Framework层之输入系统
第一篇 深入Android S (12.0) 探索Framework之输入系统IMS的构成与启动
第二篇 深入Android S (12.0) 探索Framework之输入子系统InputReader的流程
第三篇 深入Android S (12.0) 探索Framework之输入子系统InputDispatcher的流程
文章目录
- Framework层之输入系统
- 前言
- [一、InputDispatcher 前期准备](#一、InputDispatcher 前期准备)
- [二、InputDispatcher 分发 Motion 事件](#二、InputDispatcher 分发 Motion 事件)
-
- 1.InputDispacher::dispatchMotionLocked()
- 2.InputDispacher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked()
-
- [2.1 TouchState](#2.1 TouchState)
- [2.2 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked()](#2.2 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked())
- [2.3 TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow()](#2.3 TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow())
- [2.4 InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked()](#2.4 InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked())
- 3.InputDispacher::dispatchEventLocked()
- 4.InputDispacher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked()
- 5.InputDispacher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked()
- 6.InputDispacher::startDispatchCycleLocked()
- 7.InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent()
- 8.InputChannel::sendMessage()
- 9.NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent()
- 10.NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents()
- 11.InputEventReceiver#dispatchInputEvent()
- 12.ViewRootImpl#WindowInputEventReceiver#onInputEvent()
- 13.ViewRootImpl#enqueueInputEvent()
- 14.ViewRootImpl#doProcessInputEvents()
- 15.ViewRootImpl#deliverInputEvent()
- 小结
- 总结
前言
上一篇文章深入探索了 Android Framework 的输入子系统 InputReader 的工作流程,在 InputReader 的一次线程循环中,通过 EventHub::getEvent() 函数尽可能多地读取设备增删事件与原始输入事件,并将它们封装成 RawEvent 结构体,存入缓存 buffer 中供 InputReader 进行处理。InputReader 通过调用其 processEventsLocked() 函数对获取事件进行分类处理,对于设备节点事件,将根据设备的可用性来加载或移除设备对应的配置信息。我们重点关注原始输入事件,InputReader 对其进行转译、封装与加工后将结果暂存到 mQueuedListener 中。最后调用 QueuedInputListener::flush() 函数将所有暂存、已加工过的输入事件交付给 InputDispatcher 来进行分发。本篇将深入探索 InputDispatcher 的工作流程,它是如何来分发这些输入事件的?
一、InputDispatcher 前期准备
InputDispatcher 是 IMS 中的一个关键组件,运行于一个独立的线程中,在 InputDispatcher 中保管了来自 WindowManagerService 的所有窗口的信息。在一次线程循环中会获取位于派发队列队首位置的事件,然后在其保管的窗口中寻找合适的窗口,并将事件派发给此窗口。
1.InputManager
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.h
cpp
class InputManager : public InputManagerInterface, public BnInputFlinger {
protected:
~InputManager() override;
public:
InputManager(
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy);
......
private:
sp<InputReaderInterface> mReader;
sp<InputClassifierInterface> mClassifier;
sp<InputDispatcherInterface> mDispatcher;
};xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
cpp
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
// 创建 InputDispatcher 对象,使用 InputDispatcherPolicyInterface 接口,用于对事件进行分发
mDispatcher = createInputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
// 创建 InputClassifier 对象,使用 InputListenerInterface,用于对事件分类
mClassifier = new InputClassifier(mDispatcher);
// 创建 InputReader 对象,使用 InputReaderPolicyInterface 和 InputListenerInterface
// 其通过 EventHub 监听"/dev/input"事件,获取事件,然后把事件加工后,发送给 InputClassfier
mReader = createInputReader(readerPolicy, mClassifier);
}由第一篇文章的分析可知,InputDispatcher 的实例对象是在构建 InputManager 实例对象时在其构造方法中,通过调用工厂方法 createInputDispatcher() 传入 InputDispatcherPolicyInterface 接口的实现类来创建的,在该工厂方法内部直接新建 InputDispatcher 对象。继续看一下 InputDispatcher 类的声明及构造函数:
2.InputDispatcher
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.h
cpp
class InputDispatcher : public android::InputDispatcherInterface {
protected:
~InputDispatcher() override;
public:
explicit InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy);
......
private:
std::unique_ptr<InputThread> mThread;
sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface> mPolicy;
sp<Looper> mLooper;
sp<InputReporterInterface> mReporter;
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> mPendingEvent GUARDED_BY(mLock);
std::deque<std::shared_ptr<EventEntry>> mInboundQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);
std::deque<std::shared_ptr<EventEntry>> mRecentQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);
std::deque<std::unique_ptr<CommandEntry>> mCommandQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);
};xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy)
: mPolicy(policy),
......
mDispatchEnabled(false),
mDispatchFrozen(false),
mInputFilterEnabled(false),
// mInTouchMode将由WindowManager初始化为默认设备配置。为了避免在调用从未出现的情况下泄漏堆栈
// 并且为了测试,无论如何都要在这里初始化它。
mInTouchMode(true),
......
mLatencyTracker(&mLatencyAggregator),
mCompatService(getCompatService()) {
mLooper = new Looper(false); // 新建自己的 Looper 对象
mReporter = createInputReporter(); // 新建 InputReporter 对象
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = nullptr;
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}InputDispatcher 实现了 InputDispatcherInterface 接口,在分析输入子系统 InputReader 时,在其线程循环的最后,QueueInputListener 调用此接口将 InputReader 读取并处理过的事件以 NotifyArgs 结构体的形式提交给 InputDispatcher。
3.InputDispatcher::start()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake(); });
return OK;
}InputDispatcher 实例对象创建完毕后处于待命状态,等到 IMS # start() 函数调用后启动输入系统时,调用 InputDispatcher::start() 方法来启动承载 InputDispatcher 的线程。但在方法内没有看到启动线程的代码逻辑,只是通过 std::make_unique 函数来构建 InputThread 的实例对象,那就具体来看一下 InputThread 类。
4.InputThread
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/include/InputThread.h
cpp
class InputThread {
public:
explicit InputThread(std::string name, std::function<void()> loop,
std::function<void()> wake = nullptr);
virtual ~InputThread();
bool isCallingThread();
private:
std::string mName; // 线程名
std::function<void()> mThreadWake;
sp<Thread> mThread; // 承载 InputDispatcher/InputReader 运行的线程
};xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputThread.cpp
cpp
class InputThreadImpl : public Thread {
public: // explicit 关键字的作用就是防止类构造函数的隐式自动转换,且只对有一个参数的类构造函数有效
explicit InputThreadImpl(std::function<void()> loop)
: Thread(/* canCallJava */ true), mThreadLoop(loop) {}
~InputThreadImpl() {}
private:
std::function<void()> mThreadLoop; // 存储一个可调用对象,这里指的是 lambda 表达式
bool threadLoop() override {
mThreadLoop();
return true;
}
};
InputThread::InputThread(std::string name, std::function<void()> loop, std::function<void()> wake)
: mName(name), mThreadWake(wake) {
// 使用封装的可调用对象 loop 新建 InputThreadImpl 对象
mThread = new InputThreadImpl(loop);
// 启动 InputThreadImpl 线程
mThread->run(mName.c_str(), ANDROID_PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
}InputThread 类本身不是一个线程,其内部是通过 InputThreadImpl 类来实现线程的具体功能。InputThreadImpl 类继承自 Thread 类,而 C++ 中的 Thread 类有一个名为 threadLoop() 的纯虚函数 ,当线程开始运行后,将会在内建的线程循环中不断地调用 threadLoop() 函数,直到此函数返回 false,则退出线程循环结束线程。
但从 InputThreadImpl 类的定义可以看出,threadLoop() 函数会一直保持循环(因为返回值始终为 true ),且每一次循环,会调用一次 mThreadLoop() 函数。而 mThreadLoop() 函数就是在启动 InputDispacher 时,构建 InputThread 实例对象传入的封装好的可调用函数对象 InputDispacher::dispatchOnce() 函数。也就是,在 InputDispatcher 启动时,会创建一个线程,然后不断循环调用 InputDispacher::dispatchOnce() 函数。
5.InputDispacher::dispatchOnce()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{ // 获取锁
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock); // 互斥锁(mutex),与条件变量结合使用,确保线程间的安全访问共享资源。
// std::condition_variable mDispatcherIsAlive:条件变量,用于在多线程程序中实现线程间的同步和互斥。
mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all(); // 唤醒与该条件变量关联的所有等待事件
// 如果 mCommandQueue 中没有待处理的命令 Command,则执行 dispatchOnceInnerLocked() 函数进行事件派发
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
// 调用 dispatchOnceInnerLocked() 函数将事件派发给合适的 Window
// 其中的传出参数 nextWakeupTime 决定了下次派发线程循环的执行时间
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
// 如果 mCommandQueue 中有待处理的 Command,则循环从中取出并执行所有的Command
// 如果执行了任何 Command,将下次唤醒时间设置为最小值,并强制下一个poll立即唤醒。
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
// 如果此时正在等待派发出去的事件的 ack(目标应用的响应),则要更早地唤醒以检查目标应用是否正在 ANR
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked(); // 处理ANR,获取下次checkANR的时间
// 获取下次唤醒和下次检测ANR之间较小的时间
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);
// 如果唤醒时间还是 LONG_LONG_MAX 没有被修改,表示没有待处理的 Command、挂起或排队的事件,那么将进入无限期的休眠中
if (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {
mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();
}
} // 释放锁
nsecs_t currentTime = now(); // 获取当前时间,计算 Looper 的睡眠等待时间
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
// 调用 pollOnce 函数进入阻塞,等待回调、超时或唤醒
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}condition_variable :条件变量,是 C++11 标准库中的一种同步原语,头文件<condition_variable >,用于在多线程程序中实现线程间的同步和互斥。它允许一个或多个线程等待另一个线程发出信号或通知,以避免忙等待的情况,从而提高程序的效率。在使用条件变量时,通常需要与互斥锁(mutex )结合使用,以确保线程间的安全访问共享资源。
用法 :当某个线程需要等待某个条件成立时,它可以调用条件变量的 wait() 函数来等待,同时释放它所持有的互斥锁,直到另一个线程调用条件变量的 notify_one() 或 notify_all() 函数来通知等待的线程条件已经成立,等待的线程才会被唤醒并重新获得互斥锁。
,并将下次唤醒时间设置为最小值,强制下一次poll唤醒线程
在一次线程循环中,InputDispacher::dispatchOnce() 函数的执行流程如下:
- 如果 mCommandQueue 中有待处理的 Command 命令,则循环从中取出并执行所有的 Command 命令,并且如果执行了任一 Command ,则将下次唤醒时间设置为最小值,并强制下一次 poll 立即唤醒线程;如果 mCommandQueue 中没有待处理的 Command 命令,则调用 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked() 函数派发事件;
- 如果此时正在等待派发出去的事件的 ack (目标应用的响应),则需要更早地唤醒以检查目标应用是否正在发生 ANR;
- 如果唤醒时间还是 LONG_LONG_MAX 没有被修改,表示没有待处理的 Command、挂起或排队的事件,那么将进入无限期的休眠中。
- 事件分发完后,调用 Looper::pollOnce 将当前的分发线程挂起,等到后续 InputReader 的读取线程将新的事件发送给 InputDispacher 并唤醒其分发线程。
Command 实际指向一个函数 std::function<void()>,执行一些必要特殊的操作,通知 Java 层的 InputMangerService ,比如焦点改变:sendFocusChangedCommandLocked(),ANR 发生:onAnrLocked()等等。
6.InputDispacher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
c
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
// 如果设备处于非交互状态,当正常调度挂起时,需重置按键重复计时器。以确保设备刚脱离睡眠时,终止按键重复计时器
if (!mDispatchEnabled) {
resetKeyRepeatLocked();
}
......
// 优化应用程序切换的延迟,当按下类似HOME/ENDCALL键时,启动一个短暂超时机制(0.5s),当timeout时,会立即分发事件并抛弃其他挂起的事件
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
if (mAppSwitchDueTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mAppSwitchDueTime;
}
// Ready to start a new event. 准备开始一个新的 event,如果没有待处理的 event,则抓取一个
if (!mPendingEvent) { // 正常一次分发前mPendingEvent = nullptr
if (mInboundQueue.empty()) { //当 InputReader 向队列中插入一个输入事件后,此处 mInboundQueue 就不为空
......
} else {
// 从派发队列中将位于队首的一条 EventEntry 取出并保存在 mPendingEvent 成员变量中
// mPendingEvent 表示处于派发过程中的一个输入事件。之所以使用一个成员变量而不是局部变量保存它
// 是由于此次线程循环有可能不能完成此事件的派发
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();
mInboundQueue.pop_front();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
}
......
}
// 现在有一个事件要调度,且所有事件都是以这种方式出队并进行处理,即使我们打算丢弃它们
......
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
......
case EventEntry::Type::FOCUS: {
std::shared_ptr<FocusEntry> typedEntry =
std::static_pointer_cast<FocusEntry>(mPendingEvent);
// 根据事件类型调用相应函数处理 -- 分发焦点事件
dispatchFocusLocked(currentTime, typedEntry);
done = true;
dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED; // 焦点事件永远不会被丢弃
break;
}
......
case EventEntry::Type::KEY: {
std::shared_ptr<KeyEntry> keyEntry = std::static_pointer_cast<KeyEntry>(mPendingEvent);
......
// 根据事件类型调用相应函数处理 -- 分发 Key 事件
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, keyEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> motionEntry =
std::static_pointer_cast<MotionEntry>(mPendingEvent);
......
// 根据事件类型调用相应函数处理 -- 分发 Motion 事件
// 执行 dispatchMotionLocked() 进行 Motion 事件的派发。如果派发完成,无论是成功派发还是事件被丢弃,都返回true,
// 否则返回 false,以便在下次循环时再次尝试此事件的派发
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, motionEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
......
