目录
[如何修改 state](#如何修改 state)
[定义 Mutations](#定义 Mutations)
[提交 Mutations](#提交 Mutations)
[使用 Vuex 在组件内提交 Mutations](#使用 Vuex 在组件内提交 Mutations)
[为什么需要 Actions?](#为什么需要 Actions?)
[定义 Actions](#定义 Actions)
[分发 Actions](#分发 Actions)
[在组件中使用 Actions](#在组件中使用 Actions)
[Actions 的返回值](#Actions 的返回值)
不能直接修改state
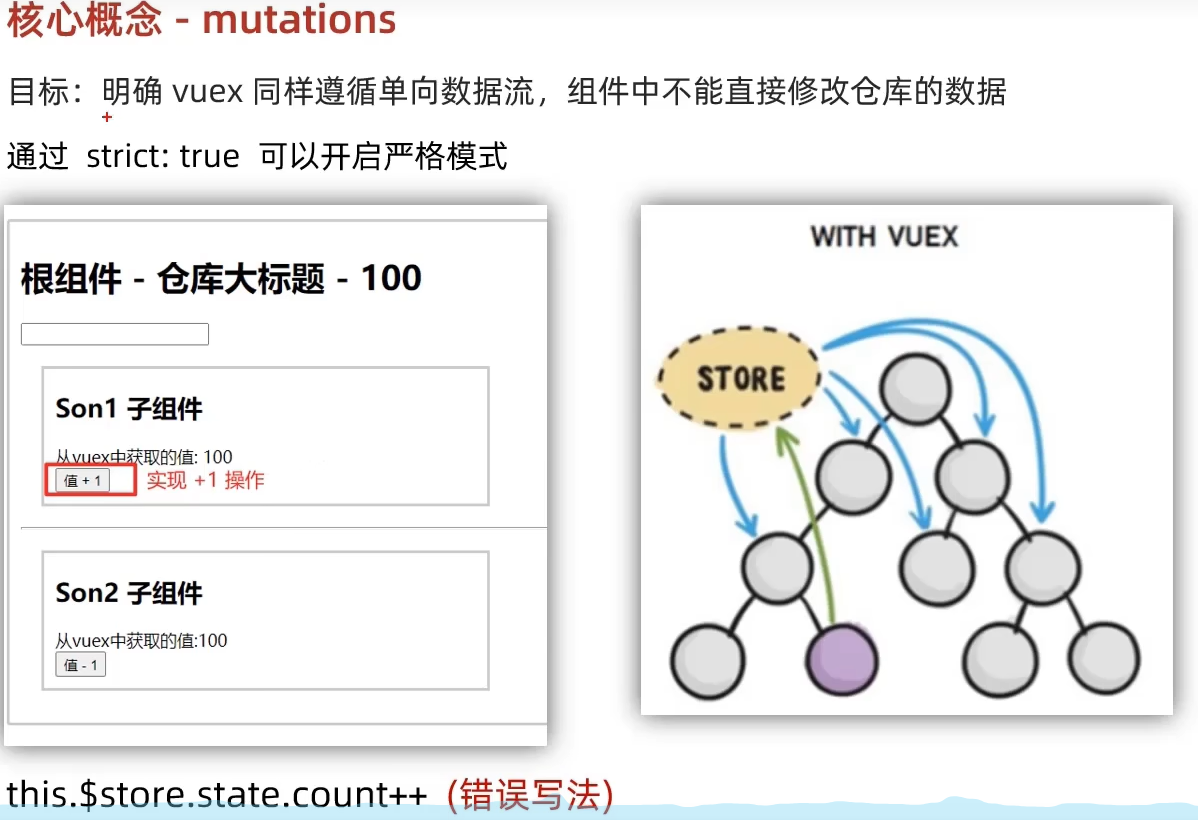
state 对象不能直接修改。这是因为 Vuex 设计的核心原则之一是状态的单一数据源和状态的不可变性(immutability)。Vuex 的 state 是响应式的,这意味着当 state 发生变化时,Vue 能够检测到这些变化并更新视图。然而,为了确保状态的变化是可追踪和预测的,Vuex 强制所有的状态变更都必须通过明确的提交(commit)来完成。
不允许直接修改的原因
-
响应式机制 :如果直接修改
state,Vue 的响应式系统可能无法检测到这些变化,导致视图不会正确更新。 -
调试和开发工具支持 :Vuex 提供了时间旅行和状态快照等功能,这些功能依赖于对状态变更的明确记录。如果可以随意修改
state,那么调试将会变得非常困难。 -
维护性和可读性:通过定义明确的 mutation 来改变状态,可以使代码更加清晰、易于理解和维护。
为了让直接修改 Vuex 的 state 报错,你可以利用 Vue 和 Vuex 提供的严格模式(strict mode)。在严格模式下,任何不在 mutation 函数中进行的 state 修改都会抛出错误。这有助于确保所有的状态变更都是通过明确的提交来完成的,从而增强应用的可维护性和调试能力。
如何启用严格模式
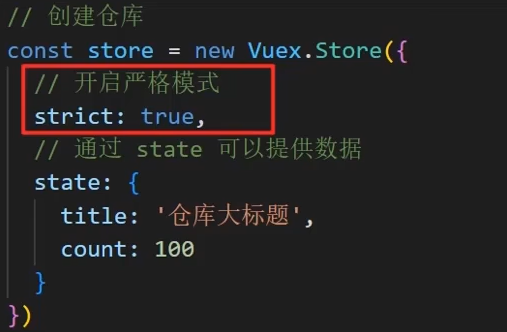
在创建 Vuex store 时,可以通过设置 strict: true 来启用严格模式:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
// your state
},
mutations: {
// your mutations
},
strict: true // 启用严格模式
})注意事项
-
开发环境:严格模式会对性能有轻微影响,因为它会在每次状态变更时进行额外的检查。因此,建议只在开发环境中启用严格模式,在生产环境中应将其关闭以避免不必要的性能开销。
-
生产环境禁用:通常情况下,你会根据环境变量来决定是否启用严格模式。例如,可以这样做:
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { // your state }, mutations: { // your mutations }, strict: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' // 根据环境变量判断 })
通过这种方式,你可以在开发过程中捕获所有对 Vuex 状态的非法直接修改,帮助你更好地遵循 Vuex 的最佳实践,即所有的状态变更都应该通过 mutation 进行。这不仅提高了代码的可维护性,也使得调试变得更加容易。
如何修改 state
Mutations
为了修改 Vuex 中的 state,你需要使用 mutations。Mutations 是唯一能够改变 state 的方式,并且它们必须是同步函数。这意味着所有状态的变更都必须通过 mutations 来进行。这样做的好处是可以集中管理和追踪所有的状态变化,有助于调试和维护。以下是一个简单的例子:
// 在 store 中定义 mutation
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
// 变更状态
state.count++
}
}
})
// 在组件中提交 mutation
