flume拓扑结构详解:从简单串联到复杂聚合的完整指南
Flume 作为分布式数据采集工具,其拓扑结构直接决定了数据流转的效率、可靠性和扩展性。官网定义了三种核心拓扑结构:简单串联 、复制与多路复用 、聚合,分别适用于不同的业务场景。本文将深入解析每种拓扑的原理、配置方法及适用场景,帮助你根据需求设计最优的数据采集链路。
拓扑结构概述
Flume 拓扑结构通过 Agent 串联 、组件复用 和 流量分配 实现数据的灵活流转。核心组件关系如下:
- Agent:Flume 的基本单位,包含 Source、Channel、Sink;
- 数据流:数据从 Source 产生,经 Channel 缓冲,由 Sink 发送到下一个目的地(可以是另一个 Agent 的 Source 或存储系统)。
三种拓扑结构的核心差异在于 Agent 之间的连接方式 和 数据分配策略。
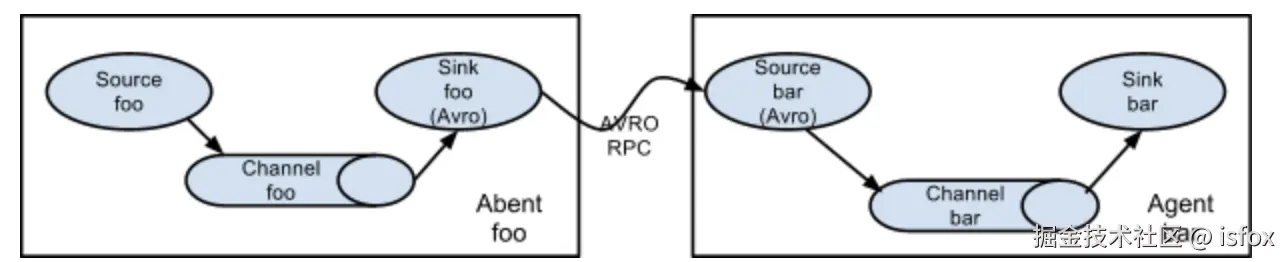
简单串联
数据从第一个 Agent 的 Source 流入,经 Sink 发送到第二个 Agent 的 Source,依次传递,最终写入目标存储(如 HDFS、Kafka)。
适用场景
- 跨网络数据传输:当数据源与目标存储不在同一网络(如边缘节点到中心集群),通过多 Agent 转发跨越网络边界;
- 分步处理:每级 Agent 负责不同的数据处理(如 Agent1 采集、Agent2 清洗、Agent3 存储)。
配置示例
以 "文件采集 → 中间转发 → HDFS 存储" 的三级串联为例:
Agent1(数据源采集)
properties
# Agent1:从文件采集数据,发送到 Agent2 的 Avro Source
agent1.sources = execSource
agent1.channels = memoryChannel
agent1.sinks = avroSink
# Source:监控本地文件
agent1.sources.execSource.type = exec
agent1.sources.execSource.command = tail -F /var/log/app.log
# Sink:发送到 Agent2 的 Avro 端口(如 41414)
agent1.sinks.avroSink.type = avro
agent1.sinks.avroSink.hostname = agent2.example.com
agent1.sinks.avroSink.port = 41414
# 绑定关系
agent1.sources.execSource.channels = memoryChannel
agent1.sinks.avroSink.channel = memoryChannel Agent2(中间转发)
properties
# Agent2:接收 Agent1 数据,转发到 Agent3
agent2.sources = avroSource
agent2.channels = memoryChannel
agent2.sinks = avroSink
# Source:监听 Avro 端口 41414
agent2.sources.avroSource.type = avro
agent2.sources.avroSource.bind = 0.0.0.0
agent2.sources.avroSource.port = 41414
# Sink:转发到 Agent3 的 Avro 端口 41415
agent2.sinks.avroSink.type = avro
agent2.sinks.avroSink.hostname = agent3.example.com
agent2.sinks.avroSink.port = 41415
# 绑定关系
agent2.sources.avroSource.channels = memoryChannel
