一、HFE是什么
HFE(Hash Field Expire) 是valkey9.0最新引入的一个新特性,支持hash类型的字段设置过期时间。
在valkey的设计中,过期时间都是针对key的,为了兼容以及性能等诸多因素,引入了很多新的数据结构以及新的命令。
二、老版本hash类型的expire逻辑
以HSET和EXPIRE为例子
bash
HSET key field value [ field value ... ]
EXPIRE key seconds [ NX | XX | GT | LT ]2.1 valkey8.0的expire逻辑
hset
bash
$ ./valkey-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET htest name zhangsan age 18调用栈
main
|-> aeMain
|-> aeProcessEvents
|-> connSocketEventHandler
|-> callHandler
|-> readQueryFromClient
|-> processInputBuffer
|-> processCommandAndRestClient
|-> processCommand
|-> call
|-> hsetCommand
c
void hsetCommand(client *c) {
...
robj *o;
// 检查key是否存在,不存在则创建
if ((o = hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(c, c->argv[1])) == NULL) return;
// 判断是否需要object从listpack转换成hashtable,满足条件则转换
hashTypeTryConversion(o, c->argv, 2, c->argc - 1);
// 添加field/value
for (i = 2; i < c->argc; i += 2) created += !hashTypeSet(o, c->argv[i]->ptr, c->argv[i + 1]->ptr, HASH_SET_COPY);
...
}检查key是否存在,不存在则创建并插入hashtable
c
robj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(client *c, robj *key) {
robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db, key);
if (checkType(c, o, OBJ_HASH)) return NULL;
if (o == NULL) {
o = createHashObject();
dbAdd(c->db, key, o);
}
return o;
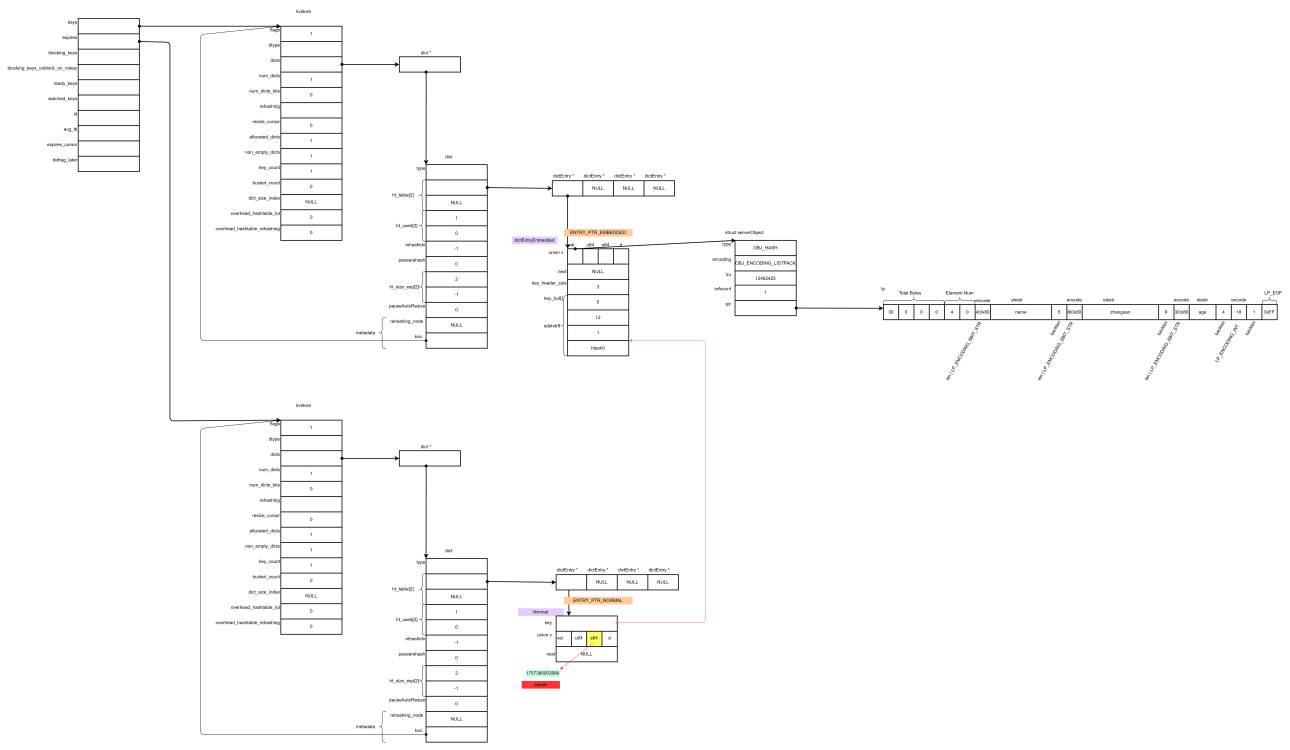
}当前key并不存在,因此调用createHashObject创建robj, 默认创建的robj是listpack结构。
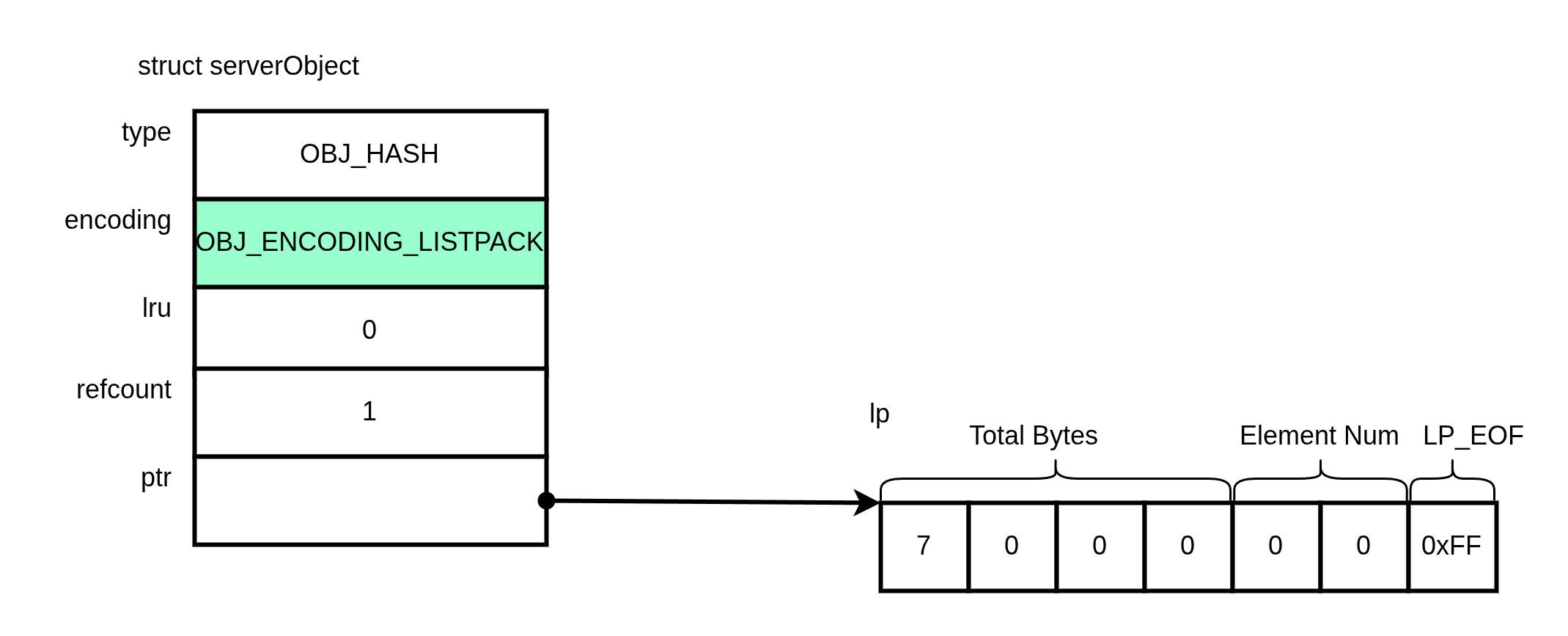
然后调用dbAdd将此robj插入到hashtable中。
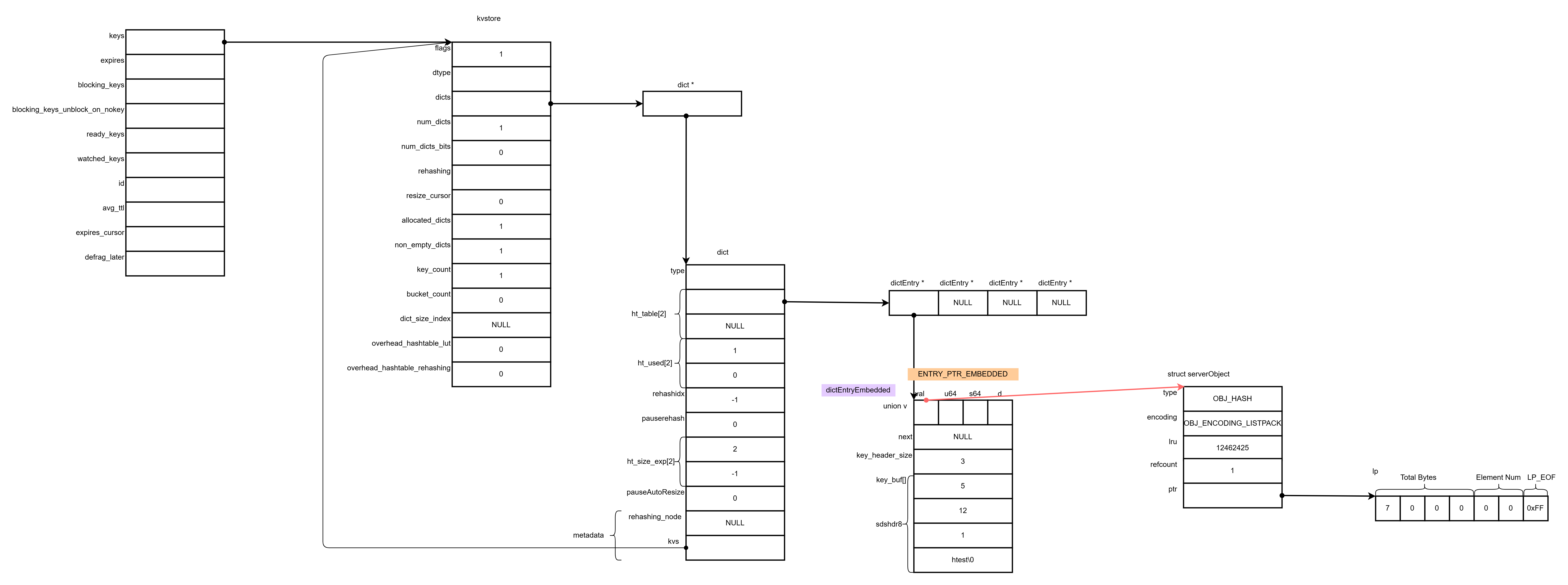
hsetCommand
|-> hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate
| |-> dbAdd
| |-> dbAddInternal
| |-> kvstoreDictAddRaw
| |-> dictAddRaw
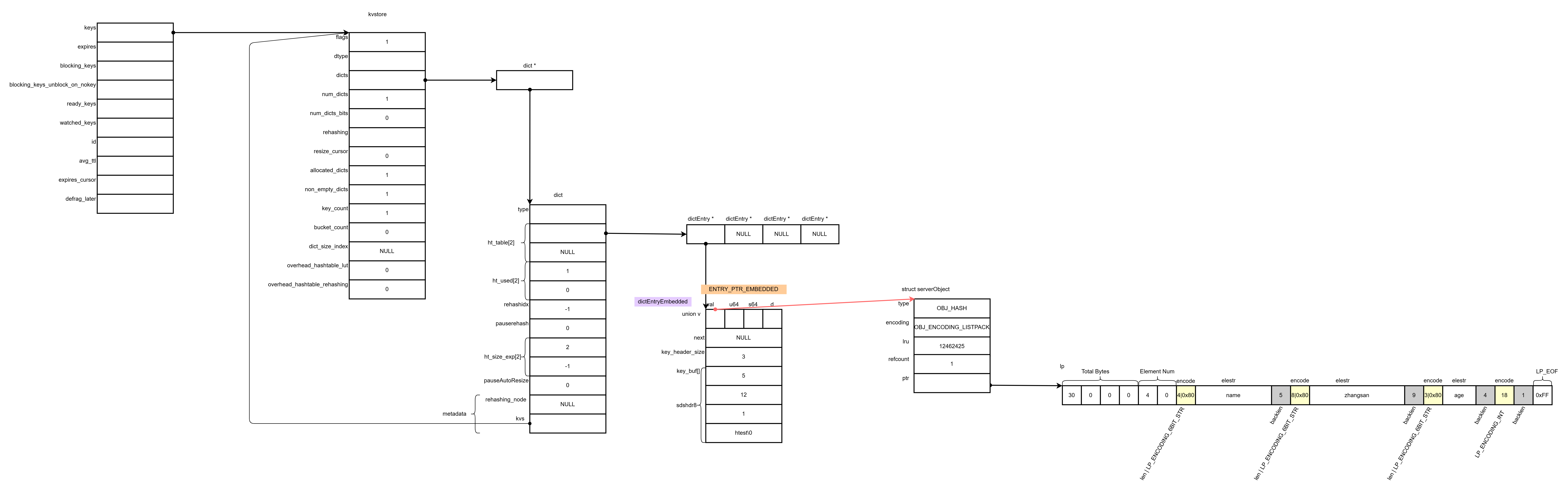
