采集数据->采样率调整
使用torchaudio进行重采样(cpu版)
-
首先导入相关包,既然使用torch作为我们的选项,安装torch环境我就不必多说了,如果你不想用torch可以使用后文提到的另一个库
1 import torch 2 import torchaudio 3 from torchaudio.transforms import Resample 4 from time import time#仅计算时间,不影响主体 -
使用
torchaudio.load导入音频文件 -
设定目标采样率并构造
resample函数 -
调用构造好的
resample函数 -
调用
torchaudio的保存函数
封装一下,总函数【记得先导入】:
1 def resample_by_cpu():
2 file_path = input("please input your file path: ")
3 start_time = time()#不影响,可去掉
4 y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path) #使用torchaudio.load导入音频文件
5
6 target_sample = 32000 #设定目标采样率
7 resampler = Resample(orig_freq=sr, new_freq=target_sample)#构造resample函数,输入原始采样率和目标采样率
8 resample_misic = resampler(y) #调用resample函数
9
10 torchaudio.save("test.mp3", resample_misic, target_sample)#调用torchaudio的保存即可
11 print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")#不影响,可去掉最后结果大概是几秒钟这样子
2.
##### 使用使用`torchaudio`进行重采样(gpu版):
有了上面cpu的基础,其实调用gpu也就更换一下设备,和放入gpu的操作就好了,因此不过多赘述
```
def resample_use_cuda():
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
start_time = time()
file_path = input("please input your file path:")
y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path)
y = y.to(device)
target_sample = 32000
resampler = Resample(orig_freq=sr, new_freq=target_sample).to(device)
resample_misic = resampler(y)
torchaudio.save("test.mp3", resample_misic.to('cpu'), target_sample) #这里注意要把结果从gpu中拿出来到cpu,不然会报错。
print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")
```
时间方面嘛,单个音频多了放入gpu取出gpu的步骤肯定会稍慢的,但是跑过cuda都知道它的强大,更多是用于后续的操作说是。-
使用librosa库进行重采样
具体步骤:
-
导入两个库文件,
librosa和音频文件读写库soundfileimport librosa import soundfile as sf from time import time#仅计算时间,不影响主体 -
导入音频文件
-
设定目标采样率
-
重采样
-
输出
综合封装成函数:
1 def resample_by_lisa(): 2 file_path = input("please input your file path:") 3 start_time = time() 4 y, sr = librosa.load(file_path) #使用librosa导入音频文件 5 target_sample_rate = 32000 6 y_32k = librosa.resample(y=y, orig_sr=sr, target_sr=target_sample_rate) #使用librosa进行重采样至目标采样率 7 sf.write("test_lisa.mp3", data=y_32k, samplerate=target_sample_rate) #使用soundfile进行文件写入 8 print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")总结:
