接上一篇博客
每个 Kotlin 程序都是由两种部分组成的:
- 1、表达式(Expressions) :用于计算值 的部分,比如
2 + 3、函数调用、变量赋值等,它们通常会返回一个结果。 - 2、语句(Statements) :用于执行动作 的部分,比如
if 条件判断、for 循环、println() 打印语句等,它们主要是完成某种操作,而不一定返回值。
这些表达式和语句可以被组织在一起,形成所谓的 代码块(Blocks)。
代码块就是一组用大括号 {} 包起来的代码,通常用在函数、控制结构(如 if、when、for)等地方。
Example:
kotlin
fun sumOf(a:Int,b:Int): Int{
return a+b
}
fun main(args: Array<String>){
val a = 10
val b = 5
var sum = sumOf(a,b)
var mul = a * b
println(sum)
println(mul)
}Output:
kotlin
15
50Kotlin if expression -Kotlin if表达式:
语法规则
kotlin
if(condition)
condition met!
else
condition not met!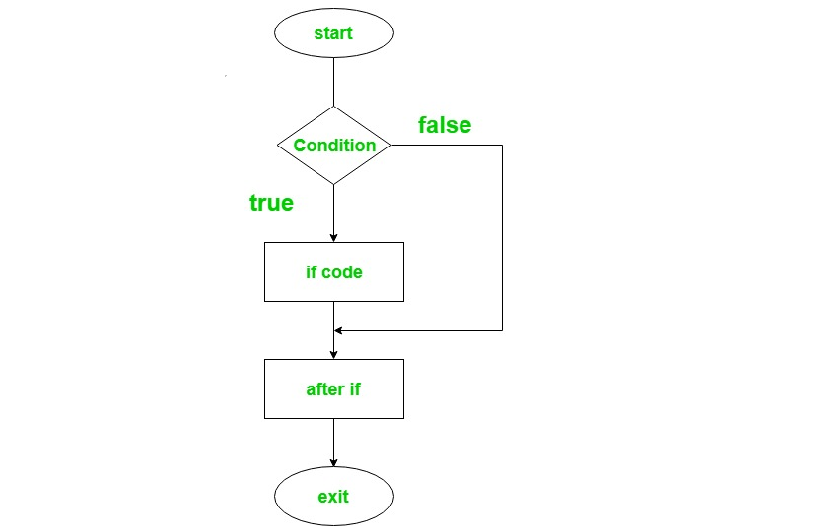
Example:
kotlin
fun main(args: Array<String>){
val a = 1000
val b = 999
var c = 1122
var max1 = if(a > b) a else b
var max2 = if(c > a) c else a
println("The maximum of ${a} and ${b} is $max1 " )
println("The maximum of ${c} and ${a} is $max2 " )
}Output:
kotlin
The maximum of 1000 and 999 is 1000
The maximum of 1122 and 1000 is 1122 Kotlin Statement
Example:
kotlin
fun main(args: Array<String>){
val sum: Int
sum = 100
// single statement
println(sum)
// Multiple statements
println("Hello");println("Geeks!")
}Output:
kotlin
100
Hello
Geeks!Kotlin Block
Example:
kotlin
// Start of main block or outer block
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val array = intArrayOf(2, 4, 6, 8)
// Start of inner block
for (element in array) {
println(element)
}
// End of inner block
}
// End of main blockOutput:
kotlin
2
4
6
8Control Flow-控制语句
Kotlin if-else expression
-
if statement
- 语法规则
kotlinif(condition) { // code to run if condition is true }- 流程图
Example:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var a = 3 if(a > 0){ print("Yes,number is positive") } }Output:
kotlinYes, number is positive -
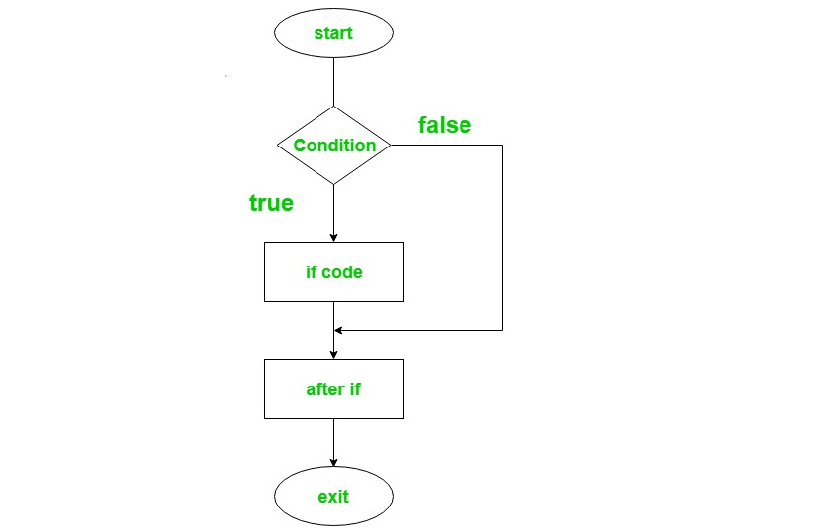
if-else statement
- 语法规则
kotlinif(condition) { // code to run if condition is true } else { // code to run if condition is false }-
流程图
Example:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var a = 5 var b = 10 if(a > b){ print("Number 5 is larger than 10") } else{ println("Number 10 is larger than 5") } }Output:
kotlinNumber 10 is larger than 5Example:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var a = 50 var b = 40 // here if-else returns a value which // is to be stored in max variable var max = if(a > b){ print("Greater number is: ") a } else{ print("Greater number is:") b } print(max) }Output:
kotlinGreater number is: 50
-
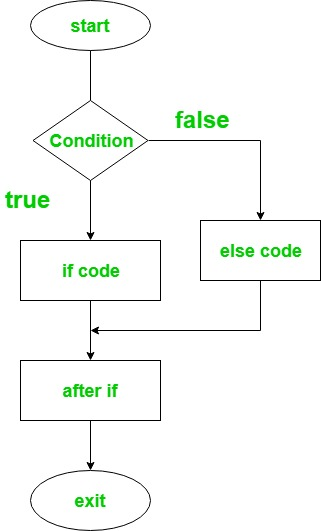
if-else-if ladder expression
-
语法规则
kotlinif(Firstcondition) { // code to run if condition is true } else if(Secondcondition) { // code to run if condition is true } else{ } -
