🔍 MyBatis 动态 SQL 精讲:告别硬编码的智能拼接艺术
文章目录
- [🔍 MyBatis 动态 SQL 精讲:告别硬编码的智能拼接艺术](#🔍 MyBatis 动态 SQL 精讲:告别硬编码的智能拼接艺术)
- [🧠 一、为什么需要动态 SQL?](#🧠 一、为什么需要动态 SQL?)
-
- [💡 JDBC 时代的痛点](#💡 JDBC 时代的痛点)
- [🛠️ 二、核心标签深度解析](#🛠️ 二、核心标签深度解析)
-
- [💡 动态 SQL 标签全景图](#💡 动态 SQL 标签全景图)
- [🔥 1. if 标签:条件分支](#🔥 1. if 标签:条件分支)
- [🔀 2. choose/when/otherwise:多路选择](#🔀 2. choose/when/otherwise:多路选择)
- [🎯 3. where 标签:智能 WHERE 子句](#🎯 3. where 标签:智能 WHERE 子句)
- [🔄 4. set 标签:智能 UPDATE](#🔄 4. set 标签:智能 UPDATE)
- [🔁 5. foreach 标签:循环遍历](#🔁 5. foreach 标签:循环遍历)
- [🎨 6. trim 标签:自定义修剪](#🎨 6. trim 标签:自定义修剪)
- [💡 三、最佳实践指南](#💡 三、最佳实践指南)
-
- [💡 可维护性设计原则](#💡 可维护性设计原则)
- [🛡️ 1. 避免冗余条件](#🛡️ 1. 避免冗余条件)
- [📝 2. 保持 SQL 可读性](#📝 2. 保持 SQL 可读性)
- [⚠️ 四、常见陷阱与优化](#⚠️ 四、常见陷阱与优化)
-
- [💡 性能与安全对比](#💡 性能与安全对比)
- [🔧 1. 空条件处理](#🔧 1. 空条件处理)
- [⚡ 2. foreach 性能优化](#⚡ 2. foreach 性能优化)
- [🛡️ 3. SQL 注入防护](#🛡️ 3. SQL 注入防护)
- [🔚 总结与延伸](#🔚 总结与延伸)
-
- [📚 核心要点回顾](#📚 核心要点回顾)
🧠 一、为什么需要动态 SQL?
💡 JDBC 时代的痛点
在传统 JDBC 开发中,我们经常遇到这样的代码:
java
// JDBC 动态拼接SQL的噩梦
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("SELECT * FROM users WHERE 1=1 ");
if (name != null) {
sql.append("AND name = '").append(name).append("' ");
}
if (email != null) {
sql.append("AND email = '").append(email).append("' ");
}
// SQL注入风险!字符串拼接地狱!MyBatis 动态 SQL 的优势:
JDBC手动拼接 SQL注入风险 代码冗长 难以维护 MyBatis动态SQL 预编译安全 标签化简洁 易于维护
🛠️ 二、核心标签深度解析
💡 动态 SQL 标签全景图
🔥 1. if 标签:条件分支
应用场景:多条件查询
xml
<select id="findUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
<where>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name LIKE #{name}
</if>
<if test="email != null">
AND email = #{email}
</if>
<if test="status != null">
AND status = #{status}
</if>
</where>
</select>输入参数:{name: "张", status: 1}
生成 SQL:
sql
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE name LIKE ? AND status = ?🔀 2. choose/when/otherwise:多路选择
应用场景:优先级条件查询
xml
<select id="findUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
<where>
<choose>
<when test="id != null">
id = #{id}
</when>
<when test="email != null">
email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
status = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>输入参数:{email: "test@example.com"}
生成 SQL:
sql
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?🎯 3. where 标签:智能 WHERE 子句
解决痛点:自动处理 AND/OR 和空条件
xml
<!-- 传统方式需要写 WHERE 1=1 -->
<select id="findUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
<where>
<if test="name != null">name = #{name}</if>
<if test="email != null">AND email = #{email}</if>
</where>
</select>输入参数:{name: null, email: "test@example.com"}
生成 SQL:
sql
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?🔄 4. set 标签:智能 UPDATE
应用场景:动态更新字段
xml
<update id="updateUser">
UPDATE users
<set>
<if test="name != null">name = #{name},</if>
<if test="email != null">email = #{email},</if>
<if test="status != null">status = #{status},</if>
</set>
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>输入参数:{id: 1, name: "张三"}
生成 SQL:
sql
UPDATE users SET name = ? WHERE id = ?🔁 5. foreach 标签:循环遍历
应用场景:批量操作和 IN 查询
xml
<select id="findUsersByIds" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE id IN