-
优点,简单小巧,
ibrosa有很多能处理音频的功能 -
缺点:无法调用cuda,保存的时候需要依赖
soundfile库。 -
时间:也是几秒左右,和
torchaudiocpu版差不多 -
小声bb:提取32k的效果好像没有torchaudio好【嘛,毕竟librosa历史有点久了,没有专注深度学习的torch好很正常啦】,你们也可以自己测一下
-
all code:
1 import torch
2 import torchaudio
3 from torchaudio.transforms import Resample
4 import librosa
5 import soundfile as sf
6 from time import time
7
8 def resample_by_cpu():
9 file_path = input("please input your file path: ")
10 start_time = time()
11 y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path) #使用torchaudio.load导入音频文件
12
13 target_sample = 32000 #设定目标采样率
14 resampler = Resample(orig_freq=sr, new_freq=target_sample)#构造resample函数,输入原始采样率和目标采样率
15 resample_misic = resampler(y) #调用resample函数
16
17 torchaudio.save("test.mp3", resample_misic, target_sample)#调用torchaudio的保存即可
18 print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")
19 def resample_use_cuda():
20
21 device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
22 start_time = time()
23 file_path = input("please input your file path:")
24 y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path)
25
26 y = y.to(device)
27 target_sample = 32000
28 resampler = Resample(orig_freq=sr, new_freq=target_sample).to(device)
29 resample_misic = resampler(y)
30 torchaudio.save("test.mp3", resample_misic.to('cpu'), target_sample)
31 print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")
32
33 def resample_by_lisa():
34 file_path = input("please input your file path:")
35 start_time = time()
36 y, sr = librosa.load(file_path)#使用librosa导入音频文件
37 target_sample_rate = 32000
38 y_32k = librosa.resample(y=y, orig_sr=sr, target_sr=target_sample_rate)#使用librosa进行重采样至目标采样率
39 sf.write("test_lisa.mp3", data=y_32k, samplerate=target_sample_rate)#使用soundfile进行文件写入
40 print(f"cost :{time() - start_time}s")
41
42 if __name__ == '__main__':
43 resample_use_cuda()
44 resample_by_cpu()
45 resample_by_lisa()2.2 提取pitch基频特征【音高提取】
使用torchaudio进行基频特征提取
其实主要使用的这个函数:torchaudio.transforms._transforms.PitchShift
让我们来看看它官方的example,仿照着来写就好啦
