通过哈希去重(ingest pipeline) :Elasticsearch ingest pipeline 会同时处理原始事件和克隆事件。它会生成脚本文本的唯一哈希值,作为去重的关键。该管道会从原始事件中剥离庞大的脚本文本,将克隆事件转换为一个最小化的 "查找" 文档,仅包含脚本文本、安全检测规则所需的相关元数据及其哈希值。"查找" 文档被存储在单分片查找索引中,重复内容会被自动覆盖。
- 按需丰富(ES|QL):ES|QL 是一个强大的管道式查询引擎,支持原生连接。在查询时,分析人员可以使用 LOOKUP JOIN 命令,将精简的事件元数据(如时间戳、主机和用户)与查找索引中的完整脚本文本无缝合并,从而按需获取完整上下文。
这种方法代表了从传统的 "在摄取时反规范化" 模式向更灵活、更具成本效益的"在查询时丰富"范式的战略转变,展示了全新 ES|QL 查询引擎的强大能力。
实施展示
本节提供技术细节来演示这一数据减少策略。
重要提示
在将其应用到生产环境之前,请彻底审查本文中列出的前提条件和实施步骤,根据你的需求进行定制,并遵循最佳实践在非生产环境中进行测试和评估,以确保该解决方案适合你的环境和数据。为方便采用和测试这一模式,所有必要的配置文件和代码片段都已在这个公共 GitHub 仓库中提供。
前提条件
在开始之前,请确保你的环境满足以下要求:
-
Elastic Stack 版本 8.18/9.0 及以上 :此模式使用 ES|QL 中的 LOOKUP JOIN 命令,该功能在 8.19/9.1 中已正式发布。这让你可以使用功能强大的新连接能力。查找索引支持这一强大的查询时操作,并且必须是单分片的。
-
启用 PowerShell 日志 :你必须在 Windows 环境中启用 PowerShell 脚本块日志(事件 ID 4104)。通常可通过组策略在 "管理模板 > Windows 组件 > Windows PowerShell > 启用 PowerShell 脚本块日志"(Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows PowerShell > Turn on PowerShell Script Block Logging)中进行配置。参考 Microsoft 文档获取更多信息。
-
Elastic Windows 集成 :此解决方案针对官方 Elastic Windows 集成进行了优化。虽然该技术可适配旧版本集成或 Winlogbeat,但建议使用最新版 Elastic Windows 集成以获得最佳效果。本指南将使用 powershell.file.script_block_hash 字段来设置去重的 document_id。
-
Logstash :此解决方案将使用 Logstash 在优化之前复制相关事件。如果你尚未部署,请按照文档进行设置。
-
了解你的数据:此解决方案重点处理未因 Windows 事件跟踪(ETW)事件大小限制而被分段的 PowerShell 脚本块。请在有意义的时间范围内审查你的数据及数据访问模式,以了解在你的环境中可能带来的收益,并据此规划数据量。
使用以下 Kibana Query Language (KQL) 示例搜索来了解你环境中目标数据的数量:
event.module: "windows" and event.dataset: "windows.powershell_operational" and event.code: 4104 and powershell.total: 1
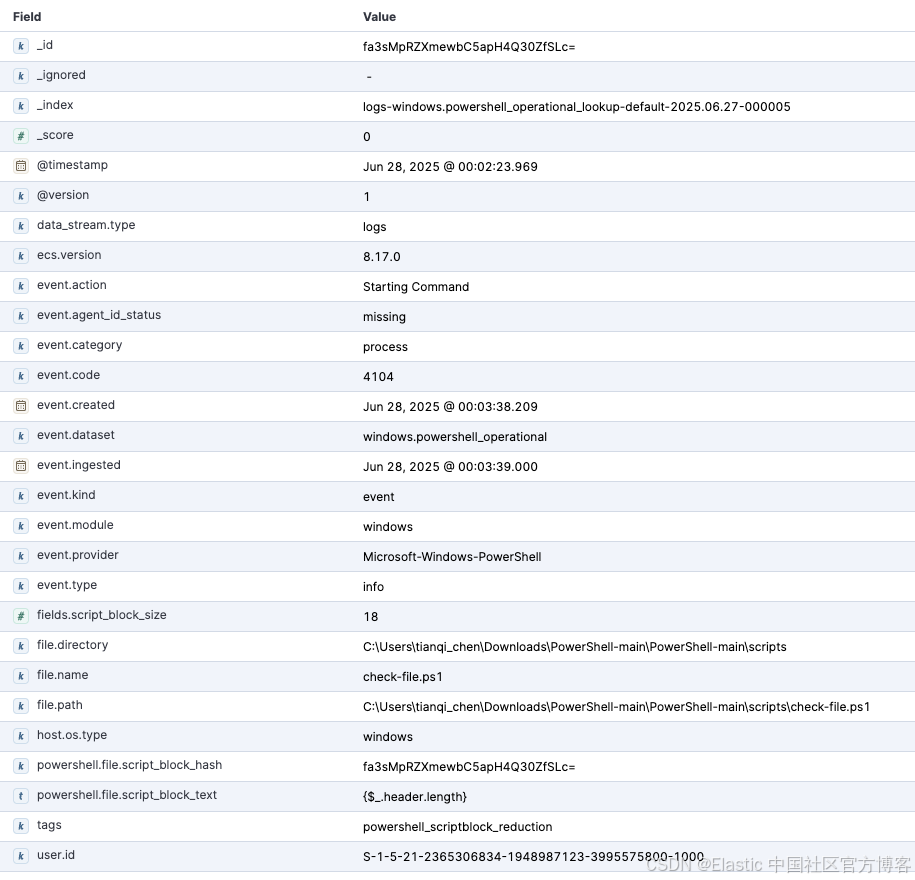
可选:创建脚本块哈希
首先,确认你的 logs-windows.powershell_operational-* 数据流中是否已有 powershell.file.script_block_hash 字段且已填充。1.45.0 之前的 Windows 集成可能需要你手动生成该字段。如果字段缺失,请升级你的集成或在 logs-windows.powershell_operational@custom ingest pipeline 中复制该过程。
步骤 1:设置查找索引
第一步是为查找索引创建模板。这包括一个具有最小映射的组件模板,以及一个将关键 index.mode 设置为 lookup 的索引模板。从一开始就使用别名和索引生命周期管理 (ILM) 策略,可以在后续自动管理大小。
使用以下请求设置具有最小映射的组件模板(见下方截图):
PUT _component_template/logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup@package
其内容来自 GitHub 仓库中的此工件或下方代码块。
PUT _component_template/logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup@package
{
"template": {
"settings": {
"index": {
"lifecycle": {
"name": "logs-powershell_script_block"
},
"default_pipeline": "logs-windows.powershell_operational-3.0.0",
"mapping": {
"total_fields": {
"limit": "1000"
}
},
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"powershell_script_analyzer": {
"pattern": "[\\W&&[^-]]+",
"type": "pattern"
}
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"@timestamp": {
"ignore_malformed": false,
"type": "date"
