在上一篇文章中,我们详细探讨了 Webpack Loader 的工作原理和使用方法。今天,我们将深入 Webpack 的另一个核心概念------Plugin(插件)。插件是 Webpack 的支柱功能,赋予了 Webpack 各种灵活强大的能力。
什么是plugin
与 Loader 用于转换特定类型的模块不同,Plugin 的功能更加广泛。Plugin 可以用于执行范围更广的任务,包括:
- 打包优化:如压缩代码、拆分代码包
- 资源管理:如拷贝静态资源、生成 HTML 文件
- 环境变量注入:定义全局常量
- 服务启动:如开发服务器、热更新
plugin与loader的区别
| 特性 | Loader | Plugin |
|---|---|---|
| 能力范围 | 处理Webpack不能识别的模块 | 在Webpack整个构建过程中干预 |
| 运行时机 | 模块加载时运行 | 在整个编译周期内都能起作用 |
| 配置方式 | 在module.rules中配置 | 在plugins数组中配置 |
| 实现原理 | 函数式,接收源码返回处理结果 | 基于Tapable的事件流机制 |
Plugin的底层原理
Plugin的底层是基于核心库Tapable的发布订阅模式机制在Webpack编译整个过程中的各个阶段进行处理。Webpack也提供了多种钩子(Hooks)类型,便于功能扩展。
Compiler和Compilation
Webpack整个的编译过程中Compiler和Compilation两个对象,扮演着重要的角色。
- Compiler 编译器实例,包含了完整的配置信息,在
Webpack整个编译过程中只有一个Compiler实例 - Compilation 编译实例,代表一次资源构建,包含了当前模块资源、编译生成资源、变化的文件等信息。
Compiler
Compiler对象是Webpack的核心编译器,代表了完整的Webpack环境配置。它在Webpack的初始化阶段被创建,并在整个构建生命周期中只有一个实例。
主要职责
- 启动和配置:处理
Webpack的配置并初始化 - 控制构建流程:管理整个构建过程的生命周期
- 插件系统:提供
tapable钩子供自定义插件进行扩展功能 - 文件监听:在
watch模式下监听文件变化
再从Webpack的底层源码中看看Compiler具体做了些什么:
实例创建时
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
constructor(context) {
this.hooks = {
// 初始化所有生命周期钩子
beforeRun: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
run: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
beforeCompile: new AsyncSeriesHook(["params"]),
compile: new SyncHook(["params"]),
compilation: new SyncHook(["compilation", "params"]),
// ... 几十个钩子
};
this.options = {};
this.context = context;
this.outputFileSystem = null;
this.inputFileSystem = null;
}
}运行构建流程
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
run(callback) {
// 1. 触发 beforeRun 钩子
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 2. 触发 run 钩子
this.hooks.run.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 3. 执行编译
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
}
compile(callback) {
// 1. 准备编译参数
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
// 2. 触发 beforeCompile 钩子
this.hooks.beforeCompile.callAsync(params, err => {
// 3. 触发 compile 钩子
this.hooks.compile.call(params);
// 4. 创建 Compilation 实例
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
// 5. 触发 compilation 钩子(插件可以在这里挂载)
this.hooks.compilation.call(compilation, params);
// 6. 执行 Compilation 的构建过程
compilation.buildModule(err => {
// 构建完成后进行封包、优化等
compilation.seal(err => {
// 触发 afterCompile 钩子
this.hooks.afterCompile.callAsync(compilation, err => {
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
});
}
}创建Compilation
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
newCompilationParams() {
const params = {
// 创建模块工厂
normalModuleFactory: this.createNormalModuleFactory(),
// 创建上下文模块工厂
contextModuleFactory: this.createContextModuleFactory(),
// 创建依赖图工厂
chunkGraph: this.createChunkGraph()
};
return params;
}
createNormalModuleFactory() {
const moduleFactory = new NormalModuleFactory({
// 配置解析器、加载器等
resolverFactory: this.resolverFactory,
options: this.options.module
});
return moduleFactory;
}
}
compile(callback) {
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
// 开始编译前hook
this.hooks.beforeCompile.callAsync(params, (err) => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 执行用户注册的compile事件
