在网页布局中,当多个元素重叠时,如何控制它们的显示顺序?z-index就是解决这个问题的关键属性!
z-index
概念:
在CSS中,当多个定位元素(position不是static)在页面上重叠时,浏览器需要决定哪个元素显示在前面,哪个在后面。这个前后顺序就是叠放次序,而z-index属性正是用来控制这个顺序的魔法工具。
基本语法:
css
selector {
z-index: auto | <integer> | inherit;
}属性值说明:
| 值 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
auto |
默认值,元素不会建立新的堆叠上下文 | z-index: auto; |
<integer> |
整数值,可以是正数、负数或0 | z-index: 1; |
inherit |
继承父元素的z-index值 | z-index: inherit; |
示例1:基础z-index使用
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>z-index基础示例</title>
<style>
.container {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
margin: 50px auto;
border: 2px solid #333;
}
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
opacity: 0.8;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
color: white;
}
.box1 {
background-color: #ff6b6b;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
z-index: 1;
}
.box2 {
background-color: #4ecdc4;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
z-index: 2;
}
.box3 {
background-color: #45b7d1;
top: 150px;
left: 150px;
z-index: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="box box1">z-index: 1</div>
<div class="box box2">z-index: 2</div>
<div class="box box3">z-index: 3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行结果如下:
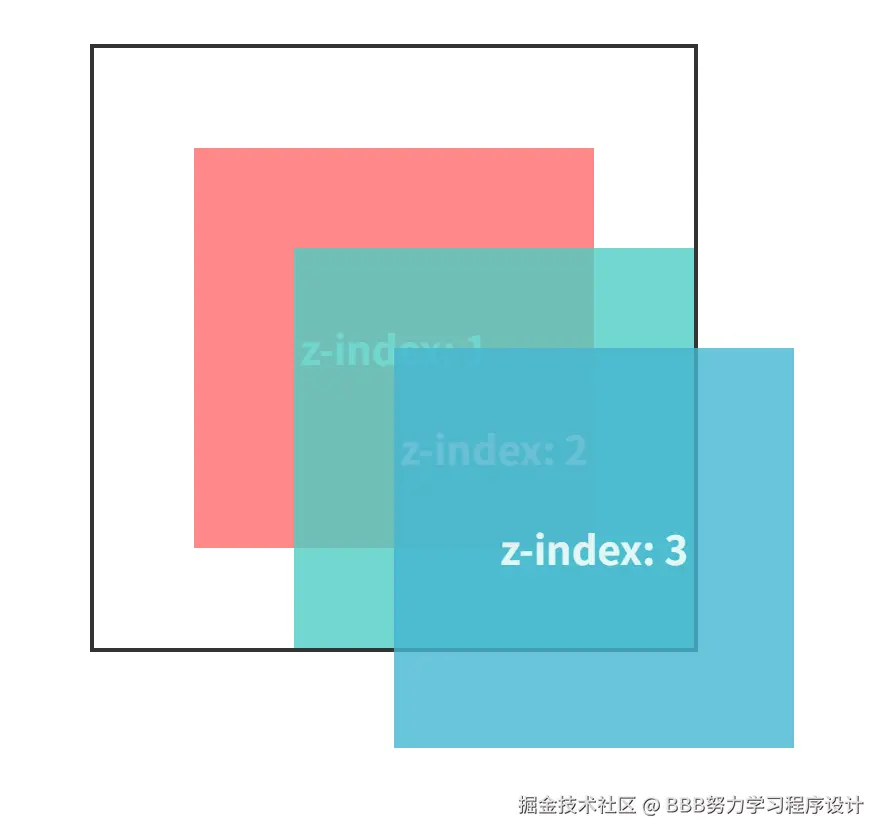
示例2:负z-index的使用
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>负z-index示例</title>
<style>
.background-container {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
background: linear-gradient(45deg, #667eea, #764ba2);
border-radius: 10px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.background-text {
position: absolute;
font-size: 120px;
font-weight: 900;
color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.1);
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
z-index: 1;
}
.content {
position: relative;
z-index: 2;
padding: 40px;
color: white;
text-align: center;
}
.background-pattern {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: repeating-linear-gradient(
45deg,
transparent,
transparent 10px,
rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.05) 10px,
rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.05) 20px
);
z-index: -1;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="background-container">
<div class="background-text">CSS</div>
<div class="background-pattern"></div>
<div class="content">
<h2>负z-index效果</h2>
<p>背景图案使用z-index: -1,位于内容后面</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行结果如下:

示例3:堆叠上下文的影响
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-wide, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>堆叠上下文示例</title>
<style>
.outer-container {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
background-color: #f8f9fa;
border: 2px solid #dee2e6;
padding: 20px;
}
.parent {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
background-color: #e9ecef;
padding: 20px;
/* 创建新的堆叠上下文 */
z-index: 1;
}
.child-high {
position: absolute;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #ff6b6b;
z-index: 100;
}
.sibling {
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #4ecdc4;
z-index: 2;
}
.outside-element {
position: absolute;
top: 150px;
left: 150px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: #45b7d1;
z-index: 3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer-container">
<div class="parent">
<div class="child-high">子元素 z-index: 100</div>
</div>
<div class="sibling">兄弟元素 z-index: 2</div>
<div class="outside-element">外部元素 z-index: 3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>运行结果如下:
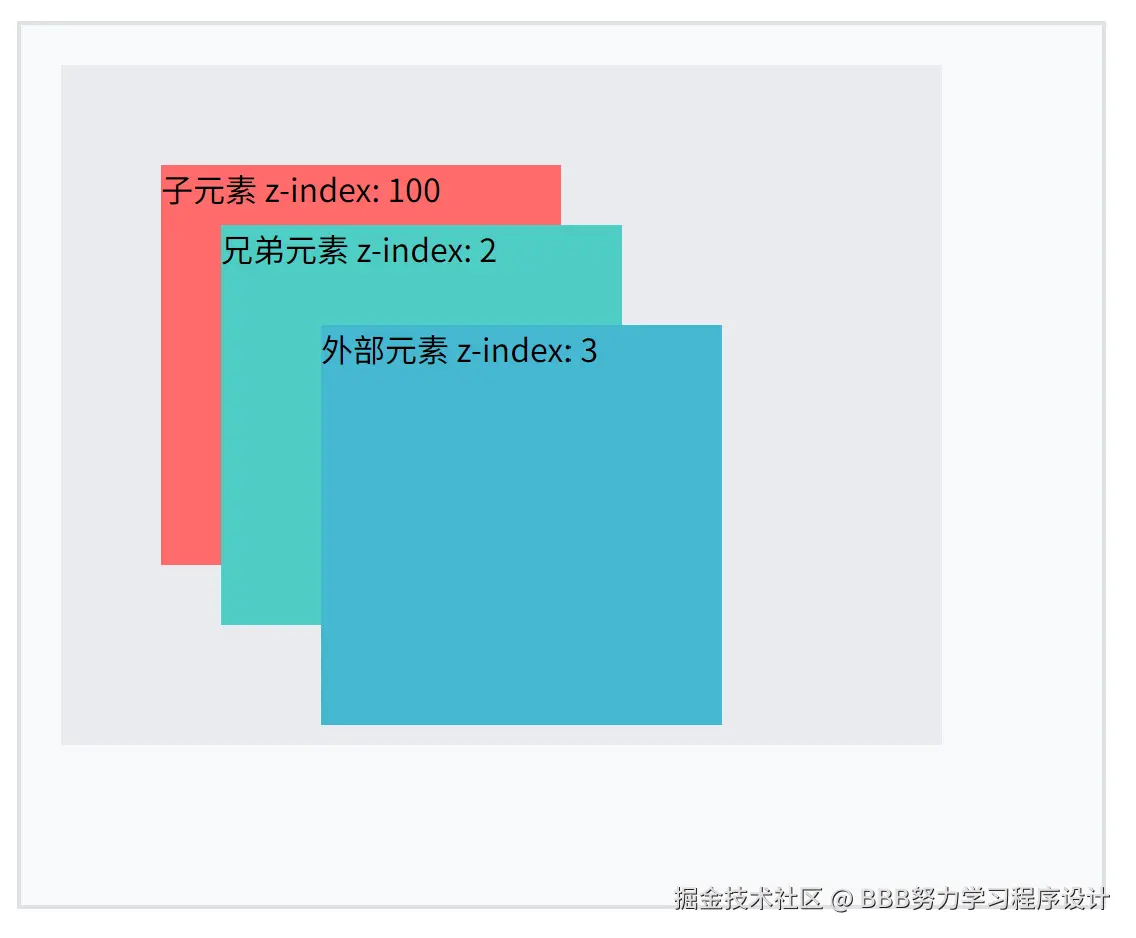
重要注意事项
1. 定位要求
z-index只对定位元素生效,包括:
position: relativeposition: absoluteposition: fixedposition: sticky- 对于
position: static(默认值)的元素,z-index无效。
2. 堆叠上下文创建
以下属性会创建新的堆叠上下文:
position: relative/absolute/fixed/sticky且z-index不为autoposition: fixed(始终创建)opacity值小于 1transform值不为nonefilter值不为none
3. 默认堆叠顺序
当z-index未设置或相同时,元素按以下顺序堆叠(从后到前):
- 根元素的背景和边框
- 普通流中非定位块级元素(按HTML顺序)
- 普通流中非定位行内元素
- 定位元素(按HTML顺序)
4. 堆叠上下文的限制
- 子元素的
z-index只在父元素的堆叠上下文中有效,无法与父堆叠上下文外的元素比较。
5. 整数值比较
z-index比较的是整数值大小,不是十进制比较z-index: 5会在z-index: 4前面z-index: 10会在z-index: 9前面
总结
掌握z-index的关键要点:
- 定位是前提:确保元素设置了非
static的position - 理解三维概念:
z-index控制的是垂直于屏幕的方向 - 注意堆叠上下文:父元素的堆叠上下文会影响子元素的显示
- 合理规划数值:使用有间隔的数值便于后续调整
- 避免过度使用:复杂的
z-index结构会增加维护难度