},
"ecs": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"version": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"error": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"code": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"event": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"sequence": {
"type": "long"
},
"ingested": {
"type": "date"
},
"code": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"provider": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"created": {
"type": "date"
},
"kind": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"module": {
"type": "constant_keyword",
"value": "windows"
},
"action": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"category": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"type": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"dataset": {
"type": "constant_keyword",
"value": "windows.powershell_operational"
},
"outcome": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"file": {
"properties": {
"directory": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
},
"path": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword",
"fields": {
"text": {
"type": "match_only_text"
}
}
}
}
},
"host": {
"properties": {
"os": {
"properties": {
"type": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
},
"message": {
"type": "match_only_text"
},
"powershell": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"file": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"script_block_text": {
"analyzer": "powershell_script_analyzer",
"type": "text"
},
"script_block_hash": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
},
"user": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"ignore_above": 1024,
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}设置引用上述组件模板的索引模板,并确保 index.mode 设置为 lookup,使用以下请求:
PUT _index_template/logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup 其内容来自 GitHub 仓库中的此工件或下方代码块。
PUT _index_template/logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup
{
"index_patterns": [
"logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-*"
],
"template": {
"settings": {
"index": {
"mode": "lookup"
}
}
},
"composed_of": [
"logs@mappings",
"logs@settings",
"logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup@package",
"logs@custom",
"ecs@mappings",
".fleet_globals-1",
".fleet_agent_id_verification-1",
"logs-windows.powershell_operational@custom"
],
"priority": 300,
"ignore_missing_component_templates": [
"logs@custom",
"logs-windows.powershell_operational@custom"
]
}使用以下请求设置上述组件模板中引用的 ILM:
PUT _ilm/policy/logs-powershell_script_block 其内容来自 GitHub 仓库中的此工件或下方代码块。
