问题描述
在做前后端分离的项目时,很有可能会遇到这样一种情况:
就是在游览器中请求后端的接口,出现了 CORS error 错误

报错信息如下:
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:8860/user/auth/login' from origin 'http://localhost:5173' has been blocked by CORS policy: Response to preflight request doesn't pass access control check: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
大概的意思就是:
跨源资源共享(CORS)策略阻止了来自端口 5173 的前端应用对运行在端口 8860 的后端服务的 XMLHttpRequest 请求
原因分析
它的产生并不是因为后端代码出错了,也不是因为前端调用时有问题,而是因为游览器的安全机制(同源策略限制)所导致的,是一个很典型的跨域问题
那游览器的同源策略是什么?
浏览器的 同源策略(Same-origin policy) 是一种安全策略,它规定了从同一个 源(origin) 加载的文档或脚本如何与来自另一个源的资源进行交互。这是浏览器提供的一个重要的安全机制,用于隔离潜在恶意文档,减少可能被攻击的媒介。
同源是指 协议 + 域名 + 端口 三者相同,也就是说,如果两个页面的协议、域名或端口中有任何一个不相同,那么它们就是不同源的。
同源策略主要限制了以下几个方面:
- Cookie、LocalStorage 和 IndexedDB:无法读取不同源的
Cookie、LocalStorage和IndexedDB,这防止了恶意网站窃取或篡改用户的敏感数据 - DOM:无法操作不同源的页面的
DOM。这确保了恶意网站不能篡改或窃取其他网站的内容 - AJAX 请求:默认情况下,无法发送
AJAX请求到不同源的服务器,这防止了恶意网站发起跨站请求伪造(CSRF)攻击
什么是跨域?
跨域就是违法了同源策略,当一个页面去请求另外一个 URL 时,两者 URL 的 协议 + 域名 + 端口 出现不一致
回到上述案例,从控制台中打印的错误信息就能看出,在 http://localhost:5173 的服务中访问了 http://localhost:8860 下的 /user/auth/login 接口,其端口就出现了不一致,出现了跨域
解决方案
现在知道了这种错误是因为跨域问题造成的,那么如何解决这种跨域问题呢?
解决跨域的方法有很多,这里简单介绍以下三种方法:
-
方案一:Jsonp
这种方法是早期的一种跨域解决方案,它对各个游览器的版本兼容性做得比较好,但是实现需要前端跟后端都去写相应的代码来进行支持,耦合度高,而且仅支持