<foreach item="id" collection="ids"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>输入参数:{ids: [1, 2, 3, 5, 8]}
生成 SQL:
sql
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)🎨 6. trim 标签:自定义修剪
应用场景:更精细的字符串处理
xml
<update id="updateUser">
UPDATE users
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">name = #{name},</if>
<if test="email != null">email = #{email},</if>
</trim>
WHERE id = #{id}
</update>💡 三、最佳实践指南
💡 可维护性设计原则
可维护性 单一职责 清晰命名 避免嵌套过深 适当注释
🛡️ 1. 避免冗余条件
不推荐:
xml
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND name = #{name}
</if>
<if test="name != null and name != ''">
AND email = #{email}
</if>推荐:
xml
<where>
<if test="condition.name != null and condition.name != ''">
name = #{condition.name}
</if>
<if test="condition.email != null">
email = #{condition.email}
</if>
</where>📝 2. 保持 SQL 可读性
复杂动态 SQL 示例:
xml
<select id="searchUsers" resultType="User">
/* 用户综合查询 */
SELECT * FROM users
<where>
<!-- 姓名条件 -->
<if test="name != null">
AND (name LIKE #{name} OR nick_name LIKE #{name})
</if>
<!-- 状态条件 -->
<if test="statusList != null and statusList.size() > 0">
AND status IN
<foreach item="status" collection="statusList"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{status}
</foreach>
</if>
<!-- 时间范围 -->
<if test="startTime != null and endTime != null">
AND create_time BETWEEN #{startTime} AND #{endTime}
</if>
</where>
ORDER BY id DESC
</select>⚠️ 四、常见陷阱与优化
💡 性能与安全对比
| 问题类型 | 问题描述 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 条件缺失 | 所有if条件都不满足,SQL语法错误 | 使用<where>标签 |
| SQL注入 | 不当使用${}导致注入风险 |
始终优先使用#{} |
| 性能问题 | foreach批量过大导致SQL过长 |
分批处理,每批1000条 |
| 空集合 | 空集合在foreach中导致SQL错误 |
先判断集合是否为空 |
🔧 1. 空条件处理
问题代码:
xml
<select id="findUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE
<if test="name != null">name = #{name}</if>
<if test="email != null">AND email = #{email}</if>
</select>当所有if都不满足时生成:
sql
SELECT * FROM users WHERE修复方案:
xml
<select id="findUsers" resultType="User">
SELECT * FROM users
<where>
<if test="name != null">name = #{name}</if>
<if test="email != null">AND email = #{email}</if>
</where>
</select>⚡ 2. foreach 性能优化
批量插入优化:
xml
<insert id="batchInsertUsers">
INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES
<foreach item="user" collection="users" separator=",">
(#{user.name}, #{user.email})
</foreach>
</insert>**风险:**一次插入10000条数据会导致SQL过长
解决方案:分批处理
java
// 服务层分批处理
public void batchInsert(List<User> users) {
int batchSize = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < users.size(); i += batchSize) {
List<User> batch = users.subList(i, Math.min(i + batchSize, users.size()));
userMapper.batchInsertUsers(batch);
}
}🛡️ 3. SQL 注入防护
危险用法(绝对避免!):
xml
<select id="findUsers">
SELECT * FROM users
ORDER BY ${orderBy} ${orderDirection}
</select>安全用法:
xml
<select id="findUsers">
SELECT * FROM users
ORDER BY
<choose>
<when test="orderBy == 'name'">name</when>
<when test="orderBy == 'email'">email</when>
<otherwise>id</otherwise>
</choose>
<choose>
<when test="orderDirection == 'desc'">DESC</when>
<otherwise>ASC</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>🔍 MyBatis 动态 SQL 精讲:告别硬编码的智能拼接艺术
作为拥有十年企业级开发经验的架构师,我将带您深入探索 MyBatis 动态 SQL 的强大功能。本文不仅解析核心标签,更通过实战案例展示如何构建灵活、高效且安全的数据库查询!
