三三要成为安卓糕手
一:使用include复用布局
1:需求
提出问题:想用两种不同的背景片段,红色和蓝色;只在一个xml布局中写代码,重复率太高了,能不能解耦合
include应运而生
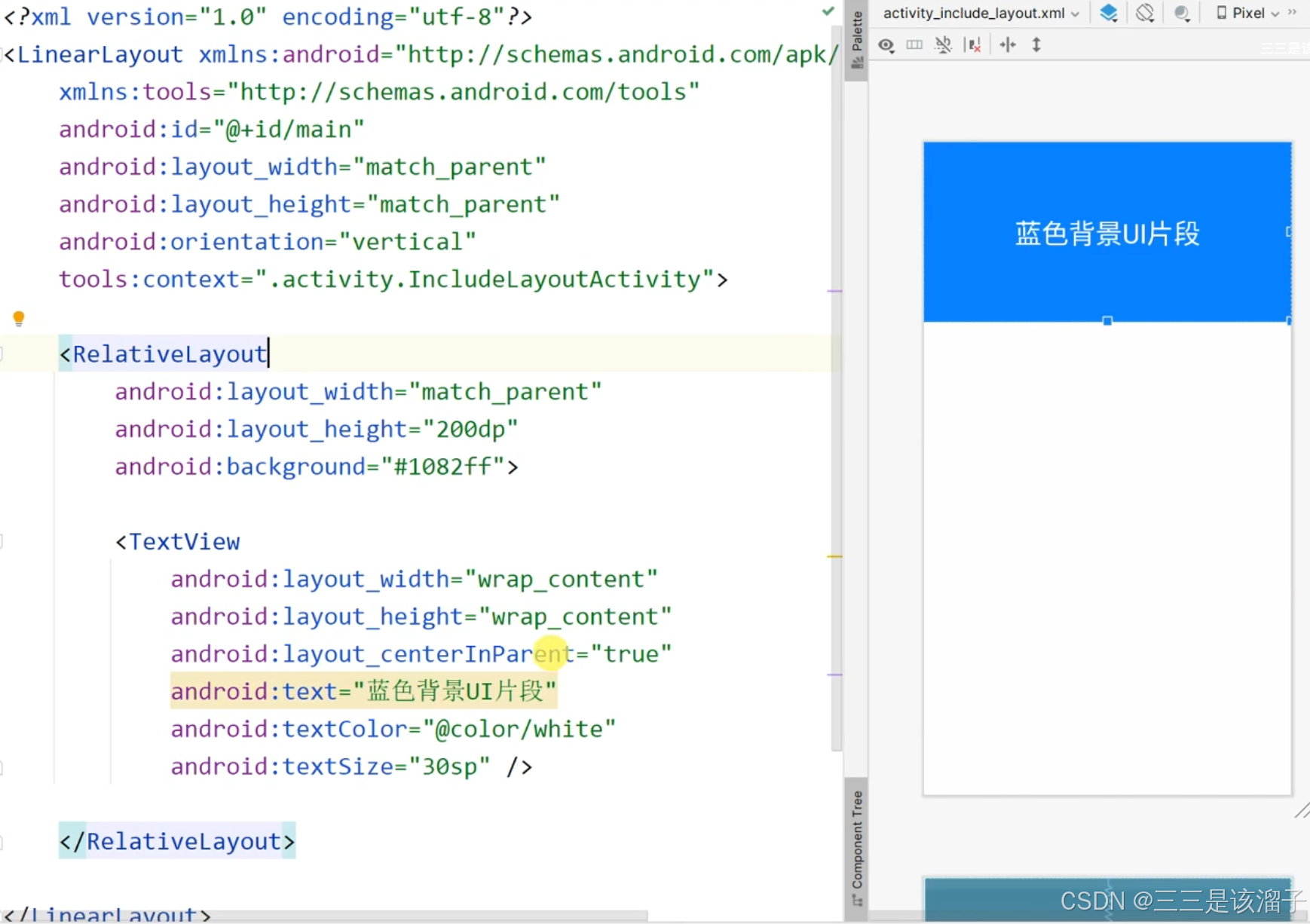
2:red和blue布局代码
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:background="#1082ff"
android:layout_height="200dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="蓝色背景UI片段"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="30sp" />
</RelativeLayout>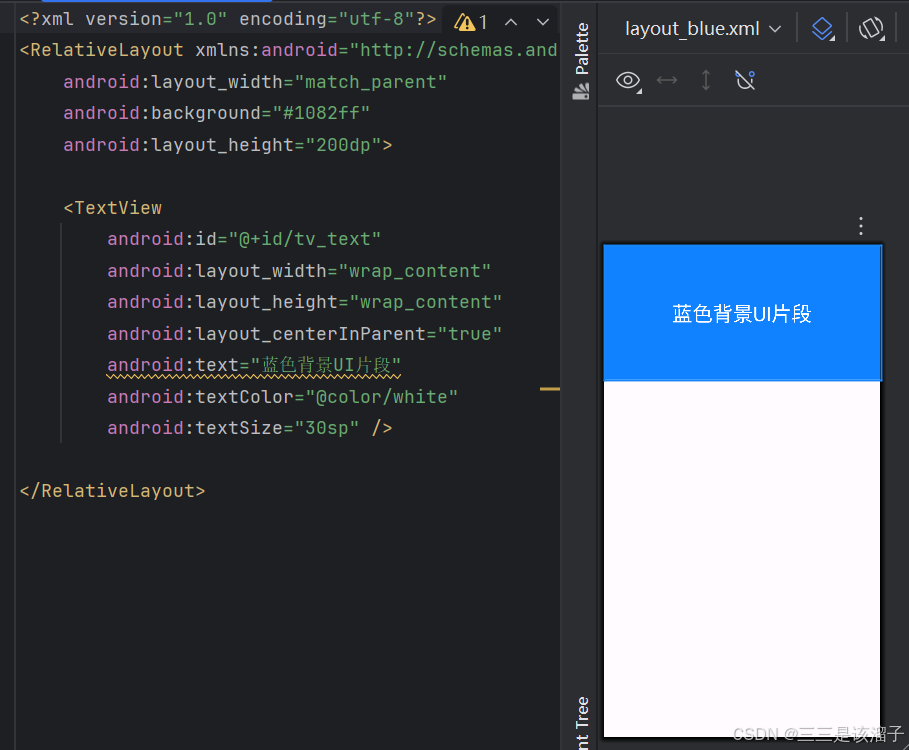