this.hooks.compile.call(params);
// 创建Compilation实例 编译器
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
/* 其他代码省略 */
});
}运行构建流程
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
run(callback) {
// 1. 触发 beforeRun 钩子
this.hooks.beforeRun.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 2. 触发 run 钩子
this.hooks.run.callAsync(this, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 3. 执行编译
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
});
}
compile(callback) {
// 1. 准备编译参数
const params = this.newCompilationParams();
// 2. 触发 beforeCompile 钩子
this.hooks.beforeCompile.callAsync(params, err => {
// 3. 触发 compile 钩子
this.hooks.compile.call(params);
// 4. 创建 Compilation 实例
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
// 5. 触发 compilation 钩子(插件可以在这里挂载)
this.hooks.compilation.call(compilation, params);
// 6. 执行 Compilation 的构建过程
compilation.buildModule(err => {
// 构建完成后进行封包、优化等
compilation.seal(err => {
// 触发 afterCompile 钩子
this.hooks.afterCompile.callAsync(compilation, err => {
return callback(null, compilation);
});
});
});
});
}
}生成最终文件
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
emitAssets(compilation, callback) {
// 1. 触发 emit 钩子(插件可以在这里修改资源)
this.hooks.emit.callAsync(compilation, err => {
// 2. 创建输出目录
this.outputFileSystem.mkdirp(this.options.output.path, err => {
// 3. 写入所有文件
this.writeFiles(compilation, err => {
// 4. 触发 afterEmit 钩子
this.hooks.afterEmit.callAsync(compilation, err => {
callback();
});
});
});
});
}
writeFiles(compilation, callback) {
// 遍历所有编译生成的资源
for (const [filename, source] of Object.entries(compilation.assets)) {
// 获取资源内容
const content = source.source();
// 写入文件系统
this.outputFileSystem.writeFile(
this.outputPath(filename),
content,
callback
);
}
}
}监听文件的变化后重新编译
js
// lib/Compiler.js
class Compiler {
watch(watchOptions, handler) {
// 1. 创建监视器
this.watchMode = true;
this.watchFileSystem = new NodeWatchFileSystem(this.inputFileSystem);
// 2. 开始监听文件
this.watcher = this.watchFileSystem.watch(
this.getWatchFiles(),
this.getWatchDirectories(),
// 文件变化时的回调
(changedFiles, removedFiles) => {
// 触发 invalid 钩子
this.hooks.invalid.callAsync(changedFiles, removedFiles, () => {
// 重新编译
this.compile(onCompiled);
});
}
);
}
}Compilation
Compilation主要负责Webpack的构建过程。包含了生成依赖图、编译生成bundle和变化的文件等信息。
主要职责
- 模块构建: 负责模块的加载、解析、转换、
- 依赖图的构建:建立模块间的依赖关系
- 资源生成:生成最终的打包文件
- 增量编译:监听模式下只重新编译变化的模块
Compiler和Compilation的关系
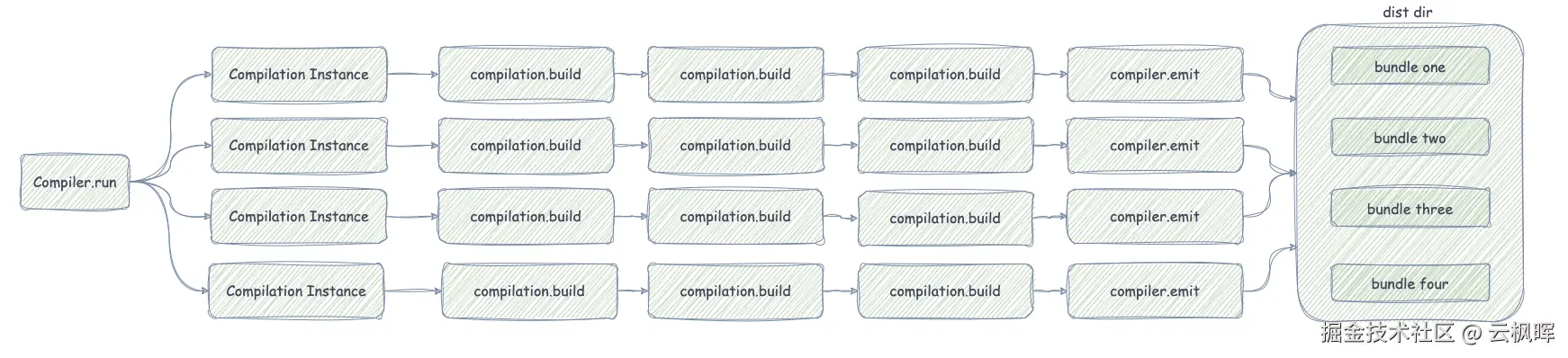
再从Webpack的底层源码中看看Compilation具体做了些什么:
Compilation初始化
js
// lib/Compilation.js
class Compilation {
constructor(compiler, params) {
this.compiler = compiler;
this.options = compiler.options;
// 核心数据结构初始化
this.modules = new Set(); // 所有模块
this.chunks = new Set(); // 所有代码块
this.assets = {}; // 输出资源
this.entries = new Map(); // 入口模块
this.moduleGraph = new ModuleGraph(); // 模块依赖图
// 工厂实例
this.moduleFactories = params.moduleFactories;
this.normalModuleFactory = params.normalModuleFactory;
// 钩子系统
this.hooks = {
buildModule: new SyncHook(["module"]),
succeedModule: new SyncHook(["module"]),
finishModules: new SyncHook(["modules"]),
// ... 更多编译钩子
