1. git 的安装 与 卸载
1.1. git 的安装
判断是否安装 git
git --version
安装 git:
centos: sudo yum -y install git
ubuntu: sudo apt-get install git -y
windows: 3.安装git和图形化界面工具_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
1.2. git 的卸载
判断是否安装 git
git --version
卸载 git:
ubuntu: sudo apt-get remove git -y
2. 初始化创建本地仓库
为什么要创建本地仓库?
要提前说的是,仓库是进行版本控制的一个文件目录。我们要想对文件进行版本控制,就必须先创建一个仓库出来。
创建本地仓库 : git init
当前目录下多了一个.git的隐藏文件,.git目录是 git 来跟踪管理仓库的, 不要手动修改这个目录里面的文件,不然改乱了,就把gi仓库给破坏了。
3. 配置本地仓库
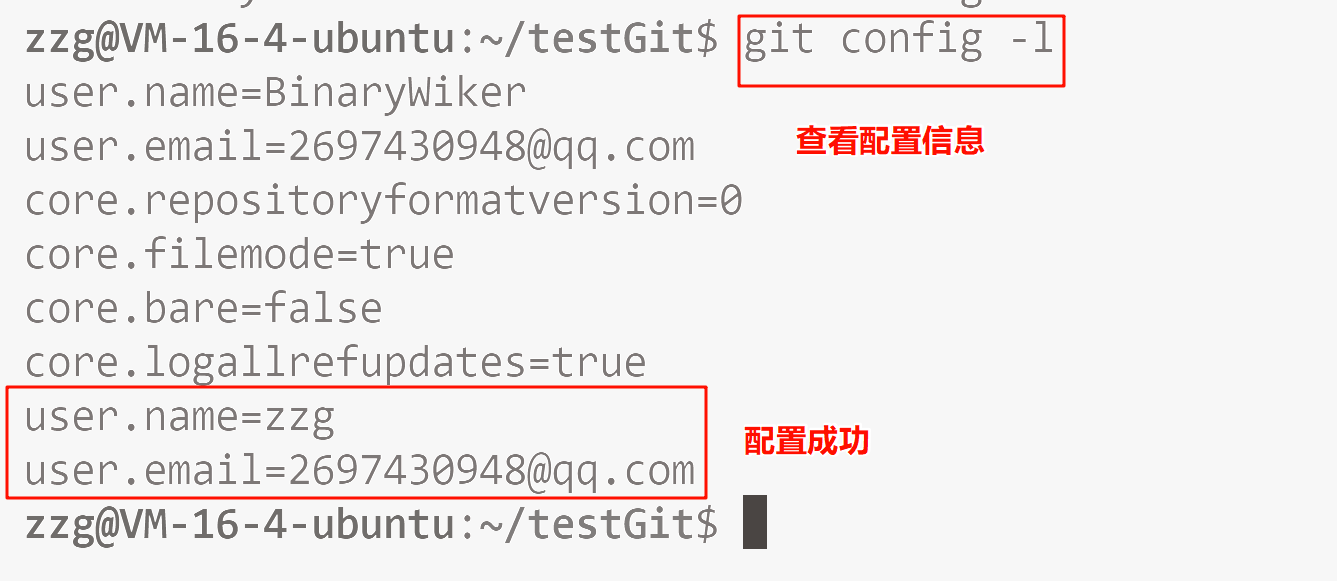
先说配置指令:
git config [--global] user.name "Your Name"
git config [--global] user.email "email@example.com"
git config [--global] --unset user.name
git config [--global] --unset user.email
// 如果你想全局配置就加 [--global] 选项.
// 如果你想取消 [--global] 配置的选项, 同样也需要带 [--global] 选项. 下面进行演示:

4. 认识工作区, 暂存区, 版本库
工作区 :是在电脑上你要写代码或文件的目录。
暂存区 :英文叫stage或index.一般存放在。 在。git目录下的index文件 (.git/index)中,我们把暂存区有时也叫作索引l(index)
版本库 :又名仓库,英文名repository.工作区有一个隐藏目录。git,它不算工作区,而是gi的版本库。这个版本库里面的所有文件都可以被gt管理起来,每个文件的修改,删除,git都能跟踪,以便任何时刻都可以追踪历史,或者在将来某个时刻可以"还原".