|-> int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, int flags) 最后调用hashTypeSet将field/value插入到robj中,此处插入listpack结构中。
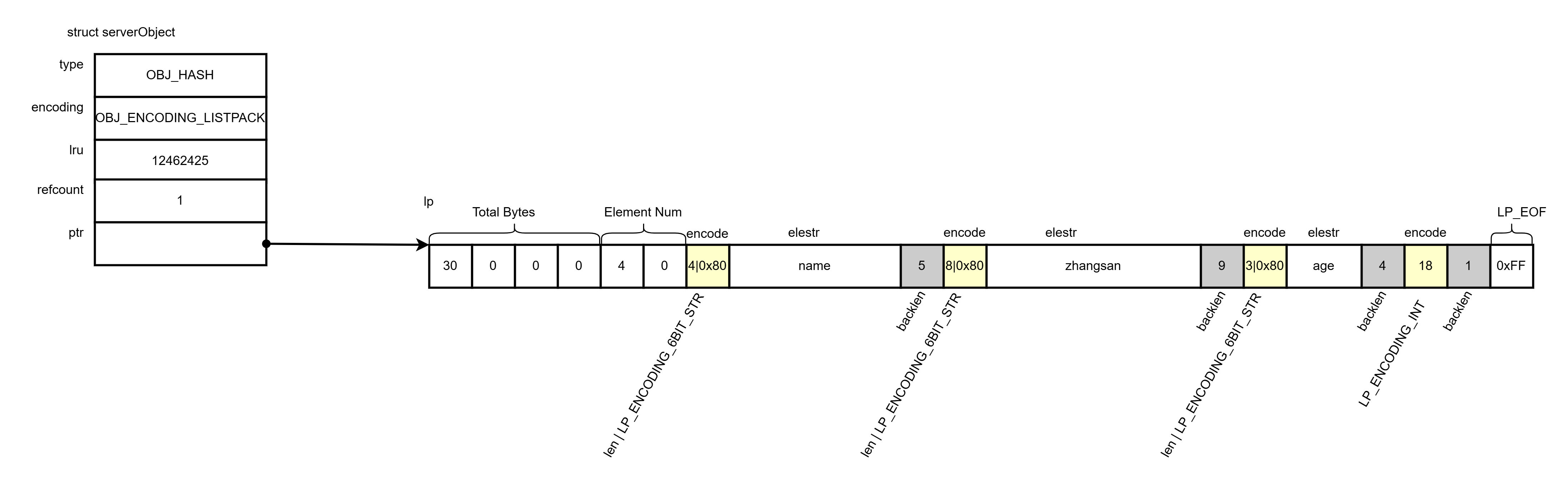
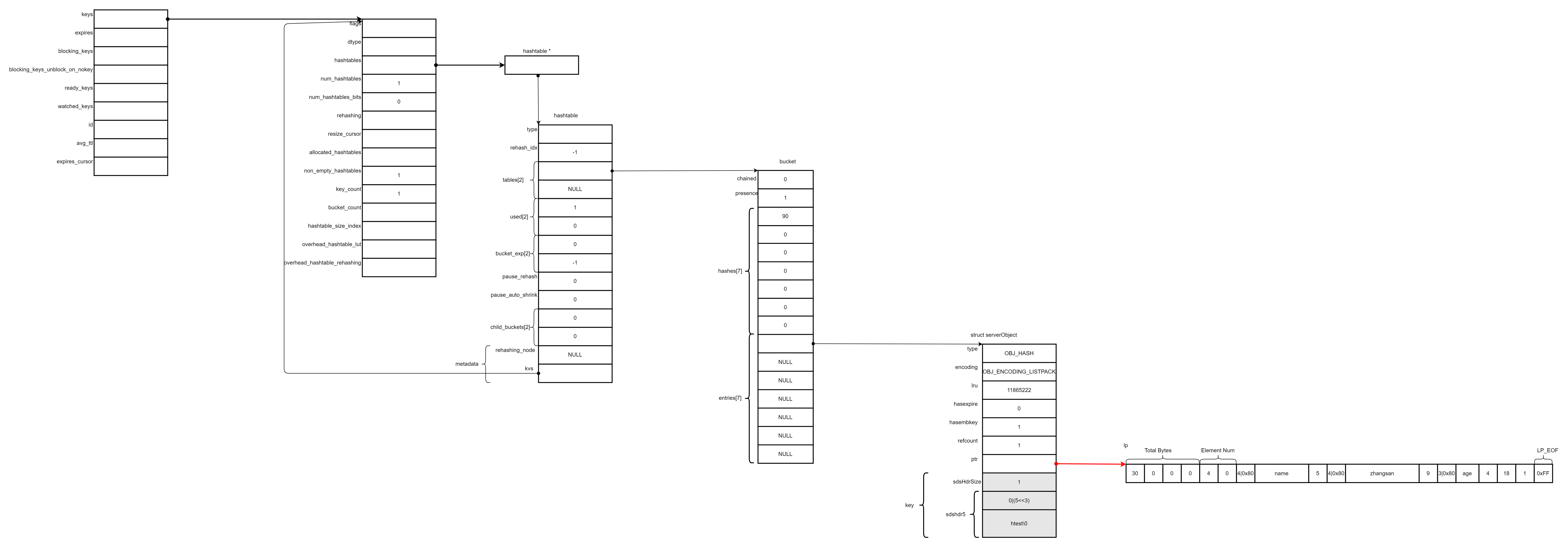
hset命令执行完后,整个内存结构如下:
expire
127.0.0.1:6379> EXPIRE htest 3调用栈
expireCommand
|-> expireGenericCommand
|-> lookupKeyWrite
|-> setExpire
|-> kvstoreDictFind
|-> kvstoreDictAddRaw检查key是否存在
首先调用lookupKeyWrite判断key是否存在,不存在则设置结束,函数返回。否则调用setExpire进行过期时间的设置。
c
/* No key, return zero. */
if (lookupKeyWrite(c->db, key) == NULL) {
addReply(c, shared.czero);
return;
}将key插入expires字典中
setExpire函数第一步调用kvstoreDictFind根据key查找到对应的dictEntry, 然后使用dictEntry中的key对象调用kvstoreDictAddRaw插入到db->expires。
过期检查逻辑
hget 查询时检查
127.0.0.1:6379> hget htest name调用栈
hgetCommand
|-> lookupKeyReadOrReply
| |-> lookupKeyRead
| |-> lookupKeyReadWithFlags
| |-> lookupKey
| |-> dictEntry *de = dbFind(db, key->ptr);
| |-> val = dictGetVal(de);
| |-> expireIfNeeded
| |-> expireIfNeededWithDictIndex
| |-> keyIsExpiredWithDictIndex
| | |-> getExpireWithDictIndex
| | |-> de = dbFindExpiresWithDictIndex
| | |-> dictGetSignedIntegerVal(de)
| |-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex
| |-> dbGenericDeleteWithDictIndex
| |-> kvstoreDictTwoPhaseUnlinkFind
| |-> kvstoreDictDelete(db->expires, dict_index, key->ptr);
| |-> kvstoreDictTwoPhaseUnlinkFree(db->keys, dict_index, de, plink, table);
|-> addHashFieldToReply
|-> hashTypeGetValue- 首先通过key查找对应的dictEntry, 找到后将调用
expireIfNeeded进行过期检查。 - 如果未配置lazy_expire_disabled, 则调用
keyIsExpiredWithDictIndex判断是否过期 - 如果过期,则调用
deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex进行删除,从db->expires和db->keys中都删除 - 如果没有过期,则调用
addhashFieldToReply获取field值,然后响应
