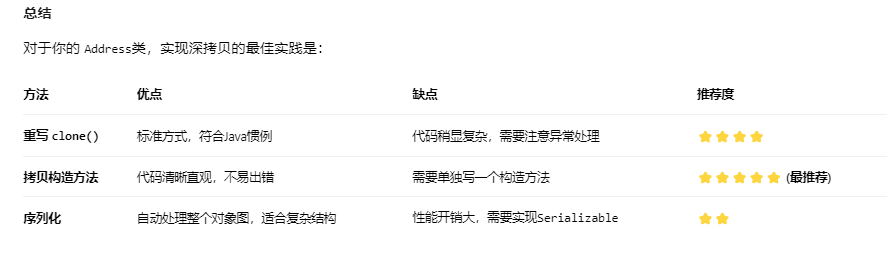
方法一:重写 clone()方法实现深拷贝(经典方式)
bash
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Address implements Cloneable {
private List<String> citys;
public Address(List<String> citys) {
this.citys = citys;
}
// Getter
public List<String> getCitys() {
return citys;
}
/**
* 重写clone()方法以实现深拷贝
*/
@Override
public Address clone() {
try {
// 1. 先调用super.clone()进行浅拷贝,得到一个新Address对象
Address cloned = (Address) super.clone();
// 2. 关键:对可变引用字段citys进行深拷贝
// 创建一个新的ArrayList,并将原list中的所有元素复制进去
if (this.citys != null) {
cloned.citys = new ArrayList<>(this.citys); // 深拷贝的核心代码
} else {
cloned.citys = null;
}
// 3. 返回深拷贝后的对象
return cloned;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
// Cloneable已实现,理论上不会发生,抛出运行时异常
throw new AssertionError(e);
}
}
}关键点分析:
- new ArrayList<>(this.citys):这是实现深拷贝的核心。这个ArrayList的构造方法会创建一个新的List对象,并将原citys列表中的所有元素拷贝到新列表中。
- 由于列表中的元素是String(不可变对象),所以只需拷贝列表结构本身即可。如果元素也是可变对象,则需要递归地对每个元素进行深拷贝。
方法二:使用拷贝构造方法(更推荐)
这种方式通常被认为比clone()更清晰、更安全,也是Effective Java中推荐的方式。
bash
class Address {
private List<String> citys;
public Address(List<String> citys) {
this.citys = citys;
}
/**
* 深拷贝构造方法
* @param other 要被拷贝的原始对象
*/
public Address(Address other) {
if (other != null) {
if (other.citys != null) {
// 创建新的List,拷贝所有元素
this.citys = new ArrayList<>(other.citys); // 深拷贝核心
} else {
this.citys = null;
}
}
}
public List<String> getCitys() {
return citys;
}
}方法三:使用序列化(适用于复杂对象图)
如果对象结构非常复杂,手动实现深拷贝会很繁琐。可以通过序列化(内存中)来实现深拷贝,但要求类实现 java.io.Serializable接口。
bash
import java.io.*;
class Address implements Serializable { // 1. 实现Serializable接口
private List<String> citys;
// ... 构造方法、getter ...
/**
* 通过序列化实现深拷贝
*/
public Address deepCopy() {
try (ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(bos)) {
// 将对象写入字节数组输出流
oos.writeObject(this);
oos.flush();
try (ByteArrayInputStream bis = new ByteArrayInputStream(bos.toByteArray());
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis)) {
// 从字节数组输入流中读出新的对象
return (Address) ois.readObject();
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Deep copy failed", e);
}
}
}