一、函数
1.1、shell的函数
1.1.1、函数的定义:将命令序列按照格式写在一起。格式指的是函数的固定格式。两种格式。
less
for i in {}
do
命令序列
done
less
if []
then
命令序列
else
命令序列
fi #可以作为一个命令序列作用:方便重复使用,函数库,集中在一起,随时可以传参调用。大的过程分割成若干个小的功能模块,提高代码的可读性。
购物
展示
结算
支付
物流
1.2、函数的格式
1.2.1、函数两种格式
less
function 函数名 {
命令序列
}
函数名 () {
命令序列
}
less
function 函数名 {
命令序列
}
函数名 ##调用函数例子:
less
function shoping {
read -p "输入一个" a
num=$(($a*2))
echo $num
}
shoping
[root@test1 opt]# sh test51.sh
输入一个3
6
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test51.sh
function shoping {
num=$(($a*2))
echo $num
}
a=10
shoping
[root@test1 opt]# sh test51.sh
20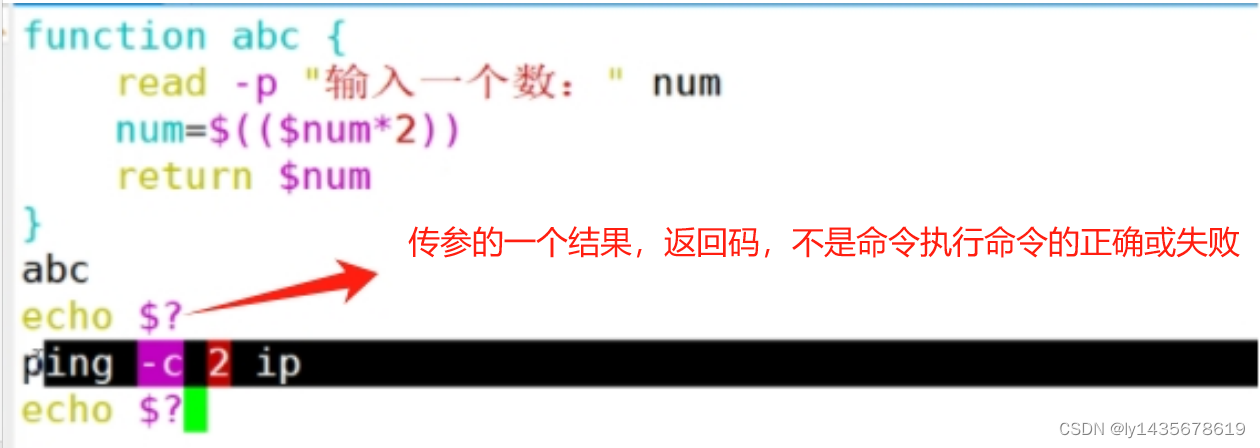
less
function shoping {
read -p "输入一个数" a
num=$(($a*2))
return $num
}
shoping
echo $?
#return 的作用:return只能写在函数的内部,目的是从函数的内部获取一个返回值
#用来判断是否执行下一个脚本。echo $? 这个时候不再是判断执行结果,只是一个函数内部的返回值。
#在使用return传回的时候,默认0是成功,非零是失败1.2.2、echo $?作用和区别
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test57.sh
abc () {
read -p "输入一个数" num
a=$(($num*2))
return $a
}
abc
[root@test1 opt]# sh test57.sh
输入一个数8
[root@test1 opt]# vim test57.sh
abc () {
read -p "输入一个数" num
a=$(($num*2))
return $a
}
abc
echo $?