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:background="#ff0000">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="红色背景UI片段"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="30sp" />
</RelativeLayout>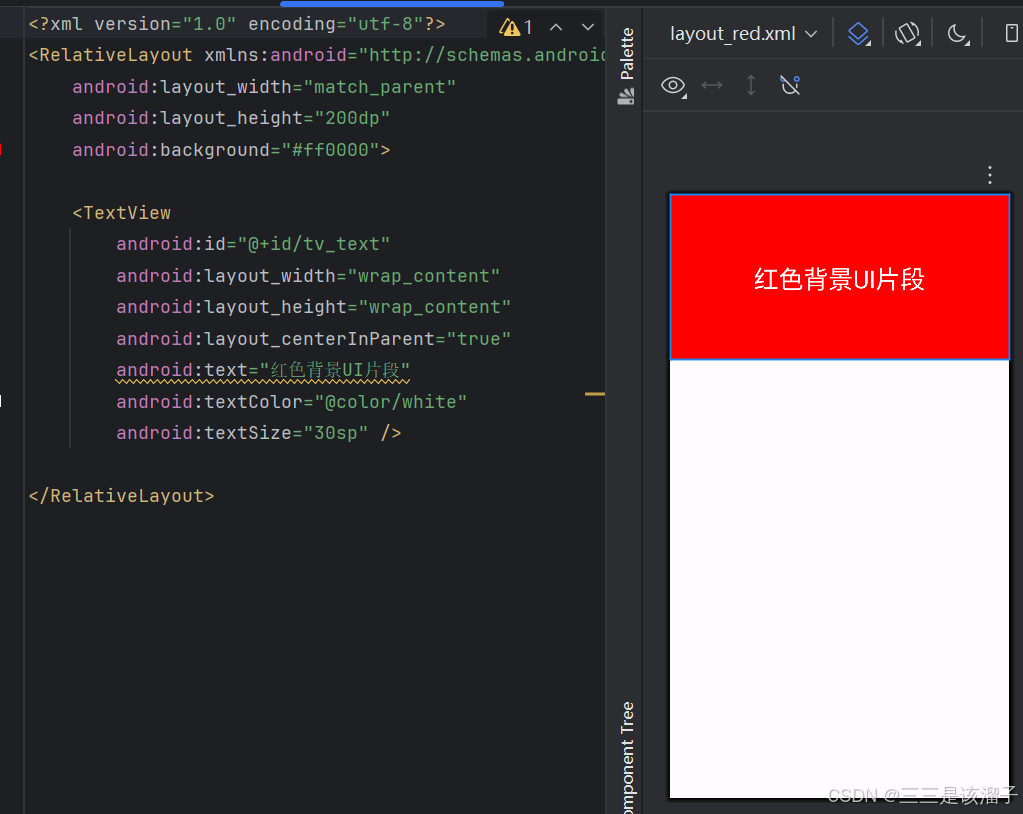
3:使用方式
我们在新的一个布局中使用蓝色背景布局和一个带有TextView控件的activity_config_changes布局;效果如下
xml
<include layout="@layout/layout_blue"/>