};
}
}构建模块
Webpack中的Compilation依靠AsyncQueue异步队列实来构建模块。
异步队列类-AsyncQueue
js
// lib/util/AsyncQueue.js
class AsyncQueue {
constructor({ name, parallelism, processor, getKey }) {
this._name = name;
this._parallelism = parallelism; // 并发数
this._processor = processor; // 处理器函数
this._getKey = getKey; // 获取唯一标识的函数
this._queued = new Map(); // 等待队列
this._processing = new Map(); // 处理中队列
this._entries = new Map(); // 所有条目
}
add(item, callback) {
const key = this._getKey(item);
// 如果已经在处理或等待中,只添加回调
if (this._entries.has(key)) {
// ... 处理重复逻辑
return;
}
// 创建新条目
const entry = {
item,
callback: [callback],
state: QUEUED_STATE
};
this._entries.set(key, entry);
this._queued.set(key, entry);
// 尝试启动处理
this._ensureProcessing();
}
}Compilation初始化创建队列
js
// lib/Compilation.js
class Compilation {
constructor(compiler, params) {
// 创建模块构建队列
this._buildModuleQueue = new AsyncQueue({
name: "build module",
parallelism: compiler.options.parallelism || 100,
processor: this._buildModule.bind(this), // 处理器是 _buildModule 方法
getKey: item => item.module.identifier() // 用模块标识符作为key
});
}
// 添加模块到构建队列
handleModuleCreation(module, callback) {
this._buildModuleQueue.add(
{ module, currentProfile: null },
(err, result) => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 模块构建完成,处理依赖
this.processModuleDependencies(module, err => {
callback(err, module);
});
}
);
}
// 实际的模块构建处理器
_buildModule({ module, currentProfile }, callback) {
// 触发 buildModule 钩子
this.hooks.buildModule.call(module);
// 执行模块构建(这是实际的构建逻辑)
module.build(
this.options,
this,
this.resolverFactory.get("normal", module.resolveOptions),
this.inputFileSystem,
(err) => {
if (err) {
this.hooks.failedModule.call(module, err);
return callback(err);
}
this.hooks.succeedModule.call(module);
callback(null, { module, currentProfile });
}
);
}
}Compilation中通过addModule开始调用processModuleDependencies方法异步处理模块依赖
js
// 简化的完整流程
class Compilation {
// 入口方法 - 添加模块到构建系统
addModule(module, callback) {
this.handleModuleCreation(
{
factory: module.factory,
dependencies: module.dependencies,
context: module.context
},
(err, module) => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 模块构建完成后,递归处理其依赖
this.processModuleDependencies(module, callback);
}
);
}
// 处理模块依赖(也是异步的)
processModuleDependencies(module, callback) {
const dependencies = new Set(module.dependencies);
// 异步处理所有依赖
asyncLib.forEach(
dependencies,
(dependency, callback) => {
this.handleModuleCreation(
{
factory: this.dependencyFactories.get(dependency.constructor),
dependencies: [dependency],
context: module.context,
issuer: module
},
callback
);
},
callback
);
}
}在AsyncQueue中通过_ensureProcessing方法并发控制
js
// 队列的并发处理机制
class AsyncQueue {
_ensureProcessing() {
// 当并发数未满且有等待任务时,继续处理
while (this._processing.size < this._parallelism && this._queued.size > 0) {
const [key, entry] = this._queued.entries().next().value;
this._queued.delete(key);
this._processing.set(key, entry);
entry.state = PROCESSING_STATE;
// 调用处理器函数
this._processor(entry.item, (err, result) => {
this._handleResult(key, entry, err, result);
});
}
}
_handleResult(key, entry, err, result) {
this._processing.delete(key);
