非最大值抑制(NMS)函数
flyfish
非最大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression, NMS)是计算机视觉中常用的一种后处理技术,主要用于目标检测任务。其作用是从一组可能存在大量重叠的候选边界框中,筛选出最具代表性的边界框,即通过置信度分数和重叠区域的过滤,保留最具代表性的边界框。
边界框(Bounding Boxes):一组表示候选目标区域的矩形框,每个框由左上角和右下角的坐标(x1, y1, x2, y2)表示。
置信度分数(Confidence Scores):每个边界框对应的一个置信度分数,表示该框内包含目标的可能性。
执行步骤
初始化:
boxes:输入的边界框列表。
scores:每个边界框对应的置信度得分列表。
confidence_threshold:过滤边界框的最低置信度阈值。
iou_threshold:用于确定边界框是否重叠的 IOU 阈值。
过滤低置信度边界框:
根据 confidence_threshold 过滤掉置信度低于该阈值的边界框。
按置信度排序:
对剩余的边界框按照置信度从高到低排序。
非极大值抑制:
从排序后的列表中选择置信度最高的边界框,并计算其与其他边界框的 Intersection-over-Union (IoU)。
如果 IoU大于 iou_threshold,则移除该边界框(表示重叠太多)。
重复该过程直到处理完所有边界框。
返回结果:
返回保留的边界框的索引。

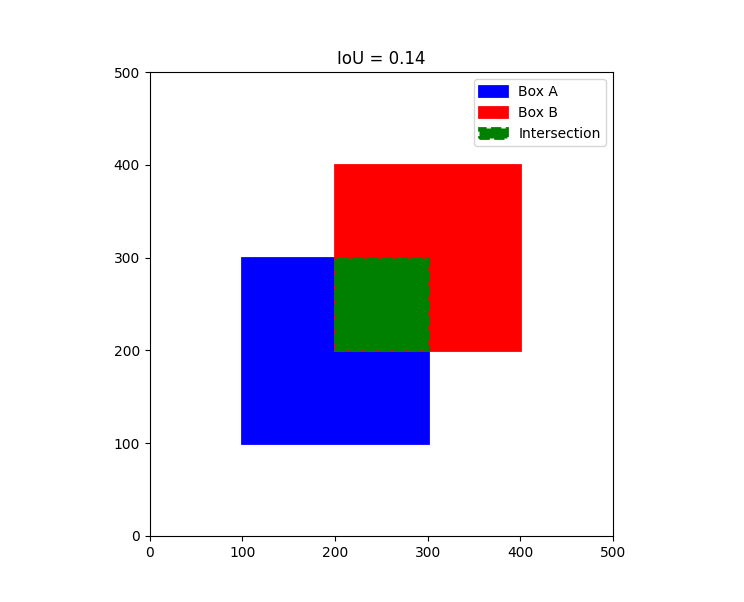
可视化 Intersection-over-Union (IoU)
蓝色矩形表示 Box A,红色矩形表示 Box B,绿色矩形表示它们的交集区域,剩余的红色和蓝色是并集区域。
torchvision.ops.nms 和 cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes 的调用
py
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision.ops as ops
import cv2
# 输入数据
boxes = np.array([
[100, 100, 210, 210], [220, 220, 320, 330], [300, 300, 400, 400],
[50, 50, 150, 200], [200, 150, 280, 320], [280, 280, 380, 380],
[80, 90, 190, 210], [250, 250, 350, 370], [290, 290, 390, 390]
])# (x1, y1, x2, y2)格式
scores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.75, 0.85, 0.7, 0.65, 0.82, 0.78, 0.6])
score_threshold = 0.5
nms_threshold = 0.4
def convert_to_xywh(boxes): #opencv用 (x, y, w, h)格式
"""
将边界框从 (x1, y1, x2, y2) 格式转换为 (x, y, w, h) 格式。
参数:
- boxes: 形状为 (N, 4) 的数组,其中 N 是边界框的数量
返回:
- boxes_xywh: 形状为 (N, 4) 的数组,包含转换后的边界框
"""
boxes_xywh = np.zeros_like(boxes)
boxes_xywh[:, 0] = boxes[:, 0] # x
boxes_xywh[:, 1] = boxes[:, 1] # y
boxes_xywh[:, 2] = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] # w
boxes_xywh[:, 3] = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] # h
return boxes_xywh
def nms_torchvision(boxes, scores, nms_threshold):
boxes_tensor = torch.tensor(boxes, dtype=torch.float32)
scores_tensor = torch.tensor(scores, dtype=torch.float32)
keep = ops.nms(boxes_tensor, scores_tensor, nms_threshold)
return keep.numpy()
def nms_opencv(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):
boxes = convert_to_xywh(boxes)
indices = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes.tolist(), scores.tolist(), score_threshold, nms_threshold)
return np.array(indices).flatten()
# 调用 NMS
keep_torchvision = nms_torchvision(boxes, scores, nms_threshold)
keep_opencv = nms_opencv(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold)
print("使用 torchvision.ops.nms 保留的边界框索引: ", keep_torchvision)
print("使用 cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes 保留的边界框索引: ", keep_opencv)输出