}
if (done) {
if (dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
dropInboundEventLocked(*mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
// 将 mPendingEvent 设置为 nullptr,使之在下次循环时可以处理派发队列中的下一条事件
releasePendingEventLcked();
// 强制下一个 poll 中立即唤醒 inputDispatcher 线程来干活,如果此时派发队列为空,
// 下次循环调用此函数时会保持 nextWakeupTime 为 LONG_LONG_MAX 并直接返回,使得派发线程进入无限期休眠
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately
}
}InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked 函数的执行流程:
- 如果待分发事件队列 mInboundQueue 为空,则会使派发线程陷入无限期休眠状态;
- InputReader 读取线程将事件封装成新的 MotionEntry 对象并调用 InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked() 函数向 InputDispatcher.mInboundQueue 加入了当前要处理的输入事件。如果当前没有待分发的事件,那就从 InputDispatcher.mInboundQueue 取出一个 EventEntry 类型的事件赋值给 mPendingEvent 。注意 :MotionEntry 是 EventEntry 的子类型;
- 判断 mPendingEvent 的类型,如果是 Key 事件则调用 InputDispatcher.dispatchKeyLocked() 函数处理,如果是 Motion 事件则调用 InputDispatcher.dispatchMotionLocked() 函数处理,当然还有其他类型的事件,不再逐一类举。
需要注意的是:
- 分发一个事件至少需要一次线程循环才能完成,根据分发函数的返回值来决定是否在下次循环继续尝试此事件的分发;
- 事件的分发是串行的,在排队首的事件完成分发或被丢弃之前,不会对后续的事件进行分发;
小结
InputDispatcher 在一次线程循环中通过 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() 函数,将 InputReader 读取线程获取的输入事件分发完后,会调用 Looper::pollOnce() 将当前分发线程挂起,等待 InputReader 的读取线程将新的事件发送过来,并再次唤醒 InputDispatcher 的分发线程。
InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() 函数将事件分发转交给 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked() 函数进行分发,首先从 InputDispatcher.mInboundQueue 取出一个 EventEntry 类型的事件,然后根据事件的类型调用相应函数处理。承接上一篇文章,接下来以 Motion 事件的分发为例进行分析。
二、InputDispatcher 分发 Motion 事件
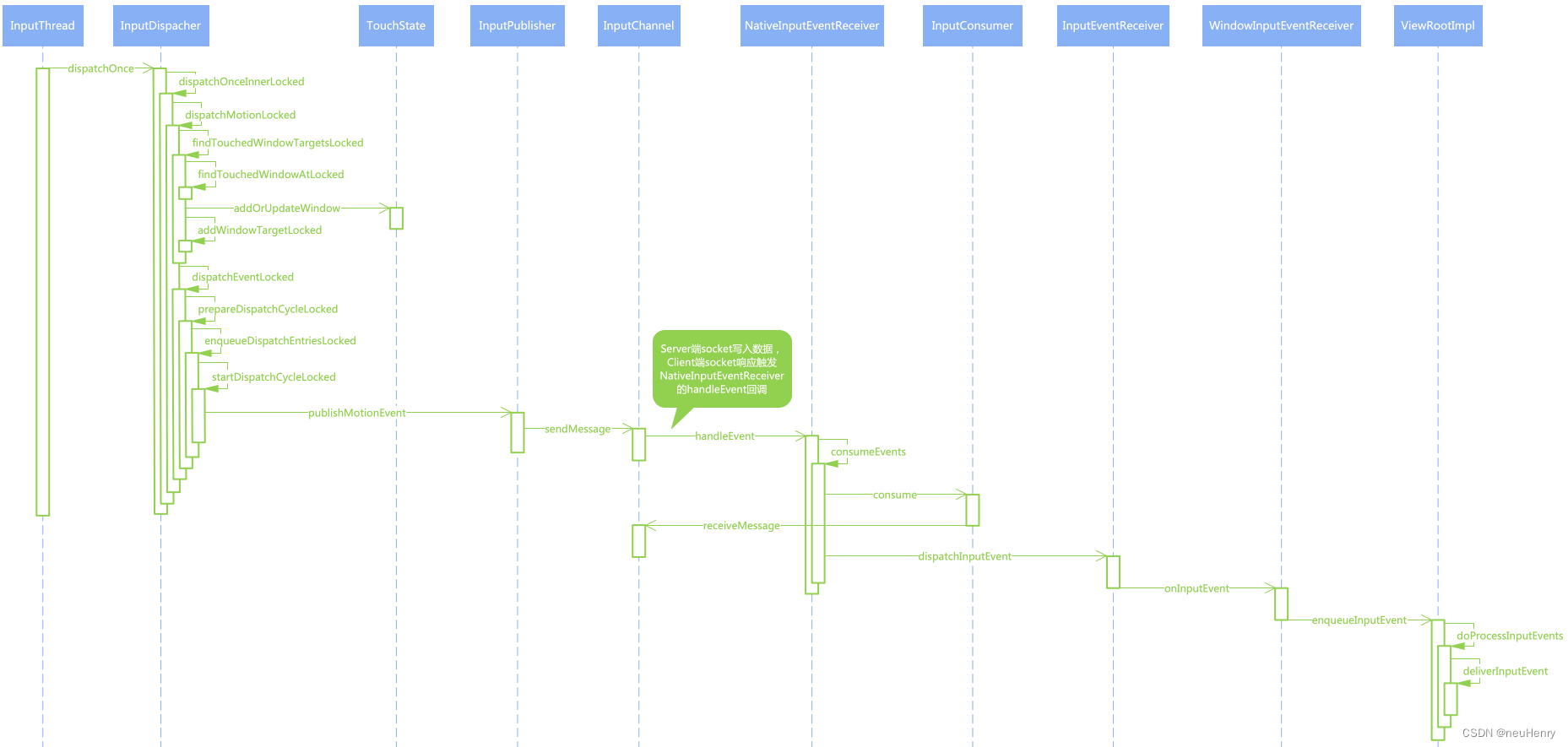
1.InputDispacher::dispatchMotionLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
ATRACE_CALL();
// Preprocessing.
if (!entry->dispatchInProgress) {
entry->dispatchInProgress = true;
logOutboundMotionDetails("dispatchMotion - ", *entry);
}
// 对于那些不幸被丢弃的事件,直接返回
if (*dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
setInjectionResult(*entry,
*dropReason == DropReason::POLICY ? InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED
: InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED);
return true;
}
bool isPointerEvent = entry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER;
// Identify targets. 确定目标-- 初始化 InputTarget 队列,存放 findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数获取的目标窗口
std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
bool conflictingPointerActions = false;
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult;
// 根据 Motion 事件的类型,寻找合适的目标窗口,
// 其返回值 injectionResult 指明寻找结果,而找到的合适的目标窗口信息将被保存在 inputTargets 队列中
if (isPointerEvent) { // 对于基于坐标点形式的事件,如触摸屏点击等,将根据坐标点、窗口ZOrder与区域寻找目标窗口
injectionResult =
findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime,
&conflictingPointerActions);
} else { // 对于其他类型的 Motion 事件(例如轨迹球),将以拥有焦点的窗口作为目标
injectionResult =
findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
}
// 返回值 PENDING 表明找到了一个窗口,不过如果窗口处于无响应状态,则返回 false,
// 也就是说这个事件尚未派发完成,将在下次派发线程的循环中再次尝试派发
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING) {
return false;
}
setInjectionResult(*entry, injectionResult);
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PERMISSION_DENIED) {
ALOGW("Permission denied, dropping the motion (isPointer=%s)", toString(isPointerEvent));
return true;
}
// 返回值不为 SUCCEEDED,表明无法为此事件找到合适的窗口,例如没有窗口处于焦点状态
// 或点击的位置没能落在任何一个窗口内,这个事件将被直接丢弃
if (injectionResult != InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED) {
CancelationOptions::Mode mode(isPointerEvent
? CancelationOptions::CANCEL_POINTER_EVENTS
: CancelationOptions::CANCEL_NON_POINTER_EVENTS);
CancelationOptions options(mode, "input event injection failed");
synthesizeCancelationEventsForMonitorsLocked(options);
return true;
}
// Add monitor channels from event's or focused display.
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));
if (isPointerEvent) {
std::unordered_map<int32_t, TouchState>::iterator it =
mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(entry->displayId);
if (it != mTouchStatesByDisplay.end()) {
const TouchState& state = it->second;
if (!state.portalWindows.empty()) {
// The event has gone through these portal windows, so we add monitoring targets of
// the corresponding displays as well.
for (size_t i = 0; i < state.portalWindows.size(); i++) {
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = state.portalWindows[i]->getInfo();
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, windowInfo->portalToDisplayId,
-windowInfo->frameLeft, -windowInfo->frameTop);
}
}
}
}
// Dispatch the motion.
if (conflictingPointerActions) {
CancelationOptions options(CancelationOptions::CANCEL_POINTER_EVENTS,
"conflicting pointer actions");
synthesizeCancelationEventsForAllConnectionsLocked(options);
}
// dispatchEventLocked() 函数继续事件的分发流程
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked() 函数的核心流程如下:
- 初始化 std::vector<InputTarget> 队列,用来存放 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数获取的目标窗口;
- 如果是触摸事件,调用 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数获取目标窗口,存放到 InputTarget 队列中;
- 找到目标窗口后调用 InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked() 函数继续事件的分发流程。
2.InputDispacher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
InputEventInjectionResult InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const MotionEntry& entry, std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets,
nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime, bool* outConflictingPointerActions) {
ATRACE_CALL();
enum InjectionPermission {
INJECTION_PERMISSION_UNKNOWN,
INJECTION_PERMISSION_GRANTED,
INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED
};
// For security reasons, we defer updating the touch state until we are sure that
// event injection will be allowed.