[root@test1 opt]# sh test57.sh
输入一个数4
8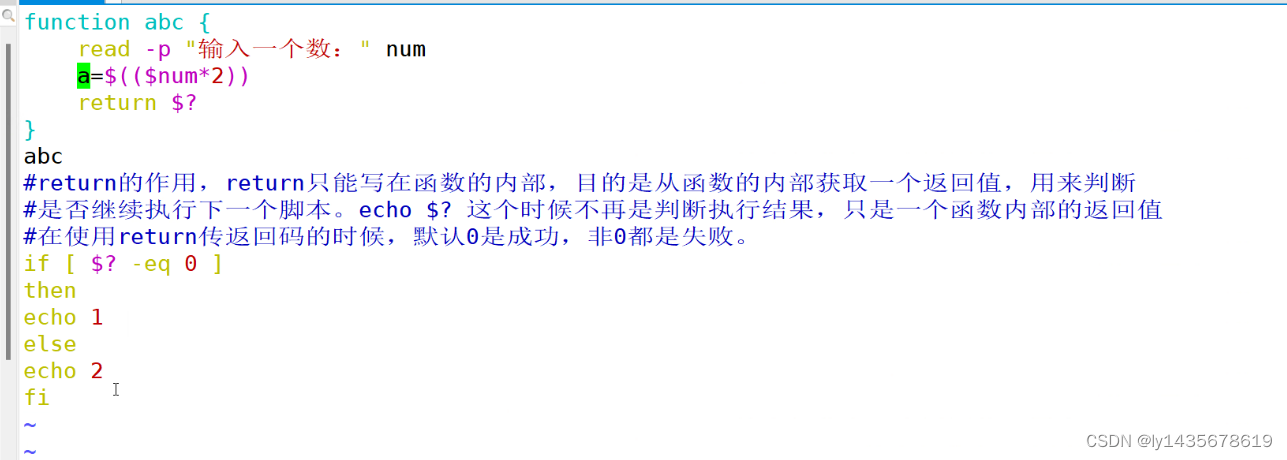
less
function shoping {
read -p "输入一个数" a
if [ $a -eq $a ] &> /dev/null
then
num=$(($a*2))
return 0
else
echo "输入错误"
return 1
fi
}
shoping
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo "ok"
else
echo "bad"
fi
[root@test1 opt]# sh test51.sh
输入一个数3
ok
[root@test1 opt]# sh test51.sh
输入一个数r
test51.sh: 第 3 行:[: r: 期待整数表达式
输入错误
bad
#返回码可以自定义,范围0-255。1.3、函数的传参方式以及函数变量的作用范围:
1.3.1、第一种传参方式:
less
sum () {
num=$(($1+$2))
echo $num
}
read -p "请输入第一个数" num1
read -p "请输入第一个数" num2
sum $num1 $num2 ##通过位置传参,给$1和$2传参。
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
请输入第一个数3
请输入第二个数4
71.3.2、第一种传参方式:
less
sum () {
num=$(($1+$2))
echo $num
}
sum $1 $2
sh test62.sh 2 3
51.3.3、函数内外赋值优先级
#展示结果,内部 a=10(全局)>外部 a=8 > 内部 local a=12
less
abc () {
a=5
local b=6
c=10
}
a=8
b=9
c=12
abc
echo $a
echo $b
echo $c
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
5
9
10
#展示结果,内部a=10(全局)>外部a=8 > 内部local a=12
#加了local(本地值)之后,就是函数内部的变量,而不再是全局变量,外部的赋值会替换内部的变量值
[root@test1 opt]# vim test52.sh
abc () {
local a=5
local b=6
c=10
}
a=8
b=9
c=12
abc
echo $a
echo $b
echo $c
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
8
9
101.3.4、内部及外部赋值输出情况
总结:
实验1:
less
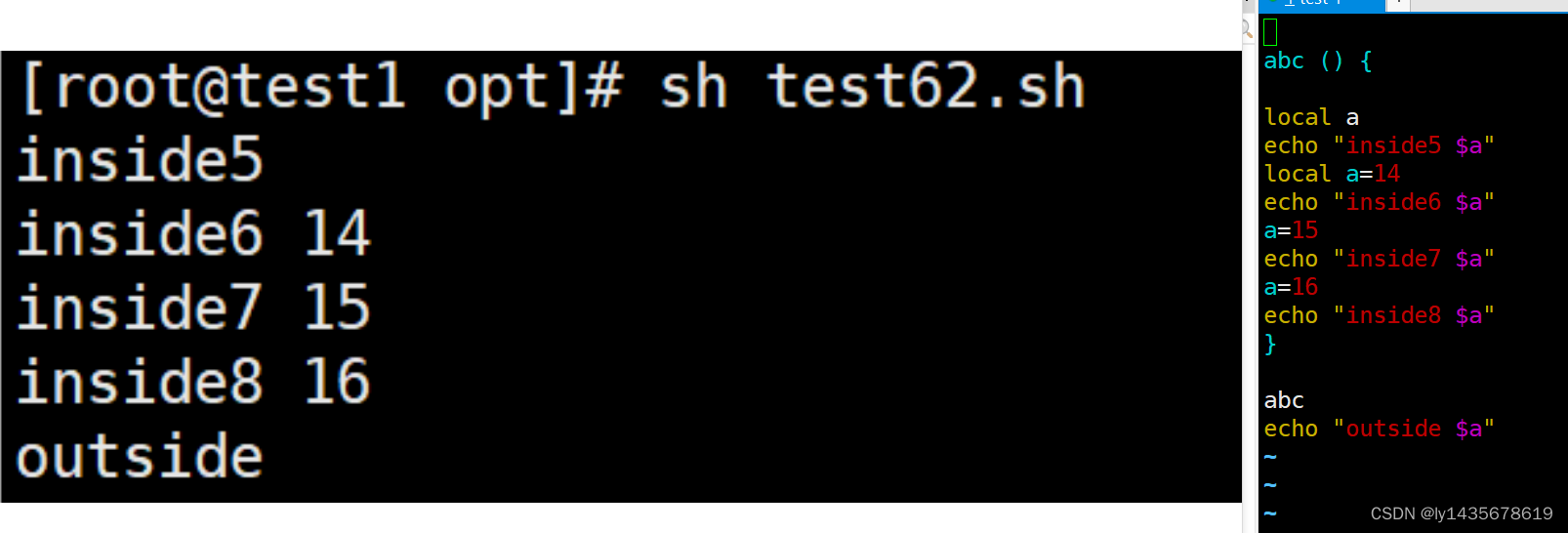
[root@test1 opt]# vim test52.sh
abc () {
echo "inside $a"
let a++