<include layout="@layout/activity_config_changes"/>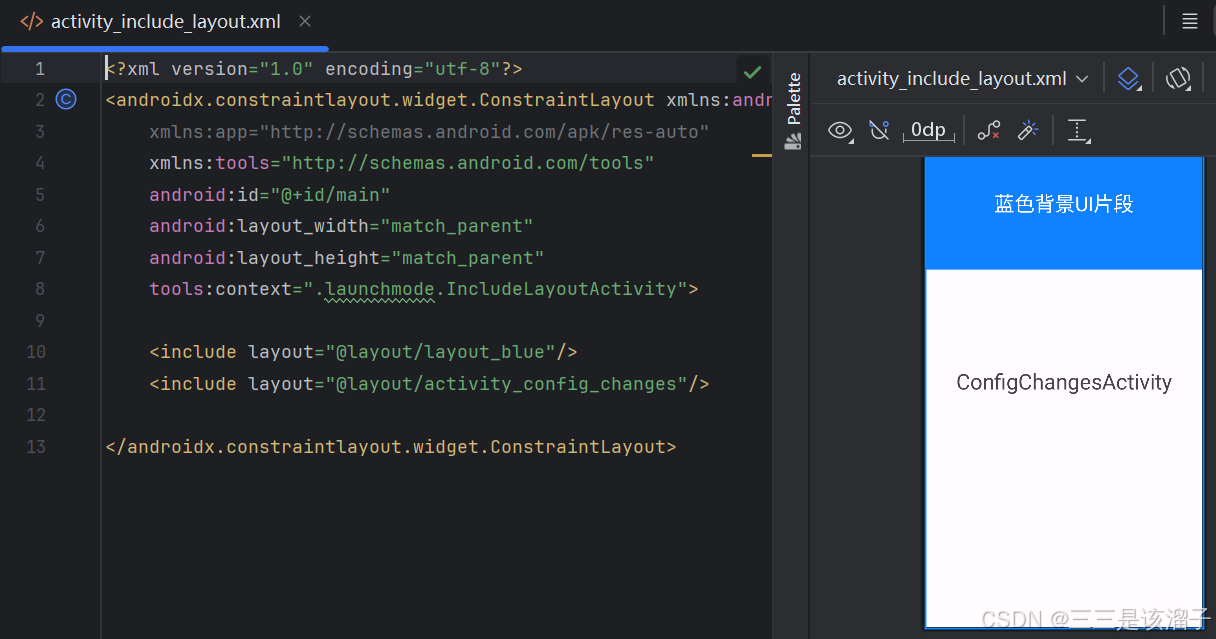
我们在Java代码里,可以通过关联的activity_include_layout布局,找到include包含布局中的控件
java
public class IncludeLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_include_layout);
findViewById(R.id.tv_label).setOnClickListener(view -> {
startActivity(new Intent
(IncludeLayoutActivity.this, ConfigChangesActivity.class));
});
}
}
上一章解决了如果xml布局中存在可以服用的代码或者布局可以用include,那么java中也出现这种情况怎么办??