GET请求,所有不常用目前也不推荐用比如说在前端使用
ajax去发送一个请求,需要指定dataType为Jsonp,这时请求就会自动加上callback=xxx这样的参数,xxx会作为密钥的形式传到后端 ,后端再将xxx返回给前端,这就相当于前后端做了一个校验,使得游览器认可这种跨域请求,就可以进行跨域访问了前端代码示范:
js$.ajax(( url: 'http://localhost:8860/user/auth/login', dataTpe: "jsonp", // Jsonp: 'callback', // 不指定默认 callback // JsonpCallBack: "xxx", // 不指定自动生成 type: 'GET', success: function(result) { alert(result.data) } ));后端代码示范:
java@GetMapping("/jsonp/{id}") public JSONPObject getUser(@PathVariable Integer id, String callback) { return new JSONPObject(callback, new Result<>(200, "success", data)) } -
方式二:Proxy 代理
使用代理服务器处理跨域问题的基本思路是,在前端和后端服务之间设置一个代理服务器。这个代理服务器位于前端应用所在的域上,因此可以绕过浏览器的同源策略限制。前端应用向代理服务器发送请求,代理服务器再将这些请求转发给实际的后端服务。后端服务处理请求后,将响应返回给代理服务器,代理服务器再将响应转发给前端应用。这样,前端应用看起来就像是直接与后端服务通信,但实际上所有的通信都是通过代理服务器进行的
现在前端的框架一般都带有
proxy反向代理功能,就是前端开发的时候一般会在本地启动一个node.js服务,让node服务去请求接口,然后再把数据传给游览器,就相当于在本地起了一个服务作为中转站示例:在
vite.config.ts文件中配置代理jsexport default defineConfig({ plugins: [vue()], server: { // 设置项目端口 port: 5173, // 运行时自动打开游览器 open: true, proxy: { '/api': { // 目标服务器地址 target: 'http://localhost:8860', // 是否改变源地址 changeOrigin: true, // 重写路径 rewrite: (path) => path.replace(new RegExp('^' + '/api'), ''), }, }, }, }) -
方式三:跨域请求 CORS
CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)是一种计算机安全机制,它允许不同源(即协议、域名和端口不同)的Web站点进行资源共享。由于浏览器的同源安全策略,通常情况下,一个域的脚本无法直接访问另一个域的资源。CORS通过在服务器端设置特定的HTTP头部,来告诉浏览器:"我允许这个域的脚本访问我的资源"。这样,浏览器就会解除对跨域请求的限制,从而允许前端应用从不同的域请求资源。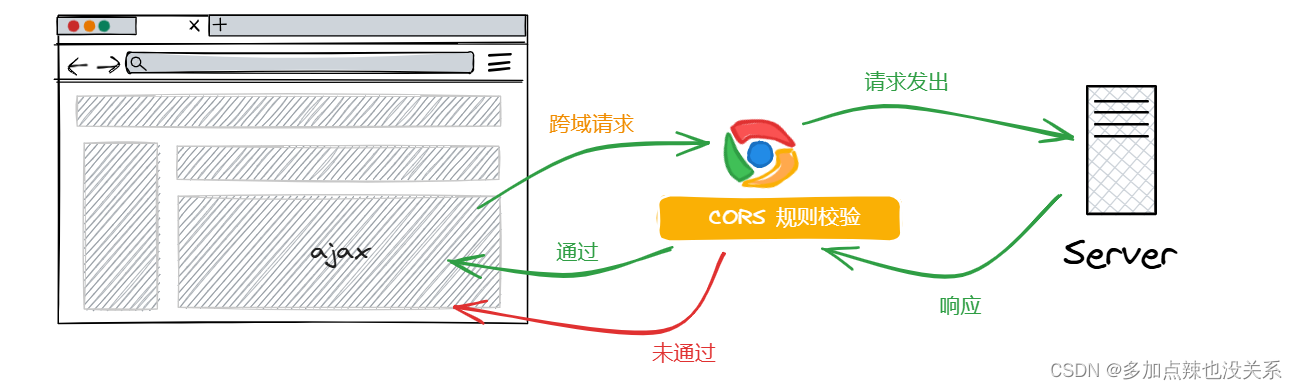
CORS主要有两种模型:- 简单模型: 支持
GET、POST、PUT、DELETE请求,但不允许自定义header且会忽略cookies。POST数据格式也有限制,主要支持text/plain、application/x-www-form-urlencoded和multipart/form-data。其中text/plain是默认支持的,后两者需要与服务器进行预检请求和协商 - 协商模型/预检请求: 当发出如
POST请求时,浏览器会首先发出一个OPTIONS请求进行预检。如果服务器返回Access-Control-Allow-Origin和Access-Control-Allow-Methods等头部,并同意来自某个域的请求,浏览器就会继续发出真正的请求
CORS从具体的代码实现上来说还是比较方便的,前端不需要编写任何代码,主要是靠服务端进行配置CORS需要游览器和服务器同时支持,目前几乎所有的游览器都支持该功能,IE游览器不能低于IE 10同时
CORS也是比较推荐的一种处理跨域请求的做法,具体实现请看后文 - 简单模型: 支持
代码实现
上述的三种解决跨域的方案中 CORS 是可以完全由后端去实现的,以下内容我就以 Spring Boot 和 Spring Cloud 为例概述如何解决跨域问题
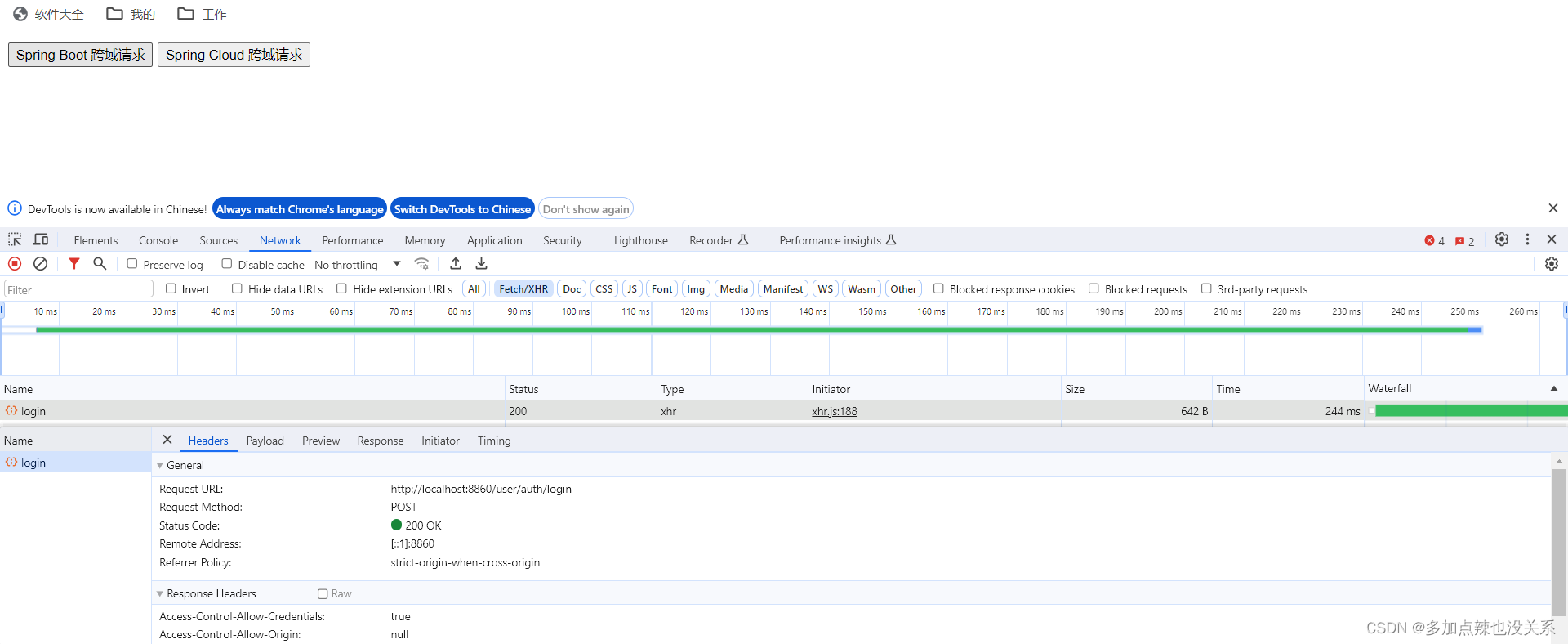
这里我在后台启动一个 Spring Cloud 的项目,其中有个 Gateway 服务和一个 User 服务,用户服务中有一个接口 /auth/loign
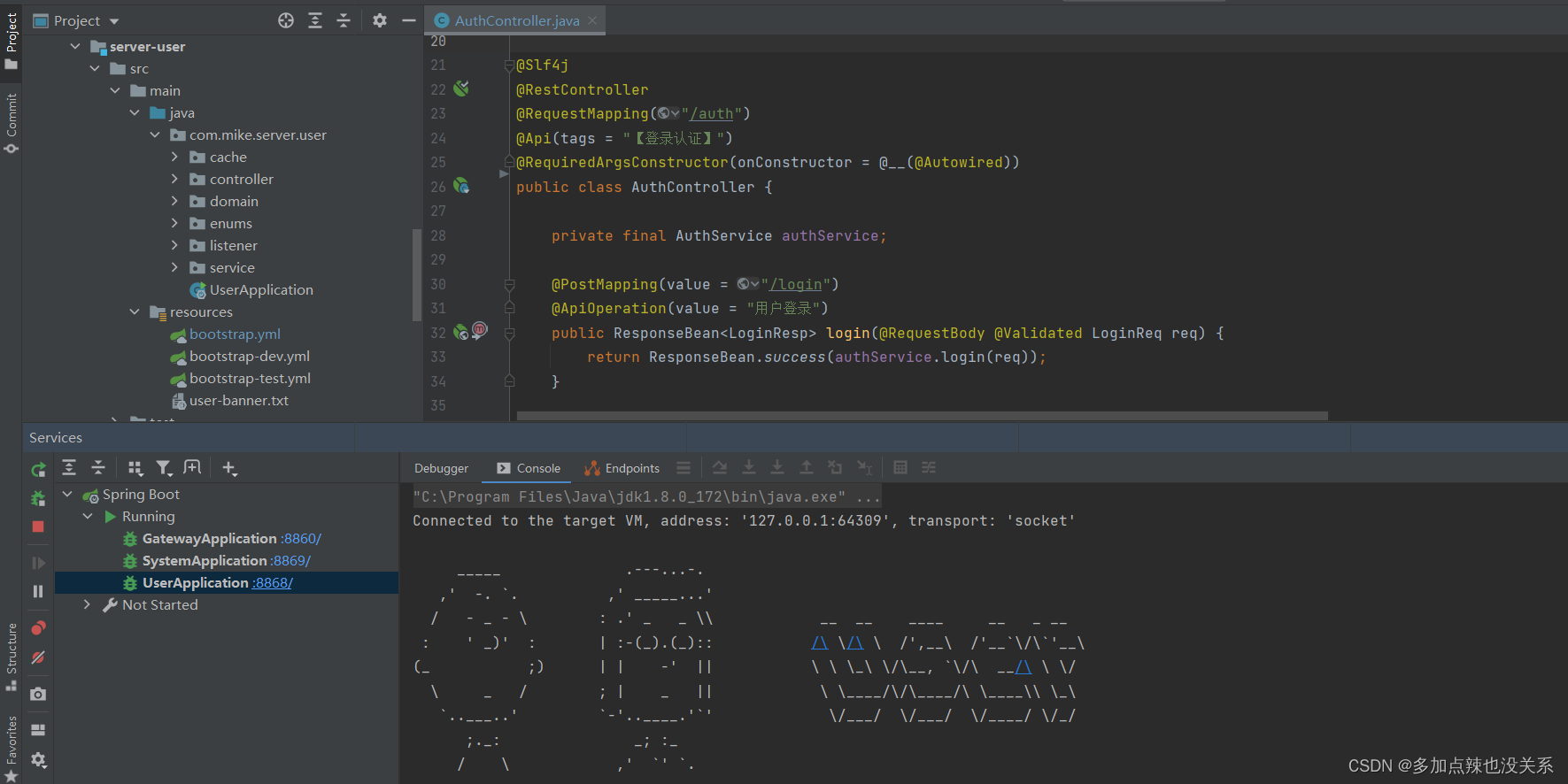
如果仅仅看 User 服务它就是一个 Spring Boot 的项目,访问该接口的 URL 为:POST http://localhost:8868/auth/login
Spring Cloud 项目的话一般请求都是走网关的,这里正确的请求 URL 为:POST http://localhost:8860/user/auth/login
前端发送请求代码如下:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>发送请求</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/axios/1.7.2/axios.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<button id="bootNpde">Spring Boot 跨域请求</button>
