一、简化Bean的注册
如果每次注册一个Bean,都要像上节一样,手动写PropertyValues相关的代码,那太复杂了,我们希望读取XML文件,自动注册Bean,这样对于使用者,甚至不知道有BeanDefinition的存在
二、统一处理资源文件
新建资源接口,Spring对所有的资源文件,统一处理
- 一个资源,最重要的就是拿到输入流,拿到输入流就可以读取文件
java
public interface Resource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}提供三个资源实现类,分别读取不同类型的文件,这就是策略模式
类路径下的文件(最常用)
java
public class ClassPathResource implements Resource{
private final String path;
private final ClassLoader classLoader;
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, null);
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = path;
this.classLoader = classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtil.getClassLoader();
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is = classLoader.getResourceAsStream(path);
if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(path + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
}文件系统下的文件
java
public class FileSystemResource implements Resource{
private File file;
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
this.file = file;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return Files.newInputStream(file.toPath());
}
}网络文件
java
public class UrlResource implements Resource{
private final URL url;
public UrlResource(URL url) {
Assert.notNull(url,"URL must not be null");
this.url = url;
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
return con.getInputStream();
}
}资源加载器接口,简化资源类的使用,自动根据路径选择合适的加载类
- 这又属于工厂方法设计模式
java
/**
* @Author 孤风雪影
* @Email gitee.com/efairy520
* @Date 2025/1/2 22:16
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface ResourceLoader {
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = "classpath:";
Resource getResource(String location);
}资源加载器接口实现
- 根据路径前缀,默认就是使用classpath策略
java
/**
* @Author 孤风雪影
* @Email gitee.com/efairy520
* @Date 2025/1/2 22:18
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader{
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
//使用类路径加载器,去掉前缀
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
else {
try {
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
return new FileSystemResource(new File(location));
}
}
}
}三、从文件中读取Bean
定义BeanDefinitionReader接口,从文件中读取BeanDefinition,并且注册到Bean工厂,这里有三要素
- 资源文件
- Bean工厂
- 读取BeanDefinition的逻辑(单个资源,多个资源,位置字符串)
java
/**
* @Author 孤风雪影
* @Email gitee.com/efairy520
* @Date 2025/1/2 22:26
* @Version 1.0
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry();
ResourceLoader getResourceLoader();
void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource);
void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources);
void loadBeanDefinitions(String location);
}用抽象类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader实现接口,模板方法设计模式
- Bean工厂和资源加载器都是确定的,抽象类直接实现
- 只有加载BeanDefinition是不确定的逻辑,交给具体的策略子类实现
java
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader {
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
public AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.registry = registry;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, new DefaultResourceLoader());
}
@Override
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getRegistry() {
return registry;
}
@Override
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return resourceLoader;
}
}XmlBeanDefinitionReader做具体实现,策略模式
java
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
super(registry, resourceLoader);
}
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
super(registry);
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) {
try {
InputStream is = resource.getInputStream();
doLoadBeanDefinitions(is);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, e);