下面这个图展示了工作区,暂存区和版本库之间的关系:
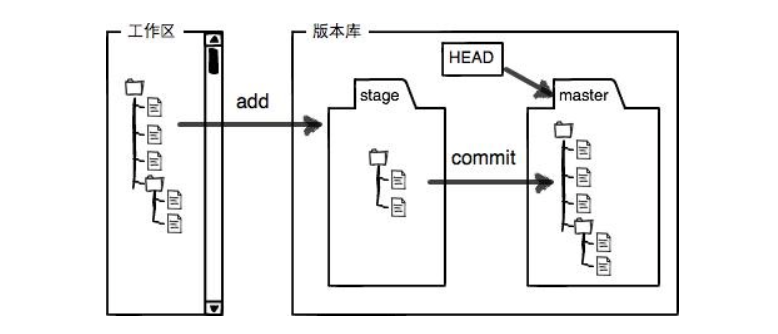
图中左侧为工作区,右侧为版本库。g的版本库里存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是暂存区。
在创建git版本库时,git会为我们自动创建一个唯一的master分支,以及指向master的一个指针叫head.(分支和head的概念后面再说)
当对工作区修改(或新增)的文件执行git add命令时,暂存区目录树的文件索引会被更新。
当执行提交操作git commit时,master分支会做相应的更新,可以简单理解为暂存区的目录树才会被真正写到版本库中。
对象库: 除了上面所说的.git 中存在的暂存区和版本库之外, 实际上 git 仓库真正存储文件的地方在对于对象库, 里面存放的是一个个对象, 每个对象里面的内容是你每次 add/commit 提交的所有文件的修改情况. 而对于暂存区和版本库实际上都是存储的是对象中文件索引的索引而已!
从上面我们可以总结出两点:
- 工作区的文件并不为 git 所直接管理, git 是通过 add 和 commit 的方式把工作区修改的文件以对象的形式保存到 git 当中然后结合索引的方式进行管理的!
- git 仓库中, 真正存储文件内容的是在对象库, 暂存库和 master 库存放的只是索引而已!
5. 场景一: 添加文件
git add filename + git commit
我们先touch一个文件, 然后给里面加两行代码.
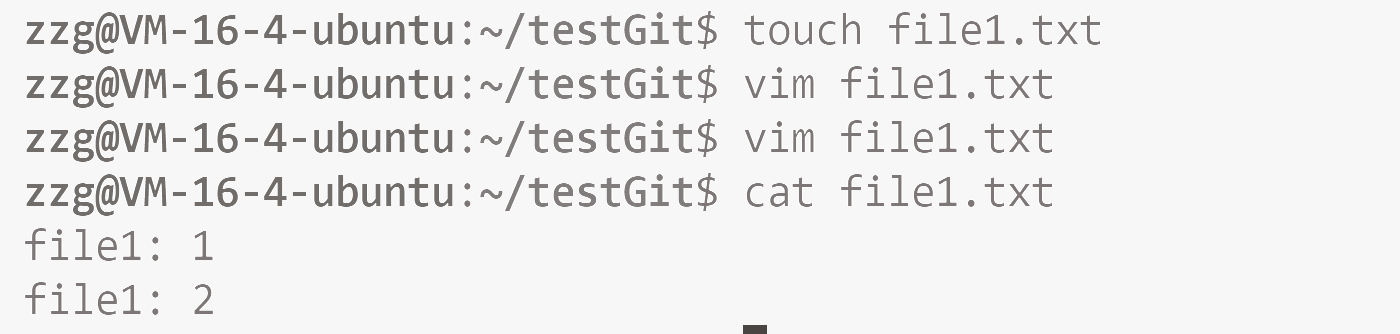
然后, 我们给他add一下, 然后commit一下.

我们可以再来写三个文件, 然后 add , commit 一下.