<button id="cloudNode">Spring Cloud 跨域请求</button>
<script>
bootNpde.onclick = function () {
const p = axios.post("http://localhost:8868/auth/login", {
username: "admin",
password: "admin"
});
console.log(p);
p.then(result => {
console.log(result);
// 获取服务器端的响应数据
const { data } = result;
console.log(data);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
})
}
cloudNode.onclick = function () {
const p = axios.post("http://localhost:8860/user/auth/login", {
username: "admin",
password: "admin"
});
console.log(p);
p.then(result => {
console.log(result);
// 获取服务器端的响应数据
const { data } = result;
console.log(data);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>目前项目没有做任何的跨域处理,所以访问这两个 URL 的时候均会出现跨域错误
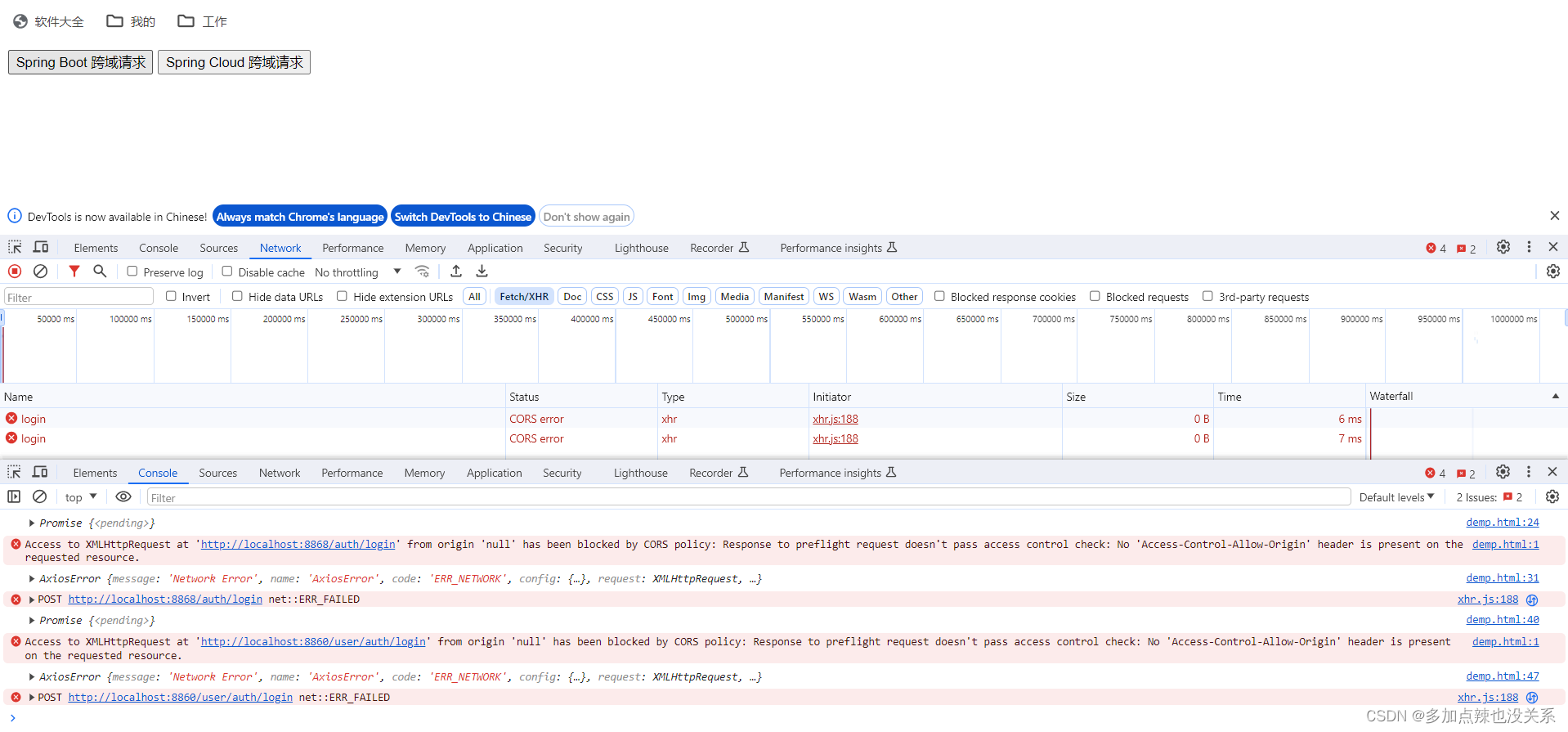
(1)Spring Boot 跨域处理
- 方式一:在接口或者方法上通过注解 @CrossOrigin 来解决跨域问题
@CrossOrigin 注解是 Spring 框架中的一个注解,它的主要作用是处理跨域资源共享(CORS)问题
使用 @CrossOrigin 注解,可以在控制器类或具体处理方法上指定哪些来源可以访问该类或方法,从而实现对 CORS 的简化配置。当在类或方法上使用此注解时,Spring 会自动在 HTTP 响应头中添加适当的 CORS 相关头部信息,如 Access-Control-Allow-Origin、Access-Control-Allow-Methods、Access-Control-Allow-Headers 等,从而允许浏览器执行跨域请求
@CrossOrigin 注解支持多种配置选项,例如允许特定来源、允许所有来源、指定请求头和响应头等。例如,可以在注解中指定 origins 属性来限制可以访问的域名列表,或使用 methods 属性来指定允许的 HTTP 请求方法