this._entries.delete(key);
// 执行所有回调
entry.callback.forEach(callback => {
callback(err, result);
});
// 继续处理下一个任务
this._ensureProcessing();
}
}Compilation实例通过addEntry方法将入口模块添加到AsyncQueue队列中开始异步构建依赖图最终生成bundle
js
// Webpack 构建的异步流程
compilation.addEntry(context, entry, name, callback) {
// 1. 创建入口模块
this._addModuleChain(context, entry, module => {
// 2. 将入口模块添加到构建队列
this.handleModuleCreation(module, err => {
if (err) return callback(err);
// 3. 所有模块构建完成后进行封包
this.seal(callback);
});
});
}为什么采用异步队列呢❓
- 避免同时构建太多模块导致内容溢出问题
- 避免相同模块重复构建
- 充分利用多核CPU提高构建速度
- 通过队列可以更好优化构建顺序
常用Plugin配置
HtmlWebpackPlugin
HtmlWebpackPlugin主要自动生成HTML文件并注入打包后的资源
js
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: './src/index.html', // 模板文件
filename: 'index.html', // 输出文件名
title: 'My App', // HTML title
minify: { // 压缩配置
removeComments: true, // 移除注释
collapseWhitespace: true, // 折叠空白
removeAttributeQuotes: true // 移除属性引号
},
chunks: ['main', 'vendor'] // 指定要注入的 chunk
})
]
};MiniCssExtractPlugin
MiniCssExtractPlugin主要将CSS资源提取到单独的文件中
js
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [
MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, // 代替 style-loader
'css-loader'
]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'css/[name].[contenthash:8].css',
chunkFilename: 'css/[name].[contenthash:8].chunk.css'
})
]
};DefinePlugin
DefinePlugin插件是Webpack的内置插件,定义了全局变量,在打包时会替换
js
const webpack = require('webpack');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env.NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV),
'API_BASE_URL': JSON.stringify('https://api.example.com'),
'APP_VERSION': JSON.stringify(require('./package.json').version)
})
]
};CopyWebpackPlugin
CopyWebpackPlugin主要是拷贝静态文件到输出目录
js
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin({
patterns: [
{
from: 'public', // 源目录
to: '', // 目标目录(相对于输出目录)
globOptions: {
ignore: ['**/index.html'] // 忽略文件
}
}
]
})
]
};自定义插件
Webpack提供很多钩子(Hooks)给到用户扩展构建应用。将通过构建时间统计插件来展示如何自定义插件
构建时间统计插件
此插件主要功能:
- 构建时间统计
- 多格式输出
- 在开发环境下,构建时间过长给出优化建议
- 构建失败时显示错误信息
- 完整构建信息,如时间、版本、hash值等详细信息
js
/**
* Webpack 构建时间统计插件
* 用于统计和展示 Webpack 构建过程的时间信息
*/
class BuildTimePlugin {
/**
* 构造函数
* @param {Object} options 插件配置选项
* @param {string} options.name 插件名称,默认为 "BuildTimePlugin"
* @param {string|null} options.outputFile 构建信息输出文件路径,为 null 时不输出文件
* @param {boolean} options.showInConsole 是否在控制台显示构建信息,默认为 true
*/
constructor(options = {}) {
// 合并用户配置和默认配置
this.options = {
name: "BuildTimePlugin", // 插件名称
outputFile: null, // 输出文件路径,null 表示不输出到文件
showInConsole: true, // 是否在控制台显示信息
...options, // 用户自定义配置会覆盖默认配置
};
// 初始化时间记录变量
this.startTime = null; // 构建开始时间戳
this.endTime = null; // 构建结束时间戳
}
/**
* 应用插件到 Webpack 编译器
* 这是 Webpack 插件的核心方法,用于注册各种钩子
* @param {Object} compiler Webpack 编译器实例
*/
apply(compiler) {
// 解构配置参数,方便使用
const { name, showInConsole } = this.options;
/**
* 注册 beforeRun 钩子 - 在开始执行构建之前触发
* 用于记录构建开始时间
*/
compiler.hooks.beforeRun.tap(name, () => {
// 记录构建开始时间
this.startTime = Date.now();
// 如果配置了在控制台显示,则输出开始信息
if (showInConsole) {
console.log("🚀 编译开始...");
}
});
/**
* 注册 done 钩子 - 在构建完成时触发
* 用于计算构建时间并输出结果
* @param {Object} stats 构建统计信息对象
