TCP多线程通信代码开发流程解析------让步骤清晰明了
在编写 TCP 通信代码时,我经常中途忘记需要实现哪些步骤。为了更好地熟悉整个流程,并提高今后的开发效率,我打算自己写一篇文章,系统地整理并总结编写 TCP 通信所需的关键代码和步骤。
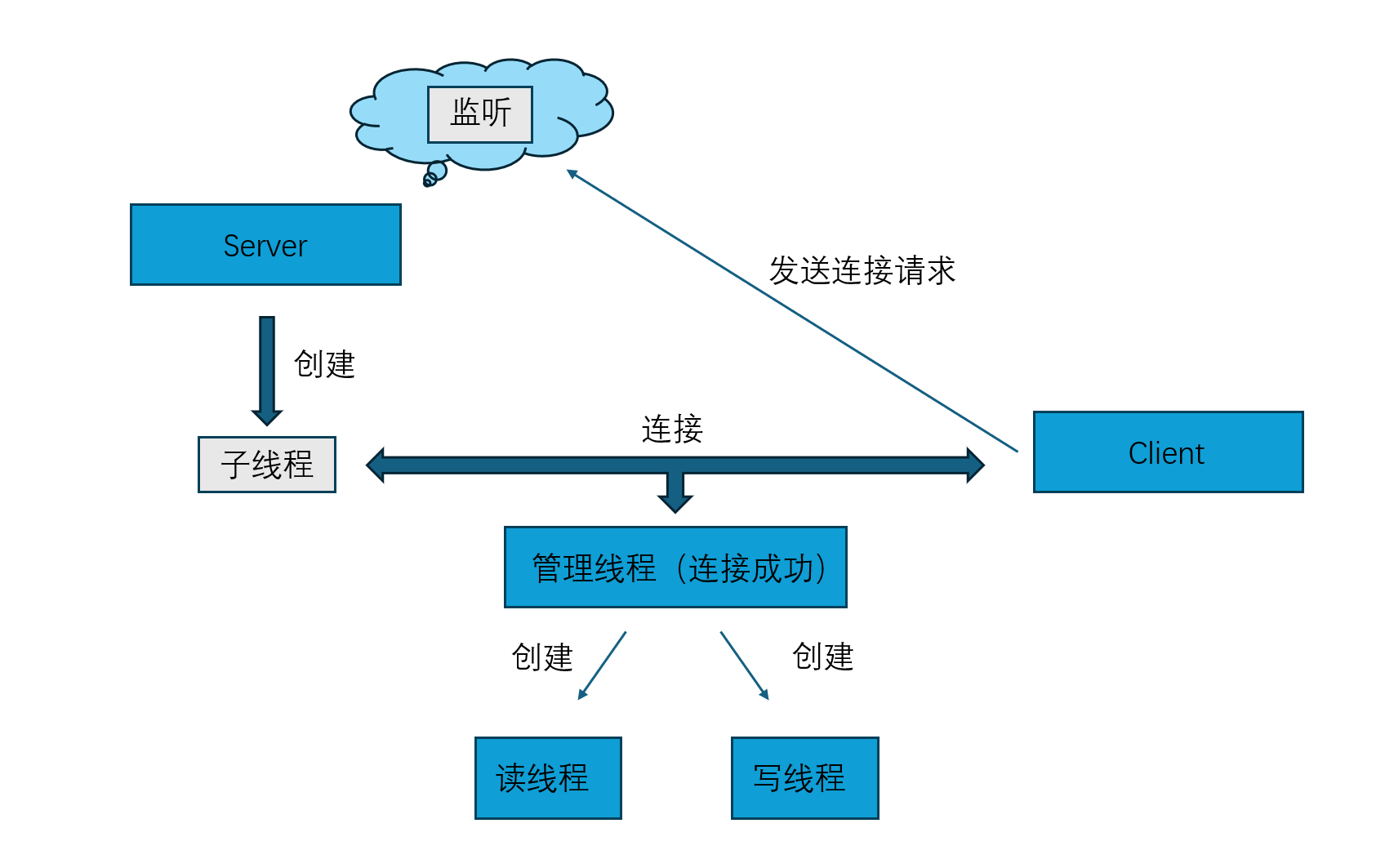
服务端的流程
服务端通过主线程接受客户端连接,并为每个连接创建独立会话线程(管理线程),在会话线程中再启两个子线程分别负责读和写。
1.接收客户端并为其分配线程
-
创建
sockaddr_in结构体及socket套接字cstruct sockaddr_in server_addr; memset(&server_addr,0,sizeof(server_addr)); server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_ANY); server_addr.sin_family=AF_INET; server_addr.sin_port=htons(port); int len_server_addr=sizeof(server_addr);//结构体的大小 //套接字 int serverfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0); -
bind绑定ctemp_result=bind(serverfd,(struct sockaddr*)&server_addr,len_server_addr); if(temp_result) { handle_error("bind",temp_result); } -
listen监听ctemp_result=listen(serverfd,10);//第二个参数是最多可以接受多少个客户端连接请求 if(temp_result) { handle_error("listen",temp_result); } -
创建线程
accept连接关键点
pthread_t fd;只是个变量。- 每次调用
pthread_create,都会把新建线程的 ID 写到fd里。 - 你紧接着又
pthread_detach(fd),把这个线程设置为**"分离态"**,这样它结束时系统能自动回收资源。 - 下一次循环时 ,
pthread_create会再次把新的线程 ID 写进fd(覆盖掉旧的)。
cpthread_t fd; struct sockaddr_in client_addr; memset(&client_addr,0,sizeof(client_addr)); int client_addr_len=sizeof(client_addr); while (1) { int *client_fd=malloc(sizeof(int)); *client_fd=accept(serverfd,(struct sockaddr*)&client_addr,&client_addr_len); printf("客户端%d,ip:%s,已成功与服务端连接\n",*client_fd,inet_ntoa(client_addr.sin_addr)); pthread_create(&fd,NULL,&raw,client_fd); pthread_detach(fd); } //释放资源 close(serverfd);
2.管理该客户端的读写子线程
为什么要传输文件描述符,这就相当于一个通道,没有他我们就找不到目标地址,也就无法进行读写操作,这就相当于一个通讯大门
c
void *read_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *read_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
temp_result = recv(server_fd, read_buf, 1024, 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("recv");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("客户端关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
read_buf[temp_result] = '\0'; // 安全添加结束符,防止乱码
printf("客户端:%s\n", read_buf);
}
free(read_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *write_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *write_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
memset(write_buf, 0, 1024);
if (fgets(write_buf, 1024, stdin) == NULL)
{
printf("输入有误\n");
break;
}
if (strncmp(write_buf, "exit", 4) == 0)
{
printf("服务端主动退出\n");
break;
}
temp_result = send(server_fd, write_buf, strlen(write_buf), 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("send");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("服务端:%s\n", write_buf);
}
}
free(write_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *raw(void * argv)
{
int sockfd=*(int*)argv;
pthread_t read_t,write_t;
//创建子线程读取数据并打印到终端
pthread_create(&read_t, NULL, read_func, argv);
//创建子线程写入数据传到服务端
pthread_create(&write_t, NULL, write_func, argv);
// 主线程等待子线程退出
pthread_join(read_t, NULL);
pthread_join(write_t, NULL);
free(argv);
printf("关闭资源\n");
close(sockfd);
}3.完整代码展示
c
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <string.h>
#define port 6666
#define handle_error(cmd, result) \
if (result < 0) \
{ \
perror(cmd); \
return -1; \
}
void *read_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *read_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