使用 torchvision.ops.nms 保留的边界框索引: [0 3 1 7 2 4]
使用 cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes 保留的边界框索引: [0 3 1 7 2 4]用纯 NumPy 实现的非最大值抑制(NMS)函数
py
import numpy as np
def nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold):
"""单类 NMS 使用 NumPy 实现。"""
# 过滤掉低置信度的框
indices = np.where(scores > score_threshold)[0]
boxes = boxes[indices]
scores = scores[indices]
# 如果没有剩余的框,返回空列表
if len(boxes) == 0:
return []
# 提取每个边界框的坐标
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
# 计算每个边界框的面积
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
# 根据分数进行排序(从高到低)
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(indices[i])
# 计算当前边界框与其余边界框的交集坐标
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
# 计算交集的宽度和高度
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
# 计算交集面积
inter = w * h
# 计算交并比(IOU)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# 只保留 IOU 小于阈值的边界框
inds = np.where(ovr <= nms_threshold)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
# 示例数据
boxes = np.array([
[100, 100, 210, 210], [220, 220, 320, 330], [300, 300, 400, 400],
[50, 50, 150, 200], [200, 150, 280, 320], [280, 280, 380, 380],
[80, 90, 190, 210], [250, 250, 350, 370], [290, 290, 390, 390]
])
scores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.75, 0.85, 0.7, 0.65, 0.82, 0.78, 0.6])
score_threshold = 0.5
nms_threshold = 0.4
# 调用NMS
keep_indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold)
print("使用 NumPy 实现的 NMS 保留的边界框索引: ", keep_indices)使用 NumPy 实现的 NMS 保留的边界框索引: [0, 3, 1, 7, 2, 4]关于语法的解释
在 NumPy 中,冒号 : 用于数组切片。它们可以用来提取数组的子集、重排数组或选取特定的元素。
示例1
scores.argsort()[::-1]
scores.argsort():返回 scores 中元素的索引数组,这些索引会将 scores 排序。
::-1\]:表示反转数组。 在这个例子中,\[::-1\] 表示从开始到结束,步长为 -1,因此数组会被反转。这里的两个冒号是为了清楚地表示切片的完整语法 \[start:stop:step\],其中省略了 start 和 stop,只指定了 step 为 -1。 ```py import numpy as np scores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.75, 0.85, 0.7, 0.65, 0.82, 0.78, 0.6]) sorted_indices = scores.argsort() # 升序排序的索引 print("sorted_indices:", sorted_indices) # 反转排序索引(降序排序) reversed_indices = sorted_indices[::-1] print("reversed_indices:", reversed_indices) ``` sorted_indices: [8 5 4 2 7 1 6 3 0] reversed_indices: [0 3 6 1 7 2 4 5 8] #### 示例2 boxes\[:, 0
boxes[:, 0]:选取 boxes 数组中第 0 列的所有元素。
: 表示选择所有行,0 表示选择第 0 列。
这段代码的作用是提取 boxes 数组中每个边界框的 x1 坐标(左上角的 x 坐标)。
py
import numpy as np
boxes = np.array([
[100, 100, 210, 210],
[220, 220, 320, 330],
[300, 300, 400, 400],
[50, 50, 150, 200]
])
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
print("x1:", x1)x1: [100 220 300 50]可视化数据的代码
py