一:include和Fragment两者的核心区别
| 维度 | include标签 |
Fragment |
|---|---|---|
| 性质 | 静态布局复用 | 动态组件(含UI+逻辑+生命周期) |
| 独立性 | 完全依赖宿主 | 相对独立 |
| 功能 | 仅用于UI复用 | 可包含复杂逻辑和交互 |
| 灵活性 | 编译期确定,无法动态修改 | 运行时可动态添加/替换 |
简单总结:include轻便,但是只能应付一些简单的场景;Fragment麻烦,但是扩展性更好;
在实际开发中,两者经常结合使用(例如在Fragment的布局中用include复用通用UI)
1:include 标签
本质:就是一个标签,把一个布局文件嵌入到另一个中
- 是一种组合,没有独立的生命周期和逻辑处理能力
- 一般用于拆分大型布局文件,维护性和可读性更好
2:fragment
本质:是具有自己生命周期、布局和逻辑的独立组件,可被多个Activity复用。
-
有自己的生命周期和逻辑处理能力
-
支持添加、移除、替换操作
-
支持动态页面切换和交互,比如京东,抖音需要左滑右滑切换不同界面的场景
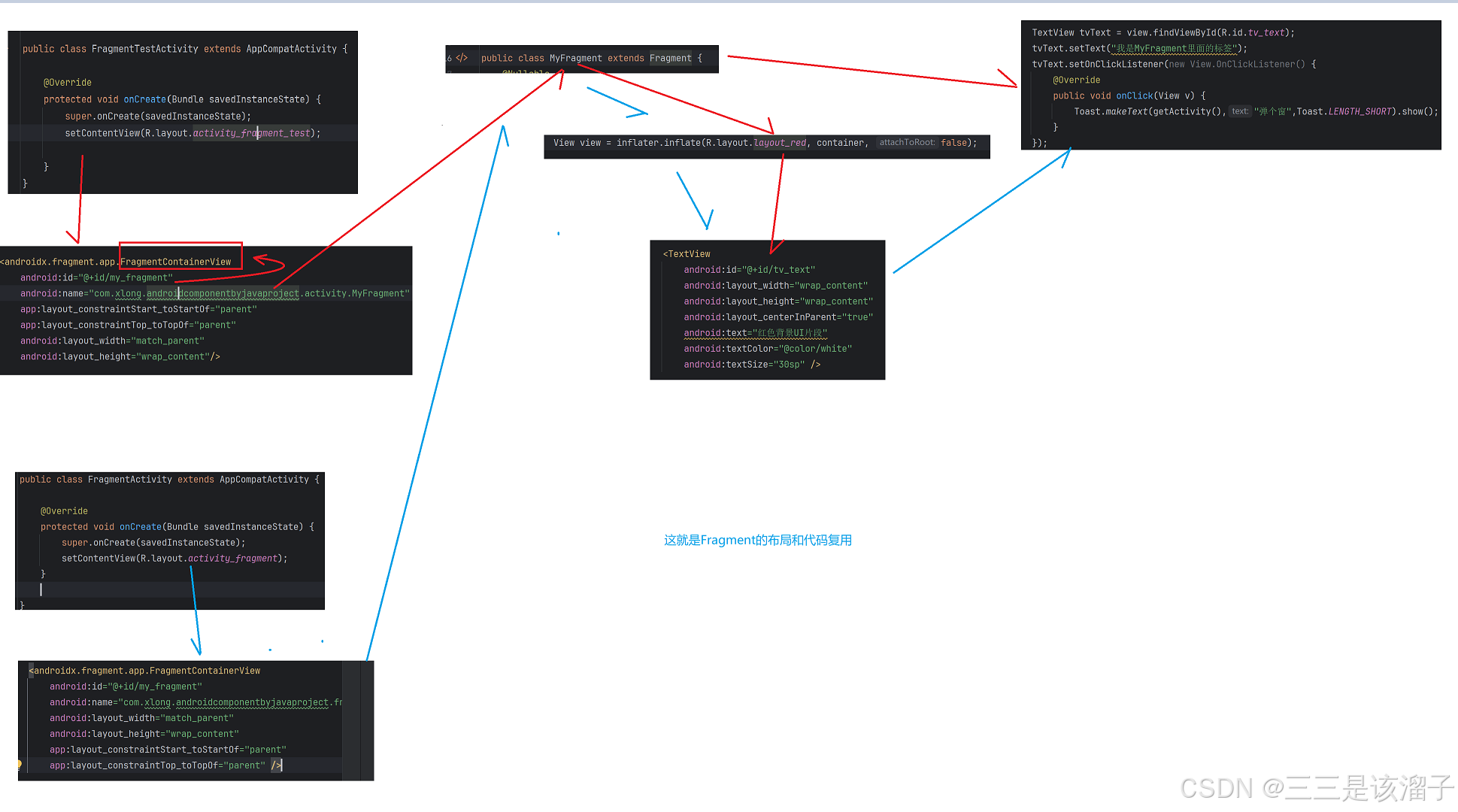
二:Fragment中关联布局和逻辑处理
1:代码
java
public class MyFragment extends Fragment {
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.layout_red, container, false);