local a
a=3
echo "inside2 $a"
}
a=8
abc
echo "outside $a"
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
inside 8
inside2 3
outside 9
[root@test1 opt]# bash -x test52.sh
+ a=8
+ abc
+ echo 'inside 8'
inside 8
+ let a++
+ local a
+ a=3
+ echo 'inside2 3'
inside2 3
+ echo 'outside 9'
outside 9实验2:
less
abc () {
echo "inside $a"
let a++
local a
echo "inside3 $a"
a=3
echo "inside2 $a"
}
a=8
abc
echo "outside $a"
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
inside 8
inside3
inside2 3
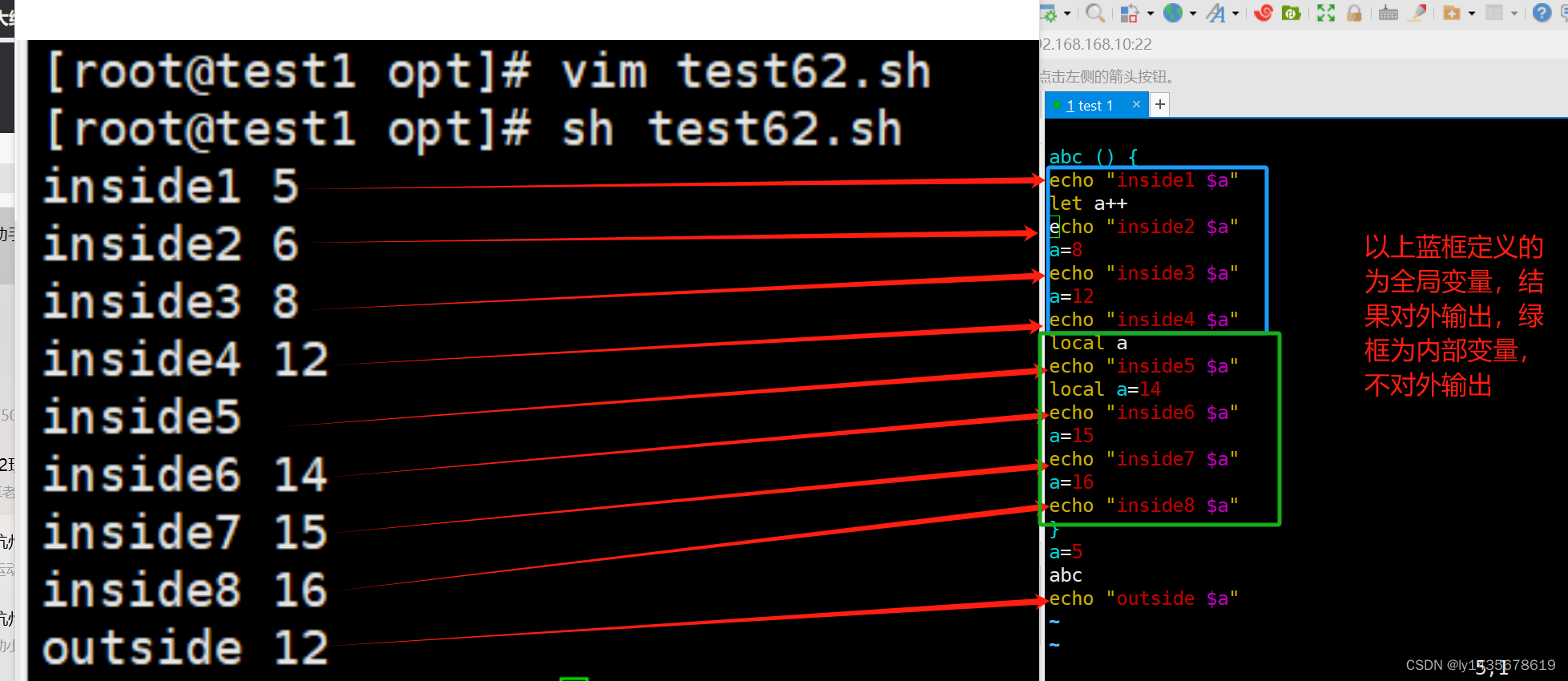
outside 9解释:流程:
先定义全局变量a=9
调用函数abc,打印 inside1 a ,此处 a,此处 a,此处a=9
a++ :全局变量a自增1,此处$a=10
local a :此时定义的a为函数内部变量,此处 a 为空,打印inside2 a为空
a=8:此处把8赋值给内部变量a,打印inside3 a ,此处 a,此处 a,此处a=8
函数结束,到外部打印 outside a ,此时外部 a 为全局变量, a,此时外部a为全局变量, a,此时外部a为全局变量,a=10
1.4、递归函数
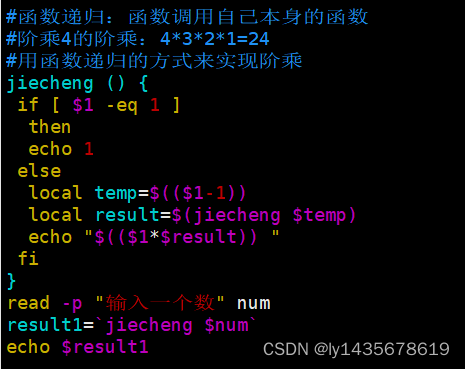
1、阶乘实验1:
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test52.sh
#函数递归:函数调用自己本身的函数
#阶乘4的阶乘:4*3*2*1=24
#用函数递归的方式来实现阶乘
jiecheng () {
if [ $1 -eq 1 ]
then
echo 1
else
local temp=$(($1-1))
local result=$(jiecheng $temp)
echo "$(($1*$result)) "
fi
}
read -p "输入一个数" num
result1=`jiecheng $num` ##`**`把命令的结果传给变量,是计算结果传给变量,而不是表面的字符串传给变量,例如a=`ls /opt`,解释opt目录下展示结果传给a
echo $result1
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
输入一个数6
7202、阶乘实验2:
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test52.sh