this.$store.commit('increment')基本概念
-
同步性: Mutations 必须是同步函数。这意味着当你调用一个 mutation handler,这个调用完成后,状态应该已经被更新了。这使得 Vuex 能够记录每一次的状态变更,并允许开发者使用 devtools 进行时间旅行调试(time travel debugging)。
-
Payload: 你可以向 mutations 提交额外的参数,这些参数被称为 payload(载荷)。这允许你传递需要的数据到 mutation 函数中。
-
提交风格: 可以使用两种方式提交 mutations:普通风格和对象风格。
定义 Mutations
在 Vuex store 中定义 mutations:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
// 修改状态
state.count++
},
decrement(state, payload) {
// 使用载荷来修改状态
state.count -= payload.amount
}
}
})在这个例子中,我们定义了两个 mutations: increment 和 decrement。increment 不接受任何参数,而 decrement 接受一个包含 amount 属性的对象作为其载荷。
提交 Mutations
可以通过 store.commit 方法来提交 mutations。有两种提交风格:
-
普通风格
store.commit('increment') -
对象风格
对象风格允许你在提交时同时指定 mutation 类型和载荷。
store.commit({ type: 'decrement', amount: 10 })
对于带载荷的 mutation 调用,你也可以这样写:
store.commit('decrement', { amount: 10 })使用 Vuex 在组件内提交 Mutations
在 Vue 组件内部,你可以通过 this.$store.commit 来提交 mutations,或者更推荐的方式是使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件的方法映射为 store.commit 调用。
使用 mapMutations:
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment',
'decrement'
]),
someMethod() {
this.increment()
this.decrement({ amount: 5 })
}
}
}这样做可以让组件的方法直接映射到对应的 mutations 上,使代码更加简洁。
Mutations 是 Vuex 中用于修改 state 的唯一合法途径,确保了所有状态的变化都是可预测和可追踪的。通过定义明确的 mutations 并遵循严格的提交规则,可以帮助开发者更好地管理应用的状态,提升代码的可读性和可维护性。
actions
如果你需要执行异步操作,应该使用 actions。Actions 可以包含任意异步操作,并且最终通过提交 mutation 来改变状态。
// 在 store 中定义 action
const store = new Vuex.Store({
actions: {
incrementAsync({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
}
}
})
// 在组件中分发 action
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync')通过这种方式,你可以确保所有状态的更改都是透明和可控的,这有助于保持应用的一致性和可维护性。
Actions 类似于 Mutations,但不同之处在于:
- Actions 提交的是 Mutations,而不是直接变更状态。
- Actions 可以包含任意异步操作。
简单来说,Actions 是处理业务逻辑(尤其是异步操作)的地方,而 Mutations 是唯一修改状态的地方。
为什么需要 Actions?