目录
•
🧠 一、为什么需要动态 SQL?
•
🛠️ 二、核心标签深度解析
•
💡 三、最佳实践指南
•
⚠️ 四、常见陷阱与优化
•
🚀 五、实战业务场景
🧠 一、为什么需要动态 SQL?
💡 JDBC 时代的痛点
在传统 JDBC 开发中,我们经常遇到这样的代码:
// JDBC 动态拼接SQL的噩梦
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("SELECT * FROM users WHERE 1=1 ");
if (name != null) {
sql.append("AND name = '").append(name).append("' ");
}
if (email != null) {
sql.append("AND email = '").append(email).append("' ");
}
// SQL注入风险!字符串拼接地狱!
MyBatis 动态 SQL 的优势:
graph LR
A[JDBC手动拼接] --> B[SQL注入风险]
A --> C[代码冗长]
A --> D[难以维护]
E[MyBatis动态SQL] --> F[预编译安全]
E --> G[标签化简洁]
E --> H[易于维护]
style B fill:#f99,stroke:#333
style C fill:#f99,stroke:#333
style D fill:#f99,stroke:#333
style F fill:#9f9,stroke:#333
style G fill:#9f9,stroke:#333
style H fill:#9f9,stroke:#333🛠️ 二、核心标签深度解析
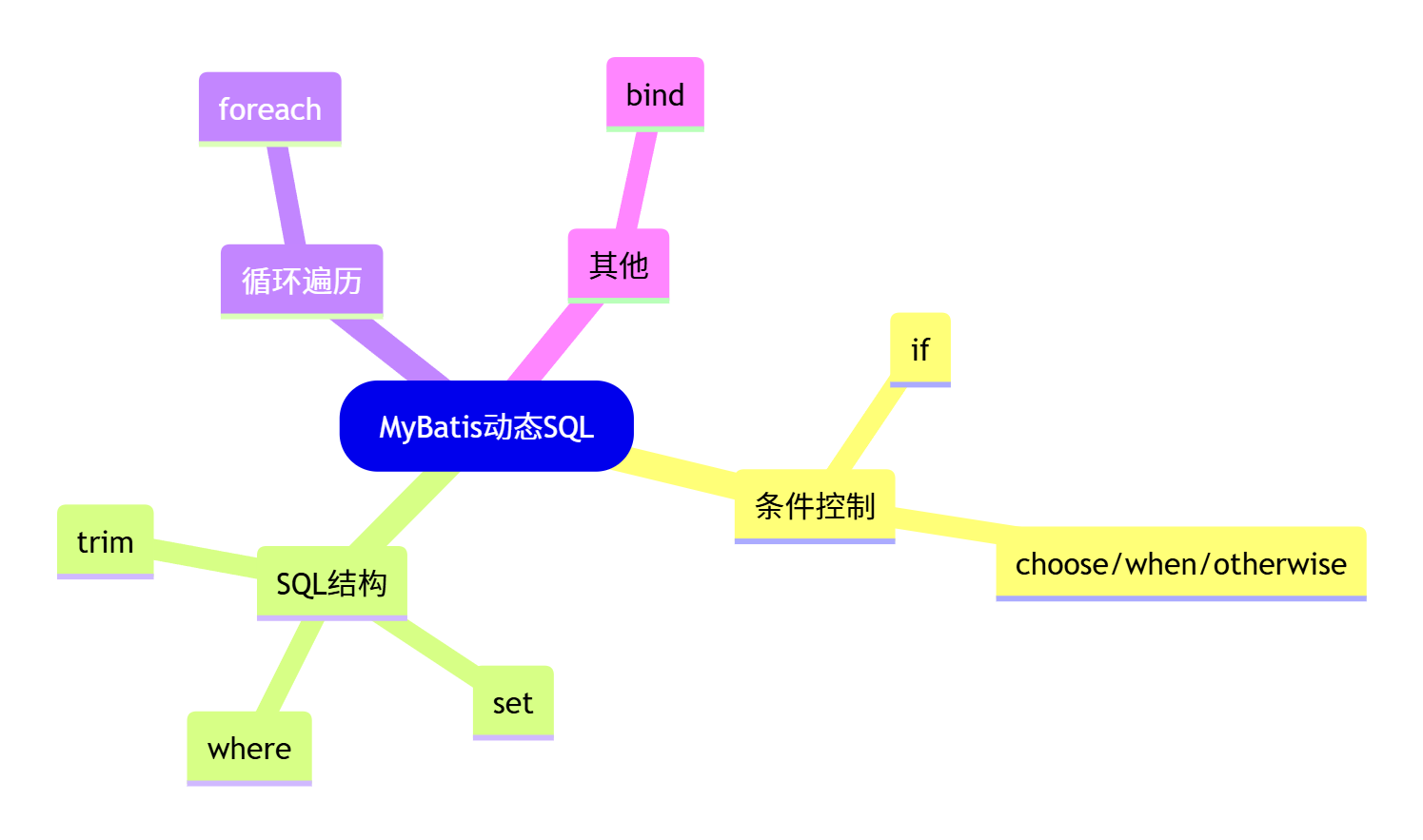
💡 动态 SQL 标签全景图
mindmap
root(MyBatis动态SQL)
条件控制
if
choose/when/otherwise
SQL结构
where
set
trim
循环遍历
foreach
其他
bind
🔥 1. if 标签:条件分支
应用场景:多条件查询
SELECT * FROM users AND name LIKE #{name} AND email = #{email} AND status = #{status} 输入参数:{name: "张", status: 1}
生成 SQL:
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE name LIKE ? AND status = ?
🔀 2. choose/when/otherwise:多路选择
应用场景:优先级条件查询
SELECT * FROM users id = #{id} email = #{email} status = 1 输入参数:{email: "test@example.com"}
生成 SQL:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?
🎯 3. where 标签:智能 WHERE 子句
解决痛点:自动处理 AND/OR 和空条件
SELECT * FROM users name = #{name} AND email = #{email} 输入参数:{name: null, email: "test@example.com"}
生成 SQL:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE email = ?
🔄 4. set 标签:智能 UPDATE
应用场景:动态更新字段
UPDATE users name = #{name}, email = #{email}, status = #{status}, WHERE id = #{id} 输入参数:{id: 1, name: "张三"}
生成 SQL:
UPDATE users SET name = ? WHERE id = ?