代码示例:
sql
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/auth")
@Api(tags = "【登录认证】")
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired))
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*", methods = {RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.GET})
public class AuthController {
private final AuthService authService;
@PostMapping(value = "/login")
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录")
//@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:5173", methods = {RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.GET})
public ResponseBean<LoginResp> login(@RequestBody @Validated LoginReq req) {
return ResponseBean.success(authService.login(req));
}
}测试:
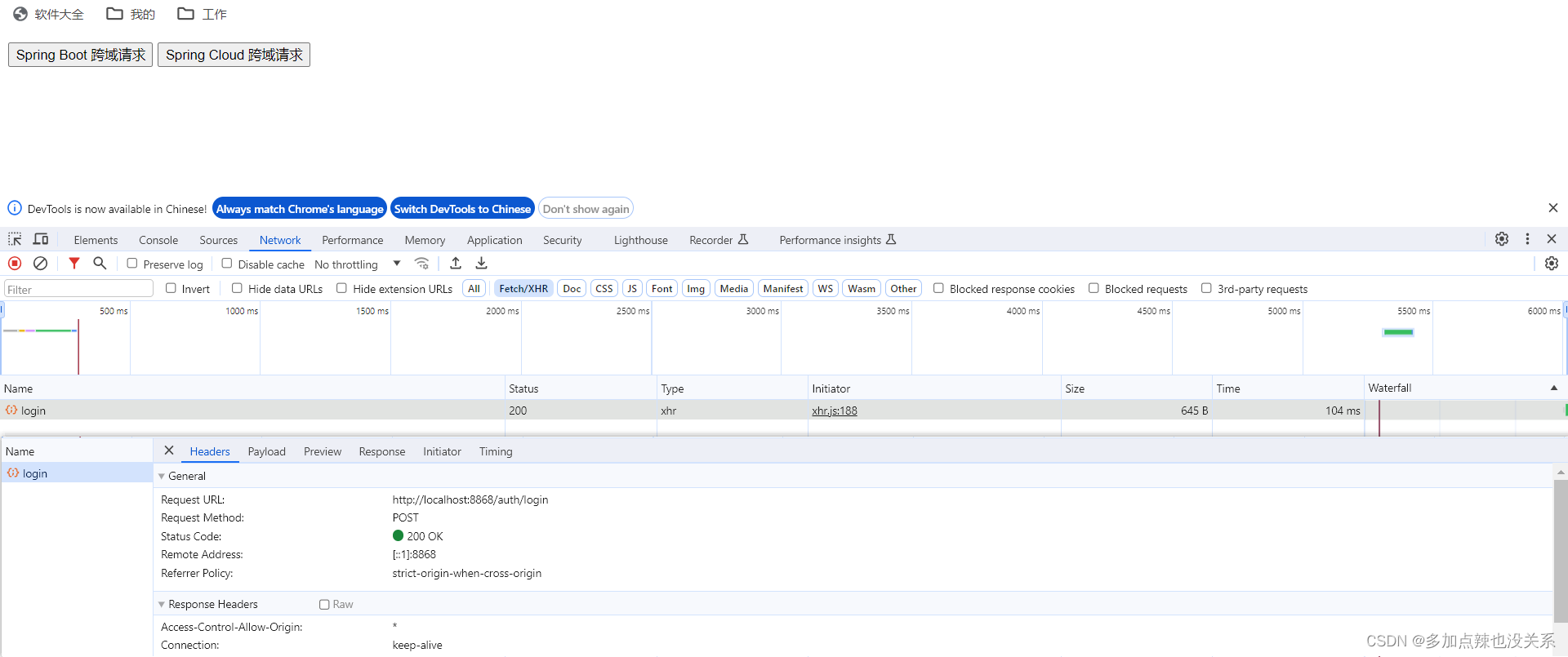
- 方式二:配置全局 CORS 映射
如果你希望全局地配置 CORS 策略,可以在 Spring Boot 配置类中添加一个 CORS 配置 bean
java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CorsFilter;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public CorsFilter corsFilter() {
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
// 允许向该服务器提交请求的 URI,* 表示全部允许,在 SpringMVC 中,如果设成 *,会自动转成当前请求头中的 Origin
//config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
// 指定允许跨域的域名
//config.addAllowedOrigin("http://localhost:5173");
