SpringMVC数据校验、数据格式化处理、国际化设置
1.数据验证
(1)使用JSR-303验证框架
JSR(Java Specification Requests),意思是Java 规范提案。JSR-303是JAVA EE 6中的一项子规范,叫做Bean Validation。JSR 303,Bean Validation规范 ,为Bean验证定义了元数据模型和API。默认的元数据模型是通过Annotations来描述的,使用规范定义的这些注解有效的替换了if-else冗长的校验代码。
引入依赖:
•validation-api
•hibernate-validator(附加了一些验证注解)
•jakarta.validation-api(Spring6以上引入此依赖)
JSR-303验证框架常用注解
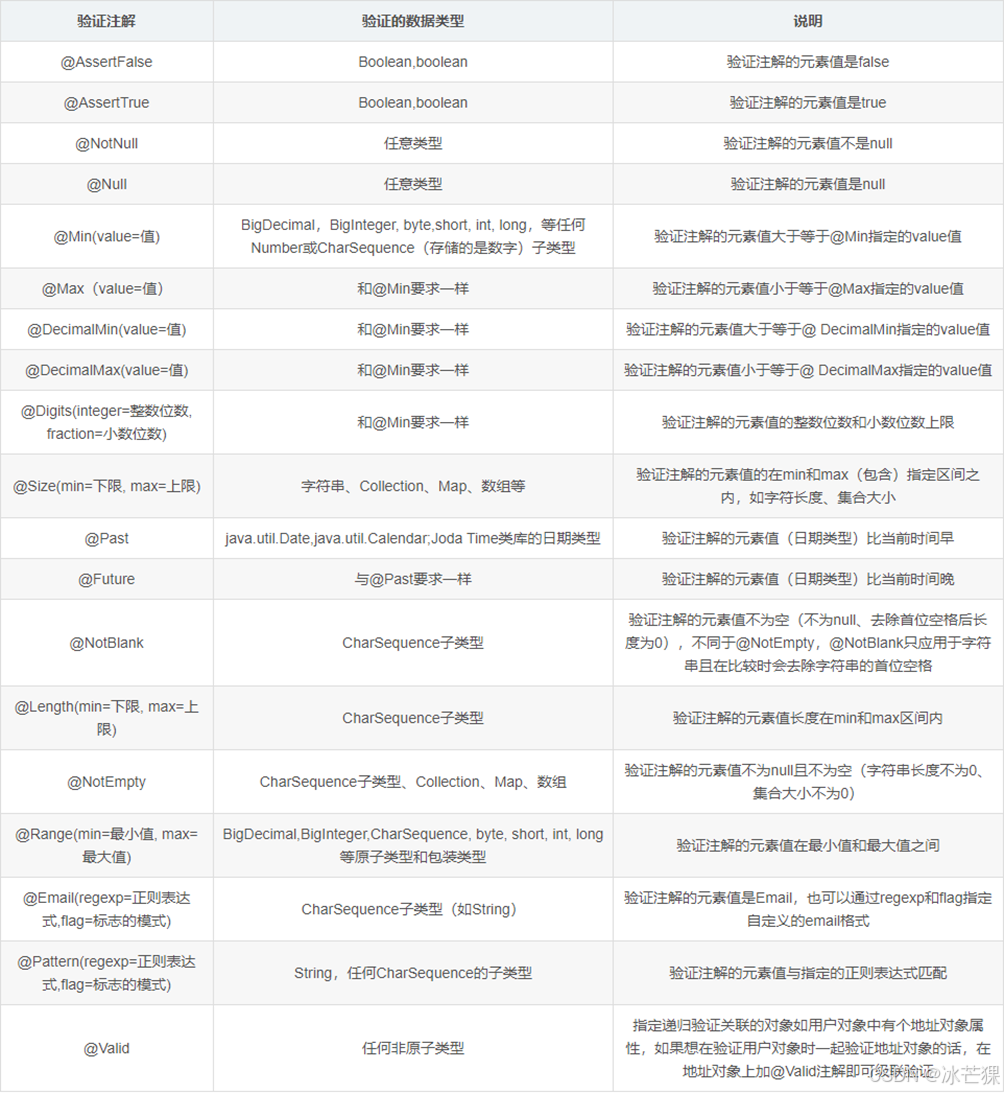
使用案例:
@Data
public class SysUser {
/*** 用户ID*/
@NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空")
private Long userId;
/** 用户名*/
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
@Length(max = 20, message = "用户名不能超过20个字符")
@Pattern(regexp = "^[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9\\*]*$", message = "用户昵称限制:最多20字符,包含文字、字母和数字")
private String username;
/** 手机号*/
@NotBlank(message = "手机号不能为空")
@Pattern(regexp = "^[1][3,4,5,6,7,8,9][0-9]{9}$", message = "手机号格式有误")
private String mobile;
/**性别*/
private String sex;
/** 邮箱*/
@NotBlank(message = "联系邮箱不能为空")
@Email(message = "邮箱格式不对")
private String email;
/** 密码*/
private String password;
/*** 创建时间 */
@Future(message = "时间必须是将来时间")
private Date startTime;
}在controller层方法参数列表前加上@Valid或@Validated注解
@PostMapping("/save/valid")
@ResponseBody
public Result save(@RequestBody @Valid User user) {
if(userService.save(user)>0)
return Result.ok();
else
return Result.fail();
}@Valid 与 @Validated的区别 :
| 区别 | @Valid | @Validated |
|---|---|---|
| 来源 | 标准JSR-303规范 | Spring's JSR-303规范,是标准JSR-303的一个变种。 |
| 分组验证 | 不支持 | 支持(使用注解的group属性设定) |
| 声明位置 | 可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(字段)上,支持嵌套验证。 | 可以用在类型、方法和方法参数上,但不能用在成员属性(字段)上,从而不支持嵌套验证功能。 |
@Valid嵌套验证
@Data
public class Food {
@Valid
private Drink drink;
@NotNull
private String type;
}
@Data
public class Drink {
@NotNull
private String name;
@Size(min = 1,max = 10000)
private String describ;
@Digits(integer = 2,fraction = 2)
private Double price;
}
//controller层
@PostMapping("/food")
public String addFood(@Valid Food food){
return food.getDrink().getName();
}数据验证全局异常定义案例:
@Component
@ResponseBody
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
/**方法参数校验(接收参数加上@RequestBody注解才会有这种异常) */
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public Result handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
log.error("方法参数校验失败", e);
return Result.fail(Objects.requireNonNull(e.getBindingResult().getFieldError()).getDefaultMessage());
}
@ExceptionHandler(BindException.class)
public Result bindException(BindException ex, HttpServletRequest request) {
log.error("数据绑定异常", ex);
try {// 拿到@NotNull,@NotBlank和 @NotEmpty等注解上的message值
String msg = Objects.requireNonNull(ex.getBindingResult().getFieldError()).getDefaultMessage();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(msg)) {
return Result.fail(msg);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder(); // 参数类型不匹配检验
List<FieldError> fieldErrors = ex.getFieldErrors();
fieldErrors.forEach((oe) ->
msg.append("参数:[").append(oe.getObjectName()).append(".").append(oe.getField())
.append("]的传入值:[").append(oe.getRejectedValue()).append("]与预期的字段类型不匹配.")
);
return Result.fail(msg.toString());
}
/**ConstraintViolationException */
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public Result handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException e) {
log.error("注解校验异常", e);
Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> violations = e.getConstraintViolations();
String message = violations.stream().map(ConstraintViolation::getMessage).collect(Collectors.joining(";"));
return Result.fail(message);
}
}自定义验证注解的步骤案例:
•定义注解接口
@Documented