后台任务检查
调用栈
main
|-> aeMain
|-> aeProcessEvents
|-> processTimeEvents
|-> serverCron
|-> databasesCron
|-> activeExpireCycle
|-> kvstoreScan(db->expires, ...)
|-> dictScan
|-> dictScanDefrag
|-> expireScanCallback
|-> activeExpireCycleTryExpire
|-> dictGetSignedIntegerVal
|-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate
|-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex调用kvstoreScan扫描db->expires,最终依然会调用deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex进行过期key的删除。
2.2 valkey8.1的expire逻辑
以HSET和EXPIRE为例子
bash
HSET key field value [ field value ... ]
EXPIRE key seconds [ NX | XX | GT | LT ]hset
bash
$ ./valkey-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> hset htest name zhangsan age 18调用栈
readQueryFromClient
|-> processCommandAndResetClient
|-> processCommand
|-> call
|-> hsetCommand
|-> hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate
c
robj *hashTypeLookupWriteOrCreate(client *c, robj *key) {
robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db, key);
if (checkType(c, o, OBJ_HASH)) return NULL;
if (o == NULL) {
o = createHashObject();
dbAdd(c->db, key, &o);
}
return o;
}检查key是否存在,不存在则创建
当前key不存在,因此会调用createHashObject创建obj
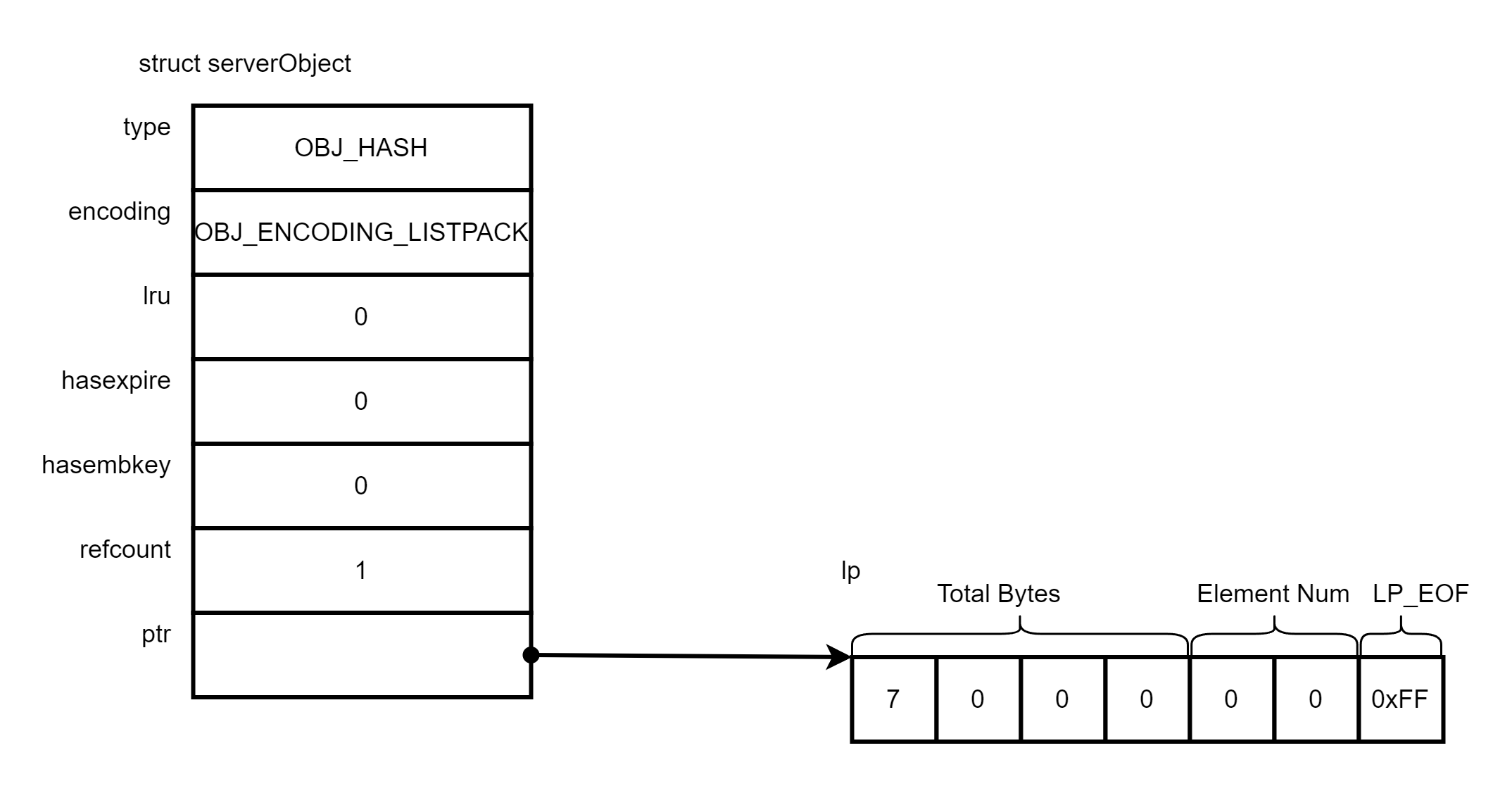
将新key插入到hashtable
然后调用dbAdd将key和obj插入到hash表中
dbAdd
|-> dbAddInternal
|-> objectSetKeyAndExpire
|-> kvstoreHashtableAdd
|-> hashtableAdd
|-> hashtableAddOrFind
|-> insert将key内嵌到object中
函数objectSetKeyAndExpire将重新创建object,将key和object进行内嵌,同时释放原先的object。
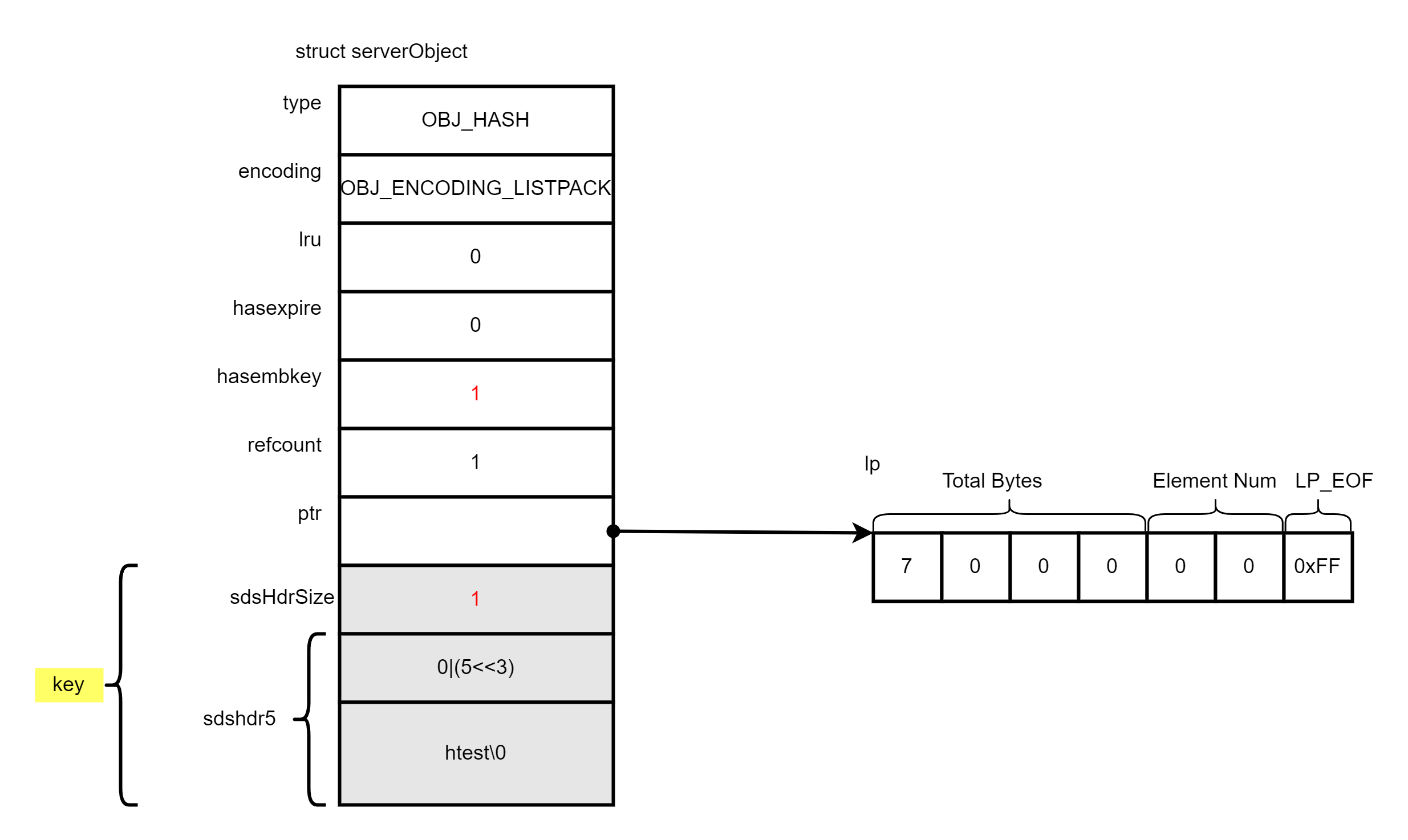
object插入hashtable
通过kvstoreHashtableAdd将object插入到hashtable中
将field/value插入object中
最后调用hashTypeSet将field/value插入到object中,当前object的value类型为ListPack。
expire