*/
compiler.hooks.done.tap(name, (stats) => {
// 记录构建结束时间
this.endTime = Date.now();
// 计算构建耗时(毫秒)
const buildTime = this.endTime - this.startTime;
// 格式化时间显示,便于阅读
const formattedTime = this.formatBuildTime(buildTime);
// 如果配置了在控制台显示,则输出构建结果
if (showInConsole) {
console.log(`✅ 编译完成!`);
console.log(`⏰ 构建时间: ${formattedTime}`);
// 在开发模式下,如果构建时间过长,显示优化提示
if (compiler.options.mode === "development") {
this.showDevelopmentTips(buildTime);
}
}
// 如果配置了输出文件,将构建信息写入文件
if (this.options.outputFile) {
this.writeBuildInfo(compiler, buildTime, formattedTime, stats);
}
});
/**
* 注册 failed 钩子 - 在构建失败时触发
* 用于处理构建失败的情况
* @param {Error} error 错误对象
*/
compiler.hooks.failed.tap(name, (error) => {
// 如果配置了在控制台显示,则输出失败信息
if (showInConsole) {
console.log("❌ 编译失败!");
console.error(error);
}
});
}
/**
* 格式化构建时间
* 将毫秒转换为更易读的格式
* @param {number} ms 构建时间(毫秒)
* @returns {string} 格式化后的时间字符串
*/
formatBuildTime(ms) {
// 如果时间小于1秒,显示毫秒
if (ms < 1000) {
return `${ms}ms`;
} else {
// 如果时间大于等于1秒,显示秒(保留2位小数)
return `${(ms / 1000).toFixed(2)}s`;
}
}
/**
* 将构建信息写入文件
* @param {Object} compiler Webpack 编译器实例
* @param {number} buildTime 构建时间(毫秒)
* @param {string} formattedTime 格式化后的构建时间
* @param {Object} stats 构建统计信息对象
*/
writeBuildInfo(compiler, buildTime, formattedTime, stats) {
// 引入文件系统模块
const fs = require("fs");
const path = require("path");
try {
// 构建完整的输出文件路径
// compiler.options.output.path 是 Webpack 配置的输出目录
const outputPath = path.join(
compiler.options.output.path,
this.options.outputFile
);
// 构建信息对象,包含各种有用的构建数据
const buildInfo = {
buildTime, // 构建耗时(毫秒)
buildTimeReadable: formattedTime, // 可读的构建时间
buildDate: new Date().toISOString(), // 构建完成时间(ISO格式)
buildTimestamp: Date.now(), // 构建完成时间戳
hash: stats.hash, // 构建哈希值
version: stats.version, // Webpack 版本
assets: Object.keys(stats.compilation.assets).length, // 资源文件数量
};
// 确保输出目录存在
const dir = path.dirname(outputPath);
if (!fs.existsSync(dir)) {
// 递归创建目录
fs.mkdirSync(dir, { recursive: true });
}
// 将构建信息写入文件
// JSON.stringify 的第三个参数 2 表示使用2个空格缩进,美化输出
fs.writeFileSync(outputPath, JSON.stringify(buildInfo, null, 2));
} catch (error) {
// 文件写入失败时的错误处理
console.warn("⚠️ 构建信息写入失败:", error.message);
}
}
/**
* 显示开发模式下的优化提示
* 当构建时间过长时,给出优化建议
* @param {number} buildTime 构建时间(毫秒)
*/
showDevelopmentTips(buildTime) {
// 如果构建时间超过10秒,显示优化提示
if (buildTime > 10000) {
console.log("💡 提示: 构建时间较长,建议检查:");
console.log(" - 是否使用了不必要的大型依赖");
console.log(" - 是否可以优化 Webpack 配置");
console.log(" - 考虑使用缓存或增量构建");
}
}
}
// 导出插件类
module.exports = BuildTimePlugin;小结
通过本文的探讨,我们深入了解了 Webpack Plugin 的核心机制和应用实践:
核心理解
- Plugin 与 Loader 的差异:Loader 专注于模块转换,而 Plugin 拥有更广泛的能力范围,可以在整个编译生命周期中干预构建过程
- 基于 Tapable 的事件流机制:Plugin 的本质是基于发布订阅模式,通过钩子(Hooks)系统扩展 Webpack 功能
架构原理
-
Compiler 与 Compilation 的分工:
- Compiler:编译器实例,控制整个构建生命周期,全局唯一
- Compilation:编译实例,负责具体的模块构建和资源生成
-
异步队列构建机制:Webpack 通过 AsyncQueue 实现高效的并发构建和增量编译
实践应用
- 丰富的插件生态:HtmlWebpackPlugin、MiniCssExtractPlugin 等提供了开箱即用的功能
- 灵活的自定义能力:通过理解 Plugin 的工作原理,我们可以开发满足特定需求的定制化插件
开发启示
- 合理选择干预时机:根据需求在适当的钩子阶段执行逻辑
- 关注构建性能:避免在频繁触发的钩子中执行重操作
- 完善的错误处理:确保插件的稳定性和可调试性
Webpack Plugin 的强大之处在于其高度可扩展的架构设计,理解这套机制不仅有助于我们更好地使用现有插件,更为我们解决特定构建需求提供了无限可能。