def plot_boxes(boxes, keep_indices):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(12, 12))
for i, box in enumerate(boxes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
width = x2 - x1
height = y2 - y1
# 所有输入框用蓝色绘制
edgecolor = 'blue'
if i in keep_indices:
# NMS 保留的框用绿色绘制
edgecolor = 'green'
else:
# 被抑制的框用红色绘制
edgecolor = 'red'
rect = patches.Rectangle((x1, y1), width, height, linewidth=2, edgecolor=edgecolor, facecolor='none')
ax.add_patch(rect)
# 设置坐标范围
ax.set_xlim(0, np.max(boxes[:, [0, 2]]) + 50)
ax.set_ylim(0, np.max(boxes[:, [1, 3]]) + 50)
ax.invert_yaxis() # 图像坐标系和实际坐标系相反时需要
plt.show()
# 示例数据
boxes = np.array([
[100, 100, 210, 210], [220, 220, 320, 330], [300, 300, 400, 400],
[50, 50, 150, 200], [200, 150, 280, 320], [280, 280, 380, 380],
[80, 90, 190, 210], [250, 250, 350, 370], [290, 290, 390, 390]
])
scores = np.array([0.9, 0.8, 0.75, 0.85, 0.7, 0.65, 0.82, 0.78, 0.6])
score_threshold = 0.5
nms_threshold = 0.4
# 调用NMS
keep_indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold)
print("使用 NumPy 实现的 NMS 保留的边界框索引: ", keep_indices)
# 绘图
plot_boxes(boxes, keep_indices)可视化 Intersection-over-Union (IoU)的代码
py
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
def plot_iou(boxA, boxB):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, figsize=(8, 8))
# 绘制 Box A
x1A, y1A, x2A, y2A = boxA
widthA = x2A - x1A
heightA = y2A - y1A
rectA = patches.Rectangle((x1A, y1A), widthA, heightA, linewidth=2, edgecolor='blue', facecolor='blue', label='Box A')
ax.add_patch(rectA)
# 绘制 Box B
x1B, y1B, x2B, y2B = boxB
widthB = x2B - x1B
heightB = y2B - y1B
rectB = patches.Rectangle((x1B, y1B), widthB, heightB, linewidth=2, edgecolor='red', facecolor='red', label='Box B')
ax.add_patch(rectB)
# 计算交集
xx1 = np.maximum(x1A, x1B)
yy1 = np.maximum(y1A, y1B)
xx2 = np.minimum(x2A, x2B)
yy2 = np.minimum(y2A, y2B)
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1)
intersection_area = w * h
# 计算并集
areaA = (x2A - x1A) * (y2A - y1A)
areaB = (x2B - x1B) * (y2B - y1B)
union_area = areaA + areaB - intersection_area
# 计算 IoU
iou = intersection_area / union_area
# 绘制交集
if w > 0 and h > 0:
rect_intersection = patches.Rectangle((xx1, yy1), w, h, linewidth=2, edgecolor='green', facecolor='green', linestyle='--', label='Intersection')
ax.add_patch(rect_intersection)
# 显示图例
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
plt.legend(handles=handles)
plt.xlim(0, 500)
plt.ylim(0, 500)
plt.gca().set_aspect('equal', adjustable='box')
plt.title(f'IoU = {iou:.2f}')
plt.show()
# 示例框
boxA = [100, 100, 300, 300]
boxB = [200, 200, 400, 400]
plot_iou(boxA, boxB)