@Target({ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = CardNoValidator.class)
public @interface CardNo {
String message() default "{edu.cqie.ssm.cardNoErrorMessage}";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}•创建ConstraintValidator接口实现类
public class CardNoValidator implements ConstraintValidator<CardNo, Object> {
@Override
public void initialize(CardNo constraintAnnotation) {
ConstraintValidator.super.initialize(constraintAnnotation);
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(Object o, ConstraintValidatorContext constraintValidatorContext) {
if (o == null) {
return true;//身份证号未传递时,不做校验
}
return IdCardValidatorUtils.isValidate18Idcard(o.toString());
}
}•使用注解
@Data
public class User {
/*** 用户ID*/
@NotNull(message = "用户id不能为空")
private Long userId;
/** 用户名*/
@NotBlank(message = "用户名不能为空")
@Length(max = 20, message = "用户名不能超过20个字符")
@Pattern(regexp = "^[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9\\*]*$", message = "用户昵称限制:最多20字符,包含文字、字母和数字")
private String username;
@CardNo
private String cardNo;
}2.数据格式化
SpringMVC Formatter
•SpringMVC类型转换器提供了一个统一的ConversionService API以及一个强类型的Converter SPI,用于实现从一种类型 到另一种类型 的转换逻辑。例如,将Short强制转换为Long。
•在Spring MVC中,HTTP中的源数据都是String类型,数据绑定需要将String转换为其他类型,同时也可能需要将数据转换为具有本地格式的字符串样式进行展示,而Converter SPI不能直接满足这种格式要求。
•Spring 3 引入了一个方便的Formatter SPI,当在客户端环境(如Web应用程序)中工作并且需要解析和输出本地化字段值时,可以使用Formatter SPI。
(1)使用Converter转换
public class StringToDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
private String pattern;
public StringToDateConverter(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
@Override
public Date convert(String source) {
try {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
dateFormat.setLenient(false);
return dateFormat.parse(source);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid date format. Please use this pattern\"" + pattern + "\"");
}
}
}注册bean
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<bean class="edu.cqie.ssm.converter.StringToDateConverter">
<constructor-arg name="pattern" value="yyyy-MM-dd"/>
</bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"/>(2)使用Formatter转换
public class DateFormatter implements Formatter<Date> {
private SimpleDateFormat sdf;
public DateFormatter(String pattern) {
this.sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern);
sdf.setLenient(false);
}
@Override
public Date parse(String s, Locale locale) throws IllegalArgumentException {
try {
return this.sdf.parse(s);
} catch (ParseException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid date format. Please use this pattern\"" + this.sdf.toPattern() + "\"");
}
}
@Override
public String print(Date date, Locale locale) {
return this.sdf.format(date);
}
}
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="formatters">
<set>
<bean class="edu.cqie.ssm.formatter.DateFormatter">
<constructor-arg name="pattern" value="yyyy-MM-dd"/>
</bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"/>(3)内置Formatter转换器
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NumberFormatter | 实现 Number 与 String 之间的解析与格式化 |
| CurrencyFormatter | 实现 Number 与 String 之间的解析与格式化(带货币符号) |
| PercentFormatter | 实现 Number 与 String 之间的解析与格式化(带百分数符号) |
| DateFormatter | 实现 Date 与 String 之间的解析与格式化 |
两个格式化注解
•@NumberFormat
•@DateTimeFormat
使用注解格式化
@DateTimeFormat(pattern="yyyy/MM/dd")
private Date birthday;
@NumberFormat(style = NumberFormat.Style.CURRENCY )
private Double balance;//货币金额 ¥5000
@NumberFormat(pattern = "#,###.##")
private Double salary; //工资 10,000.00
@NumberFormat(style = NumberFormat.Style.PERCENT)
private Double percent;//不加%按p*100来显示,加上按提交精度来显示3.国际化
什么是国际化?
