c
#include<stdio.h>
struct stu
{
int num;
float score;
struct stu *next;
};
void main()
{
struct stu a,b,c,*head;//静态链表
a.num = 1;
a.score = 10;
b.num = 2;
b.score = 20;
c.num = 3;
c.score = 30;
head = &a;
a.next = &b;
b.next = &c;
do
{
printf("%d,%5.1f\n",head->num,head->score);
head = head->next;
}while(head != NULL);
}
c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct stu)
int n;
struct stu
{
int num;
float score;
struct stu *next;
};
struct stu *creat()//建立动态链表
{
struct stu *p1,*p2,*head;
p1 = p2 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
head = NULL,n = 0;
while(p1->num != 0)
{
n++;
if(n == 1)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;//
p1 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct stu *head)
{
struct stu *p;
printf("there are %d record stu\n",n);
p = head;
if(head != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("num = %d,score = %f\n",p->num,p->score);
p = p->next;
}while(p);//直到p为空结点退出循环
}
}
void main()
{
struct stu *p;
p = creat();
print(p);
}
c
#include<stdio.h>//增删改查
#include<stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct stu)
struct stu *del(struct stu *head,int n);
struct stu *creat();
void print(struct stu *head);
int n;
struct stu
{
int num;
float score;
struct stu *next;
};
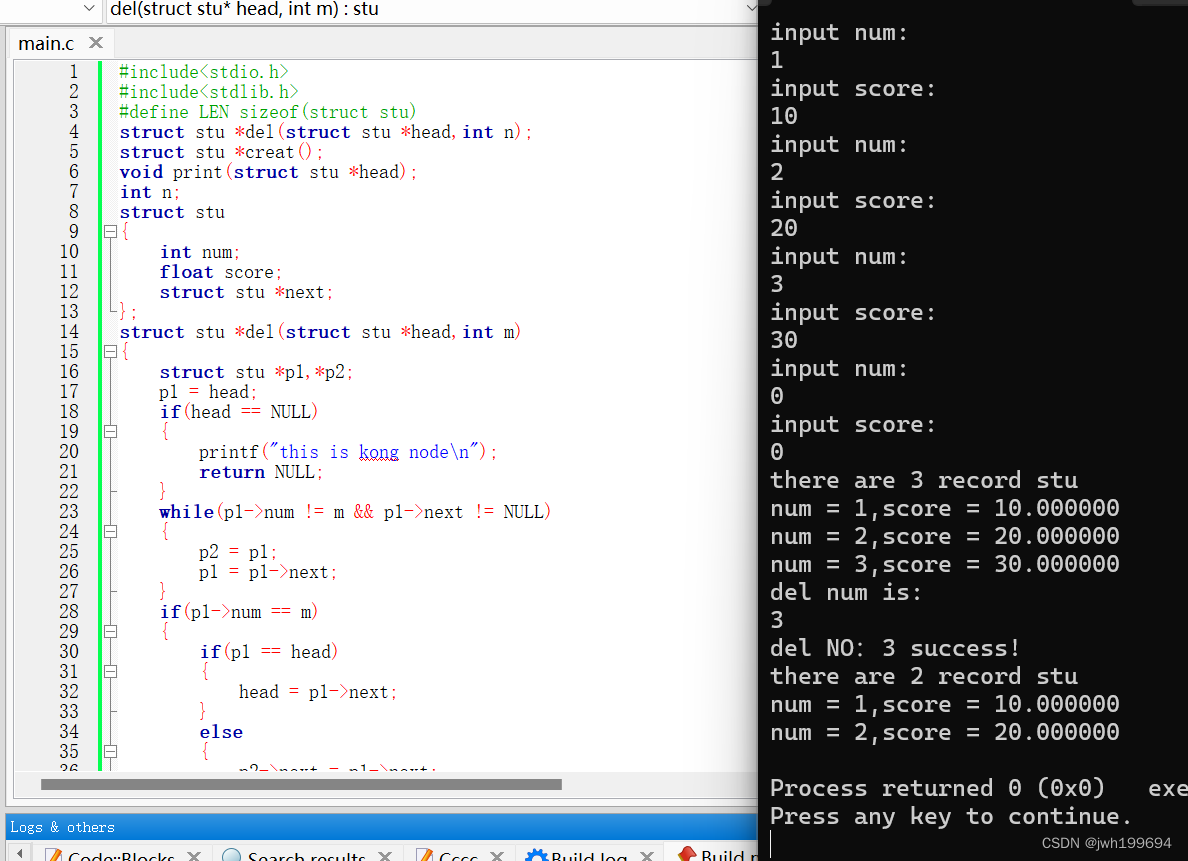
struct stu *del(struct stu *head,int m)
{
struct stu *p1,*p2;
p1 = head;
if(head == NULL)//判断是否为空链表
{
printf("this is kong node\n");
return NULL;
}
while(p1->num != m && p1->next != NULL)//删除的值不是当前结点,且当前结点不为尾节点
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if(p1->num == m)//找到节点
{
if(p1 == head)//如果当前节点为头结点
{
head = p1->next;
}
else//此时为普通结点
{
p2->next = p1->next;
}
printf("del NO:%d success!\n",m);
n = n-1;
}
else
{
printf("%d no found!\n",n);
}
return head;
}
struct stu *creat()
{
struct stu *p1,*p2,*head;
p1 = p2 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
head = NULL,n = 0;
while(p1->num != 0)
{
n++;
if(n == 1)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct stu *head)
{
struct stu *p;
printf("there are %d record stu\n",n);
p = head;
if(head != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("num = %d,score = %f\n",p->num,p->score);
p = p->next;
}while(p);
}
}
void main()
{
struct stu *stu,*p;
int k;
stu = creat();
p = stu;
print(p);
printf("del num is:\n");
scanf("%d",&k);
print(del(p,k));
}

c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define LEN sizeof(struct stu)
struct stu *del(struct stu *head,int n);
struct stu *creat();
void print(struct stu *head);
struct stu *inser(struct stu *head,struct stu *ins);
struct stu *lookfor(struct stu *head,struct stu *look);
struct stu *wrilink(struct stu *head,struct stu *stu4);
struct stu
{
int num;
float score;
struct stu *next;
};
int n;
struct stu *wrilink(struct stu *head,struct stu *stu4)
{
struct stu *p;
p = head;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("无数据可修改!\n");