127.0.0.1:6379> EXPIRE htest 30调用栈
expireCommand
|-> expireGenericCommand
|-> lookupKeyWrite
|-> setExpire
|-> objectSetExpire
| |-> objectSetKeyAndExpire
| |-> createObjectWithKeyAndExpire
|-> kvstoreHashtableAdd- 调用
lookupKeyWrite函数,以确定key是否存在, 不存在则返回 - 存在则调用
setExpire将key添加到expire字典中, setExpire首先调用objectSetExpire将expire内嵌到object中,将新的object插入到expire hashtable中
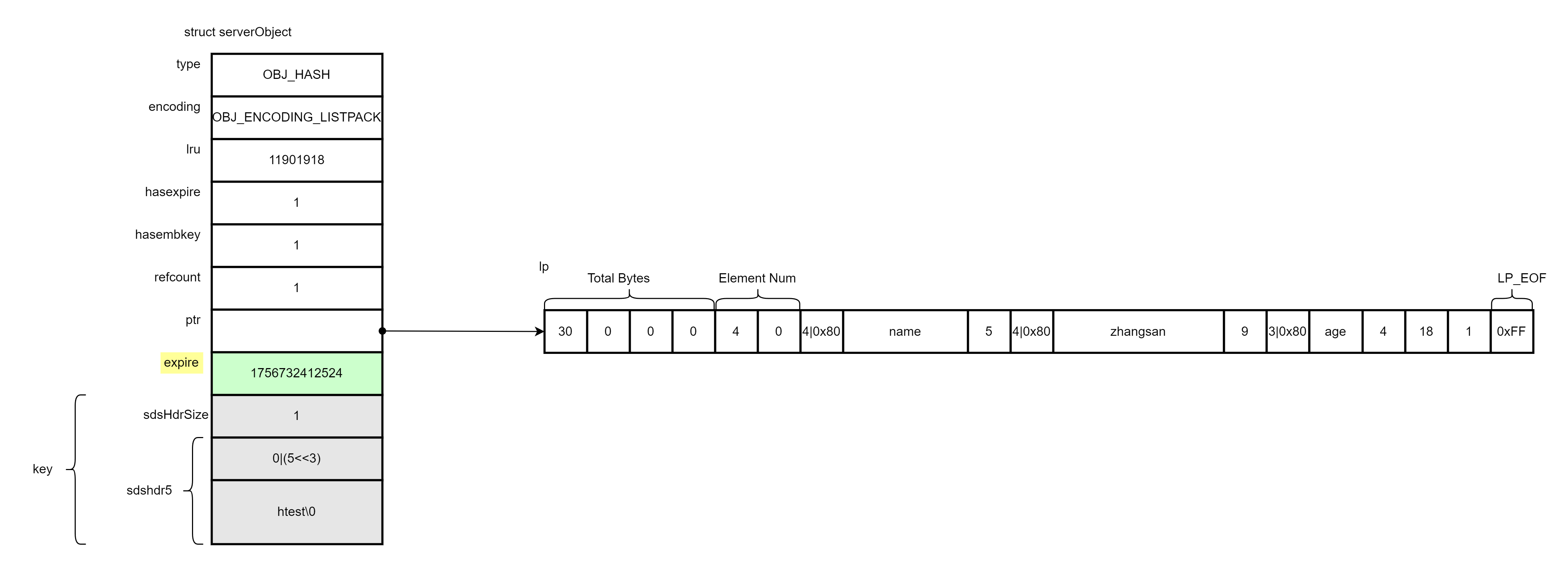
最后将新的object插入到expires字典中。
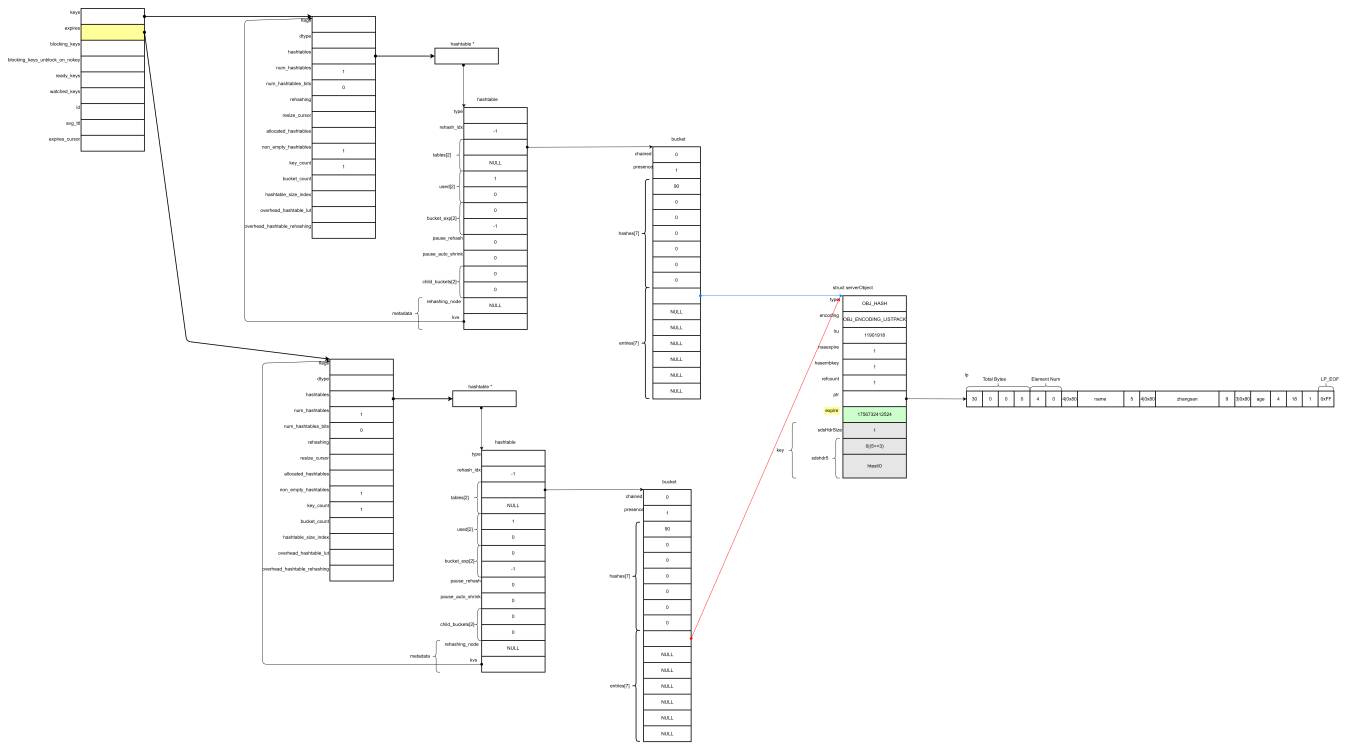
过期检查逻辑
hget 查询时检查
127.0.0.1:6379> hget htest name调用栈
hgetCommand
|-> lookupKeyReadOrReply
| |-> lookupKeyRead
| |-> lookupKeyReadWithFlags
| |-> lookupKey
| |-> val = dbFindWithDictIndex(db, key->ptr, dict_index)
| |-> expireIfNeededWithDictIndex
| |-> objectIsExpired(val)
| | |-> timestampIsExpired(objectGetExpire(val))
| |-> keyIsExpiredWithDictIndexImpl
| | |-> getExpireWithDictIndex
| | |-> when = getExpireWithDictIndex(db, key, dict_index)
| | | |-> val = dbFindExpiresWithDictIndex(db, key->ptr, dict_index)
| | | | |-> kvstoreHastableFind(db->expires, dict_index, key, &existing)
| | | |-> objectGetExpire(val)
| | |-> timestampIsExpired(when)
| |-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex
| |-> dbGenericDeleteWithDictIndex
| |-> kvstoreHashtableTwoPhasePopFindRef(db->keys, dict_index, key->ptr, &pos)
| |-> kvstoreHashtableTwoPhasePopDelete(db->keys, dict_index, &pos);
| |-> kvstoreHashtableDelete(db->expires, dict_index, key->ptr);
|-> addHashFieldToReply
|-> hashTypeGetValue当val存在时,直接调用objectIsExpired以判断是否过期,否则调用keyIsExpiredWithDictIndexImpl判断key是否过期,实际上两个分支最终都调用objectGetExpire获取过期时间,以判断是否过期。
c
long long objectGetExpire(const robj *val) {
if (val->hasexpire) {