agent2.sinks.avroSink.channel = memoryChannel Agent3(目标存储)
properties
# Agent3:接收 Agent2 数据,写入 HDFS
agent3.sources = avroSource
agent3.channels = fileChannel
agent3.sinks = hdfsSink
# Source:监听 Avro 端口 41415
agent3.sources.avroSource.type = avro
agent3.sources.avroSource.bind = 0.0.0.0
agent3.sources.avroSource.port = 41415
# Sink:写入 HDFS
agent3.sinks.hdfsSink.type = hdfs
agent3.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.path = hdfs://cluster/flume/logs/%Y%m%d
# 绑定关系
agent3.sources.avroSource.channels = fileChannel
agent3.sinks.hdfsSink.channel = fileChannel 优缺点与注意事项
- 优点:结构简单,易于配置和调试;
- 缺点:单点故障风险高(任一 Agent 宕机导致整条链路中断),延迟累积;
- 建议 :
- 核心链路使用
File Channel替代Memory Channel,避免数据丢失; - 每级 Agent 配置监控告警,及时发现故障。
- 核心链路使用
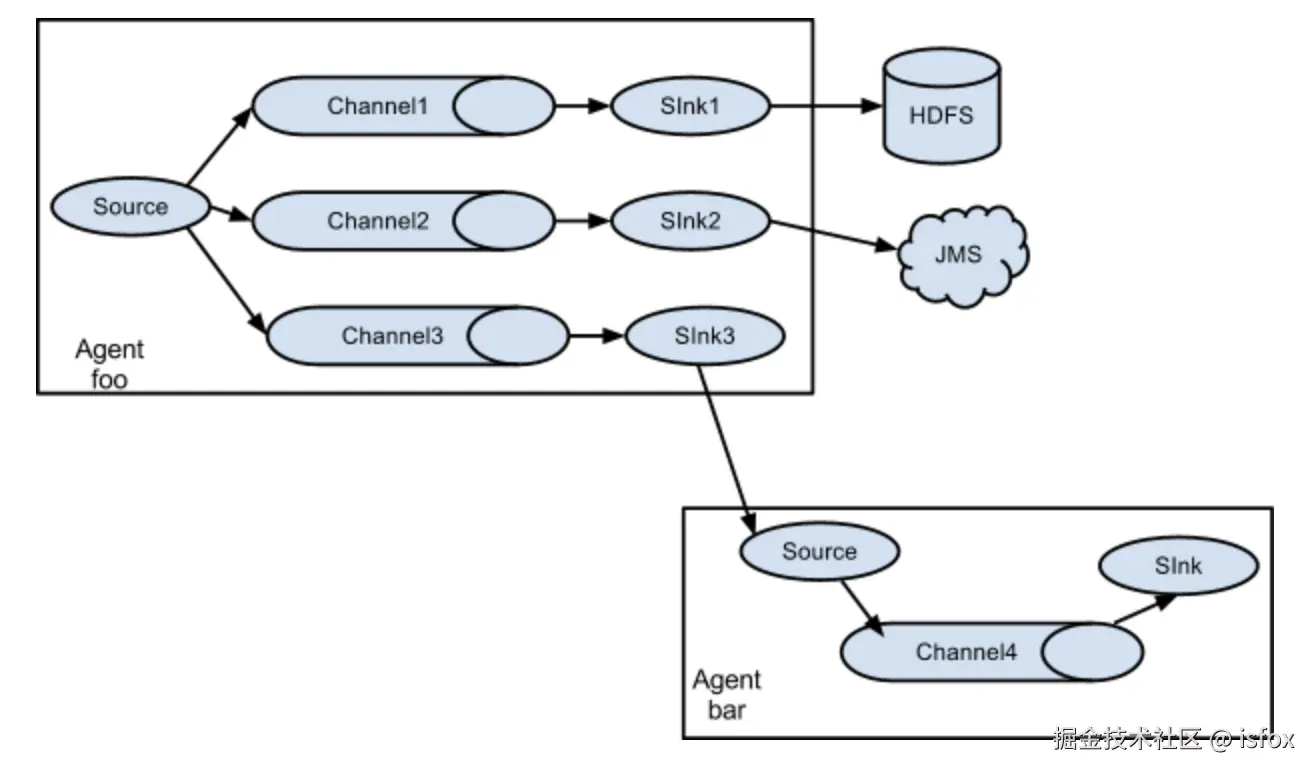
复制和多路复用
该拓扑通过一个 Source 连接多个 Channel 和 Sink,实现数据的复制分发 或按条件路由,满足 "一份数据多目标存储" 的需求。
结构原理
- 复制(Replication):同一份数据发送到所有 Sink(如同时写入 HDFS 和 Kafka);
- 多路复用(Multiplexing):根据 Event 的 Header 信息路由到不同 Sink(如按日志级别分发给不同存储)。
适用场景
- 数据多副本存储:一份数据同时写入 HDFS(归档)和 Kafka(实时分析);
- 数据分类处理:按数据类型(如用户日志、系统日志)路由到不同存储或处理链路。
配置示例
1. 复制模式(同一份数据多目标存储)
properties
# Agent:将数据同时写入 HDFS 和 Kafka
agent.sources = tailSource
agent.channels = hdfsChannel kafkaChannel
agent.sinks = hdfsSink kafkaSink
# Source:监控日志文件
agent.sources.tailSource.type = exec
agent.sources.tailSource.command = tail -F /var/log/app.log
# 复制模式:数据发送到所有 Channel
agent.sources.tailSource.channels = hdfsChannel kafkaChannel
# Sink1:写入 HDFS
agent.sinks.hdfsSink.type = hdfs
agent.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.path = hdfs://cluster/logs/
agent.sinks.hdfsSink.channel = hdfsChannel
# Sink2:写入 Kafka
agent.sinks.kafkaSink.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink
agent.sinks.kafkaSink.kafka.topic = app-logs
agent.sinks.kafkaSink.channel = kafkaChannel
# 配置 Channels
agent.channels.hdfsChannel.type = file
agent.channels.kafkaChannel.type = memory 2. 多路复用模式(按条件路由)
结合自定义拦截器添加 Header,按 log_type 字段路由到不同 Sink:
properties
# Agent:按日志类型路由到 HDFS 或 Kafka
agent.sources = tailSource
agent.channels = hdfsChannel kafkaChannel
agent.sinks = hdfsSink kafkaSink
# Source:配置拦截器添加 log_type 头信息
agent.sources.tailSource.type = exec
agent.sources.tailSource.command = tail -F /var/log/app.log
agent.sources.tailSource.interceptors = typeInterceptor
agent.sources.tailSource.interceptors.typeInterceptor.type = com.example.TypeInterceptor$Builder
# 多路复用:按 Header 中的 log_type 路由
agent.sources.tailSource.selector.type = multiplexing
agent.sources.tailSource.selector.header = log_type # 路由依据的 Header 字段
agent.sources.tailSource.selector.mapping.user = hdfsChannel # log_type=user → HDFS
agent.sources.tailSource.selector.mapping.system = kafkaChannel # log_type=system → Kafka
# Sink 与 Channel 绑定(同复制模式)
# ...(省略 HDFS Sink 和 Kafka Sink 配置) 优缺点与注意事项
- 优点:灵活满足多目标存储需求,无需重复采集数据;
- 缺点:资源消耗较高(多 Channel 和 Sink 占用更多内存 / CPU);
- 建议 :
- 复制模式下确保各 Sink 性能匹配,避免某一 Sink 拖慢整体链路;
- 多路复用通过拦截器精准分类,减少无效数据传输。
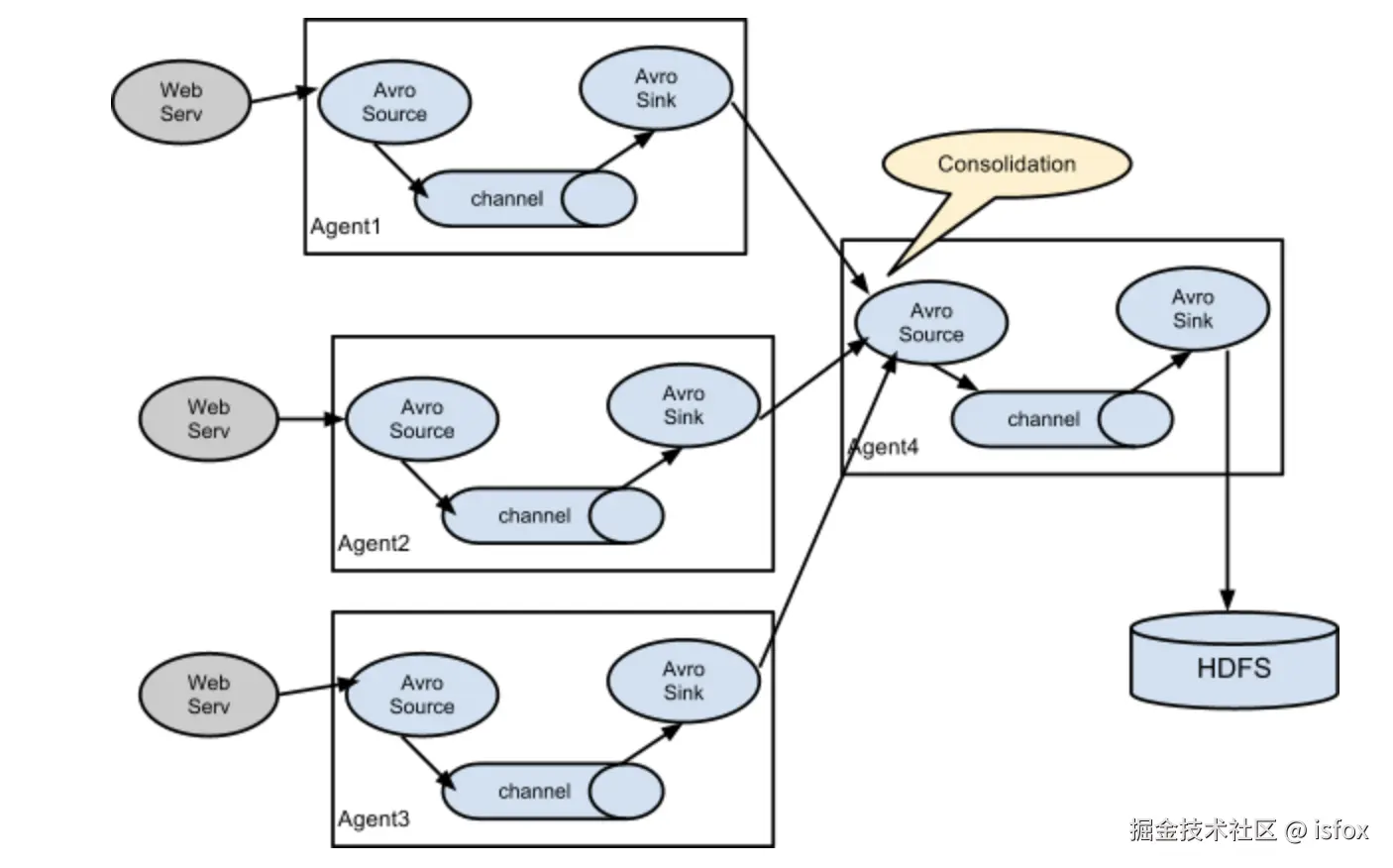
聚合
该拓扑通过多个 Agent 采集数据,汇总到一个或多个中心 Agent 处理,适用于 "分布式数据源 → 集中存储" 的场景。
结构原理
边缘节点的 Agent 采集本地数据,发送到中心 Agent,由中心 Agent 统一写入目标存储,实现数据聚合。
适用场景
- 大规模集群日志采集:从数百台服务器采集日志,汇总到中心集群处理;
- 区域数据汇总:不同机房或区域的数据源汇总到统一存储。
配置示例
以 "3 个边缘 Agent 采集日志 → 1 个中心 Agent 聚合写入 HDFS" 为例:
边缘 Agent(如 Agent1)
properties
# 边缘 Agent1:采集本地日志,发送到中心 Agent
agent1.sources = execSource
agent1.channels = memoryChannel
agent1.sinks = avroSink
# Source:监控本地日志
agent1.sources.execSource.type = exec