temp_result = recv(server_fd, read_buf, 1024, 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("recv");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("客户端关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
read_buf[temp_result] = '\0'; // 安全添加结束符,防止乱码
printf("客户端:%s\n", read_buf);
}
free(read_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *write_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *write_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
memset(write_buf, 0, 1024);
if (fgets(write_buf, 1024, stdin) == NULL)
{
printf("输入有误\n");
break;
}
if (strncmp(write_buf, "exit", 4) == 0)
{
printf("服务端主动退出\n");
break;
}
temp_result = send(server_fd, write_buf, strlen(write_buf), 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("send");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("服务端:%s\n", write_buf);
}
}
free(write_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *raw(void * argv)
{
int sockfd=*(int*)argv;
pthread_t read_t,write_t;
//创建子线程读取数据并打印到终端
pthread_create(&read_t, NULL, read_func, argv);
//创建子线程写入数据传到服务端
pthread_create(&write_t, NULL, write_func, argv);
// 主线程等待子线程退出
pthread_join(read_t, NULL);
pthread_join(write_t, NULL);
free(argv);
printf("关闭资源\n");
close(sockfd);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int temp_result;
//声明server结构体以及初始化
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
memset(&server_addr,0,sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr=htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server_addr.sin_family=AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_port=htons(port);
int len_server_addr=sizeof(server_addr);
//套接字
int serverfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
//绑定
temp_result=bind(serverfd,(struct sockaddr*)&server_addr,len_server_addr);
if(temp_result)
{
handle_error("bind",temp_result);
}
//监听
temp_result=listen(serverfd,10);
if(temp_result)
{
handle_error("listen",temp_result);
}
//接收
pthread_t fd;
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
memset(&client_addr,0,sizeof(client_addr));
int client_addr_len=sizeof(client_addr);
while (1)
{
int *client_fd=malloc(sizeof(int));
*client_fd=accept(serverfd,(struct sockaddr*)&client_addr,&client_addr_len);
printf("客户端%d,ip:%s,已成功与服务端连接\n",*client_fd,inet_ntoa(client_addr.sin_addr));
pthread_create(&fd,NULL,&raw,client_fd);
pthread_detach(fd);
}
//释放资源
close(serverfd);
return 0;
}客户端的流程
- 创建
sockaddr_in初始化 connect连接
1.连接服务端
c
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// 套接字
int client_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// 初始化
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
memset(&client_addr, 0, sizeof(client_addr));
client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
client_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
client_addr.sin_port = htons(6666);
int client_addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
int sockfd = connect(client_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, client_addr_len);
if (sockfd == -1)
{
handle_error("connect", sockfd);
}
pthread_t read_t, write_t;
// 创建子线程读取数据并打印到终端
pthread_create(&read_t, NULL, &read_func, (void *)&client_fd);
// 创建子线程写入数据传到服务端