unsigned char *data = (void *)(val + 1);
return *(long long *)data;
} else {
return -1;
}
}后台任务检查
调用栈
main
|-> aeMain
|-> aeProcessEvents
|-> processTimeEvents
|-> serverCron
|-> databasesCron
|-> activeExpireCycle
|-> kvstoreScan(db->expires, ...)
|-> hastableScan
|-> hashtableScanDefrag
|-> expireScanCallback
|-> activeExpireCycleTryExpire
|-> t = objectGetExpire(val)
|-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagate
|-> deleteExpiredKeyAndPropagateWithDictIndex整个流程和valkey8.0一致,稍微不同的是获取获取时间的方式不同,因为存储方式的改变。
三、新版HFE
为了兼容老版本,因此新增了一套相关的命令,hsetex,hgetex,hexpire,hexpireat,hpexpire,hpexpireat,hpersist,httl,hpttl,hexpiretime,hpexpiretime
以及相应的数据结构。
hsetex
bash
HSETEX key [NX] seconds field value [field value ...]和hset命令相似,只是多了seconds作为field的过期时间,看起来就像hset和expire命令的结合体。
bash
$ ./valkey-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> hsetex htest fnx ex 3 fields 2 name zhangsan age 18提取命令参数,并进行语法校验
c
void hsetexCommand(client *c) {
robj *o;
...
for (; fields_index < c->argc - 1; fields_index++) {
if (!strcasecmp(c->argv[fields_index]->ptr, "fields")) {
/* checking optional flags */
if (parseExtendedCommandArgumentsOrReply(c, &flags, &unit, &expire, &comparison, COMMAND_HSET, fields_index++) != C_OK) return;
if (getLongLongFromObjectOrReply(c, c->argv[fields_index++], &num_fields, NULL) != C_OK) return;
break;
}
}
/* Check that the parsed fields number matches the real provided number of fields */
if (!num_fields || num_fields != (c->argc - fields_index) / 2) {
addReplyError(c, "numfields should be greater than 0 and match the provided number of fields");
return;
}
...查询key, 并作校验
c
o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db, c->argv[1]);