PUT _ilm/policy/logs-powershell_script_block
{
"policy": {
"phases": {
"hot": {
"min_age": "0ms",
"actions": {
"rollover": {
"min_primary_shard_size": "1gb",
"max_age": "90d",
"max_docs": 200000000,
"max_primary_shard_size": "30gb"
},
"set_priority": {
"priority": 100
}
}
},
"delete": {
"min_age": "30d",
"actions": {
"delete": {}
}
}
},
"_meta": {
"description": "sample policy for the logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup index template"
}
}
}可选
使用别名初始化查找索引,并配置 ILM 策略以自动执行 rollover。
注意:我们的示例组件模板包含一个自定义 ILM 策略:logs-powershell_script_block。
PUT %3Clogs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default2-%7Bnow%2Fd%7D-000001%3E
{
"aliases": {
"logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default": {
"is_write_index": true
}
},
"settings": {
"index.lifecycle.rollover_alias": "logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default"
}
}专家见解:在正常使用中将查找索引从 Kibana 中排除
你可能希望排除查找索引,以确保查找文档只在使用 ES|QL LOOKUP JOIN 时可见,从而避免其他分析被这些文档干扰。在索引模式中设置带有 ,-lookup 的数据视图,例如
logs-windows.powershell*,-*lookup*,以在 Classic Discovery 模式下将其从日常 Kibana 体验中排除。在其他场景下使用 ES|QL 时,可以通过WHERE tags!="powershell_scriptblock_reduction"来排除该标签。
步骤 2:在 Logstash 中处理事件
接下来,在 Logstash 管道中拦截 PowerShell 脚本块日志(事件 ID 4104),并使用 clone 过滤器创建副本。
在这个过滤器块中,我们仅针对未被分段的相关 PowerShell 脚本块事件。clone 过滤器会创建一个副本,并为其添加标签 powershell_scriptblock_reduction。原始事件会标记 fields.duplicated: true 以便后续处理。我们还会更新数据流命名空间,将其路由到新的数据流(可选)。
filter {
if ([event][module] == "powershell" or [event][provider] == "Microsoft-Windows-PowerShell") and [event][code] == "4104" and [winlog][event_data][MessageTotal] == "1" {
clone {
clones => ["powershell_scriptblock_reduction"]
ecs_compatibility => v8
}
## Indicate the event has been cloned
if !("powershell_scriptblock_reduction" in [tags]) {
mutate {
## Send data to a custom datastream via renaming the namespace for demonstration
update => { "[data_stream][namespace]" => "default_reduced" }
add_field => {
"[fields][duplicated]" => true
}
}
}
}
}专家见解:了解你的源数据
你可能会注意到,一个较大的 PowerShell 脚本可能会生成多个 4104 事件。这是源数据的预期行为,它会将大脚本分段以适应事件大小限制,甚至会随机化分段大小以阻碍规避技术(参见代码)。我们的哈希技术会跳过这些随机分段,以减少查找索引中可能来自同一脚本的数据增长。
步骤 3:路由到不同目标
在事件被克隆并打上标签后,下面的 Logstash 输出配置会将它们路由到不同的目标。原始事件进入标准数据流,而克隆事件会被发送到专用的查找索引。
该配置使用了一个简单的条件判断:
-
如果存在
powershell_scriptblock_reduction标签,则该事件是要发送到查找索引的克隆事件。我们会显式命名此索引(logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default),并使用 index 动作(查找索引不是数据流,并且只能是单分片)。 -
否则,它就是原始事件,会像往常一样发送到它的数据流(在此示例中是
logs-windows.powershell_operational-default_reduced)。output {
if "powershell_scriptblock_reduction" in [tags]{
elasticsearch {
cloud_id => "..."