流程图
Example:kotlinimport java.util.Scanner fun main(args: Array<String>) { // create an object for scanner class val reader = Scanner(System.`in`) print("Enter any number: ") // read the next Integer value var num = reader.nextInt() var result = if ( num > 0){ "$num is positive number" } else if( num < 0){ "$num is negative number" } else{ "$num is equal to zero" } println(result) }Output:
kotlinEnter any number: 12 12 is positive number Enter any number: -11 -11 is negative number Enter any number: 0 0 is zero
-
-
nested if expression
- 语法规则
kotlinif(condition1){ // code 1 if(condition2){ // code2 } }-
流程图
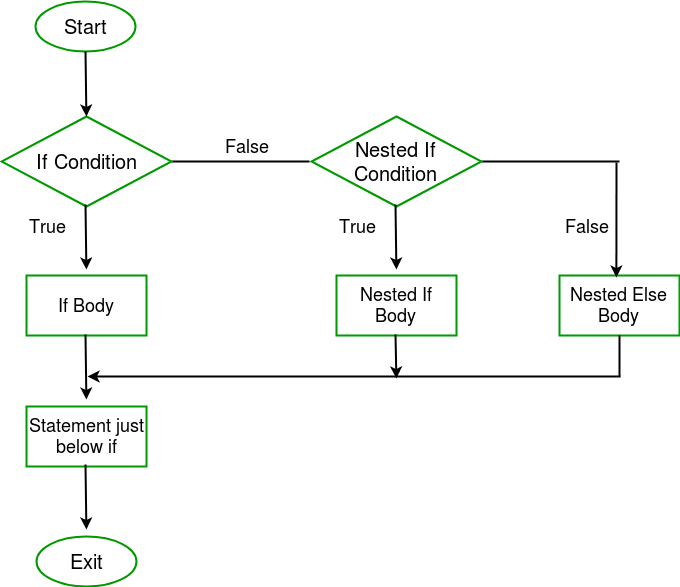
Example:kotlinimport java.util.Scanner fun main(args: Array<String>) { // create an object for scanner class val reader = Scanner(System.`in`) print("Enter three numbers: ") var num1 = reader.nextInt() var num2 = reader.nextInt() var num3 = reader.nextInt() var max = if ( num1 > num2) { if (num1 > num3) { "$num1 is the largest number" } else { "$num3 is the largest number" } } else if( num2 > num3){ "$num2 is the largest number" } else{ "$num3 is the largest number" } println(max) }Output:
kotlinEnter three numbers: 123 231 321 321 is the largest number
Kotlin while loop
-
语法规则
kotlinwhile(condition) { // code to run } -
流程图
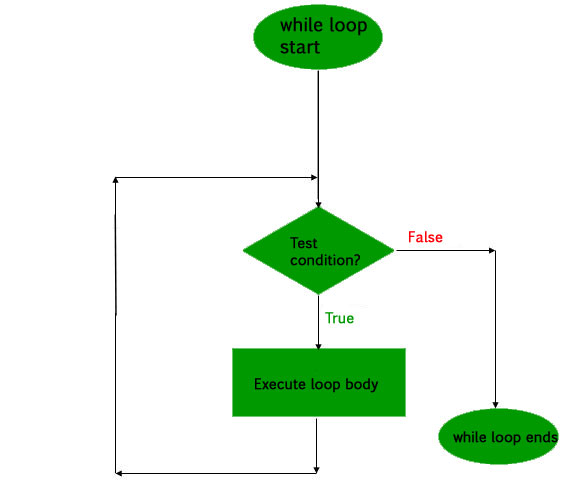
Example:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var number = 1 while(number <= 10) { println(number) number++; } }Output:
kotlin1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10Example:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var names = arrayOf("Praveen","Gaurav","Akash","Sidhant","Abhi","Mayank") var index = 0 while(index < names.size) { println(names[index]) index++ } }Output:
kotlinPraveen Gaurav Akash Sidhant Abhi Mayank
Kotlin do-while loop
-
语法规则
kotlindo { // code to run } while(condition) -
流程图
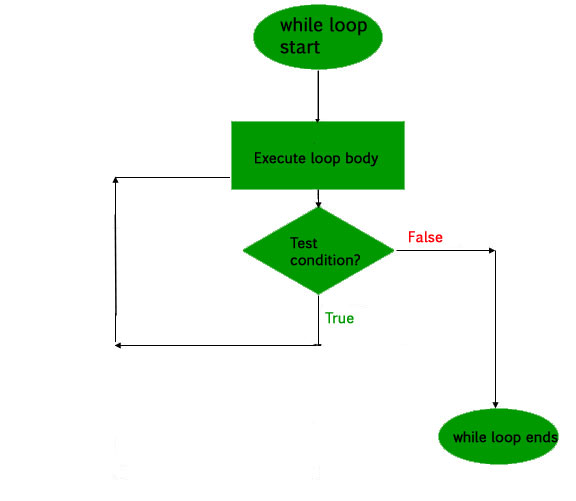
Example:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var number = 6 var factorial = 1 do { factorial *= number number-- }while(number > 0) println("Factorial of 6 is $factorial") }Output:
kotlinFactorial of 6 is 720
Kotlin for loop
-
语法规则
kotlinfor(item in collection) { // code to execute } -
Range Using a for loop-使用for循环
Example1:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { for (i in 1..6) { print("$i ") } }kotlin1 2 3 4 5 6Example2:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { for (i in 1..10 step 3) { print("$i ") } }kotlin1 4 7 10Example3:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { for (i in 5..1) { print("$i ") } println("It prints nothing") }kotlinIt prints nothingExample4:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { for (i in 5 downTo 1) { print("$i ") } }kotlin5 4 3 2 1Example5:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { for (i in 10 downTo 1 step 3) { print("$i ") } }kotlin10 7 4 1 -
