简介
图结构本质上还有多叉树的变种,图结构在逻辑上,由于若干个节点和边组成。但在实际落地中,一般用邻接表,邻接矩阵来存储图
在标准的树结构中,一般都是单链表表示,即只允许父节点指向子节点,两个子节点之间也不允许互相指向。
而图中,则是双链表放飞自我版,既可以父子之间互相指向,又可以子节点互相链接,形成复杂的网络结构。
图的逻辑视图
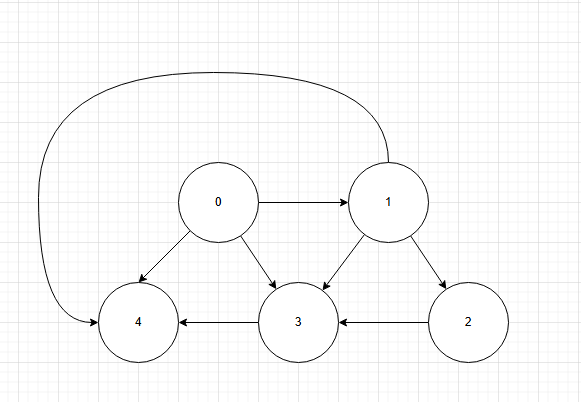
可以看到一幅图由节点(Vertex)与边(Edge)组成,那么从直觉出发,我们可以认为它的数据结构应该是这个样子的
public class Vertex
{
public int Value { get; set; }
Vertex[] Neighbors { get; set; }
}可以看到,与多叉树并无区别,所以图在本质上还是树.因此适用于树的DFS/BFS算法同样适用于图
Degree
图论中有一个独特的概念,叫度(Degree).
在没有方向的图中,Degree就是每个节点相连边的条数。在有方向的图中,Degree被细分为indegree和outdegree

比如在此图中,节点3的indegree为3,outdegree为1。节点4的indegree为3,outdegree为0
图的实际视图
与上面代码相反的是,图的实际存储方式如下
邻接表
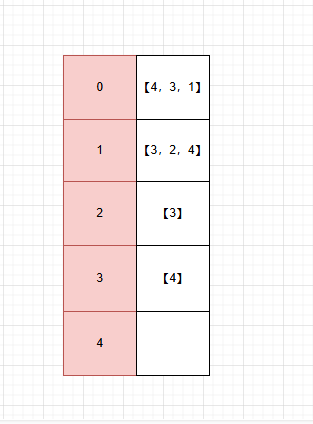
0号节点存储着它的indegree,【4,3,1】
2号节点存储着它的indegree,【3,2,4】
......
代码结构如下:
//邻接表
//List存节点,Int[]存储相邻节点
List<int[]> grath = new List<int[]>();邻接矩阵
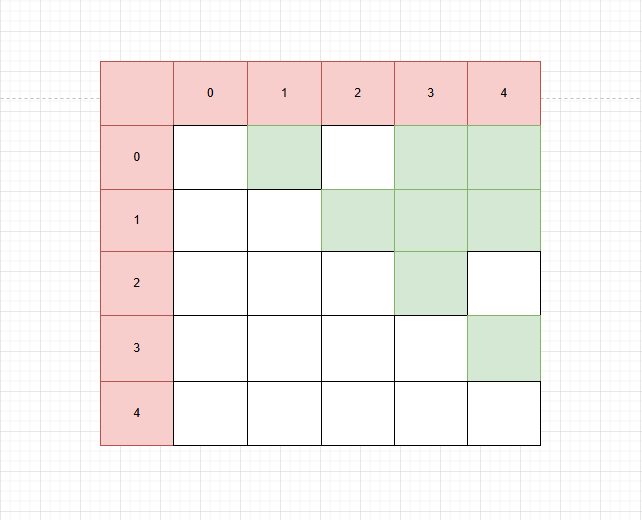
邻接矩阵则是把所有可能的节点都穷举描绘出来,然后再到上面标点。
代码结构如下:
//邻接矩阵
//二维数组
bool[,] matrix = new bool[5,5];为什么会有两种不同存储方式?