index => "logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default"
action => "index"
api_key => "{ES_API}" ssl_enabled => true } } else { elasticsearch { cloud_id => "..." data_stream => "true" api_key => "{ES_API}"
ssl_enabled => true
}
}
}
专家见解:index 动作是删除后添加的操作
你可能会注意到查找索引的大小先增长然后缩小。这是因为 index 动作实际上是删除后添加的操作,而不是底层的原地更新。
步骤 4:使用 ingest pipelines 处理
基于 Elastic 集成的 ingest 处理流程,两个事件都会通过一个自定义 ingest pipeline,该管道使用条件逻辑,根据 Logstash 中添加的标记应用不同的处理器。
下表详细说明了处理路径以便更清晰理解。
|--------------------|-----------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 事件路径 | 标记识别 | 关键处理器应用情况 | 生成的文档 |
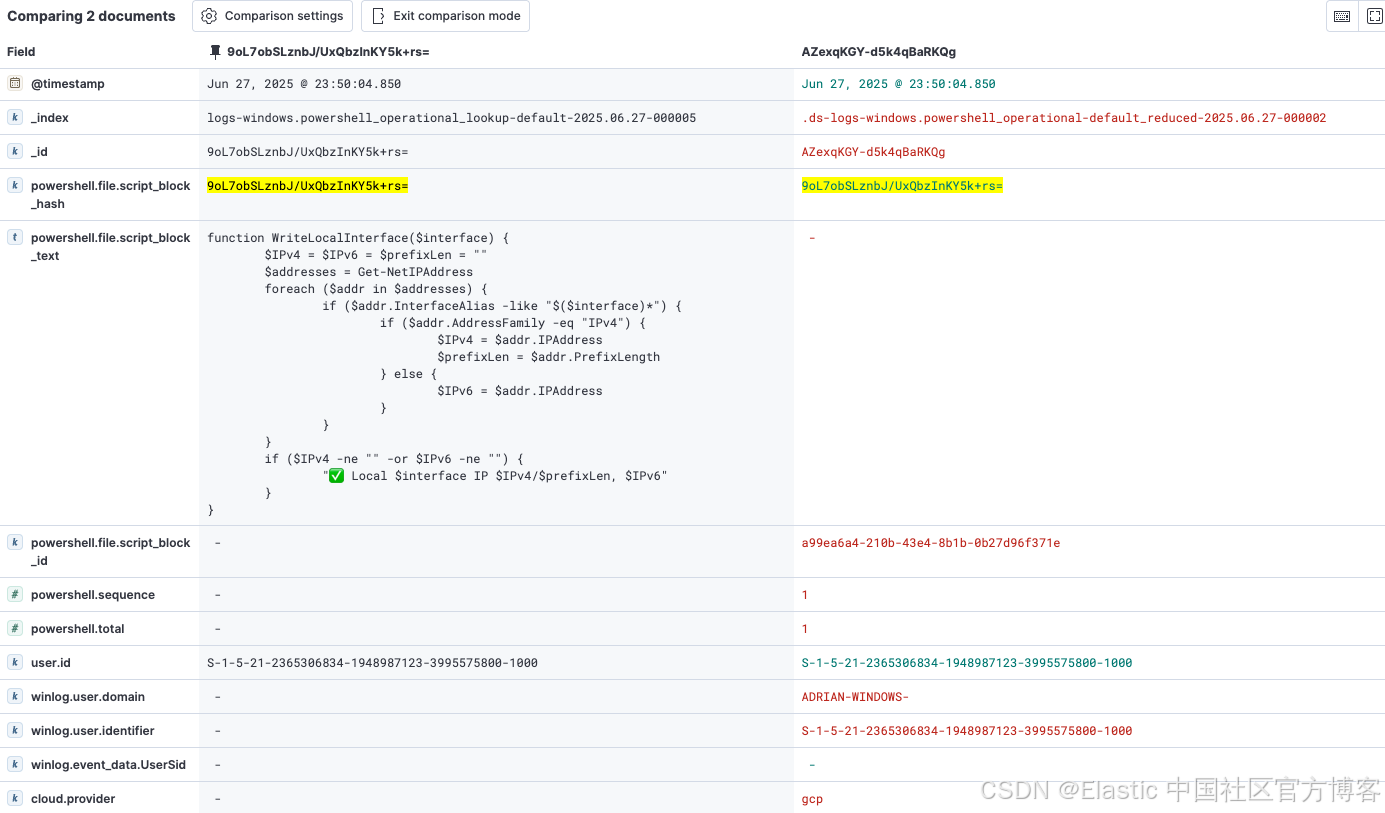
| Original event | fields.duplicated == true | 1. 删除 (message 字段) 2. 删除 (powershell.file.script_block_text 字段) | 一个优化后的事件,包含所有原始元数据(主机、用户等),但不包含庞大的脚本文本。 |
| Cloned event | tags contain powershell_scriptblock_reduction | 1. 脚本(保留 host.os.type 字段以支持检测规则匹配) 2. 脚本(保留 user.id 字段以支持检测规则匹配或过滤) 3. 脚本(保留 file.name、file.path 和 file.directory 字段以支持检测规则匹配或过滤) 4. 删除(所有其他非必要的元数据) 5. 脚本(将 _id 设置为哈希值) | 一个最小化的 minimal lookup document,仅包含检测所需的关键元数据字段(脚本文本及其哈希),并将文档 ID 设置为哈希值以实现自动去重。 |
将 _id 设置为脚本哈希的方法在架构上更优越,在大规模下性能远超另一种方法(即对每条日志事件执行 "先搜索再插入" 的查询)。虽然在 Logstash 中克隆事件并在 ingest pipeline 中处理两次会增加一些开销,但这是为了减少存储空间而做出的刻意权衡。
使用以下请求设置 ingest pipeline:
PUT _ingest/pipeline/logs-windows.powershell_operational@custom 其内容来自 GitHub 仓库中的工件或下方代码块。
这将生成两个文档:左侧为最小化查找文档,右侧为优化后的事件文档。
{
"processors": [
{
"remove": {
"ignore_missing": true,
"field": "message",
"if": "ctx.powershell?.file?.script_block_hash!= null && ctx.fields?.duplicated!= null && (ctx.fields?.duplicated == true || ctx.fields?.duplicated == 'true')",
"description": "Remove message for lean event"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"ignore_missing": true,