int32_t displayId = entry.displayId;
int32_t action = entry.action;
int32_t maskedAction = action & AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MASK;
// 根据触摸事件的属性,更新触摸状态
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;
InjectionPermission injectionPermission = INJECTION_PERMISSION_UNKNOWN;
sp<InputWindowHandle> newHoverWindowHandle(mLastHoverWindowHandle);
sp<InputWindowHandle> newTouchedWindowHandle;
// 将当前触摸状态复制到 tempTouchState,此状态将用于在此功能结束时更新 mTouchStatesByDisplay
// 如果不存在指定显示的状态,那么初始状态将为空
const TouchState* oldState = nullptr;
TouchState tempTouchState;
std::unordered_map<int32_t, TouchState>::iterator oldStateIt =
mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(displayId);
if (oldStateIt != mTouchStatesByDisplay.end()) { // 获取上一次查找的结果 oldStateIt
oldState = &(oldStateIt->second);
tempTouchState.copyFrom(*oldState);
}
bool isSplit = tempTouchState.split;
bool switchedDevice = tempTouchState.deviceId >= 0 && tempTouchState.displayId >= 0 &&
(tempTouchState.deviceId != entry.deviceId || tempTouchState.source != entry.source ||
tempTouchState.displayId != displayId);
bool isHoverAction = (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_MOVE ||
maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_ENTER ||
maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_EXIT);
bool newGesture = (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN ||
maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_SCROLL || isHoverAction);
const bool isFromMouse = entry.source == AINPUT_SOURCE_MOUSE;
bool wrongDevice = false;
if (newGesture) {
bool down = maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
......
// 如果当前事件是这一系列事件的起点,如:ACTION_DOWN,那本次降不会复用上一次的查找结果,且会清除、重置 tempTouchState 的状态
tempTouchState.reset();
tempTouchState.down = down;
tempTouchState.deviceId = entry.deviceId;
tempTouchState.source = entry.source;
tempTouchState.displayId = displayId;
isSplit = false;
} else if (switchedDevice && maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE) {
......
}
if (newGesture || (isSplit && maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)) {
/* Case 1: New splittable pointer going down, or need target for hover or scroll. */
int32_t x;
int32_t y;
int32_t pointerIndex = getMotionEventActionPointerIndex(action);
// Always dispatch mouse events to cursor position.
if (isFromMouse) {
x = int32_t(entry.xCursorPosition);
y = int32_t(entry.yCursorPosition);
} else {
x = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X));
y = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y));
}
bool isDown = maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
// InputDispatcher.findTouchedWindowAtLocked() 函数寻找可接收触摸事件的窗口
newTouchedWindowHandle =
findTouchedWindowAtLocked(displayId, x, y, &tempTouchState,
isDown /*addOutsideTargets*/, true /*addPortalWindows*/);
...... // 检验 newTouchedWindowHandle 的有效性
if (newTouchedWindowHandle != nullptr) { // 添加窗口 Flag 标志位
// FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS:声明事件应该按原样发送,除非事件被转化;
int32_t targetFlags = InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;
if (isSplit) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT;
}
if (isWindowObscuredAtPointLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle, x, y)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED;
} else if (isWindowObscuredLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED;
}
// Update hover state.
......
// Update the temporary touch state.
BitSet32 pointerIds;
......
tempTouchState.addOrUpdateWindow(newTouchedWindowHandle, targetFlags, pointerIds);
}
tempTouchState.addGestureMonitors(newGestureMonitors);
} else {
/* Case 2: Pointer move, up, cancel or non-splittable pointer down. */
// If the pointer is not currently down, then ignore the event.
......
// Check whether touches should slip outside of the current foreground window.
// 寻找触摸窗口------非DOWN事件的处理
if (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE && entry.pointerCount == 1 &&
tempTouchState.isSlippery()) {
int32_t x = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[0].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X));
int32_t y = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[0].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y));
sp<InputWindowHandle> oldTouchedWindowHandle =
tempTouchState.getFirstForegroundWindowHandle();
newTouchedWindowHandle = findTouchedWindowAtLocked(displayId, x, y, &tempTouchState);
if (oldTouchedWindowHandle != newTouchedWindowHandle &&
oldTouchedWindowHandle != nullptr && newTouchedWindowHandle != nullptr) {
if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {
ALOGD("Touch is slipping out of window %s into window %s in display %" PRId32,
oldTouchedWindowHandle->getName().c_str(),
newTouchedWindowHandle->getName().c_str(), displayId);
}
// Make a slippery exit from the old window.
tempTouchState.addOrUpdateWindow(oldTouchedWindowHandle,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT,
BitSet32(0));
// Make a slippery entrance into the new window.
if (newTouchedWindowHandle->getInfo()->supportsSplitTouch()) {
isSplit = true;
}
// FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER:声明应将事件作为初始的 DOWN 事件进行调度,
// 用于在触摸滑入新窗口时将 ACTION_MOVE 转换为 ACTION_DOWN
int32_t targetFlags =
InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER;
if (isSplit) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT;
}
if (isWindowObscuredAtPointLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle, x, y)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED;
} else if (isWindowObscuredLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED;
}
BitSet32 pointerIds;
if (isSplit) {
pointerIds.markBit(entry.pointerProperties[0].id);
}
tempTouchState.addOrUpdateWindow(newTouchedWindowHandle, targetFlags, pointerIds);
}
}
}
......
// 检查是否允许注入所有已触摸的前台窗口,并确保至少有一个已触摸的前台窗口
{ // 进行必要的权限检查
bool haveForegroundWindow = false;
for (const TouchedWindow& touchedWindow : tempTouchState.windows) {
if (touchedWindow.targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND) {
haveForegroundWindow = true;
if (!checkInjectionPermission(touchedWindow.windowHandle, entry.injectionState)) {
injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PERMISSION_DENIED;
injectionPermission = INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED;
goto Failed;
}
}
}
bool hasGestureMonitor = !tempTouchState.gestureMonitors.empty();
if (!haveForegroundWindow && !hasGestureMonitor) {
......
injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED;
goto Failed;
}
// 权限允许注入所有已触摸的前台窗口
injectionPermission = INJECTION_PERMISSION_GRANTED;
}
// 检查监听外部触摸的窗口是否属于同一 UID,如果设置了策略标志,将不会向该窗口显示坐标信息
......
// Success! Output targets.
injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED;
// 通过 addWindowTargetLocked 将 tempTouchState 的结果传给 inputTargets
for (const TouchedWindow& touchedWindow : tempTouchState.windows) {
addWindowTargetLocked(touchedWindow.windowHandle, touchedWindow.targetFlags,
touchedWindow.pointerIds, inputTargets);
}
for (const TouchedMonitor& touchedMonitor : tempTouchState.gestureMonitors) {
addMonitoringTargetLocked(touchedMonitor.monitor, touchedMonitor.xOffset,
touchedMonitor.yOffset, inputTargets);
}
// 丢弃外部或悬停触摸窗口,因为我们在下一次迭代中不会关心它们
// 裁剪 tempTouchState
tempTouchState.filterNonAsIsTouchWindows();
Failed:
// Check injection permission once and for all. -- 检查 injection 权限
if (injectionPermission == INJECTION_PERMISSION_UNKNOWN) {
if (checkInjectionPermission(nullptr, entry.injectionState)) {
injectionPermission = INJECTION_PERMISSION_GRANTED;
} else {
injectionPermission = INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
}
if (injectionPermission != INJECTION_PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
return injectionResult;
}
// 如果 injector 获取到权限,则更新最终的触摸状态
if (!wrongDevice) {
......