因为任何结构都有两个考虑因素,时间与空间。这是一个万能公式。
- 可以直观的看到,邻接矩阵是空间换时间,通过填充整个矩阵,只需要matrix[i,j]就能以O(1)的复杂度实现查找。
- 而邻接表则是时间换空间,只存储必要的信息,节省了空间,但查找复杂度退化为O(N)
加权图
上面介绍的图最基本的结构,是不是很简单?所有的复杂结构都是在简单上一步一步演化的,图也不例外。
那加权图又如何实现呢?回忆我们的套路.算法共一石,空间换时间独占八斗。
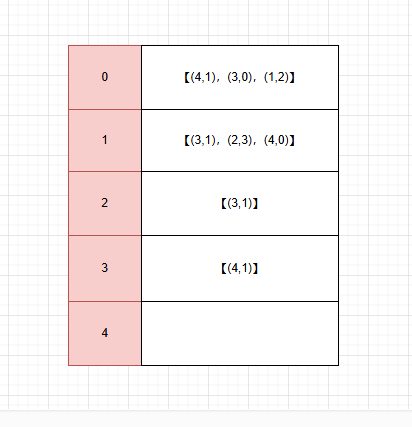
邻接表加权
//List<int[]> grath = new List<int[]>();
// 空间换时间,加一个字段存权重不就好了?
List<Edge[]> grath = new List<Edge[]>();
public struct Edge
{
public int Indegree { get; set; }
public int Weight { get; set; }
}
矩阵表加权
//bool[,] matrix = new bool[5,5];
//由bool二维数组切换成int二维数组
//=0 代表没有边,!=0 代表有边且与权重
int[,] matrix = new int[5,5];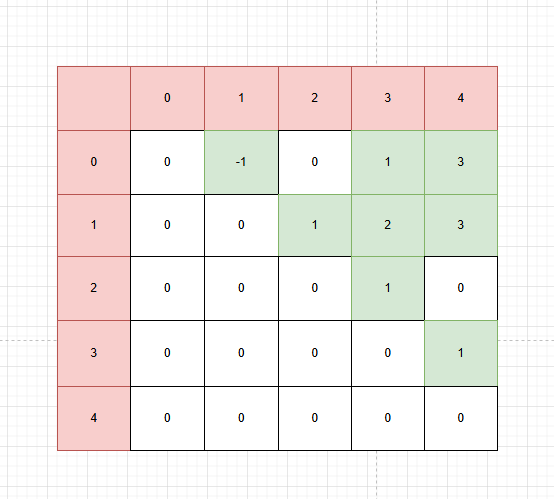
无向图
上面我们介绍的,都是有向无权图与有向加权图。那什么是无向图呢?
很简单,无向图=双向图
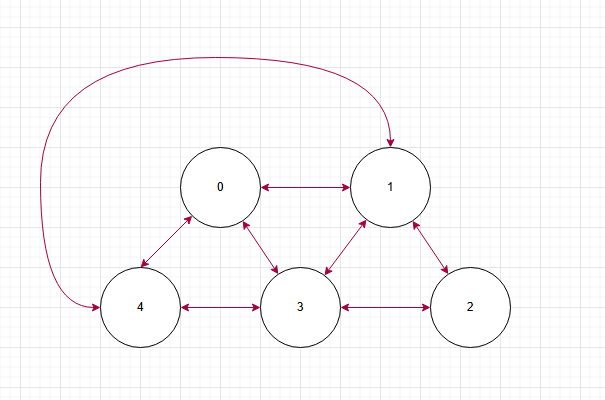
所以你无脑数,有几条边就有几个节点,不再区分indegree,outdegree
一个简单的图
public interface IGraphSimple
{
/// <summary>
/// 添加一条边
/// </summary>
/// <param name="from"></param>
/// <param name="to"></param>
/// <param name="weight"></param>
void AddEdge(int from, int to, int weight);
/// <summary>
/// 删除一条边
/// </summary>
/// <param name="from"></param>
/// <param name="to"></param>
void RemoveEdge(int from, int to);
/// <summary>
/// 判断两个节点是否相等
/// </summary>
/// <param name="from"></param>
/// <param name="to"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
bool IsEdge(int from, int to);
/// <summary>
/// 返回一条边的权重
/// </summary>
/// <param name="from"></param>
/// <param name="to"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
int? Weight(int from, int to);
List<Edge> Neighbors(int v);
}
public struct Edge
{
/// <summary>
/// 相邻的节点
/// </summary>
public int Indegree { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 权重
/// </summary>
public int Weight { get; set; }
}
/// <summary>
/// 邻接表实现图
/// </summary>
public class AdjacencySimple : IGraphSimple
{
public static void Run()
{
var s = new AdjacencySimple(10);
s.AddEdge(0, 1, 0);
s.AddEdge(0, 2, 0);
s.AddEdge(2, 5, 0);
s.AddEdge(2, 6, 0);
s.AddEdge(1, 3, 0);
s.AddEdge(1, 4, 0);
s.AddEdge(3, 6, 0);
s.AddEdge(3, 0, 0);
s.AddEdge(6, 0, 0);
s.DFSTraverse(0);
}
private List<List<Edge>> _graph;
private bool[] _visited;
private LinkedList<int> _path=new LinkedList<int>();
public AdjacencySimple(int capacity)
{
//init
_graph = new List<List<Edge>>(capacity);
_visited=new bool[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++)
{
_graph.Add(new List<Edge>());
}
}
public void Add(int from, int to, int weight)
{
//如果是无向加权表,就调用此方法
AddEdge(from, to, weight);
//多维护一遍关系
AddEdge(from,to, weight);
}
public void AddEdge(int from, int to, int weight)
{
var neighbor = new Edge()
{
Indegree = to,
Weight = weight
};
_graph[from].Add(neighbor);
}
public bool IsEdge(int from, int to)
{
