在Spring中,@Transactional注解的处理涉及到多个关键组件,包括Advisor、Target、ProxyFactory等。下面是详细的解析和代码示例,解释这些组件是如何协同工作的。
1. 关键组件介绍
1.1 Advisor
Advisor是一个Spring AOP的概念,它包含了切点(Pointcut)和通知(Advice)。在事务管理中,TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor是一个典型的Advisor。
1.2 Target
Target是指被代理的目标对象,即实际执行业务逻辑的对象。
1.3 ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory是Spring提供的用于创建代理对象的工厂类。它可以使用JDK动态代理或CGLIB创建代理对象。
2. @Transactional的处理流程
- 解析注解 :Spring扫描
@Transactional注解。 - 创建Advisor :创建包含事务处理逻辑的
Advisor。 - 创建代理对象 :使用
ProxyFactory为目标对象创建代理对象,并将Advisor加入到代理对象中。
3. 代码示例
3.1 配置类
首先,通过@EnableTransactionManagement启用事务管理。
java
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class AppConfig {
// DataSource, EntityManagerFactory, TransactionManager beans configuration
}3.2 目标对象和接口
定义一个业务接口和其实现类:
java
public interface MyService {
void myTransactionalMethod();
}
@Service
public class MyServiceImpl implements MyService {
@Override
@Transactional
public void myTransactionalMethod() {
// 业务逻辑
System.out.println("Executing myTransactionalMethod");
}
}3.3 ProxyFactory和Advisor
使用ProxyFactory和TransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor来创建代理对象并处理事务:
java
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;
import org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor;
import org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAttributeSource;
import org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource;
public class ProxyFactoryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建目标对象
MyService target = new MyServiceImpl();
// 创建事务属性源
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource = new NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource();
// 创建事务拦截器
TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);
// 创建Advisor
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor();
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);
// 创建ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);
// 创建代理对象
MyService proxy = (MyService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
// 调用代理对象的方法
proxy.myTransactionalMethod();
}
}4. 详细解释
4.1 创建目标对象
java
MyService target = new MyServiceImpl();这是被代理的目标对象,它包含了业务逻辑,并使用了@Transactional注解。
4.2 创建事务属性源
java
TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource = new NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource();TransactionAttributeSource用于解析事务属性。NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource是一个实现类,可以基于方法名称匹配事务属性。
4.3 创建事务拦截器
java
TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
transactionInterceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource);TransactionInterceptor实现了MethodInterceptor接口,用于在方法调用前后处理事务逻辑。
4.4 创建Advisor
java
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor();
advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor);DefaultPointcutAdvisor包含了事务拦截器,可以在匹配的方法上应用事务逻辑。
4.5 创建ProxyFactory
java
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvisor(advisor);ProxyFactory用于创建代理对象。它将目标对象和Advisor结合起来,生成代理对象。
4.6 创建代理对象并调用方法
java
MyService proxy = (MyService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
proxy.myTransactionalMethod();通过ProxyFactory.getProxy()方法创建代理对象,并调用代理对象的方法。这时,事务拦截器会在方法调用前后执行事务处理逻辑。
5. 总结
通过以上代码示例,可以看出Spring如何解析@Transactional注解,并使用Advisor、Target和ProxyFactory创建代理对象来处理事务逻辑。这些组件协同工作,实现了自动的事务管理。
proxyFactory源码
targetSource与代理对象是两个对象,
在调用代理对象的时候,实际上是要被DynamicAdvisedInterceptor拦截,之后在拦截方法中执行执行拦截器调用链,并把targetSource传给拦截器。
相当于把targetSource对象(非类)作为成员变量传递给代理对象,然后对targetSource对象的方法调用增强。
类->BeanDefinition->bean初始化->为bean添加后置处理器,替换bean对象为proxy对象,其中bean对象作为代理对象的成员变量targetSource,代理对象通过在拦截方法中对targetSource对象的方法调用前后执行advisor的方法。
对比 @Configuration对@bean方法的处理,是直接生成子类,子类重写@bean方法,子类作为BeanDefinition替换原始@Configuration注解的类, 因此在子类中的this调用就是对子类重写的方法调用。
java
//CglibAopProxy
/**
* General purpose AOP callback. Used when the target is dynamic or when the
* proxy is not frozen.