// springboot2.4.2 中 addAllowedOrigin 不允许设置为 *,要改成使用 AllowedOriginPattern
config.addAllowedOriginPattern("*");
// 允许访问的头信息,* 表示全部
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
// 允许提交请求的方法,*表示全部允许
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
// 允许 cookies 跨域
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
// 预检请求的缓存时间(秒),即在这个时间段里,对于相同的跨域请求不会再预检了
config.setMaxAge(18000L);
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return new CorsFilter(source);
}
}或者写成:
java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer corsConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry
// 映射到所有路径
.addMapping("/**")
// 允许所有域名进行跨域调用
//.allowedOrigins("*")
// springboot2.4.2 后 addAllowedOrigin 不允许设置为 *,要改成使用 AllowedOriginPattern
.allowedOriginPatterns("*")
// 允许所有请求方式跨域调用
.allowedMethods("*")
// 放行全部原始头信息
.allowedHeaders("*")
// 允许携带 Cookie 信息
.allowCredentials(true)
// 预检请求的缓存时间
.maxAge(18000L);
}
};
}
}测试:

(2)Spring Cloud 跨域处理
- 方式一:配置全局 CORS 映射
和 Spring boot 配置全局 CORS 差不多,不过是在 Gateway 服务的配置类中添加一个 CORS 配置 bean
java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.CorsWebFilter;
import org.springframework.web.cors.reactive.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.util.pattern.PathPatternParser;