if (checkType(c, o, OBJ_HASH))
return;如果不存在,则创建,并将key插入
c
if (o == NULL) {
o = createHashObject();
dbAdd(c->db, c->argv[1], &o);
}
和valkey8.1一样,可以看出valkey8.1就在为HFE特性做准备。
接下来将进行field/value的插入,此处将出现不同之处。
c
int hashTypeSet(robj *o, sds field, sds value, long long expiry, int flags);设置field/value的接口改变,增加了long long expire参数
c
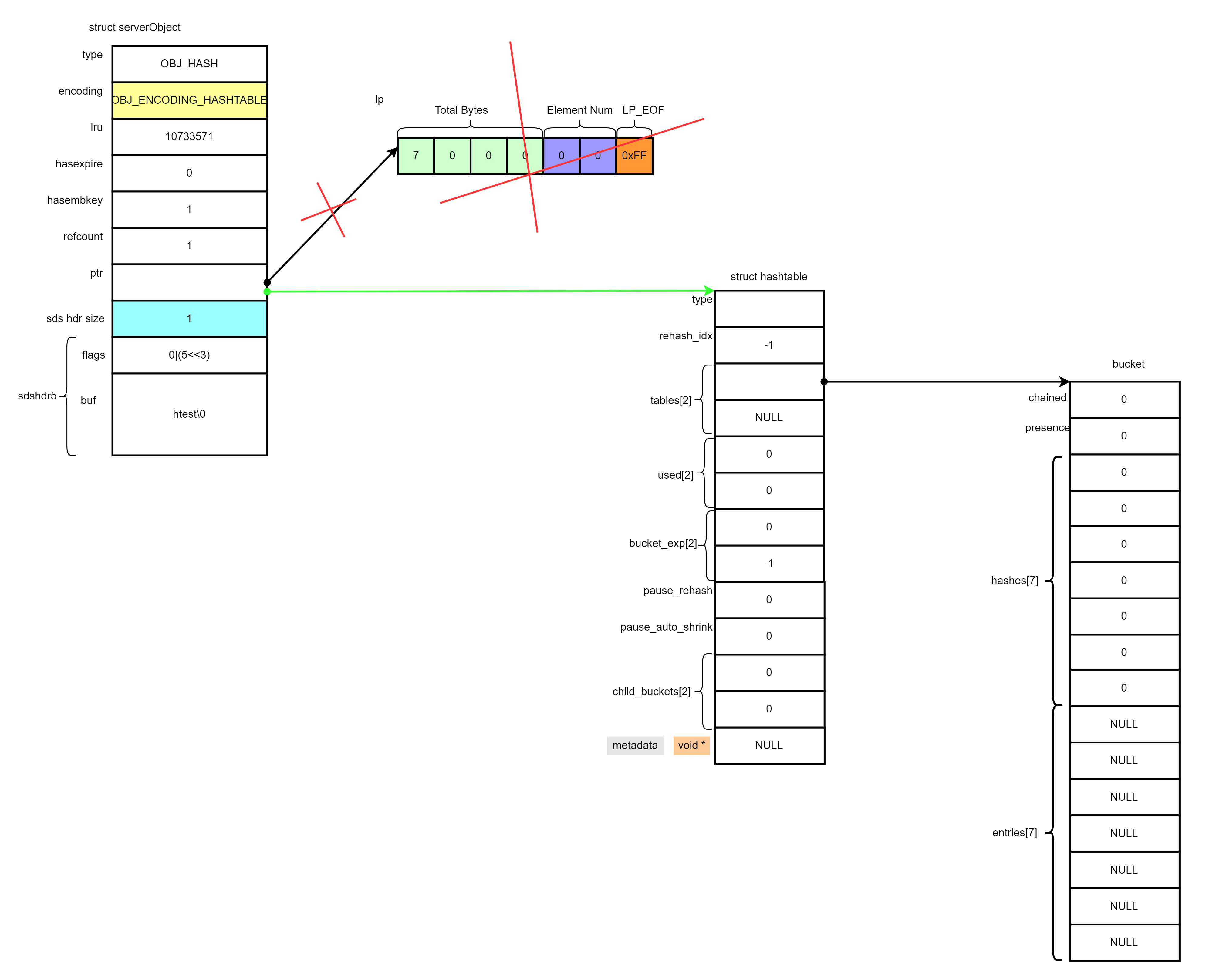
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_LISTPACK) {
if (expiry > 0 || sdslen(field) > server.hash_max_listpack_value || sdslen(value) > serve r.hash_max_listpack_value)
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HASHTABLE);
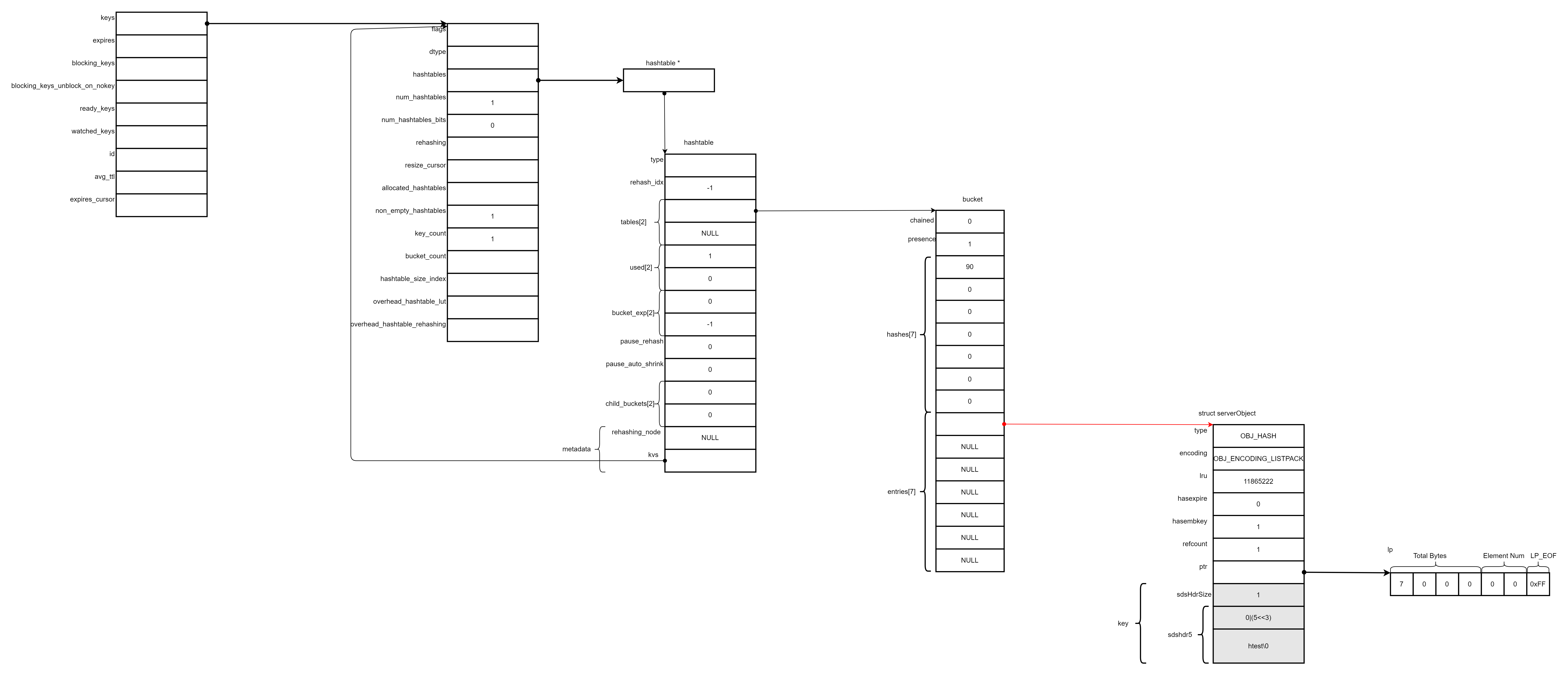
}可以看到,当expire大于0时,将编码从LISTPACK转换成HASTABLE。
因此这里一开始就从LISTPACK转换成HASTABLE。
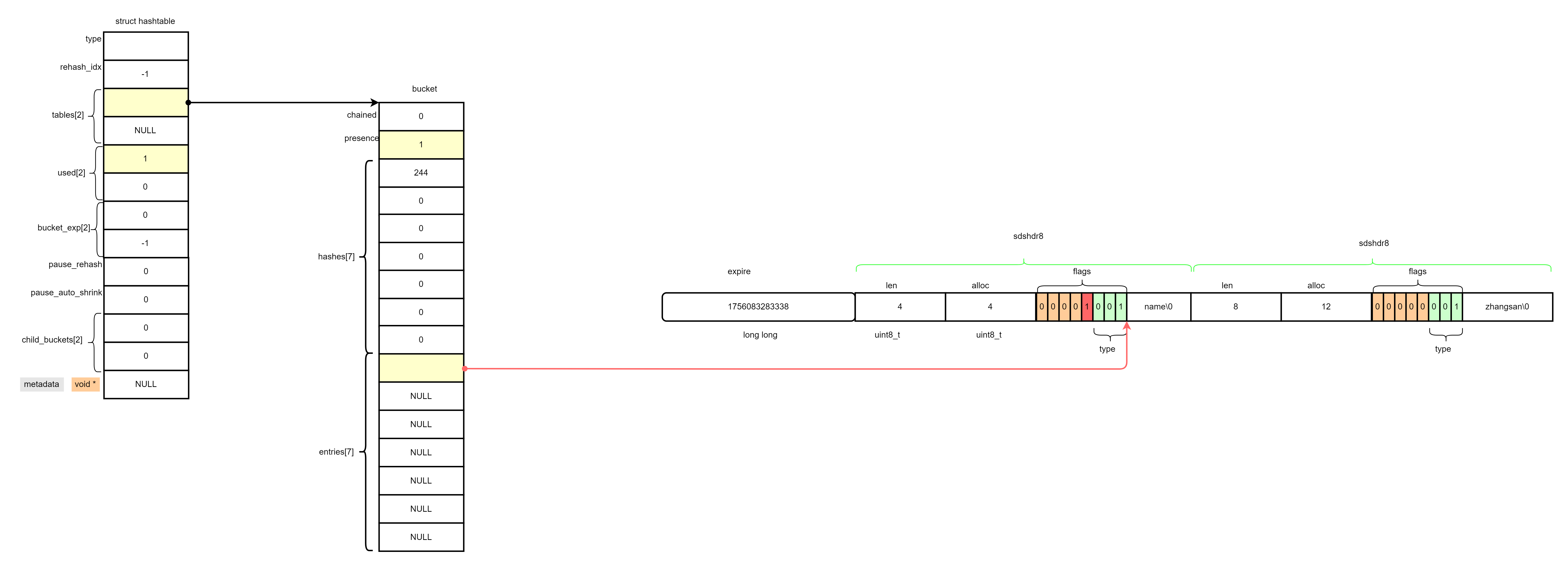
hashTypeConvert函数执行完后,o的内存结构如下图:
然后调用hashtableInsertAtPosition 将field/value插入hashtable中
将field/value创建成entry
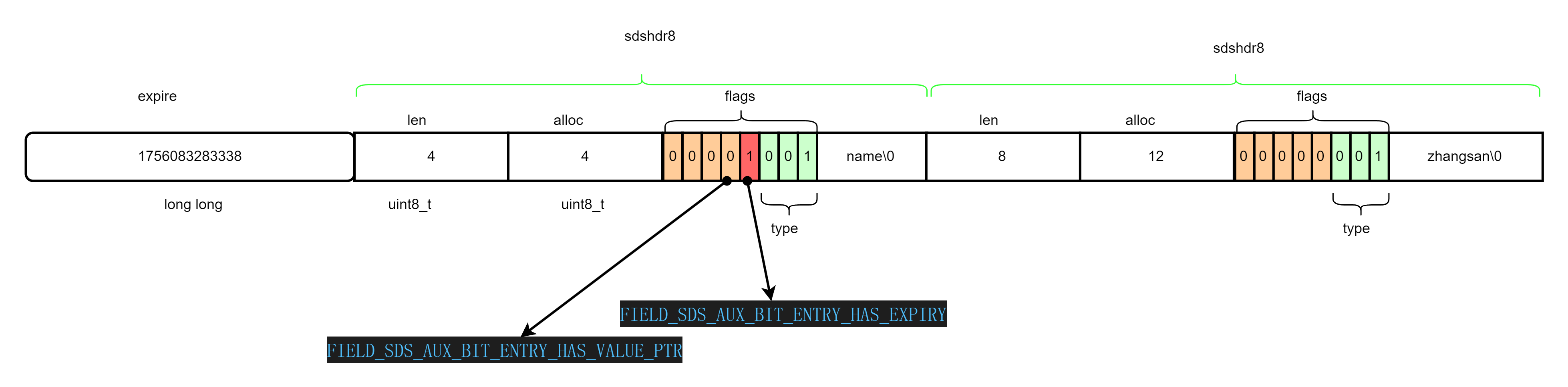
将entry插入hashtable中
追踪此field
hashTypeTrackEntry
c
void hashTypeTrackEntry(robj *o, void *entry) {
vset *set;
// 1. 首先判断是否已经存在vset
if (hashTypeHasVolatileFields(o)) {
// 1.1 存在则直接获取
set = hashTypeGetVolatileSet(o);
} else {
// 1.2 不存在,则创建
set = hashTypeGetOrcreateVolatileSet(o);
}
// 2. 将entry插入vset中
bool added = vsetAddEntry(set, entryGetExpiry, entry);
serverAssert(added);
}vset初始化

将entry插入vset中
c
bool vsetAddEntry(vset *set, vsetGetExpiryFunc getExpiry, void *entry) {
long long expiry = getExpiry(entry);
vsetBucket *expiry_buckets = *set;
assert(expiry_buckets);
int bucket_type = vsetBucketType(expiry_buckets);
switch (bucket_type) {
case VSET_BUCKET_NONE:
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_NONE(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry);