}
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String location) {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
/**
* 真正解析XMl文件的方法
*
* @param inputStream
*/
private void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) {
Document doc = XmlUtil.readXML(inputStream);
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList childNodes = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < childNodes.getLength(); i++) {
// 判断元素
if (!(childNodes.item(i) instanceof Element)) continue;
// 判断对象
if (!"bean".equals(childNodes.item(i).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签
Element bean = (Element) childNodes.item(i);
String id = bean.getAttribute("id");
String name = bean.getAttribute("name");
String className = bean.getAttribute("class");
// 获取 Class,方便获取类中的名称
Class<?> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = Class.forName(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("不存在的类名" + className);
}
// 优先级 id > name,此处是Bean自己的id和name
String beanName = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(id) ? id : name;
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(beanName)) {
beanName = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
// 定义Bean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(clazz);
// 读取属性并填充
for (int j = 0; j < bean.getChildNodes().getLength(); j++) {
if (!(bean.getChildNodes().item(j) instanceof Element)) continue;
if (!"property".equals(bean.getChildNodes().item(j).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签:property
Element property = (Element) bean.getChildNodes().item(j);
String attrName = property.getAttribute("name");
String attrValue = property.getAttribute("value");
String attrRef = property.getAttribute("ref");
// 获取属性值:引入对象、值对象
Object value = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(attrRef) ? new BeanReference(attrRef) : attrValue;
// 创建属性信息
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(attrName, value);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
if (getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
throw new RuntimeException("Duplicate beanName[" + beanName + "] is not allowed");
}
// 注册 BeanDefinition
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
}BeanDefinitionReader接口、资源接口,层次结构图
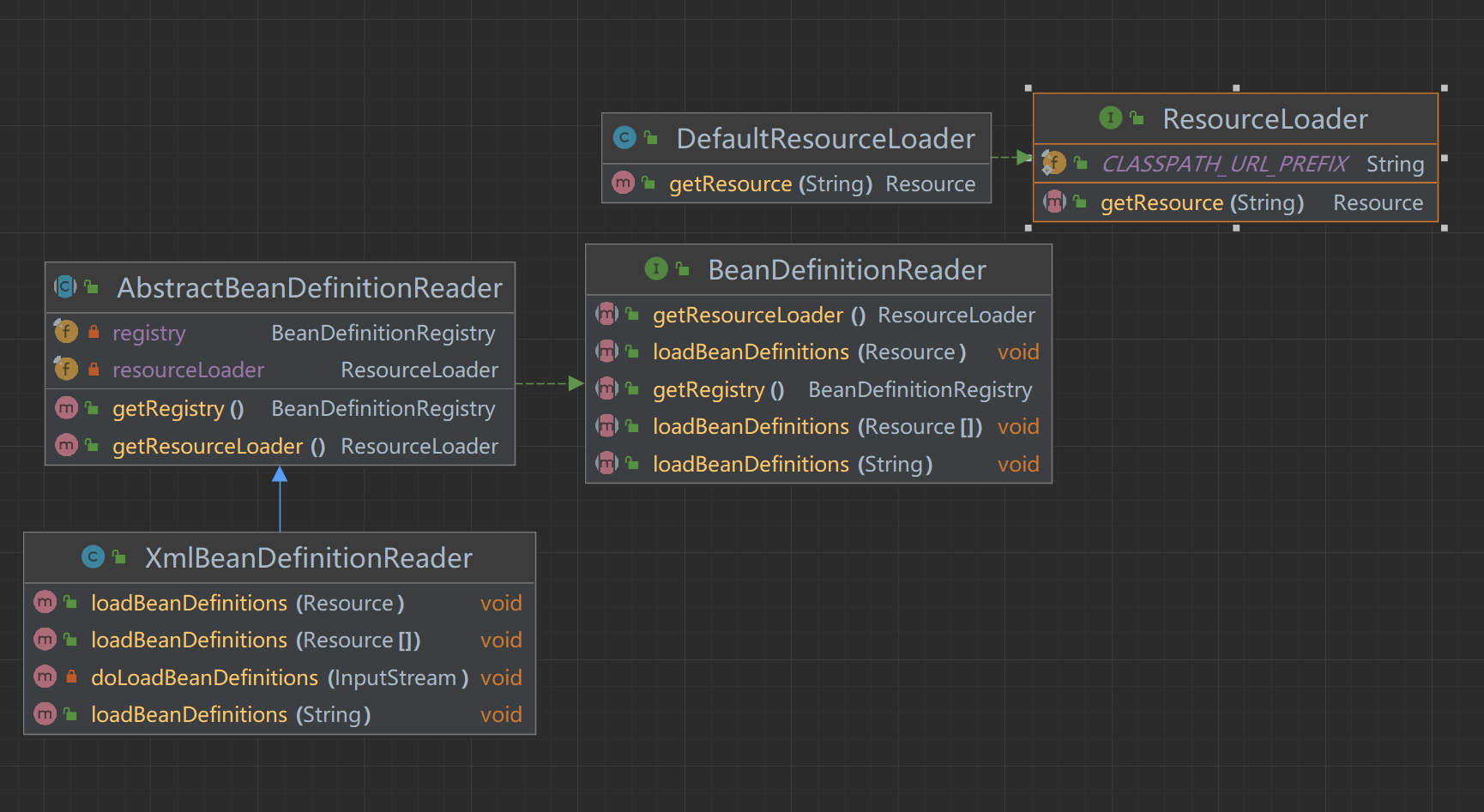
四、测试
新建Person类
java
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Cat cat;
}新建Cat类
java
@Data
@ToString
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@EqualsAndHashCode
public class Cat {
private String name;
private int weight;
}编写一个spring.xml文件
java
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<bean id="cat" class="cn.shopifymall.springframework.test.bean.Cat">
<property name="name" value="tomcat"/>
<property name="weight" value="2000"/>
</bean>
<bean id="person" class="cn.shopifymall.springframework.test.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="10001"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
<property name="cat" ref="cat"/>
</bean>
</beans>新建测试类
java
public class ApiTest {
@Test
public void testGetBeanFromXml() {
// 1.初始化 BeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// 2. 读取配置文件&注册Bean
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions("classpath:spring.xml");
// 3. 获取Bean对象调用方法
Person person = (Person) beanFactory.getBean("person");
System.out.println("person:" + person);
}
}控制台输出
java
person:Person(name=10001, age=18, cat=Cat(name=tomcat, weight=2000))五、总结
- 通过引入spring.xml配置文件,我们就可以简化Bean的注册
- 用户只需要编写一个xml文件,由XmlBeanDefinitionReader自动解析xml文件,生成BeanDefinition并注册到BeanFactory