agent1.sources.execSource.command = tail -F /var/log/server1.log
# Sink:发送到中心 Agent 的 Avro 端口
agent1.sinks.avroSink.type = avro
agent1.sinks.avroSink.hostname = central-agent.example.com
agent1.sinks.avroSink.port = 41414
# 绑定关系
agent1.sources.execSource.channels = memoryChannel
agent1.sinks.avroSink.channel = memoryChannel 中心 Agent(聚合写入 HDFS)
properties
# 中心 Agent:接收多个边缘 Agent 数据,写入 HDFS
central.sources = avroSource
central.channels = fileChannel
central.sinks = hdfsSink
# Source:监听 Avro 端口,接收所有边缘 Agent 数据
central.sources.avroSource.type = avro
central.sources.avroSource.bind = 0.0.0.0
central.sources.avroSource.port = 41414
# 支持高并发:增加工作线程数
central.sources.avroSource.threads = 20
# Sink:聚合写入 HDFS
central.sinks.hdfsSink.type = hdfs
central.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.path = hdfs://cluster/aggregated-logs/%Y%m%d/
central.sinks.hdfsSink.hdfs.filePrefix = aggregated-
# 通道:使用 File Channel 确保可靠性
central.channels.fileChannel.type = file
central.channels.fileChannel.checkpointDir = /var/flume/checkpoint
central.channels.fileChannel.dataDirs = /var/flume/data
# 绑定关系
central.sources.avroSource.channels = fileChannel
central.sinks.hdfsSink.channel = fileChannel 优缺点与注意事项
- 优点:集中管理数据链路,降低边缘节点配置复杂度;
- 缺点:中心 Agent 可能成为性能瓶颈,需做好扩容;
- 建议 :
- 中心 Agent 使用
File Channel和多线程 Source(threads参数)提升吞吐量; - 边缘 Agent 配置故障重试机制,避免数据丢失;
- 中心 Agent 部署多个实例,结合负载均衡(如 DNS 轮询)分散压力。
- 中心 Agent 使用
拓扑结构对比与选择建议
| 拓扑结构 | 核心优势 | 局限性 | 最佳实践场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 简单串联 | 配置简单,支持分步处理 | 单点故障风险高,延迟累积 | 跨网络传输、分步清洗链路 |
| 复制 / 多路复用 | 数据多目标分发,灵活路由 | 资源消耗高,需平衡各 Sink 性能 | 数据多副本存储、按类型分类处理 |
| 聚合 | 分布式数据源集中管理 | 中心 Agent 可能成瓶颈,需扩容 | 大规模集群日志采集、区域数据汇总 |
参考文献