🔁 5. foreach 标签:循环遍历
应用场景:批量操作和 IN 查询
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id IN #{id} 输入参数:{ids: [1, 2, 3, 5, 8]}
生成 SQL:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE id IN (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
🎨 6. trim 标签:自定义修剪
应用场景:更精细的字符串处理
UPDATE users name = #{name}, email = #{email}, WHERE id = #{id} 💡 三、最佳实践指南 💡 可维护性设计原则 graph TD A[可维护性] --> B[单一职责] A --> C[清晰命名] A --> D[避免嵌套过深] A --> E[适当注释]
style B fill:#9f9,stroke:#333
style C fill:#9f9,stroke:#333🛡️ 1. 避免冗余条件
不推荐:
AND name = #{name} AND email = #{email} 推荐: name = #{condition.name} email = #{condition.email} 📝 2. 保持 SQL 可读性 复杂动态 SQL 示例: /* 用户综合查询 */ SELECT * FROM users AND (name LIKE #{name} OR nick_name LIKE #{name})
<!-- 状态条件 -->
<if test="statusList != null and statusList.size() > 0">
AND status IN
<foreach item="status" collection="statusList"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{status}
</foreach>
</if>
<!-- 时间范围 -->
<if test="startTime != null and endTime != null">
AND create_time BETWEEN #{startTime} AND #{endTime}
</if>ORDER BY id DESC ⚠️ 四、常见陷阱与优化 💡 性能与安全对比 | 问题类型 | 问题描述 | 解决方案 | |---------|---------|---------| | **条件缺失** | 所有if条件都不满足,SQL语法错误 | 使用``标签 | | **SQL注入** | 不当使用`${}`导致注入风险 | 始终优先使用`#{}` | | **性能问题** | `foreach`批量过大导致SQL过长 | 分批处理,每批1000条 | | **空集合** | 空集合在`foreach`中导致SQL错误 | 先判断集合是否为空 | 🔧 1. 空条件处理 问题代码: SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = #{name} AND email = #{email} 当所有if都不满足时生成:
SELECT * FROM users WHERE
修复方案:
SELECT * FROM users name = #{name} AND email = #{email} ⚡ 2. foreach 性能优化 批量插入优化: INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES (#{user.name}, #{user.email}) 风险:一次插入10000条数据会导致SQL过长
解决方案:分批处理
// 服务层分批处理
public void batchInsert(List users) {
int batchSize = 1000;
for (int i = 0; i < users.size(); i += batchSize) {
List batch = users.subList(i, Math.min(i + batchSize, users.size()));
userMapper.batchInsertUsers(batch);
}
}
🛡️ 3. SQL 注入防护
危险用法(绝对避免!):
SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY {orderBy} {orderDirection} 安全用法: SELECT * FROM users ORDER BY name email id DESC ASC # 🚀 五、实战业务场景 ## 💡 电商平台商品查询
xml
<select id="searchProducts" resultType="Product">
SELECT * FROM products
<where>
<!-- 关键词搜索 -->
<if test="keyword != null">
AND (name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{keyword}, '%')
OR description LIKE CONCAT('%', #{keyword}, '%'))
</if>
<!-- 价格范围 -->
<if test="minPrice != null">
AND price >= #{minPrice}
</if>
<if test="maxPrice != null">
AND price <= #{maxPrice}
</if>
<!-- 类目筛选 -->
<if test="categoryIds != null and categoryIds.size() > 0">
AND category_id IN
<foreach item="categoryId" collection="categoryIds"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{categoryId}
</foreach>
</if>
<!-- 商品状态 -->
<if test="status != null">
AND status = #{status}
</if>
</where>
ORDER BY
<choose>
<when test="sortBy == 'price'">price</when>
<when test="sortBy == 'sales'">sales_count</when>
<otherwise>create_time</otherwise>
</choose>
<choose>
<when test="sortOrder == 'desc'">DESC</when>
<otherwise>ASC</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>🔍 执行流程全景
客户端 Mapper接口 动态SQL引擎 数据库 调用查询方法(参数) 解析动态SQL 应用if/where/foreach 发送最终SQL 返回结果 结果映射 返回业务对象 客户端 Mapper接口 动态SQL引擎 数据库
🔚 总结与延伸
📚 核心要点回顾
1.if/choose:条件分支控制
2.where/set:智能SQL结构处理
3.foreach:循环遍历操作
安全第一:始终优先使用#{}
5.性能优化:批量操作分批处理