/**
* 跨域处理
*/
@Configuration
public class GlobalCorsConfiguration {
@Bean
public CorsWebFilter corsFilter() {
// 配置跨域信息
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
// 允许跨域的请求来源:允许所有域名进行跨域调用
config.addAllowedOriginPattern("*");
// 允许跨域的头:放行全部原始头信息
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
// 允许跨域的请求方式:允许所有请求方式跨域调用
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
// 允许携带 Cookie 信息
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
// 添加映射路径
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource(new PathPatternParser());
// 任意 url 都要进行跨域配置
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return new CorsWebFilter(source);
}
}
- 方式二:在配置文件中设置 CORS 策略
在 Gateway 服务的配置文件 application.yml 中设置 CORS 策略
示例:
yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
# 全局的跨域处理
globalcors:
# 解决 options 请求被拦截问题
add-to-simple-url-handler-mapping: true
cors-configurations:
'[/**]':
allowedOrigins: # 允许哪些网站的跨域请求
- "http://localhost:5173"
allowedMethods: # 允许的跨域 ajax 的请求方式
- "GET"
- "POST"
- "DELETE"
- "PUT"
- "OPTIONS"
# 允许在请求中携带的头信息
allowedHeaders: "*"
# 是否允许携带 cookie
allowCredentials: true
# 这次跨域检测的有效期
maxAge: 36000需要注意的问题:
对于 Spring Cloud Gateway,你可以通过全局 CORS 配置或者特定路由的 CORS 配置来设置 CORS。确保没有其他过滤器或配置在之后覆盖了你的 CORS 设置