*/
private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
private final AdvisedSupport advised;
public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) {
this.advised = advised;
}
@Override
@Nullable
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Object target = null;
TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource();
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = targetSource.getTarget();
Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null);
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
if (chain.isEmpty() && CglibMethodInvocation.isMethodProxyCompatible(method)) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = invokeMethod(target, method, argsToUse, methodProxy);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
// 链式调用
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) {
targetSource.releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) {
return (this == other ||
(other instanceof DynamicAdvisedInterceptor &&
this.advised.equals(((DynamicAdvisedInterceptor) other).advised)));
}
/**
* CGLIB uses this to drive proxy creation.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.advised.hashCode();
}
}
java
//ReflectiveMethodInvocation
@Override
@Nullable
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
Class<?> targetClass = (this.targetClass != null ? this.targetClass : this.method.getDeclaringClass());
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//调用 @Transactional事务拦截器
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
java
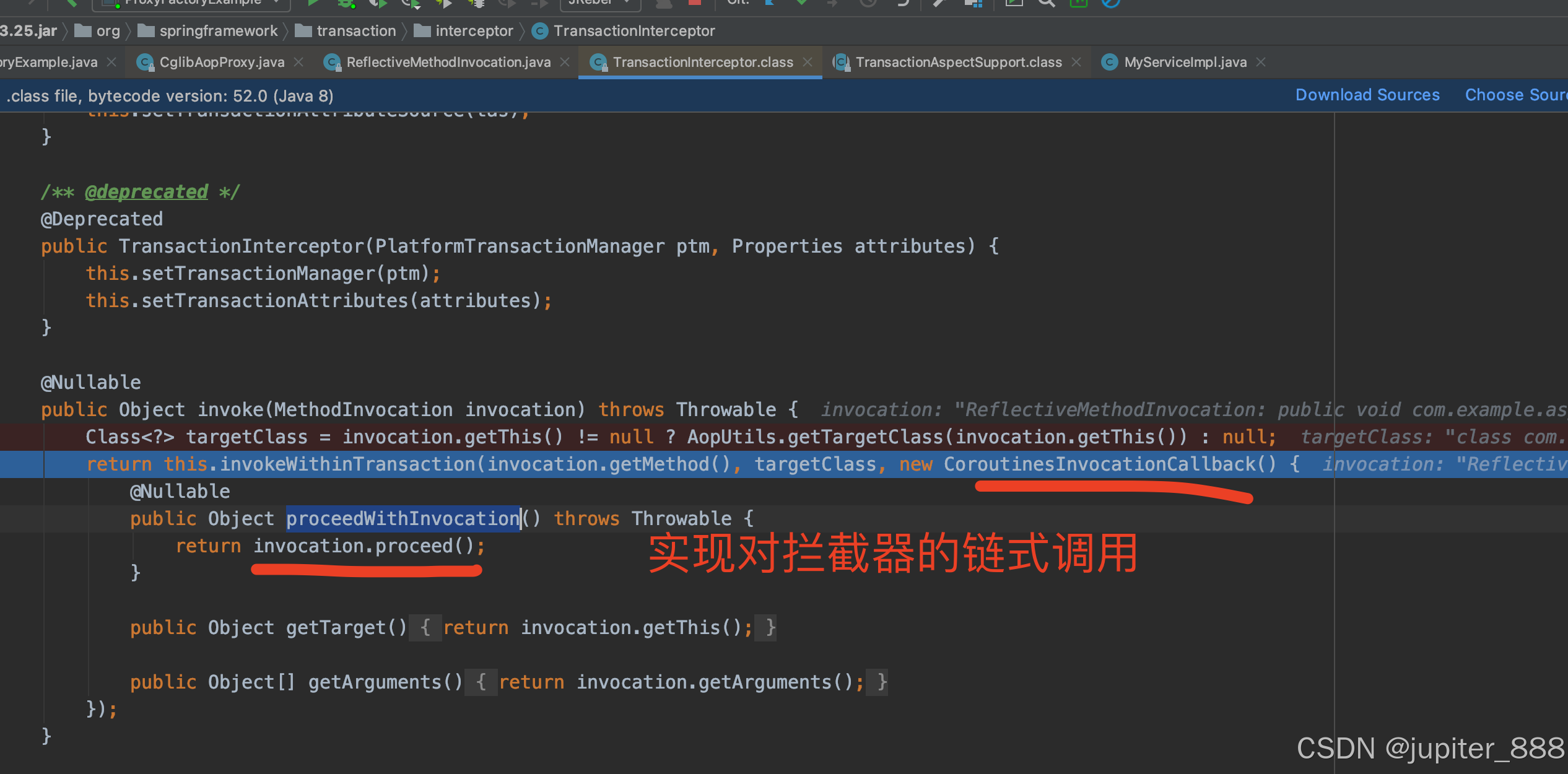
//TransactionInterceptor
@Nullable
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<?> targetClass = invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null;
return this.invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new CoroutinesInvocationCallback() {
@Nullable
public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
// 拦截器链式调用
return invocation.proceed();
}
public Object getTarget() {
return invocation.getThis();
}
public Object[] getArguments() {
return invocation.getArguments();
}
});
}