"field": "powershell.file.script_block_text",
"if": "ctx.powershell?.file?.script_block_hash!= null && ctx.fields?.duplicated!= null && (ctx.fields?.duplicated == true || ctx.fields?.duplicated == 'true')",
"description": "Remove script_block_text for lean event"
}
},
{
"script": {
"if": "ctx.tags!= null && ctx.tags.contains('powershell_scriptblock_reduction') && (ctx.host?.os?.type != null)",
"source": """
ctx._temp = ctx._temp != null ? ctx._temp : new HashMap();
if (ctx.host?.os?.type != null) {
ctx._temp.os_type = ctx.host.os.type;
ctx.remove('host');
ctx.host = [:]; ctx.host.os = [:];
ctx.host.os.type = ctx._temp.os_type;
ctx.remove('_temp');
} """,
"description": "Example 1 to retain a field for the lookup index - host.os.type"
}
},
{
"script": {
"if": "ctx.tags!= null && ctx.tags.contains('powershell_scriptblock_reduction') && (ctx.user?.id != null)",
"source": """
if (ctx.user instanceof Map) {
def userFieldsToKeep = ['id']; ctx.user.keySet().removeIf(key -> !userFieldsToKeep.contains(key));
}""",
"description": "Example 2 to retain a field for the lookup index - user.id"
}
},
{
"script": {
"if": "ctx.tags!= null && ctx.tags.contains('powershell_scriptblock_reduction') && (ctx.file?.name != null || ctx.file?.path != null || ctx.file?.directory != null)",
"source": """
if (ctx.file instanceof Map) {
def fileFieldsToKeep = ['name', 'path', 'directory']; ctx.file.keySet().removeIf(key -> !fileFieldsToKeep.contains(key));
}""",
"description": "Retain field for the lookup index - file.name, file,path, file.directory"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"ignore_missing": true,
"field": [
"winlog",
"log",
"agent",
"powershell.sequence",
"powershell.total",