TextView tvText = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_text);
tvText.setText("我是MyFragment里面的标签");
tvText.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getActivity(),"弹个窗",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
return view;
}
}这里就体现出来Fragment相较于include的优势了,可以处理一些代码逻辑,比如控件的点击监听,弹窗之类的
2:第三个参数几乎总是用false的原因。
解析xml中的布局,转换为可操作的view对象,之前用打气筒的比喻解析过,这里再加深一下印象,关于第二个参数和第三个参数有一个很奇妙的比喻:
第二个参数:类型是 ViewGroup ,这里填null表示仅仅是将 XML 布局文件实例化为 View 对象,但不会将该 View 对象添加到任何父容器中
为false时相当于:
- 先把 "照片" 冲洗出来(把 XML 布局转换成 View 对象)
- 参考 "相框" 的大小来调整 "照片" 尺寸(用 container 的布局参数约束 View)
- 但不马上把照片放进相框,而是先拿在手里(返回这个 View 对象)
- 后续如果需要将该视图添加到
container,可以通过其他方式(比如container.addView(view))来操作。
为true时相当于:
在冲洗照片的同时,直接把照片钉死在相框上了。
因为 Fragment 系统之后还会再试一次把照片放进相框,结果就会导致同一张照片被放两次,出现重复显示的问题。
简单说:第三个参数设为false是 "先准备好 View,等系统安排时机添加";设为true是 "立刻添加",但会和 Fragment 的自动处理冲突。
三:注意事项
1:自定义fragment继承关系
之前用到的DialogFragment也是继承自Fragment


2:使用需继承AppCompatActivity
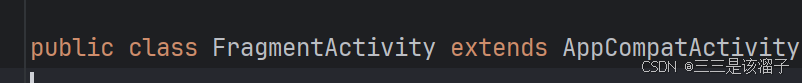
在一些老版本中直接继承Activity,是不可以嵌套Fragment的

要用Fragment必须继承FragmentActivity这个父类

3:FragmentContainerView
FrameLayout真布局,好比RelativeLayout,LinearLayout

四:Activity与Fragment关联
1:java使用代码
java
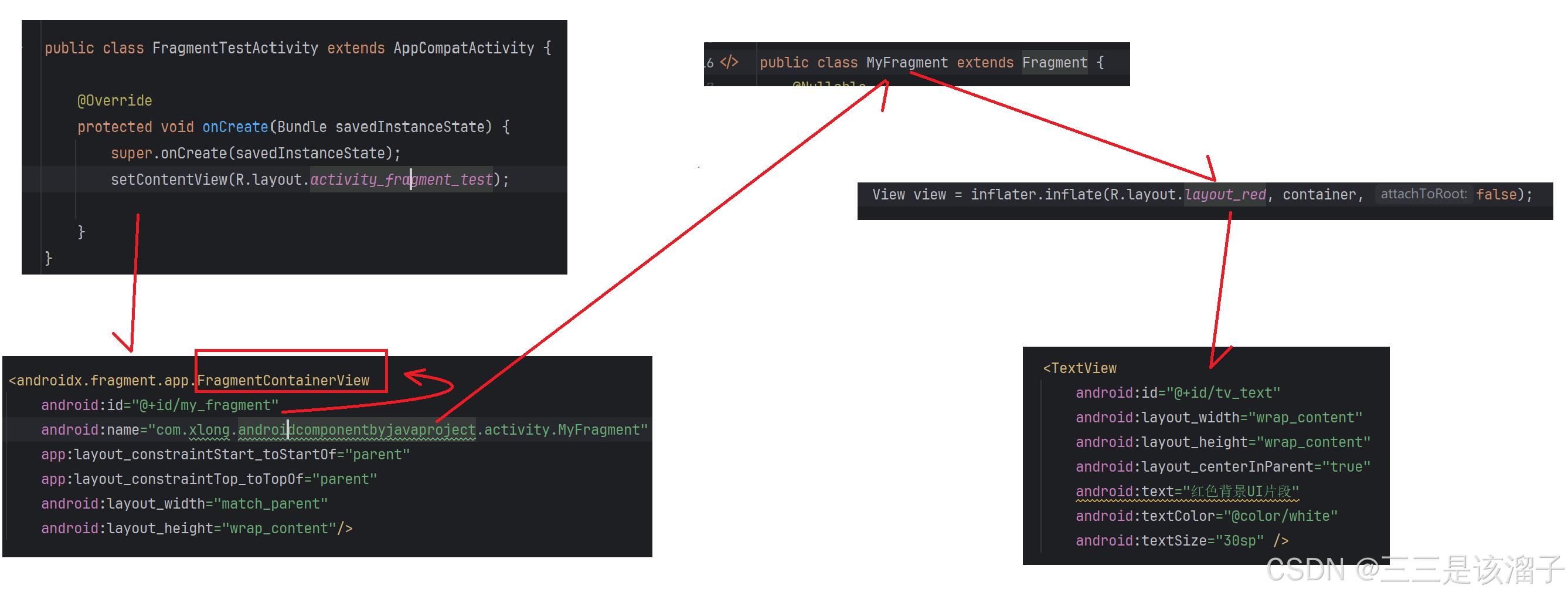
public class FragmentTestActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment_test);
findViewById(R.id.btn_next_page).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