pthread_create(&write_t, NULL, &write_func, (void *)&client_fd);
// 主线程等待子线程退出
pthread_join(read_t, NULL);
pthread_join(write_t, NULL);
printf("关闭资源\n");
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}2.客户端的读写子线程
和服务端实现方法一样
c
void *read_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *read_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
temp_result = recv(server_fd, read_buf, 1024, 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("recv");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
read_buf[temp_result] = '\0'; // 安全添加结束符,防止乱码
printf("服务器:%s\n", read_buf);
}
free(read_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *write_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *write_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
memset(write_buf, 0, 1024);
if (fgets(write_buf, 1024, stdin) == NULL)
{
printf("输入有误\n");
break;
}
if (strncmp(write_buf, "exit", 4) == 0)
{
printf("客户端主动退出\n");
break;
}
temp_result = send(server_fd, write_buf, strlen(write_buf), 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("send");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("客户端:%s\n", write_buf);
}
}
free(write_buf);
return NULL;
}3.完整代码
c
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define handle_error(cmd, result) \
if (result < 0) \
{ \
perror(cmd); \
return -1; \
}
void *read_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *read_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
temp_result = recv(server_fd, read_buf, 1024, 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("recv");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
read_buf[temp_result] = '\0'; // 安全添加结束符,防止乱码
printf("服务器:%s\n", read_buf);
}
free(read_buf);
return NULL;
}
void *write_func(void *arg)
{
int server_fd = *(int *)arg;
char *write_buf = malloc(1024);
int temp_result;
while (1)
{
memset(write_buf, 0, 1024);
if (fgets(write_buf, 1024, stdin) == NULL)
{
printf("输入有误\n");
break;
}
if (strncmp(write_buf, "exit", 4) == 0)
{
printf("客户端主动退出\n");
break;
}
temp_result = send(server_fd, write_buf, strlen(write_buf), 0);
if (temp_result == -1)
{
perror("send");
}
else if (temp_result == 0)
{
printf("服务器关闭了连接\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("客户端:%s\n", write_buf);
}
}
free(write_buf);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
// 套接字
int client_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// 初始化
struct sockaddr_in client_addr;
memset(&client_addr, 0, sizeof(client_addr));
client_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
client_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
client_addr.sin_port = htons(6666);
int client_addr_len = sizeof(client_addr);
int sockfd = connect(client_fd, (struct sockaddr *)&client_addr, client_addr_len);
if (sockfd == -1)
{
handle_error("connect", sockfd);
}
pthread_t read_t, write_t;
// 创建子线程读取数据并打印到终端
pthread_create(&read_t, NULL, &read_func, (void *)&client_fd);
// 创建子线程写入数据传到服务端
pthread_create(&write_t, NULL, &write_func, (void *)&client_fd);
// 主线程等待子线程退出
pthread_join(read_t, NULL);
pthread_join(write_t, NULL);
printf("关闭资源\n");
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}总结
TCP 多线程服务端的实现,看似复杂,但本质就是"主线程接收连接、子线程处理读写"。掌握文件描述符和线程管理,你就掌握了网络通信的核心钥匙。希望本文能帮助你对网络编程有更直观的理解。