Array using for loop-使用for循环的数组
Example1:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var numbers = arrayOf(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10) for (num in numbers){ if(num%2 == 0){ print("$num ") } } }kotlin2 4 6 8 10Example2:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var planets = arrayOf("Earth", "Mars", "Venus", "Jupiter", "Saturn") for (i in planets.indices) { println(planets[i]) } }kotlinEarth Mars Venus Jupiter SaturnExample3:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var planets = arrayOf("Earth", "Mars", "Venus", "Jupiter", "Saturn") for ((index,value) in planets.withIndex()) { println("Element at $index th index is $value") } }kotlinElement at 0 th index is Earth Element at 1 th index is Mars Element at 2 th index is Venus Element at 3 th index is Jupiter Element at 4 th index is Saturn -
String using a for loop-使用for循环的字符串
Example1:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var name = "Geeks" var name2 = "forGeeks" // traversing string without using index property for (alphabet in name) print("$alphabet ") // traversing string with using index property for (i in name2.indices) print(name2[i]+" ") println(" ") // traversing string using withIndex() library function for ((index,value) in name.withIndex()) println("Element at $index th index is $value") }Output:
kotlinG e e k s f o r G e e k s Element at 0 th index is G Element at 1 th index is e Element at 2 th index is e Element at 3 th index is k Element at 4 th index is s -
collection using for loop-使用for循环的集合
Example:kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { // read only, fix-size var collection = listOf(1,2,3,"listOf", "mapOf", "setOf") for (element in collection) { println(element) } }Output:
kotlin1 2 3 listOf mapOf setOf
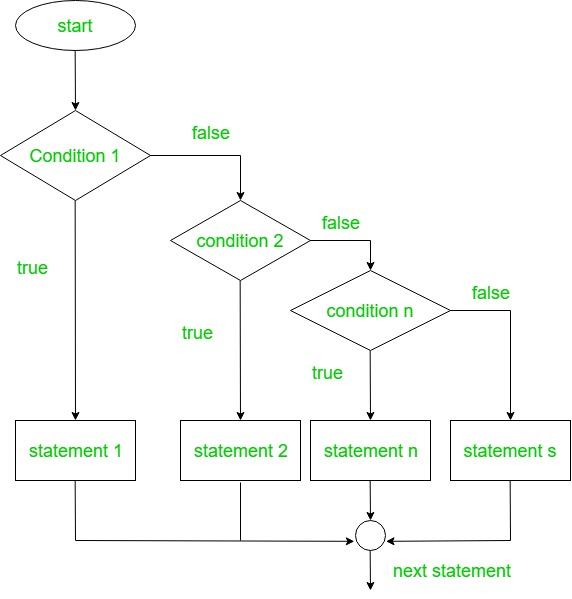
Kotlin when expression
-
when as a statement
Example1:kotlinfun main (args : Array<String>) { print("Enter the name of heavenly body: ") var name= readLine()!!.toString() when(name) { "Sun" -> print("Sun is a Star") "Moon" -> print("Moon is a Satellite") "Earth" -> print("Earth is a planet") else -> print("I don't know anything about it") } }kotlinEnter the name of heavenly body: Sun Sun is a Star Enter the name of heavenly body: Mars I don't know anything about itExample2:
kotlinfun main (args : Array<String>) { print("Enter the name of heavenly body: ") var name= readLine()!!.toString() when(name) { "Sun" -> print("Sun is a Star") "Moon" -> print("Moon is a Satellite") "Earth" -> print("Earth is a planet") } }kotlinEnter the name of heavenly body: Mars Process finished with exit code 0 -
when as an expression
Example1:
注意 作为表达式else不能缺失,否则会报错:Kotlin: 'when' expression must be exhaustive, add necessary 'else' branchkotlinfun main(args : Array<String>) { print("Enter number of the Month: ") var monthOfYear = readLine()!!.toInt() var month= when(monthOfYear) { 1->"January" 2->"February" 3->"March" 4->"April" 5->"May" 6->"June" 7->"July" 8->"August" 9->"September" 10->"October" 11->"November" 12->"December" else-> "Not a month of year" } print(month) }kotlinEnter number of the Month: 8 AugustExample2:
kotlinfun main (args :Array<String>) { print("Enter name of the planet: ") var name=readLine()!!.toString() when(name) { "Mercury","Earth","Mars","Jupiter" ,"Neptune","Saturn","Venus","Uranus" -> print("This is a planet") else -> print("This not a planet") } }Output:
kotlinEnter name of the planet: Earth This is a PlanetExample3:
kotlinfun main (args:Array<String>) { print("Enter the month number of year: ") var num= readLine()!!.toInt() when(num) { in 1..3 -> print("Spring season") in 4..6 -> print("Summer season") in 7..8 -> print("Rainy season") in 9..10 -> print("Autumn season") in 11..12 -> print("Winter season") !in 1..12 -> print("Enter valid month of the year") } }kotlinEnter the month number of year: 5 Summer season Enter the month number of year: 14 Enter valid month of the yearExample4:
kotlinfun main(args: Array<String>) { var num: Any = "xx" when(num){ is Int -> println("It is an Integer") is String -> println("It is a String") is Double -> println("It is a Double") } }Output:
kotlinIt is a StringExample5:
kotlin// returns true if x is odd fun isOdd(x: Int) = x % 2 != 0 // returns true if x is evevn fun isEven(x: Int) = x % 2 == 0 fun main(args: Array<String>) { var num = 8 when{ isOdd(num) ->println("Odd") isEven(num) -> println("Even") else -> println("Neither even nor odd") } }Output:
kotlinEvenExample6:
kotlin// Return s True if company start with "xx" fun hasPrefix(company: Any):Boolean{ return when (company) { is String -> company.startsWith("xx") else -> false } } fun main(args: Array<String>) { var company = "xx is a computer science portal" var result = hasPrefix(company) if(result) { println("Yes, string started with xx") } else { println("No, String does not started with xx") } }Output:
kotlinYes, string started with xx