jiecheng () {
if [ $1 -eq 1 ]
then
echo 1
else
local a=$(($1-1))
local b=$(jiecheng $a)
echo " $(($1*$b)) "
fi
}
jiecheng $1
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh 7
5040 3、使用for循环写阶乘:
less
read -p "请输入一个数" a
b=$a
for ((i=a;i>=2;i--))
do
b=$(($b*($i-1)))
done
echo $b
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh
请输入一个数6
720
[root@test1 opt]# bash -x test52.sh
+ read -p 请输入一个数 a
请输入一个数5
+ b=5
+ (( i=a ))
+ (( i>=2 ))
+ b=20
+ (( i-- ))
+ (( i>=2 ))
+ b=60
+ (( i-- ))
+ (( i>=2 ))
+ b=120
+ (( i-- ))
+ (( i>=2 ))
+ b=120
+ (( i-- ))
+ (( i>=2 ))
+ echo 120
120#面试题:递归目录。把/etc目录下,所有文件递归出来,如果只是目录且该目录下没有文件
就打印目录。否则继续打印,直到目录里面没有文件为止。
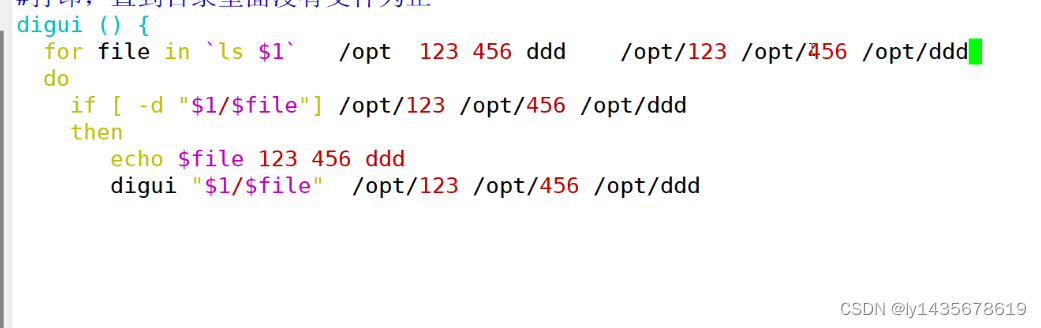

4、递归实验4:
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test52.sh
digui () {
for file in `ls $1`
do
test -d $file
if [ $? -eq 0 ] ##以上两行==if [ -d $1/$file ]
then
echo "这是一个目录,$1/$file"
digui "$1/$file"
else
echo "这是一个文件,$1/$file"
fi
done
}
digui $1
[root@test1 opt]# sh test52.sh /opt
[root@test1 opt]# sh test63.sh /opt
这是一个文件,/opt/!
这是一个目录,/opt/11
这是一个文件,/opt/11/123
这是一个文件,/opt/11/456
这是一个目录,/opt/111
这是一个文件,/opt/111/1231.5、调用脚本
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test54.sh
jiafa () {
result=$(($1+$2))
echo $result
}
jianfa () {
result=$(($1-$2))
echo $result
}
chengfa () {
result=$(($1*$2))