foreach (var edge in _graph[from])
{
if (edge.Indegree.Equals(to))
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public List<Edge> Neighbors(int from)
{
return _graph[from];
}
public void Remove(int from, int to)
{
//如果是无向加权表,就调用此方法
RemoveEdge(from, to);
//多维护一遍关系
RemoveEdge(to, from);
}
public void RemoveEdge(int from, int to)
{
var neighbors = _graph[from];
foreach (var edge in neighbors)
{
if (edge.Indegree.Equals(to))
{
neighbors.Remove(edge);
break;
}
}
}
public int? Weight(int from, int to)
{
var neighbors = _graph[from];
foreach (var edge in neighbors)
{
if (edge.Indegree.Equals(to))
{
return edge.Weight;
}
}
return null;
}
public void DFSTraverse(int startIndex)
{
if (startIndex < 0 || startIndex >= _graph.Count)
return;
if (_visited[startIndex])
return;
_visited[startIndex] = true;
//前序遍历
Console.WriteLine($"index={startIndex}");
if (_graph[startIndex]?.Count > 0)
{
foreach (var item in _graph[startIndex])
{
DFSTraverse(item.Indegree);
}
}
//后序遍历
//Console.WriteLine($"index={index}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 邻接矩阵实现图
/// </summary>
public class MatrixSimple : IGraphSimple
{
private int[,] _matrix;
private bool[] _visited;
public static void Run()
{
var s = new MatrixSimple(10);
s.AddEdge(0, 1, 1);
s.AddEdge(0, 2, 2);
s.AddEdge(2, 5, 3);
s.AddEdge(2, 6, 4);
s.AddEdge(1, 3, 5);
s.AddEdge(1, 4, 6);
s.AddEdge(3, 6, 7);
s.AddEdge(3, 0, 8);
s.AddEdge(6, 0, 9);
s.DFSTraverse(0);
}
public MatrixSimple(int capacity)
{
_matrix = new int[capacity, capacity];
_visited = new bool[capacity];
}
public void Add(int from, int to, int weight)
{
//如果是无向加权表,就调用此方法
AddEdge(from, to, weight);
//多维护一遍关系
AddEdge(to, from, weight);
}
public void AddEdge(int from, int to, int weight)
{
_matrix[from, to] = weight;
}
public bool IsEdge(int from, int to)
{
return _matrix[from, to] != 0;
}
public List<Edge> Neighbors(int from)
{
var result=new List<Edge>();
var columns = _matrix.GetLength(from);
for (int i = 0; i < columns; i++)
{
if (_matrix[columns, i] > 0)
{
result.Add(new Edge { Indegree = i, Weight = _matrix[columns, i] });
}
}
return result;
}
public void Remove(int from, int to)
{
//如果是无向加权表,就调用此方法
RemoveEdge(from, to);
//多维护一遍关系
RemoveEdge(to, from);
}
public void RemoveEdge(int from, int to)
{
//0代表未使用
_matrix[from, to] = 0;
}
public int? Weight(int from, int to)
{
return _matrix[from, to];
}
public void DFSTraverse(int startIndex)
{
if (_visited[startIndex])
return;
_visited[startIndex] = true;
//前序遍历
Console.WriteLine($"index={startIndex}");
for (int i = 0; i < _visited.Length; i++)
{
//为0代表未使用
if (_matrix[startIndex, i] == 0)
continue;
DFSTraverse(i);
}
//后序遍历
//Console.WriteLine($"index={index}");
}
}