// 保存 tempTouchState 到 mTouchStatesByDisplay
if (maskedAction != AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_SCROLL) {
if (tempTouchState.displayId >= 0) {
mTouchStatesByDisplay[displayId] = tempTouchState;
} else {
mTouchStatesByDisplay.erase(displayId);
}
}
// Update hover state.-- 更新悬停状态
mLastHoverWindowHandle = newHoverWindowHandle;
}
return injectionResult;
}InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数的核心流程如下:
- 创建 TouchState 类型的 tempTouchState ,并将当前触摸状态赋值到 tempTouchState ,用于后续更新 mTouchStatesByDisplay;
- 调用 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked() 函数寻找可接收当前触摸事件的窗口,检验刚查找到的窗口的有效性,并为窗口添加 Flag 标志位,然后通过 TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow() 函数将其添加到 tempTouchState.windows 中保存;
- 经过重重的检验与判断操作,如果没有问题,则通过 addWindowTargetLocked() 函数将 tempTouchState 的结果传给 inputTargets;
- 函数的最后将 tempTouchState 保存到 mTouchStatesByDisplay 中以便下一次使用。
2.1 TouchState
结构体 TouchState 用来跟踪记录触摸事件状态,其有一个窗口队列 std::vector<TouchedWindow> windows 用来保存当前 Display 中所有可以接收 Motion 事件的窗口。
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/TouchState.h
cpp
struct TouchState {
bool down;
bool split;
int32_t deviceId; // id of the device that is currently down, others are rejected
uint32_t source; // source of the device that is current down, others are rejected
int32_t displayId; // id to the display that currently has a touch, others are rejected
std::vector<TouchedWindow> windows;
std::vector<sp<android::InputWindowHandle>> portalWindows;
std::vector<TouchedMonitor> gestureMonitors;
TouchState();
~TouchState();
void reset();
void copyFrom(const TouchState& other);
void addOrUpdateWindow(const sp<android::InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle, int32_t targetFlags, BitSet32 pointerIds);
void addPortalWindow(const sp<android::InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle);
void addGestureMonitors(const std::vector<TouchedMonitor>& monitors);
void removeWindowByToken(const sp<IBinder>& token);
void filterNonAsIsTouchWindows();
void filterNonMonitors();
sp<InputWindowHandle> getFirstForegroundWindowHandle() const;
bool isSlippery() const;
};xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/TouchState.cpp
cpp
TouchState::TouchState()
: down(false), split(false), deviceId(-1), source(0), displayId(ADISPLAY_ID_NONE) {}
TouchState::~TouchState() {}
void TouchState::reset() {
down = false;
split = false;
deviceId = -1;
source = 0;
displayId = ADISPLAY_ID_NONE;
windows.clear();
portalWindows.clear();
gestureMonitors.clear();
}
void TouchState::copyFrom(const TouchState& other) {
down = other.down;
split = other.split;
deviceId = other.deviceId;
source = other.source;
displayId = other.displayId;
windows = other.windows;
portalWindows = other.portalWindows;
gestureMonitors = other.gestureMonitors;
}
void TouchState::filterNonAsIsTouchWindows() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < windows.size();) {
TouchedWindow& window = windows[i];
if (window.targetFlags &
(InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER)) {
window.targetFlags &= ~InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK;
window.targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;
i += 1;
} else {
windows.erase(windows.begin() + i);
}
}
}
......在 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数的开始创建了一个 TouchState 类型的 tempTouchState ,每次开始寻找接收 Motion 的窗口前,都先通过 mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(displayId) 根据传入的 displayId 获取到 oldState 并拷贝给 tempTouchState 。那创建 tempTouchState 的作用是什么?
在 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数的最后,会把函数开始时创建的 tempTouchState 保存到 mTouchStatesByDisplay 中,因此在函数的开始 tempTouchState 获取到的是上一次寻找的结果。这么做的目的是为了下一次再进到这个函数时,直接取上一次执行后的结果,就不需要再次遍历所有的窗口来寻找可以接收当前输入事件的窗口(比如:在 DOWN 的时候遍历所有窗口,找到了所有可以接收当前输入事件的窗口,那么后续分发 MOVE 、UP 等事件的时候,不必重复再去遍历所有窗口进行查找,提升效率)。
2.2 InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
sp<InputWindowHandle> InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked(int32_t displayId, int32_t x,
int32_t y, TouchState* touchState,
bool addOutsideTargets,
bool addPortalWindows,
bool ignoreDragWindow) {
if ((addPortalWindows || addOutsideTargets) && touchState == nullptr) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL(
"Must provide a valid touch state if adding portal windows or outside targets");
}
// Traverse windows from front to back to find touched window.
const std::vector<sp<InputWindowHandle>>& windowHandles = getWindowHandlesLocked(displayId);
for (const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle : windowHandles) {
if (ignoreDragWindow && haveSameToken(windowHandle, mDragState->dragWindow)) {
continue;
}
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
if (windowInfo->displayId == displayId) {
auto flags = windowInfo->flags;
if (windowInfo->visible) { // 当前窗口必须是可见的
// 窗口不能包含InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCHABLE 标志位,设置了这个 flag 的窗口不能接收Motion事件
if (!flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCHABLE)) {
bool isTouchModal = !flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_FOCUSABLE) &&
!flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCH_MODAL);
if (isTouchModal || windowInfo->touchableRegionContainsPoint(x, y)) {
int32_t portalToDisplayId = windowInfo->portalToDisplayId;
if (portalToDisplayId != ADISPLAY_ID_NONE &&
portalToDisplayId != displayId) {
if (addPortalWindows) {
// For the monitoring channels of the display.
touchState->addPortalWindow(windowHandle);
}
return findTouchedWindowAtLocked(portalToDisplayId, x, y, touchState,
addOutsideTargets, addPortalWindows);
}
// Found window.