也就是说最好只配置一个 CORS,比如你在配置文件中配置了全局跨域处理,允许 http://localhost:5173 进行跨域,那么就不要用 @CrossOrigin 在接口上设置了 CORS
例如:
sql
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/auth")
@Api(tags = "【登录认证】")
@RequiredArgsConstructor(onConstructor = @__(@Autowired))
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*", methods = {RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.GET})
public class AuthController {
private final AuthService authService;
@PostMapping(value = "/login")
@ApiOperation(value = "用户登录")
//@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:5173", methods = {RequestMethod.POST, RequestMethod.GET})
public ResponseBean<LoginResp> login(@RequestBody @Validated LoginReq req) {
return ResponseBean.success(authService.login(req));
}
}不然就会因为响应头 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 包含多个值时,被浏览器拒绝该响应
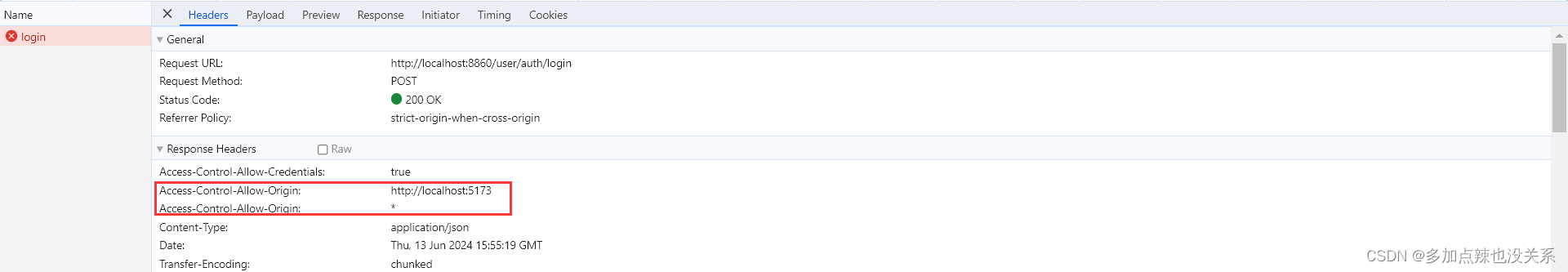
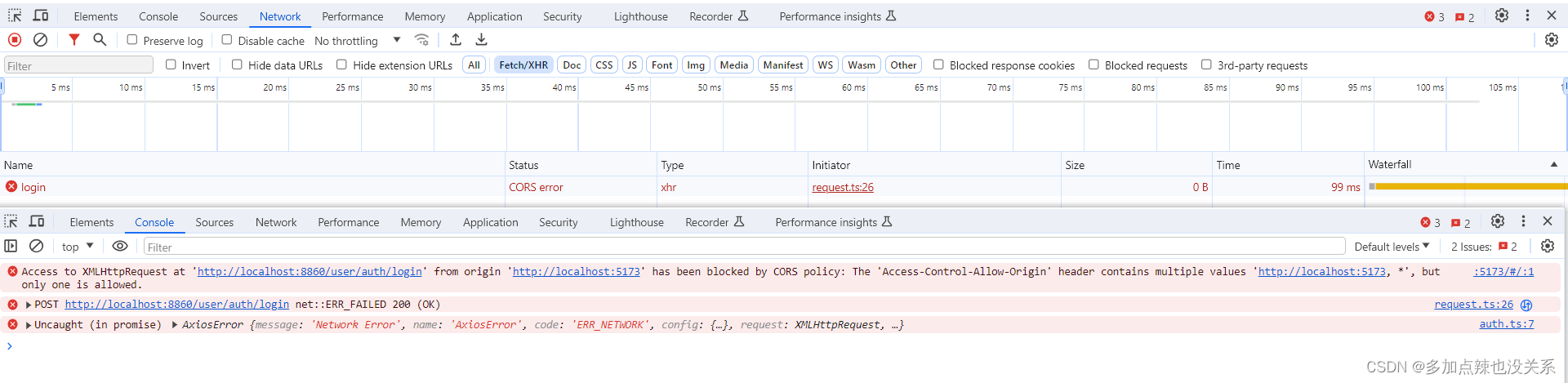
报错信息:
Access to XMLHttpRequest at 'http://localhost:8860/user/auth/login' from origin 'http://localhost:5173' has been blocked by CORS policy: The 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header contains multiple values 'http://localhost:5173, *', but only one is allowed.
这样就导致了即使你配置了跨域,但是还是会出现跨域的问题的