echo $result
}
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test55.sh
. /opt/test54.sh
read -p "输入第一个数" num1
read -p "输入第一个数" num2
sum=`jiafa $num1 $num2`
sub=`jianfa $num1 $num2`
mult=`chengfa $num1 $num2`
echo $sum
echo $sub
echo $mult
[root@test1 opt]# sh test55.sh
输入第一个数5
输入第一个数6
11
-1
30作业1:

less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test54.sh
jiafa () {
result=$(echo " scale=2 ; $1 + $2 " | bc )
echo $result
}
jianfa () {
result=$(echo " scale=2 ; $1 - $2 " | bc )
echo $result
}
chengfa () {
result=$(echo " scale=2 ; $1 * $2 " | bc )
echo $result
}
[root@test1 opt]# vim test55.sh
. /opt/test54.sh
read -p "输入第一个数" num1
read -p "输入第一个数" num2
#小数和整数都可以运算,小数点后两位。
sum=`jiafa $num1 $num2`
sub=`jianfa $num1 $num2`
mult=`chengfa $num1 $num2`
echo $sum
echo $sub
echo $mult
[root@test1 opt]# sh test55.sh
输入第一个数4.5
输入第一个数5.5
10.0
-1.0
24.75作业2:
#上午我们递归文件的代码,实现了递归出所有目录下的文件。
#所有文件,把后缀名是.txt的文件复制到/opt/dec当中。
less
[root@test1 opt]# vim test56.sh
digui () {
for file in `ls $1`
do
if [ -d $file ]
then
echo "这是一个目录,$file"
digui "$1/$file"
else
echo "这是一个文件,$1/$file"
case $1/$file in
*.txt)
cp $1/$file /opt/dec
;;
*)
esac
fi
done
}
digui $1
[root@test1 opt]# mkdir dec
[root@test1 opt]# sh test56.sh
[root@test1 opt]# cd dec
[root@test1 dec]# ls
1.txt hosts1.txt passwd.txt xy102.txt
erjinzhi.txt hosts.txt users.txt