- 处理异步操作 :Vuex 的核心原则是 Mutations 必须是同步函数。这是为了确保状态变更的可预测性,使得 Vue Devtools 可以准确地记录每一次状态变更。如果允许在 Mutations 中执行异步操作,我们就无法确切知道状态是在何时、以何种顺序发生的改变。
- 封装复杂逻辑:Actions 允许你在提交 Mutation 之前执行复杂的业务逻辑,比如数据验证、组合多个异步请求、条件判断等。
定义 Actions
在 Vuex store 的 actions 选项中定义 Actions。每个 Action 函数接收一个名为 context 的对象作为第一个参数。这个 context 对象包含以下属性和方法:
state: 指向store.state。rootState: 指向根模块的 state(在模块化 store 中使用)。commit: 用于提交 Mutation。dispatch: 用于分发(调用)其他 Action。getters: 指向store.getters。rootGetters: 指向根模块的 getters(在模块化 store 中使用)。
通常,我们使用 ES2015 的参数解构语法来直接提取 commit(以及 state, getters 等),使代码更简洁。
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0,
userInfo: null
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.count++
},
setUserInfo(state, userInfo) {
state.userInfo = userInfo
}
},
actions: {
// 基本形式:使用 context.commit
incrementAsync(context) {
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment') // 提交 mutation
}, 1000)
},
// 使用参数解构:直接解构出 commit
incrementAsync2({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('increment')
}, 1000)
},
// 包含异步操作和复杂逻辑
fetchUserInfo({ commit, state }) {
// 可以检查当前状态,例如避免重复请求
if (state.userInfo) {
console.log('User info already exists, skipping fetch.')
return
}
// 模拟异步 API 调用
api.getUserInfo().then(userInfo => {
commit('setUserInfo', userInfo) // 成功后提交 mutation
}).catch(error => {
console.error('Failed to fetch user info:', error)
// 可以提交一个错误处理的 mutation
// commit('setError', error.message)
})
},
// 组合多个 actions (使用 dispatch)
initializeApp({ dispatch }) {
// 可以并行或串行地调用其他 actions
dispatch('fetchUserInfo')
dispatch('fetchSettings')
// ... 其他初始化逻辑
}
}
})分发 Actions
使用 store.dispatch 方法来触发(分发)Actions。与 commit 不同,dispatch 可以返回一个 Promise(如果 Action 内部返回了 Promise),这使得你可以处理异步操作的完成状态。
// 1. 基本分发
store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
// 2. 分发时携带载荷 (Payload)
store.dispatch('fetchUserInfo', { userId: 123 }) // 载荷作为第二个参数
// 在 Action 中,可以通过第二个参数接收载荷
// actions: { fetchUserInfo({ commit }, payload) { ... } }
// 3. 使用对象风格分发
store.dispatch({
type: 'fetchUserInfo',
userId: 123
})
// 4. 处理返回的 Promise
store.dispatch('fetchUserInfo').then(() => {
console.log('User info fetched successfully!')
}).catch(error => {
console.error('Fetch failed:', error)
})在组件中使用 Actions
在 Vue 组件中,可以通过 this.$store.dispatch 来分发 Actions,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数。
方法一:直接使用 this.$store.dispatch
export default {
methods: {
async handleFetchUser() {
try {
await this.$store.dispatch('fetchUserInfo')
console.log('User loaded!')
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error)
}
}
}
}方法二:使用 mapActions 辅助函数
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
// 将 this.incrementAsync() 映射为 this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync')
...mapActions([
'incrementAsync',
'fetchUserInfo'
]),
// 也可以将 action 映射到不同的方法名
...mapActions({
loadUser: 'fetchUserInfo' // 将 this.loadUser() 映射为 this.$store.dispatch('fetchUserInfo')
}),
async handleInitialize() {
// 使用映射后的方法
await this.loadUser()
// 或者
// await this.fetchUserInfo()
}
}
}Actions 的返回值
Actions 可以返回任何值,但通常返回一个 Promise,以便调用者可以知道异步操作何时完成。
actions: {
async fetchUserInfoAsync({ commit }) {
try {
const userInfo = await api.getUserInfo() // 假设 api.getUserInfo 返回 Promise
commit('setUserInfo', userInfo)
return userInfo // 返回获取到的数据
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
throw error // 重新抛出错误,让调用者处理
}
}
}
// 在组件中使用
methods: {
async loadUser() {
try {
const userInfo = await this.$store.dispatch('fetchUserInfoAsync')
console.log('Fetched user:', userInfo)
} catch (error) {
// 处理错误
}
}
}总结
- Actions 是处理异步操作和复杂业务逻辑的中心。
- Actions 通过
context.commit来提交 Mutations 以修改状态。 - 使用
store.dispatch(或this.$store.dispatch/mapActions) 来触发 Actions。 - Actions 支持载荷和对象风格的分发。
- Actions 可以返回 Promise,便于处理异步流程。
遵循 "Actions 处理逻辑,Mutations 修改状态" 的模式,是构建可维护、可调试的 Vuex 应用的关键。
写在最后.
能入手一个可以的项目. 框架是基础. 底层的js+html+css 也需要打牢.
博主也完结了 前端 基础课程 .参考 https://blog.csdn.net/chxii/category_12913839.html