一、中间操作
1、fileter的使用
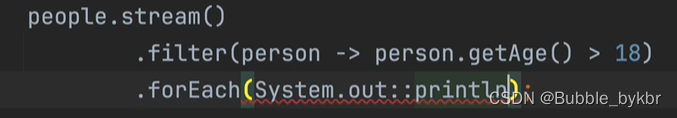
filter起到过滤筛选的作用,一般在filter中衔接lambda表达式起到筛选作用
2、Map方法的使用
Map方法的适用场景,接上例,对当前的包含对象的流数据转换为仅包含人名的流,那么就适合使用map方法来进行类型的转换。
eg:
开发中遇到的使用实例:
java
// 1.查询用户,若不存在返回空列表
List<User> users = listByIds(ids);
if(CollUtil.isEmpty(users)){
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 2.1.查询地址;获取用户id集合
List<Long> idList = users.stream().map(User -> User.getId()).collect(Collectors.toList());二、终结操作
1、Aggreation操作

count方法可直接调用
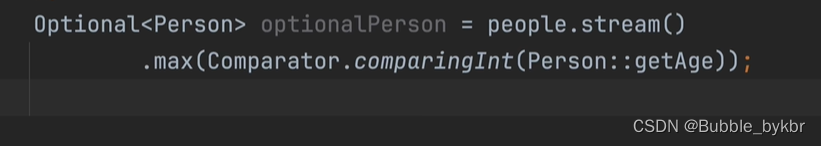
max和min方法,需要在其中定义比较器,指明比较依据
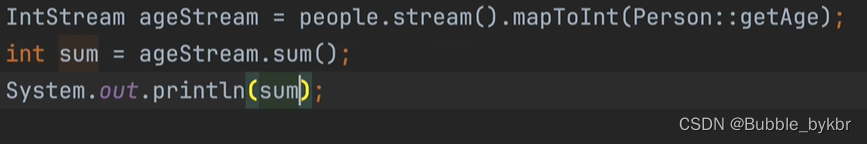
average和sum方法,需要将当前的流转换为数据流,再进行操作
2、reduce方法
reduce通过特定的函数对流中的元素进行反复操作,适用于求和、字符串拼接等操作
java
List<String> strings = Arrays.asList("Java", "Stream", "API");
String combinedStream = strings.stream().reduce("", (a, b) -> a + b);
return combinedStream;3、collect收集方法
常规使用:在collect中指定collector收集器,进行对应类型的转换,如List、Set、Map等
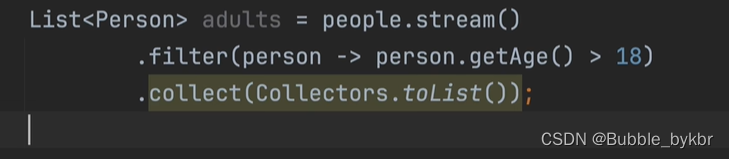
实用的方法:分组、分区、字符串连接
分组groupingBy开发遇到的:
java
// 2.4.分类整理,将一个用户id对应的多个地址分组到一起
Map<Long, List<AddressVO>> addressMap =
addresses.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(AddressVO::getUserId));**分区partioning,**可以在partioning中衔接lambda表达式,表明分区条件,返回值为Map,键为true和false,根据条件分开的两类数据分在两个分区中。

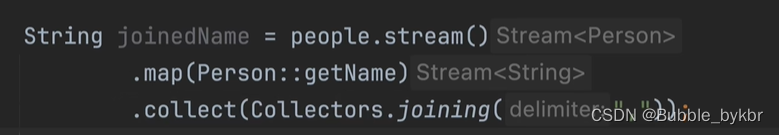
字符串连接joining