return windowHandle;
}
}
if (addOutsideTargets && flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH)) {
touchState->addOrUpdateWindow(windowHandle,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE,
BitSet32(0));
}
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked() 函数通过遍历所有窗口,寻找可以接收输入事件的窗口,目标窗口需要满足以下条件:
- 当前窗口必须是 visible 可见的;
- 当前窗口不能包含 InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCHABLE 标志位,设置了这个 flag 的窗口不能接收 Motion 事件;
- 当前窗口不能包含 InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_FOCUSABLE 和 InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCH_MODAL 这两个 flag 标志位,如果某个窗口没有 NOT_TOUCH_MODAL 这个 flag,表示这个窗口将会消费掉所有坐标事件,无论这些事件是否落在了这个窗口区域里面;
- 当前输入事件的坐标落在当前窗口的 Motion 区域里,那么返回当前窗口。
2.3 TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/TouchState.cpp
cpp
void TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow(const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle, int32_t targetFlags,
BitSet32 pointerIds) {
if (targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT) {
split = true;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < windows.size(); i++) {
TouchedWindow& touchedWindow = windows[i];
if (touchedWindow.windowHandle == windowHandle) { // 如果已存在,则直接更新对应的值
touchedWindow.targetFlags |= targetFlags;
if (targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT) {
touchedWindow.targetFlags &= ~InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;
}
touchedWindow.pointerIds.value |= pointerIds.value;
return;
}
}
// 新建 TouchedWindow 并赋值,然后加入 windows 中
TouchedWindow touchedWindow;
touchedWindow.windowHandle = windowHandle;
touchedWindow.targetFlags = targetFlags;
touchedWindow.pointerIds = pointerIds;
windows.push_back(touchedWindow);
}TouchState::addOrUpdateWindow() 函数,首先遍历 TouchState.windows 查找是否已存在同一个 TouchedWindow 实例对象,如已存在则使用传入的参数更新其对应的值,然后返回即可,如不存在则新建一个 TouchWindow 对象,整合之前的所有信息,然后加入到 tempTouchState 的 windows 队列中。
2.4 InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked(const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
int32_t targetFlags, BitSet32 pointerIds,
std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
std::vector<InputTarget>::iterator it =
std::find_if(inputTargets.begin(), inputTargets.end(),
[&windowHandle](const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
return inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken() ==
windowHandle->getToken();
});
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
if (it == inputTargets.end()) {
InputTarget inputTarget;
std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel =
getInputChannelLocked(windowHandle->getToken());
if (inputChannel == nullptr) {
ALOGW("Window %s already unregistered input channel", windowHandle->getName().c_str());
return;
}
inputTarget.inputChannel = inputChannel;
inputTarget.flags = targetFlags;
inputTarget.globalScaleFactor = windowInfo->globalScaleFactor;
inputTarget.displaySize =
int2(windowHandle->getInfo()->displayWidth, windowHandle->getInfo()->displayHeight);
inputTargets.push_back(inputTarget);
it = inputTargets.end() - 1;
}
ALOG_ASSERT(it->flags == targetFlags);
ALOG_ASSERT(it->globalScaleFactor == windowInfo->globalScaleFactor);
it->addPointers(pointerIds, windowInfo->transform);
}std::find_if :C++ 中 STL 库中的一个函数,它可以在一个给定的范围内查找第一个符合指定条件的元素。它接收一个范围和一个谓词(即一个判断条件的函数)作为参数,返回第一个满足该条件的元素的迭代器。如果在整个范围内都找不到满足条件的元素,则返回 last 参数指向的位置。
InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked 函数执行流程如下:
- 通过 std::find_if 库函数,在 inputTargets 队列中检查当前焦点窗口是否已经在里面,避免重复加入;
- 如果 inputTargets 里面还没有,则根据焦点窗口的 IBinder 类型的 token 找到对应的 InputChannel ,然后根据该 InputWindowHandle 创建一个对应的 InputTarget 对象并添加到 inputTargets 中。
cpp
// All registered connections mapped by input channel token.
std::unordered_map<sp<IBinder>, sp<Connection>, StrongPointerHash<IBinder>> mConnectionsByToken
GUARDED_BY(mLock);在为 Server 端和 Client 端创建 InputChannel 对的时候,会创建一个 BBinder 对象,并将键值对 <IBinder token, Connection connection> 加入到了 InputDispatcher 维护的 mConnectionsByToken 中,并且该 token 后续会返回给 InputWindowHandle ,那么就可以根据 InputWindowHandle 存储的 IBinder 对象找到一个对应的 Connection 对象,进而找到一个 InputChannel 对象。
3.InputDispacher::dispatchEventLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
......
updateInteractionTokensLocked(*eventEntry, inputTargets);
ALOG_ASSERT(eventEntry->dispatchInProgress); // should already have been set to true
// 该方法会最终调用到 PowerManagerService 内部的 userActivityFromNative() 方法,用来表示
// 用户点击了当前界面,主要用于屏保相关的倒计时打断处理
pokeUserActivityLocked(*eventEntry);
for (const InputTarget& inputTarget : inputTargets) {
// 通过 InputDispatcher::getConnectionLocked() 函数获取服务端 InputChannel 的 Connection 对象
sp<Connection> connection =
getConnectionLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
if (connection != nullptr) {
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
} else {
......
}
}
}InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked() 函数的核心作用如下:
- 遍历传入的 inputTargets ,首先通过 InputDispatcher::getConnectionLocked() 函数获取服务端 InputChannel 的 Connection 对象,调用 InputDispatcher.prepareDispatchCycleLocked() 函数来分发事件,这里说明了对于一个输入事件来说,会传递给多个窗口进行处理。
- 对于每一个服务端 InputChannel ,InputDispatcher 都创建了一个 Connection 对象来保存这个 InputChannel 对象,可以通过 IBinder 类型的 token 来检索得到该 Connection 对象,那么这里便可以通过 InputTarget 的 InputChannel 对象中的 token 来得到持有服务端 InputChannel 的 Connection 对象。
4.InputDispacher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
......
// 如果连接状态不正常,比如进程已经死了,那么就不向它分发了,跳过此事件。如果连接断开,我们不希望将其他 outbound 事件排入队列
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dropping event because the channel status is %s",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), connection->getStatusLabel());
#endif
return;
}
// Split a motion event if needed.-- FLAG_SPLIT:用来声明当前输入事件是否支持被拆分,分给多个窗口
if (inputTarget.flags & InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(eventEntry->type != EventEntry::Type::MOTION,
"Entry type %s should not have FLAG_SPLIT",
NamedEnum::string(eventEntry->type).c_str());
const MotionEntry& originalMotionEntry = static_cast<const MotionEntry&>(*eventEntry);
if (inputTarget.pointerIds.count() != originalMotionEntry.pointerCount) {
std::unique_ptr<MotionEntry> splitMotionEntry =
splitMotionEvent(originalMotionEntry, inputTarget.pointerIds);
if (!splitMotionEntry) {
return; // split event was dropped
}
if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Split motion event.",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());
logOutboundMotionDetails(" ", *splitMotionEntry);
}
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, std::move(splitMotionEntry),
inputTarget);
return;
}
}
// 没有拆分,则按原来的事件队列来分派事件
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked() 函数主要判断当前输入事件是否支持拆分,如果支持拆分则把当前事件拆分。然后调用 InputDispatcher.enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked() 继续进行分发。
5.InputDispacher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
if (ATRACE_ENABLED()) {
std::string message =
StringPrintf("enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(inputChannel=%s, id=0x%" PRIx32 ")",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), eventEntry->id);
ATRACE_NAME(message.c_str());
}
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.empty();
// Enqueue dispatch entries for the requested modes.
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER);
// If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked() 函数的执行流程如下:
- 调用 InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked() 函数,其作用是如果目标窗口设置了以下几种 flag ,表示目标窗口需要处理这类事件,那么就把输入事件封装为相应的 DispatchEntry 类型,加入到 Connection.outBoundQueue 队列中;
- 如果Coonection.outBoundQueue 队列之前为空,但是经过 InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked() 后不为空,那么调用InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked() 函数开始分发事件。
6.InputDispacher::startDispatchCycleLocked()
xref: /frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
cpp
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
......
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
// Connection 的状态正常,并且 Connection.outboundQueue 不为空
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front(); // 获取 DispatchEntry 实例
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime; // 设置分发事件的时间
const std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout =
getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
dispatchEntry->timeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count(); // 设置分发事件的超时时间,如果超时会引发 ANR
// Publish the event. --- 发布事件
status_t status;
const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry); // 获取待调度的事件
switch (eventEntry.type) { // 根据 EventEntry::Type 类型分别调用不同的发布方法
......
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: { // 分发 Motion 事件
const MotionEntry& motionEntry = static_cast<const MotionEntry&>(eventEntry);
PointerCoords scaledCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
const PointerCoords* usingCoords = motionEntry.pointerCoords;
......
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac = getSignature(motionEntry, *dispatchEntry);
// Publish the motion event.-- 发布 Motion 事件
status = connection->inputPublisher
.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId,
motionEntry.deviceId, motionEntry.source,
motionEntry.displayId, std::move(hmac),
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction,
motionEntry.actionButton,
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
motionEntry.edgeFlags, motionEntry.metaState,
motionEntry.buttonState,
motionEntry.classification,
dispatchEntry->transform,
motionEntry.xPrecision, motionEntry.yPrecision,
motionEntry.xCursorPosition,
motionEntry.yCursorPosition,
dispatchEntry->displaySize.x,
dispatchEntry->displaySize.y,
motionEntry.downTime, motionEntry.eventTime,
motionEntry.pointerCount,
motionEntry.pointerProperties, usingCoords);
break;
}
case EventEntry::Type::FOCUS: {
......