"cloud",
"elastic_agent",
"data_stream",
"message",
"_temp",
"input",
"powershell.file.script_block_id"
],
"if": "ctx.tags!= null && ctx.tags.contains('powershell_scriptblock_reduction')",
"description": "Remove unnecessary fields from the lookup index"
}
},
{
"script": {
"if": "ctx.tags!= null && ctx.tags.contains('powershell_scriptblock_reduction') && ctx.powershell?.file?.script_block_hash!= null",
"source": "ctx._id = ctx.powershell.file.script_block_hash",
"description": "Specific the id for the unique script_block_text based on hash"
}
},
{
"remove": {
"ignore_missing": true,
"field": "fields.duplicated",
"if": "ctx.fields?.duplicated!= null",
"description": "Remove metadata used to indicate the original event"
}
}
]
}专家见解:Logstash 处理
你可能知道 Logstash 也能执行与 ingest pipeline 相同的处理。该方案使用 @custom ingest pipeline 自动处理 PowerShell 操作日志,并继承了 Windows 集成中的哈希操作及其他数据处理。如果你想用 Logstash 来完成这些处理,务必确保哈希过程保持一致,这样数据才能匹配(包括哈希算法、输出格式等)。
步骤 5:用 ES|QL 重建上下文
实施后,你的主数据流包含精简事件,查找索引保存唯一的未分段 PowerShell 脚本集。最后一步是在分析时将这些上下文合并,这正是 ES|QL LOOKUP JOIN 的优势所在。
分析人员现在可以运行简单的管道查询,调查 PowerShell 活动,顺畅地将精简事件与查找索引中的完整脚本文本结合起来。
我们分解一下查询的操作内容:
-
FROM logs-windows.powershell_operational-default_reduced*:从主精简事件数据开始查询。
-
LOOKUP JOIN... ON powershell.file.script_block_hash:这是关键操作。对每个事件,它会在查找索引中寻找 _id(即哈希值)与事件的 powershell.file.script_block_hash 匹配的文档。
-
找到匹配时,查找文档中的所有字段------最重要的是 powershell.file.script_block_text------都会被加入结果中。
-
来自数据流的重复元数据字段会被重命名,防止被覆盖,然后再重命名回原名。
FROM logs-windows.powershell_operational-default_reduced*
| WHERE powershell.file.script_block_hash IS NOT NULL
| RENAME @timestamp AS original_timestamp, user.id AS original_user.id, file.name AS original_file.name, file.path AS original_file.path, file.directory AS original_file.directory