break;
case VSET_BUCKET_SINGLE:
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_SINGLE(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry);
break;
case VSET_BUCKET_VECTOR: {
pVector *vec = vsetBucketVector(expiry_buckets);
uint32_t len = pvLen(vec);
/* in case the vector is full, we need to turn into RAX */
if (len == VOLATILESET_VECTOR_BUCKET_MAX_SIZE) {
rax *r = raxNew();
long long min_expiry = getExpiry(pvGet(vec, 0));
long long max_expiry = getExpiry(pvGet(vec, len - 1));
if (get_max_bucket_ts(min_expiry) == get_max_bucket_ts(max_expiry)) {
/* In case we can just insert the bucket, no need to iterate and insert it's elements. we can just push the bucket as a whole. */
unsigned char key[VSET_BUCKET_KEY_LEN] = {0};
size_t key_len = encodeNewExpiryBucketKey(key, max_expiry);
raxInsert(r, key, key_len, expiry_buckets, NULL);
expiry_buckets = vsetBucketFromRax(r);
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_RAX(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry);
} else {
/* We need to migrate entries to the new set of buckets since we do not know all entries are in the same bucket */
expiry_buckets = vsetBucketFromRax(r);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < len; i++) {
void *moved_entry = pvGet(vec, i);
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_RAX(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, moved_entry, getExpiry(moved_entry));
}
/* free the vector */
pvFree(vec);
/* now insert the new entry to the buckets */
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_RAX(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry);
}
} else {