}
case EventEntry::Type::POINTER_CAPTURE_CHANGED: {
......
}
case EventEntry::Type::DRAG: {
......
}
case EventEntry::Type::CONFIGURATION_CHANGED:
case EventEntry::Type::DEVICE_RESET:
case EventEntry::Type::SENSOR: {
......
return;
}
}
// Check the result.
if (status) { // 检测分发的结果,正常时status = 0
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (connection->waitQueue.empty()) {
......
// 当前 waitQueue 是空的,说明 socket 中也应该是空的,但是却是 WOULD_BLOCK,说明这时一个异常的情况,中断分发
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
} else {
...... // socket满了,等待应用进程处理掉一些事件
}
} else {
......
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
}
return;
}
// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.
// 将已经分发的事件 dispatchEntry 从 outboundQueue 中移除
connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),
connection->outboundQueue.end(),
dispatchEntry));
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
// 将已经分发的事件 dispatchEntry 加入目标窗口 waitQueue中,记录下已经分发到目标窗口侧的事件,便于监控 ANR 等行为
connection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);
// 如果目标窗口进程(例如应用进程)可响应,则将这个事件超时事件点和目标窗口连接对象 token 加入 mAnrTracker 中监控
// 如果不可响应,则不再向它分发更多的事件,直到它消耗了已经分发给它的事件
if (connection->responsive) {
mAnrTracker.insert(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,
connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
}
traceWaitQueueLength(*connection); //systrace 中跟踪 waitQueue 的长度
}
}InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked() 函数中,如果 Connection 的状态正常,并且 Connection.outboundQueue 不为空,则循环遍历 Connection.outboundQueue,然后根据 EventEntry::Type 类型分别调用不同的发布方法,这里我们只关心 Motion 类型的事件发布。
7.InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent()
xref: /frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
cpp
status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(
uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId, int32_t source, int32_t displayId,
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac, int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t edgeFlags, int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState,
MotionClassification classification, const ui::Transform& transform, float xPrecision,
float yPrecision, float xCursorPosition, float yCursorPosition, int32_t displayWidth,
int32_t displayHeight, nsecs_t downTime, nsecs_t eventTime, uint32_t pointerCount,
const PointerProperties* pointerProperties, const PointerCoords* pointerCoords) {
......
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::MOTION;
msg.header.seq = seq;
msg.body.motion.eventId = eventId;
msg.body.motion.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.motion.source = source;
msg.body.motion.displayId = displayId;
msg.body.motion.hmac = std::move(hmac);
msg.body.motion.action = action;
msg.body.motion.actionButton = actionButton;
msg.body.motion.flags = flags;
msg.body.motion.edgeFlags = edgeFlags;
msg.body.motion.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.motion.buttonState = buttonState;
msg.body.motion.classification = classification;
msg.body.motion.dsdx = transform.dsdx();
msg.body.motion.dtdx = transform.dtdx();
msg.body.motion.dtdy = transform.dtdy();
msg.body.motion.dsdy = transform.dsdy();
msg.body.motion.tx = transform.tx();
msg.body.motion.ty = transform.ty();
msg.body.motion.xPrecision = xPrecision;
msg.body.motion.yPrecision = yPrecision;
msg.body.motion.xCursorPosition = xCursorPosition;
msg.body.motion.yCursorPosition = yCursorPosition;
msg.body.motion.displayWidth = displayWidth;
msg.body.motion.displayHeight = displayHeight;
msg.body.motion.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.motion.eventTime = eventTime;
msg.body.motion.pointerCount = pointerCount;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < pointerCount; i++) {
msg.body.motion.pointers[i].properties.copyFrom(pointerProperties[i]);
msg.body.motion.pointers[i].coords.copyFrom(pointerCoords[i]);
}
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent() 函数把输入事件的信息重新封装到一个 InputMessage 类型的结构体中,然后调用 InputChannel::sendMessage() 函数发送封装好的 InputMessage。
8.InputChannel::sendMessage()
xref: /frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
cpp
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
const size_t msgLength = msg->size();
InputMessage cleanMsg;
msg->getSanitizedCopy(&cleanMsg);
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
nWrite = ::send(getFd(), &cleanMsg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
......
return OK;
}InputChannel::sendMessage() 函数调用 socket 的 send() 函数向服务端 InputChannel 保存的 socket 文件描述符发送封装好的 InputMessage 信息。
在 ViewRootImpl#setView() 函数中会创建一个 WindowInputEventReceiver 对象,进而会构建一个 Native 层的 NativeInputEventReceiver 对象,并且在初始化的过程中会调用 NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents() 函数:
xref: /frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);
return OK;
}
......
void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
if (mFdEvents != events) {
mFdEvents = events;
int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();
if (events) {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, nullptr);
} else {
mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
}
}
}NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents() 函数通过 MessageQueue 的 Looper 对象的 addFd() 函数来对客户端 InputChannel 中保存的客户端 socket 文件描述符进行监听,如果服务端有数据写入那么就调用 NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent() 函数回调。
9.NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
cpp
int NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent(int receiveFd, int events, void* data) {
......
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT) { // ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT 表示文件描述符可读
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, false /*consumeBatches*/, -1, nullptr);
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "handleReceiveCallback");
return status == OK || status == NO_MEMORY ? KEEP_CALLBACK : REMOVE_CALLBACK;
}
......
return KEEP_CALLBACK;
}在 NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() 函数注册文件描述监听时,传入的 events 类型就是 ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT ,因此流程走 ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT 流程,继续调用 NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents() 函数。
10.NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
......
if (consumeBatches) {
mBatchedInputEventPending = false;
}
if (outConsumedBatch) {
*outConsumedBatch = false;
}
ScopedLocalRef<jobject> receiverObj(env, nullptr);
bool skipCallbacks = false;
for (;;) {
uint32_t seq;
InputEvent* inputEvent;
// 读取客户端 InputChannel 发送的事件并转化为 InputEvent
status_t status = mInputConsumer.consume(&mInputEventFactory,
consumeBatches, frameTime, &seq, &inputEvent);
......
if (!skipCallbacks) {
// 获取到 Java 对象 InputEventReceiver 对象
if (!receiverObj.get()) {
receiverObj.reset(jniGetReferent(env, mReceiverWeakGlobal));
......
}
jobject inputEventObj;
switch (inputEvent->getType()) {
......
case AINPUT_EVENT_TYPE_MOTION: {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Received motion event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
// 将 Native 层输入事件对象转换为上层输入事件对象
MotionEvent* motionEvent = static_cast<MotionEvent*>(inputEvent);
if ((motionEvent->getAction() & AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE) && outConsumedBatch) {
*outConsumedBatch = true;
}
inputEventObj = android_view_MotionEvent_obtainAsCopy(env, motionEvent);
break;
}
......
}
if (inputEventObj) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
// 最后通过 JNI 调用 Java 层对象 InputEventReceiver 的 dispatchInputEvent 方法
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
ALOGE("Exception dispatching input event.");
skipCallbacks = true;
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
}
......