| LOOKUP JOIN logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default-2025.06.26-000004 ON powershell.file.script_block_hash
| RENAME @timestamp AS lookup_timestamp, original_timestamp AS @timestamp, original_user.id AS user.id, original_file.name AS file.name, original_file.path AS file.path, original_file.directory AS file.directory
以下是示例查询结果:
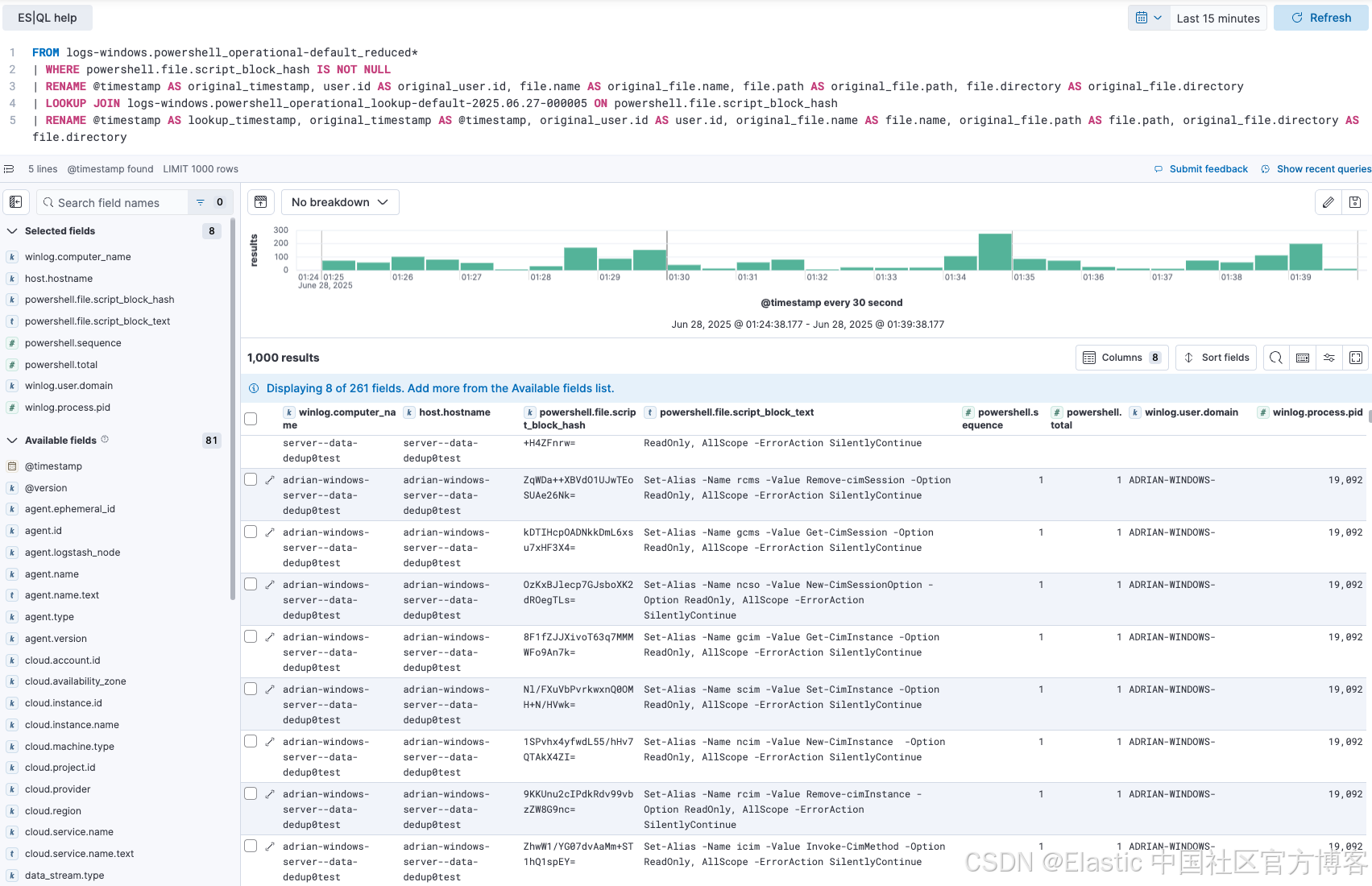
这个功能对安全分析师和站点可靠性工程师(SRE)都非常重要。SRE 在排查系统时,可以看到事件发生时执行的精确脚本。安全分析师在调查检测警报时,可以立即获取完整的、去混淆的恶意脚本进行取证分析,就像以前一样,但现在使用的是更具成本效益的数据存储。
该设计的一个特别强大之处是查找索引的命名约定:logs-windows.powershell_operational_lookup-default。Elastic Security 的预置检测规则设计为针对特定索引模式运行,比如 logs-windows.powershell*。由于我们的查找索引名匹配该模式,检测规则会自动扫描它。这意味着检测 PowerShell 脚本中可疑内容的规则仍能完美工作,分析完整且去重的脚本文本集合。这个巧妙的设计保证了大幅减少数据量的同时,不会为自动安全分析造成盲点。
数据减少常见的担忧是会产生盲点,但该架构巧妙地避免了这一风险。
该设计对分析师的工作流程有关键影响。查找索引中文档的时间戳反映了脚本最后一次出现的时间。如果检测规则对查找索引中的恶意内容发出警报,分析师就得到了"是什么"(脚本文本)。下一步是利用警报中的 powershell.file.script_block_hash 跳转到主数据流 ...-default_reduced。在那里,他们可以找到该脚本的每次执行记录,附带正确的原始时间戳、主机和用户上下文,实现完整的取证调查。这种两步流程 ------ 检测唯一内容并调查所有执行情况 ------ 非常强大。
智能日志的初窥
这种 "哈希、存储、连接" 模式展示了一种强大的方法,打破了安全可见性与数据成本之间的僵局。它应被视为适用于任何包含庞大或重复数据的高流量日志源的可复用蓝图,比如 API 负载或应用堆栈跟踪。
对于希望将数据优化提升到新高度的团队,这种技术可以与其他 Elastic Stack 功能叠加使用。在利用此方法去除高流量重复内容后,你可以在主数据流上启用 Elasticsearch logsdb index mode(该模式在 9.0 及以上集群默认启用)。logsdb index mode 是一种专门的存储模式,通过先进的压缩和数据结构化技术进一步减少结构化日志数据的磁盘占用。将内容感知的去重与 logsdb index mode 及合理的 ILM 策略结合,架构师能够构建一个复杂的多层数据管理策略,平衡现代数据驱动企业的成本、性能和可访问性。
今天就迈出第一步
审查并理解你的数据,判断该解决方案是否适用于你的环境,同时探索 Elastic 提供的强大数据存储和分析选项,如 ES|QL 查询引擎、时间序列数据流(TSDS)和logsdb index mode。
本文中描述的任何功能或特性的发布和时间安排均由 Elastic 全权决定。当前不可用的功能或特性可能无法按时发布或根本不会发布。
原文:Hash, store, join: A modern solution to log deduplication with ES|QL LOOKUP JOIN | Elastic Blog