uint32_t pos = findInsertPosition(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, expiry);
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_VECTOR(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry, pos);
}
break;
}
case VSET_BUCKET_RAX:
expiry_buckets = insertToBucket_RAX(getExpiry, expiry_buckets, entry, expiry);
break;
default:
panic("Cannot insert to bucket which is not single, vector or rax");
}
/* update the set */
*set = expiry_buckets;
return true;
} NONE
|
v
SINGLE (1 entry)
|
v
VECTOR (sorted, up to 127)
|
v
RAX (holds multiple buckets, keyed by each bucket's end timestamp)
Bucket types within a RAX:
SINGLE
|
v
VECTOR (sorted, up to 127, can split
| into multiple vectors)
|
v
HASHTABLE (only when a vector can't split)首先从NONE到SINGLE
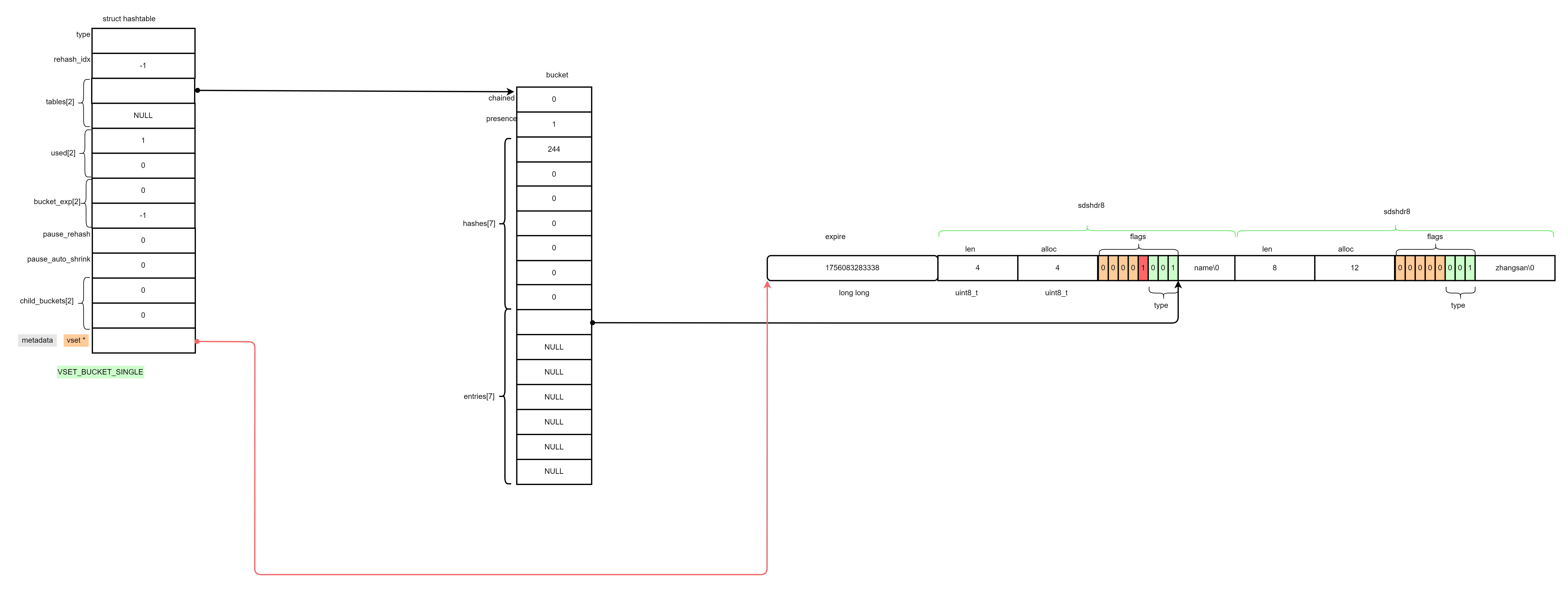
将field/value创建entry
将entry插入hashtable中
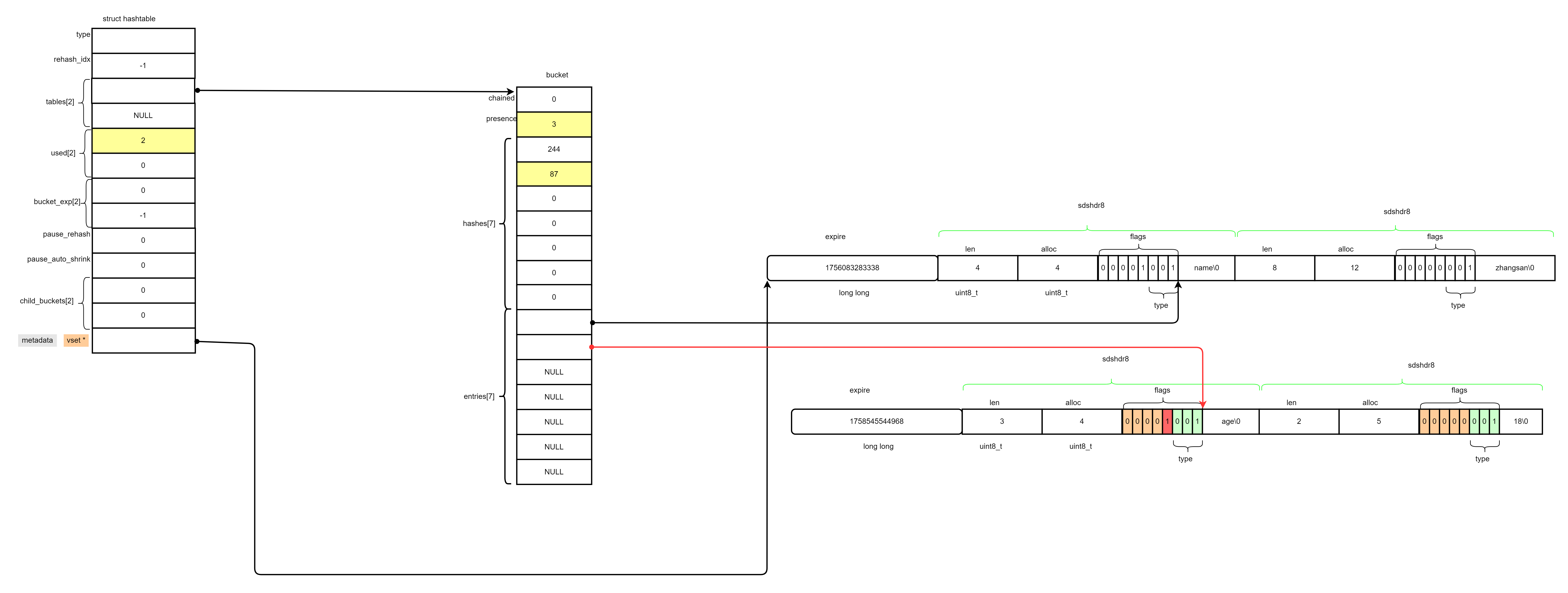
hashTypeTrackEntry
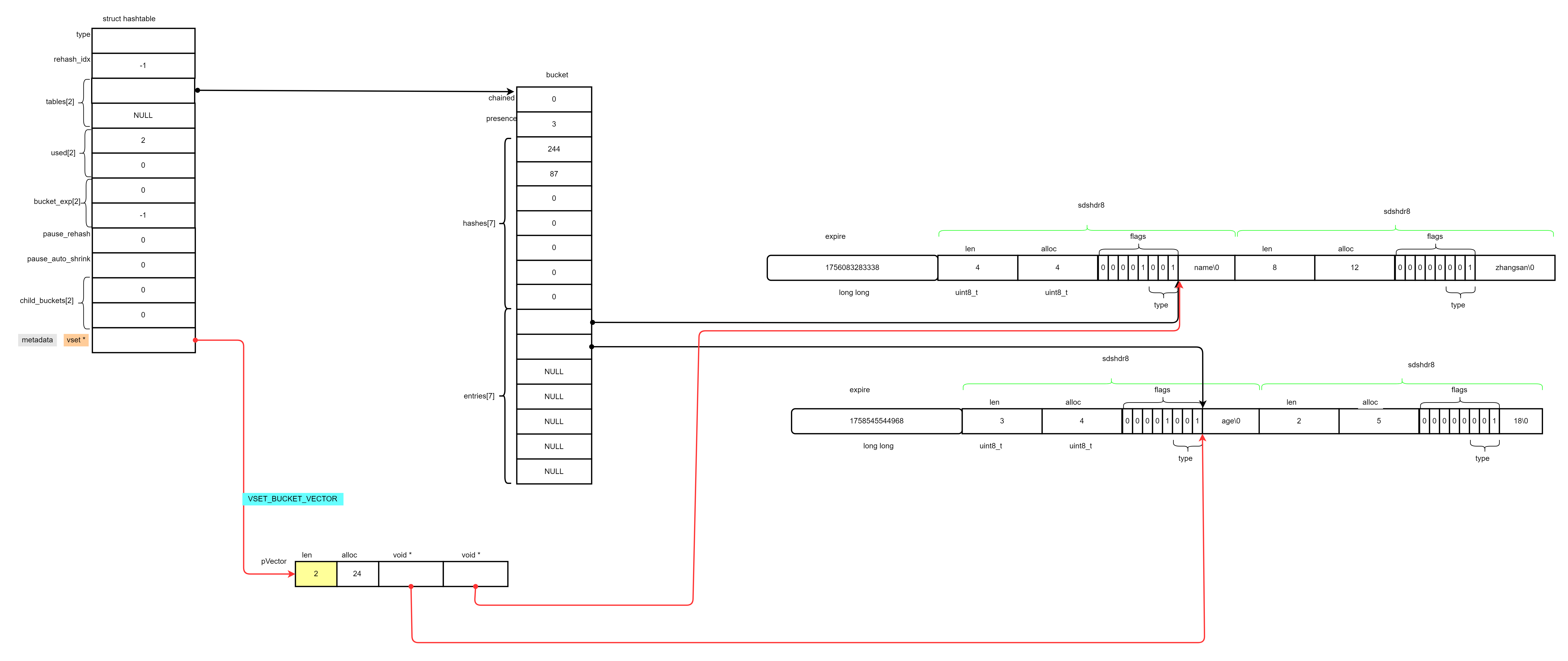
将SINGLE转换成vector, 分配空间,并根据expire大小进行插入,小的在前
c
static inline vsetBucket *insertToBucket_SINGLE(vsetGetExpiryFunc getExpiry, vsetBucket *bucket, void *entry, long long expiry) {
/* Upgrade to vector */
pVector *pv = pvNew(2);
void *curr_entry = vsetBucketSingle(bucket);
long long curr_expiry = getExpiry(curr_entry);
if (curr_expiry < expiry) {
pv = pvPush(pv, curr_entry);
pv = pvPush(pv, entry);
} else {
pv = pvPush(pv, entry);
pv = pvPush(pv, curr_entry);
}
bucket = vsetBucketFromVector(pv);
return bucket;
}
最后将调用
dbUpdateObjectWithVolatileItemsTracking
|-> dbTrackKeyWithVolatileItems
|-> kvstoreHashtableAdd(db->keys_with_volatile_items, dict_index, o);将o插入keys_with_volatile_items hashtable中
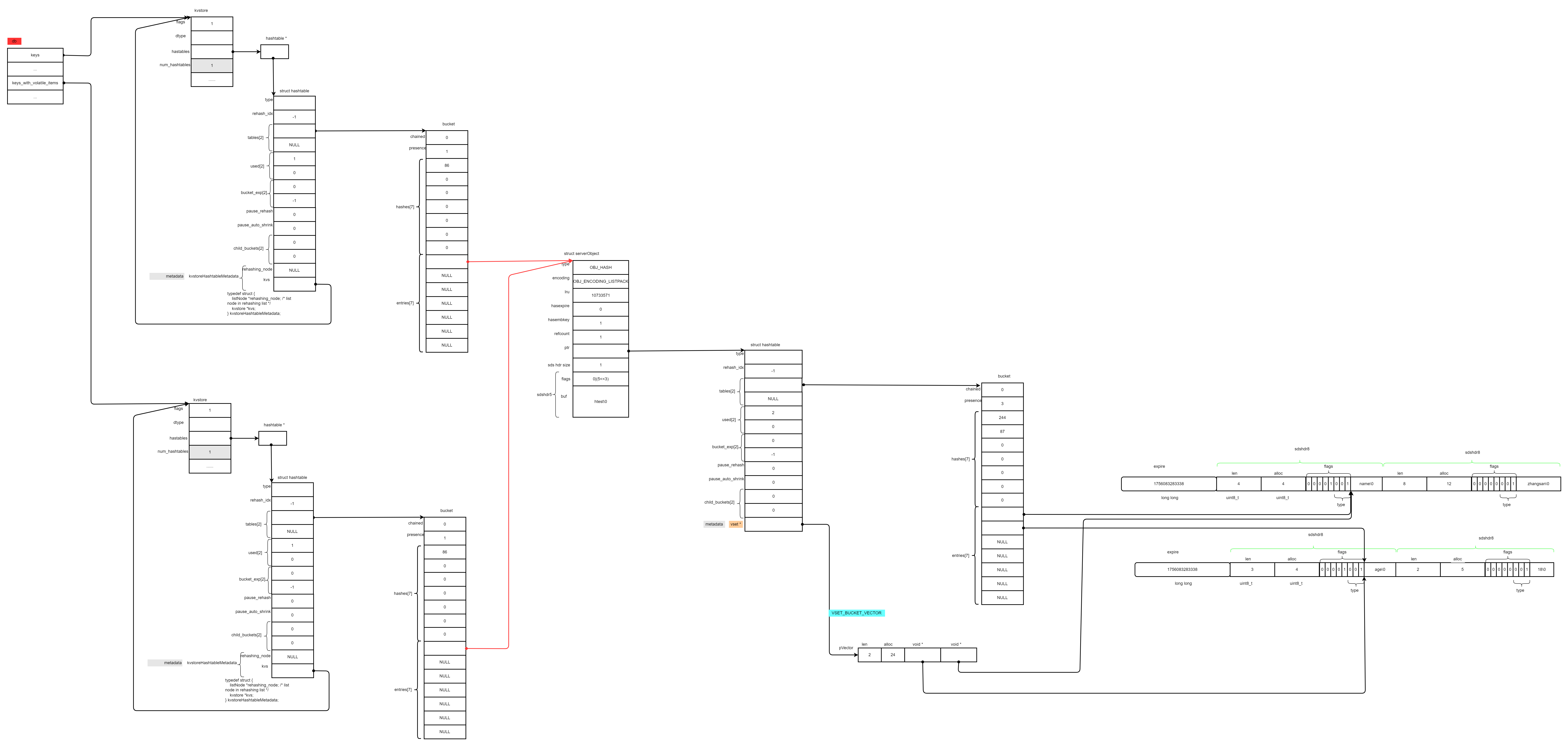
后续继续学习HFE的过期逻辑