国际化(也叫 i18n),由于国际化英文单词是 internationalization,在 i 和 n 之间有 18 个字母,因此国际化又叫做 i18n。国际化是指程序在不做任何修改的情况下,就可以在不同的国家或地区和不同的语言环境下,按照当地的语言和格式习惯的显示字符,例如MyBatis官方网站等。
国际化设置场景:
•Spring标签国际化
•接口方法国际化
LocaleResolver
•AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver:根据请求头中的 Accept-Language 字段来确定当前的区域语言。
•SessionLocaleResolver:根据请求参数来确定区域语言,确定后会保存在 Session 中,只要 Session不变,Locale 对象就一直有效。
•CookieLocaleResolver:根据请求参数来确定区域语言,确定后会保存在Cookie中,只要Cookie不变Locale对象就一直有效。
•FixedLocaleResolver:配置时直接提供一个 Locale 对象,以后不能修改。


(1)AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
步骤一:添加多语言配置文件



步骤二:修改****spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="i18n.message"/>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>步骤三:在页面中引用
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title><spring:message code="login.title"/></title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="toRegister" method="post">
<div><spring:message code="login.content.title"/></div>
<div>
<span><spring:message code="login.account"/></span>
<input type="tel" name="phone" maxlength="11" placeholder='<spring:message code="login.account.holder"/>'/>
</div>
<div>
<span><spring:message code="login.password"/></span>
<input type="password" name="pwd" minlength="8" maxlength="20" placeholder='<spring:message code="login.password.holder"/>'/>
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value='<spring:message code="login.submit"/>'/>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>步骤四:在接口中引用
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
MessageSource messageSource;
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login() {
String username = messageSource.getMessage("login.username", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
String password = messageSource.getMessage("login.password", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("password = " + password);
return "login";
}
}(2)SessionLocaleResolver
**步骤一:添加多语言配置文件(与上面一样)
步骤二:修改****spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="i18n.message"/>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor">
<property name="paramName" value="locale"/>
</bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver">
</bean>步骤三:在接口中使用
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
MessageSource messageSource;
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(String locale,HttpSession session) {
if ("zh-CN".equals(locale)) {
session.setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, new Locale("zh", "CN"));
} else if ("en-US".equals(locale)) {
session.setAttribute(SessionLocaleResolver.LOCALE_SESSION_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, new Locale("en", "US"));
}
String username = messageSource.getMessage("login.username", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
String password = messageSource.getMessage("login.password", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("password = " + password);
return "login";
}
}(3)CookieLocaleResolver
**步骤一:添加多语言配置文件(与上面一样)
步骤二:修改****spring-mvc.xml
<bean id="messageSource"
class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource">
<property name="basename" value="i18n.message"/>
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
</bean>
<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver"/>步骤三:在接口中使用
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(String locale, HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
CookieLocaleResolver resolver = new CookieLocaleResolver();
if ("zh-CN".equals(locale)) {
resolver.setLocale(req, resp, new Locale("zh", "CN"));
} else if ("en-US".equals(locale)) {
resolver.setLocale(req, resp, new Locale("en", "US"));
}
String username = messageSource.getMessage("login.username", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
String password = messageSource.getMessage("login.password", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("password = " + password);
return "login";
}
resolver.setLocale(req, resp, new Locale("zh", "CN"));
} else if ("en-US".equals(locale)) {
resolver.setLocale(req, resp, new Locale("en", "US"));
}
String username = messageSource.getMessage("login.username", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
String password = messageSource.getMessage("login.password", null, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale());
System.out.println("username = " + username);
System.out.println("password = " + password);
return "login";}