>>> waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load("test.wav", normalize=True)
>>> transform = transforms.PitchShift(sample_rate, 4)
>>> waveform_shift = transform(waveform) # (channel, time)步骤:
-
导入依赖
import torchaudio import torchaudio.transforms as Tf import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #画图依赖
-
导入音频
-
构造
PitchShift -
使用这个函数对歌曲进行基频提取
code:
def get_pitch_by_torch():
file_path = input("file path:")
y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path)
"""specimen:
>>> waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load("test.wav", normalize=True)
>>> transform = transforms.PitchShift(sample_rate, 4)
>>> waveform_shift = transform(waveform) # (channel, time)
"""
pitch_tf = Tf.PitchShift(sample_rate=sr, n_steps=0)
feature = pitch_tf(y)
# 绘制基频特征 这部分可以忽略,只是画图而已,可以直接复制不用理解
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
plt.plot(feature[0].numpy(), label='Pitch')
plt.xlabel('Frame')
plt.ylabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.title('Pitch Estimation')
plt.legend()
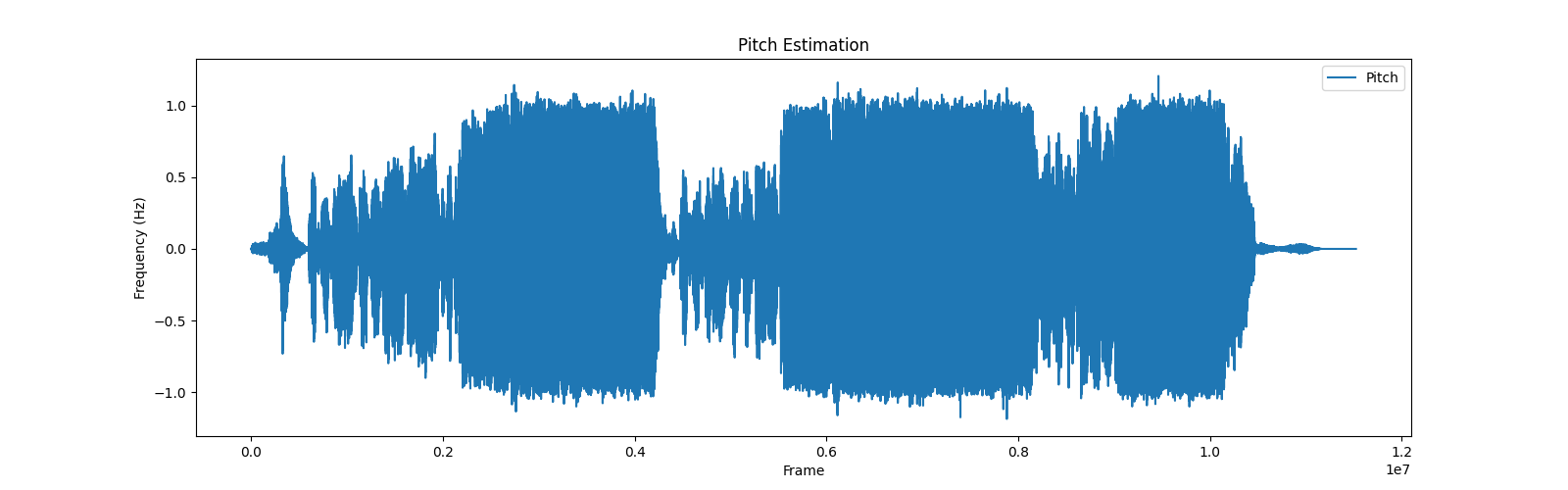
plt.show()输出图片【总歌曲】效果:
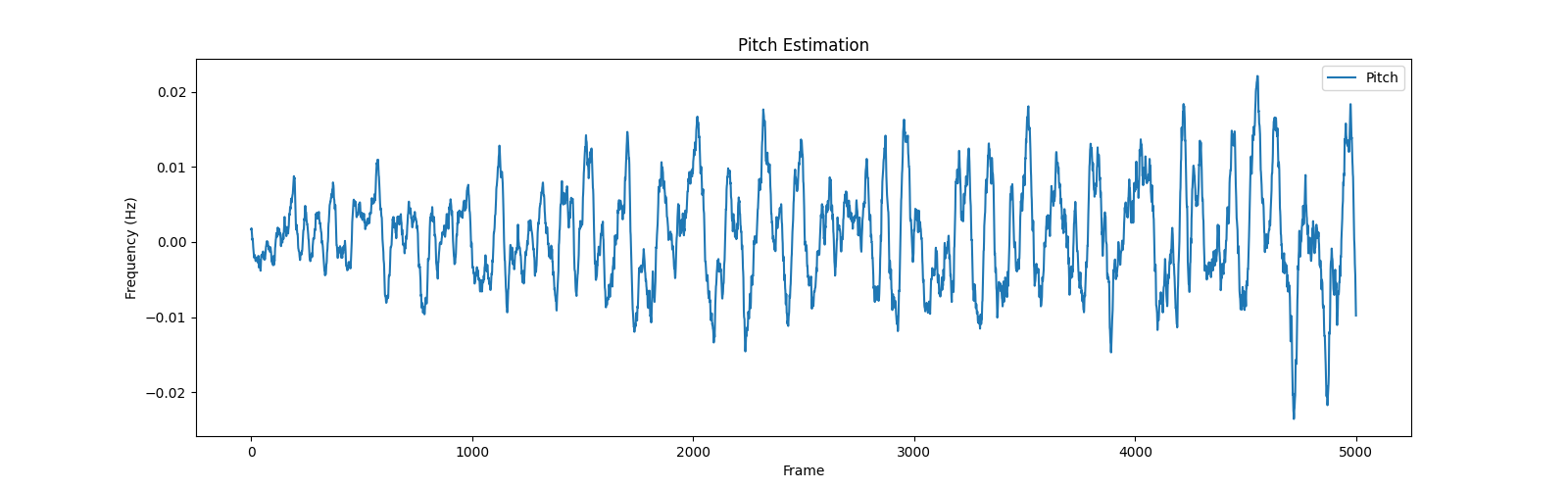
将输出的范围稍微改一下,切分特征的一部分,就是歌曲部分的音高特征啦,效果就很明显了
改为:plt.plot(feature[0][5000:10000].numpy(), label='Pitch')
2.
使用librosa提取基频特征
-
步骤:
-
导入包
-
提取基频特征
-
(可选)绘制基频特征
-
-
主要函数:
librosa.pyin,请见官方example
#Computing a fundamental frequency (F0) curve from an audio input >>> y, sr = librosa.load(librosa.ex('trumpet')) >>> f0, voiced_flag, voiced_probs = librosa.pyin(y, ... sr=sr, ... fmin=librosa.note_to_hz('C2'), ... fmax=librosa.note_to_hz('C7')) >>> times = librosa.times_like(f0, sr=sr)
code:
1 def get_pitch_by_librosa():
2
3 file_path = input("请输入音频文件路径:")
4 y, sr = librosa.load(file_path)
5 """librosa.pyin(y,sr=sr,fmin=librosa.note_to_hz('C2'),fmax=librosa.note_to_hz('C7'))"""
6 # 使用pyin提取基频特征
7 f0, voiced_flag, voiced_probs = librosa.pyin(y, sr=sr, fmin=librosa.note_to_hz('C2'), fmax=librosa.note_to_hz('C7'))
8
9 # 绘制基频特征,可忽略
10 plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