startActivity(new Intent(FragmentTestActivity.this, FragmentActivity.class));
}
});
}
}2:FragmentContainer使用
把Fragment与当前xml做关联
xml
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/my_fragment"
android:name="com.xlong.androidcomponentbyjavaproject.fragment.MyFragment"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>注意:(非常重要)系统是通过一个id来对Fragment做管理的,这里要添加Fragment的id
name是指定我们关联到的Fragment
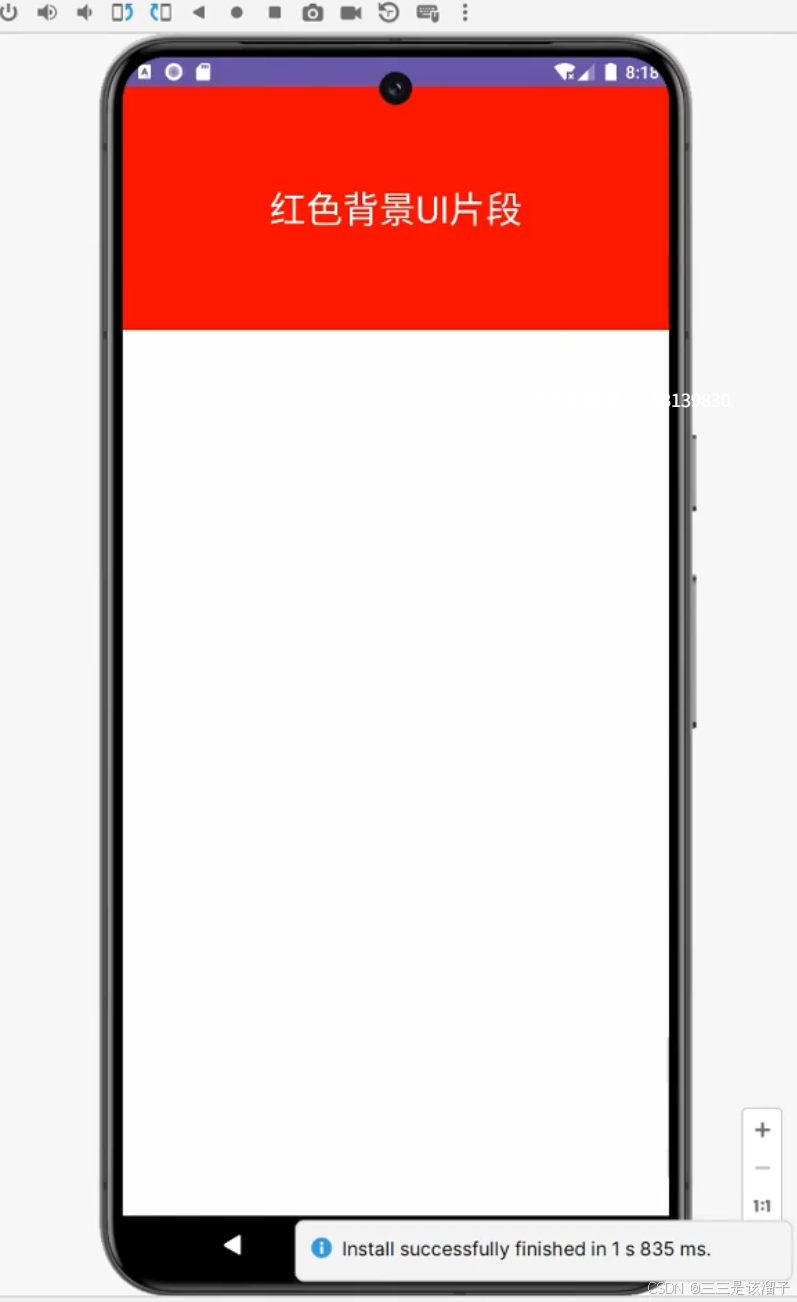
3:效果
这就把MyFragment中关联到的R.layout.layout_red布局拿过来用上了
五:逻辑梳理图
1:单个Activity关联
如果有两个Activity都要使用我们定义出来的MyFragment呢?
2:多个Activity关联
其实也很简单,xml中在搞一个FragmentContainer关联一下就行了,还是非常简单的;
所以说Fragment不仅仅是ui达成了复用,java里面的代码也达成了复用