}
if (skipCallbacks) {
mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(seq, false);
}
}
}NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents() 函数的核心流程如下:
- 调用 InputConsumer::comsume() 函数,其通过客户端对应的 InputChannel::receiveMessage() 函数读取发送过来的输入事件,并对不同的事件类型创建对应的事件对象,如:InputMessage::Type::MOTION 类型的事件为其创建 MotionEvent 对象,并将刚读取的 InputMessage 的信息取出传给新建的 MotionEvent 对象,也即将输入事件最终转化为一个 InputEvent 对象(MotionEvent 是 InputEvent 的子类);
- 获取 Java 层 InputEventReceiver 对象,在 ViewRootImpl 中创建 WindowInputEventReceiver 的时候,会把 Java 层的 InputEventReceiver 对象的弱引用作为初始化 NativeInputEventReceiver 的参数,后续 NativeInputEventReceiver 的全局变量 mReceiverWeakGlobal 便会持有这个引用;
- 通过 android_view_MotionEvent_obtainAsCopy() 函数将 Native 层输入事件对象转换为 Java 层的输入事件对象,综述分析,最后通过 JNI 调用到 InputEventReceiver#dispatchInputEvent() 函数将输入事件传递给 Java 层。
11.InputEventReceiver#dispatchInputEvent()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
java
public abstract class InputEventReceiver {
private static final String TAG = "InputEventReceiver";
......
// Called from native code.
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event);
}
......
}InputEventReceiver 是一个抽象类,由于我们分析的是 ViewRootImpl#setView() 函数中的监听输入事件注册流程,因此这里 InputEventReceiver 的实现是 ViewRootImpl 的内部类 WindowInputEventReceiver 类。
12.ViewRootImpl#WindowInputEventReceiver#onInputEvent()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java#WindowInputEventReceiver.java
java
final class WindowInputEventReceiver extends InputEventReceiver {
public WindowInputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
super(inputChannel, looper);
}
@Override
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "processInputEventForCompatibility");
List<InputEvent> processedEvents;
try {
processedEvents =
mInputCompatProcessor.processInputEventForCompatibility(event);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
if (processedEvents != null) {
if (processedEvents.isEmpty()) {
// InputEvent consumed by mInputCompatProcessor
finishInputEvent(event, true);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < processedEvents.size(); i++) {
enqueueInputEvent(
processedEvents.get(i), this,
QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_MODIFIED_FOR_COMPATIBILITY, true);
}
}
} else {
enqueueInputEvent(event, this, 0, true);
}
}
}ViewRootImpl#WindowInputEventReceiver#onInputEvent() 函数继续调用 ViewRootImpl#enqueueInputEvent() 函数进行处理。
13.ViewRootImpl#enqueueInputEvent()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
java
@SuppressWarnings({"EmptyCatchBlock", "PointlessBooleanExpression"})
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks,
AttachedSurfaceControl {
......
@UnsupportedAppUsage
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,
InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
QueuedInputEvent q = obtainQueuedInputEvent(event, receiver, flags);
if (event instanceof MotionEvent) {
MotionEvent me = (MotionEvent) event;
if (me.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { // 事件取消
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.VIEW_ENQUEUE_INPUT_EVENT, "Motion - Cancel",
getTitle());
}
} else if (event instanceof KeyEvent) {
KeyEvent ke = (KeyEvent) event;
if (ke.isCanceled()) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.VIEW_ENQUEUE_INPUT_EVENT, "Key - Cancel",
getTitle());
}
}
// Always enqueue the input event in order, regardless of its time stamp.
// We do this because the application or the IME may inject key events
// in response to touch events and we want to ensure that the injected keys
// are processed in the order they were received and we cannot trust that
// the time stamp of injected events are monotonic.
QueuedInputEvent last = mPendingInputEventTail;
if (last == null) {
mPendingInputEventHead = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
} else {
last.mNext = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
}
mPendingInputEventCount += 1;
Trace.traceCounter(Trace.TRACE_TAG_INPUT, mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName,
mPendingInputEventCount);
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents();
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
}
......
}ViewRootImpl#enqueueInputEvent() 函数首先调用 ViewRootImpl#obtainQueuedInputEvent() 函数获取一个 QueuedInputEvent 实例对象,并将其添加到 mPendingInputEventTail 输入事件的队列尾部,由于传递进来的值 processImmediately 为 true,因此调用 ViewRootImpl#doProcessInputEvents() 函数来处理输入事件。
14.ViewRootImpl#doProcessInputEvents()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
java
@SuppressWarnings({"EmptyCatchBlock", "PointlessBooleanExpression"})
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks,
AttachedSurfaceControl {
......
void doProcessInputEvents() {
// 交付队列中所有挂起的输入事件
while (mPendingInputEventHead != null) {
QueuedInputEvent q = mPendingInputEventHead;
mPendingInputEventHead = q.mNext;
if (mPendingInputEventHead == null) {
mPendingInputEventTail = null;
}
q.mNext = null;
mPendingInputEventCount -= 1;
Trace.traceCounter(Trace.TRACE_TAG_INPUT, mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName,
mPendingInputEventCount);
mViewFrameInfo.setInputEvent(mInputEventAssigner.processEvent(q.mEvent));
deliverInputEvent(q);
}
// We are done processing all input events that we can process right now
// so we can clear the pending flag immediately.
if (mProcessInputEventsScheduled) {
mProcessInputEventsScheduled = false;
mHandler.removeMessages(MSG_PROCESS_INPUT_EVENTS);
}
}
......
}ViewRootImpl#doProcessInputEvents() 函数遍历取出 mPendingInputEventHead 中的输入事件,转交给 ViewRootImpl#deliverInputEvent() 函数来处理刚取出的 QueuedInputEvent。
15.ViewRootImpl#deliverInputEvent()
xref: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
java
@SuppressWarnings({"EmptyCatchBlock", "PointlessBooleanExpression"})
public final class ViewRootImpl implements ViewParent,
View.AttachInfo.Callbacks, ThreadedRenderer.DrawCallbacks,
AttachedSurfaceControl {
......
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "deliverInputEvent",
q.mEvent.getId());
......
try {
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "verifyEventConsistency");
try {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onInputEvent(q.mEvent, 0);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "preDispatchToUnhandledKeyManager");
try {
mUnhandledKeyManager.preDispatch((KeyEvent) q.mEvent);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
if (stage != null) {
handleWindowFocusChanged();
// 分发要处理的事件
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
......
}ViewRootImpl#deliverInputEvent() 函数在处理输入事件之前,如果 InputEventConsistencyVerifier 对象不为空,则调用 InputEventConsistencyVerifier#onInputEvent() 函数来验证输入事件的一致性。随后调用 InputStage#deliver() 函数进行事件分发,InputStage 代表了输入事件的处理阶段,使用责任链设计模式,限于篇幅问题后续有时间再继续 ViewRootImpl 事件派发流程。
小结
通过跟踪代码进行深入分析,在此对 InputDispatcher 分发 Motion 事件做个小结:
- 首先根据事件的类型,寻找所有可以接收当前输入事件的窗口,并构建一个 InputTarget 队列存放 InputDispacher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked() 函数获取到的目标窗口;
- 遍历 InputTarget 队列,通过 InputDispatcher::getConnectionLocked() 函数获取服务端 InputChannel 的 Connection 对象,由 Connection 对象的 InputPublishe 调用其 publishMotionEvent() 函数,将输入事件信息封装成 InputMessage 对象,然后通过服务端 InputChannel 调用 socket 的 send 函数将 InputMessage 写入服务端 socket 的发送缓冲区;
- 客户端通过注册的 NativeInputEventReceiver 的 Looper 监听到客户端 socket 的接收缓冲区有数据写入,则回调NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent() 函数,收集服务端传过来的 InputMessage 信息,最终将输入事件封装为 Java 层的 MotionEvent 等类型,然后调用 Java 层的 InputEventReceiver#DispatchInputEvent() 函数完成输入事件从 Native 层到 Java 层的传递(此时,输入事件从 InputDispatcher 分发给对应的 ViewRootImpl,由其继续进行事件分发)。
总结
InputDispatcher 分发事件的流程分析完毕,此时输入事件交给对应的 ViewRootImpl 由其继续进行事件分发,后续有时间会继续深入学习 ViewRootImpl 的事件分发流程,并产出文章。本文如有错误,还望大家帮助纠正,互相探讨学习哈!