11 librosa.display.waveshow(y, sr=sr, alpha=0.5)
12 plt.plot(librosa.times_like(f0), f0, label='f0 (fundamental frequency)', color='r')
13 plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
14 plt.ylabel('Frequency (Hz)')
15 plt.title('Pitch (fundamental frequency) Estimation')
16 plt.legend()
17 plt.show()-
总结:
- 比torchaudio略微麻烦一点,不过多了两个参数
voiced_flag, voiced_probs,看起来的视觉图好像也有些不一样,不过都是按照官方的这个来了,这也不对的话我也不会了
- 比torchaudio略微麻烦一点,不过多了两个参数
-
输出:
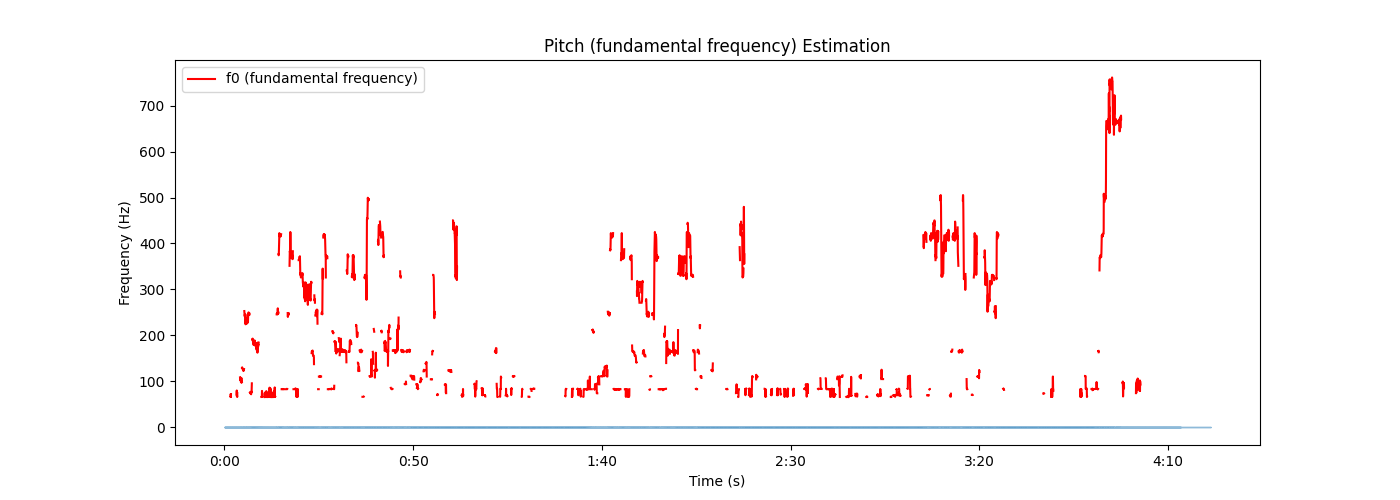
all code:
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.transforms as Tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import librosa
def get_pitch_by_torch():
file_path = input("file path:")
y, sr = torchaudio.load(file_path)
"""specimen:
>>> waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load("test.wav", normalize=True)
>>> transform = transforms.PitchShift(sample_rate, 4)
>>> waveform_shift = transform(waveform) # (channel, time)
"""
pitch_tf = Tf.PitchShift(sample_rate=sr, n_steps=0)
feature = pitch_tf(y)
# 绘制基频特征
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5))
plt.plot(feature[0][5000:10000].numpy(), label='Pitch')
plt.xlabel('Frame')
plt.ylabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.title('Pitch Estimation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
def get_pitch_by_librosa():
file_path = input("请输入音频文件路径:")
y, sr = librosa.load(file_path)
"""librosa.pyin(y,sr=sr,fmin=librosa.note_to_hz('C2'),fmax=librosa.note_to_hz('C7'))"""
# 使用pyin提取基频特征
f0, voiced_flag, voiced_probs = librosa.pyin(y, sr=sr, fmin=librosa.note_to_hz('C2'), fmax=librosa.note_to_hz('C7'))
# 绘制基频特征,可忽略
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
librosa.display.waveshow(y, sr=sr, alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(librosa.times_like(f0), f0, label='f0 (fundamental frequency)', color='r')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.ylabel('Frequency (Hz)')
plt.title('Pitch (fundamental frequency) Estimation')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# get_pitch_by_torch()
# get_pitch_by_librosa()