}
else
{
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->num == stu4->num)
{
p->score = stu4->score;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
struct stu *lookfor(struct stu *head,struct stu *look)
{
struct stu *p;
p = head;
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("没有数据!\n");
}
else
{
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->num == look->num)
{
printf("找到第%d个数据,分数为%f\n",p->num,p->score);
}
p = p->next;
}
}
return head;
}
struct stu *inser(struct stu *head,struct stu *ins)
{
struct stu *p1,*p2,*p0;
p0 = ins;
p1 = head;
if(head == NULL)
{
head = p0;
p0->next = NULL;
}
else
{
while((p0->num >p1->num) && (p1->next != NULL))
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if(p0->num <= p1->num)
{
if(p1 == head)
{
head = p0;
}
else
{
p2->next = p0;
}
p0->next = p1;
}
else
{
p1->next = p0;
p0->next = NULL;
}
n = n+1;
return head;
}
}
struct stu *del(struct stu *head,int m)
{
struct stu *p1,*p2;
p1 = head;
if(head == NULL)
{
printf("this is kong node\n");
return NULL;
}
while(p1->num != m && p1->next != NULL)
{
p2 = p1;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if(p1->num == m)
{
if(p1 == head)
{
head = p1->next;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1->next;
}
printf("del NO:%d success!\n",m);
n = n-1;
}
else
{
printf("%d no found!\n",n);
}
return head;
}
struct stu *creat()
{
struct stu *p1,*p2,*head;
p1 = p2 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
head = NULL,n = 0;
while(p1->num != 0)
{
n++;
if(n == 1)
{
head = p1;
}
else
{
p2->next = p1;
}
p2 = p1;
p1 = (struct stu *)malloc(LEN);
printf("input num:\n");
scanf("%d",&p1->num);
printf("input score:\n");
scanf("%f",&p1->score);
}
p2->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void print(struct stu *head)
{
struct stu *p;
printf("there are %d record stu\n",n);
p = head;
if(head != NULL)
{
do
{
printf("num = %d,score = %f\n",p->num,p->score);
p = p->next;
}while(p != NULL);
}
}
void main()
{
struct stu *stu,*p,stu2,stu3,stu4;
int k;
stu = creat();
p = stu;
print(p);
printf("del num is:\n");
scanf("%d",&k);
print(del(p,k));
printf("insert into the num:");
scanf("%d",&stu2.num);
printf("insert into the score:");
scanf("%f",&stu2.score);
p = inser(stu,&stu2);
print(p);
printf("请输入查找的数据是:");
scanf("%d",&stu3.num);
lookfor(stu,&stu3);
printf("请输入修改的学号:");
scanf("%d",&stu4.num);
printf("请输入修改的学号数据:");
scanf("%f",&stu4.score);
p = wrilink(stu,&stu4);
print(p);
}typedef 声明新的类型名来代替已有的类型名,有利于程序通用与移植
c
#include<stdio.h>
typedef struct
{
int year;
int month;
int day;
}date;
void main()
{
date da;
da.year = 1995;
da.month = 8;
da.day = 9;
printf("%d--%d--%d\n",da.year,da.month,da.day);
}
c
#include<stdio.h>
typedef int num[100];//声明um为整型数组类型
void main()
{
num n = {0};
printf("%d\n",sizeof(n));
}
c
#include<stdio.h>
typedef void (*p)();
void fun()
{
printf("funny\n");
}
void main()
{
p p1;
p1 = fun;//函数指针指向函数的入口
p1();
}