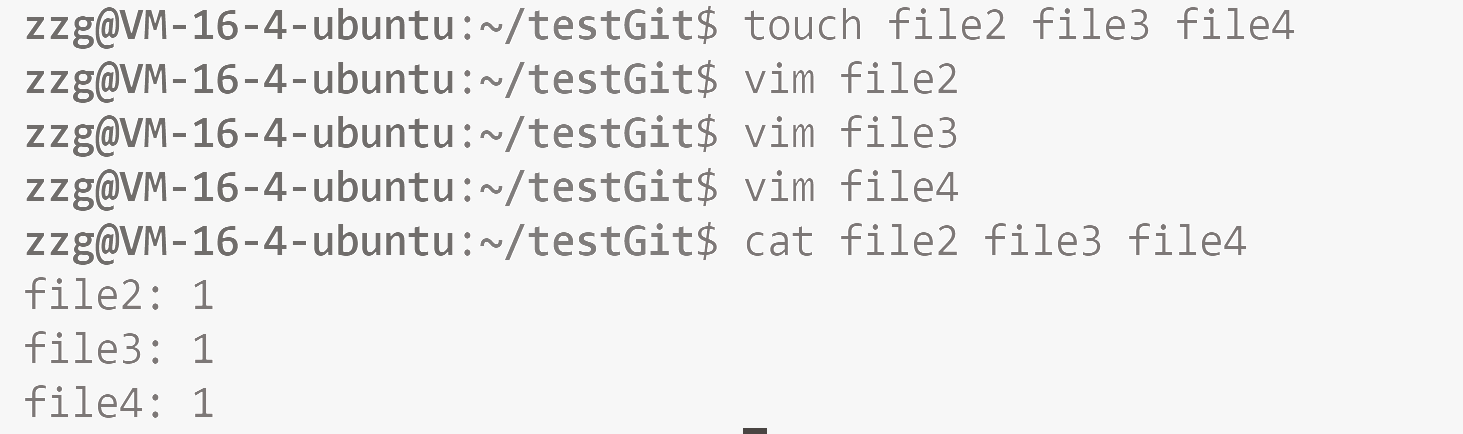
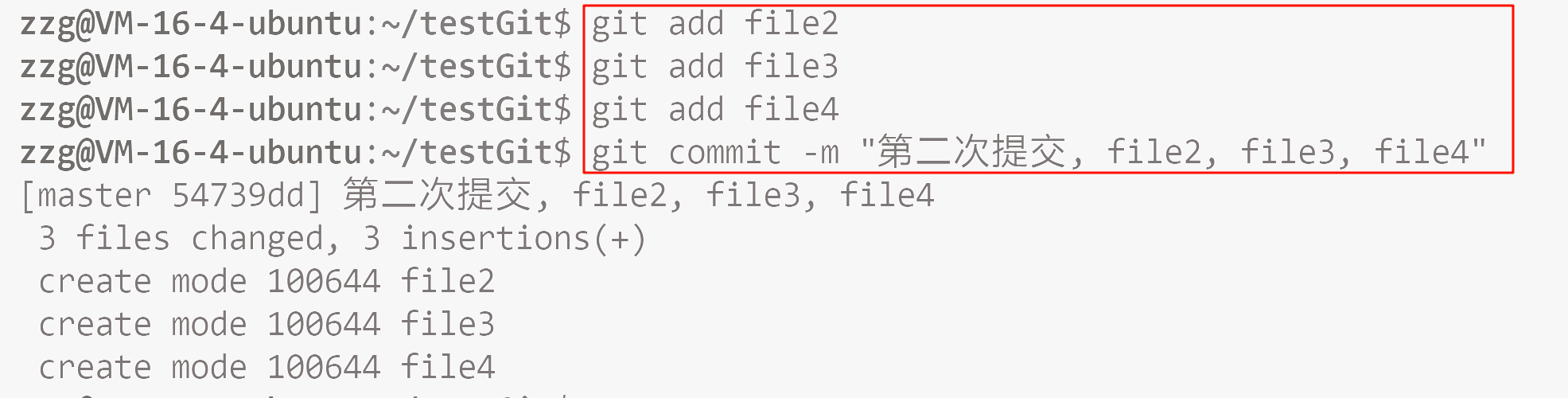
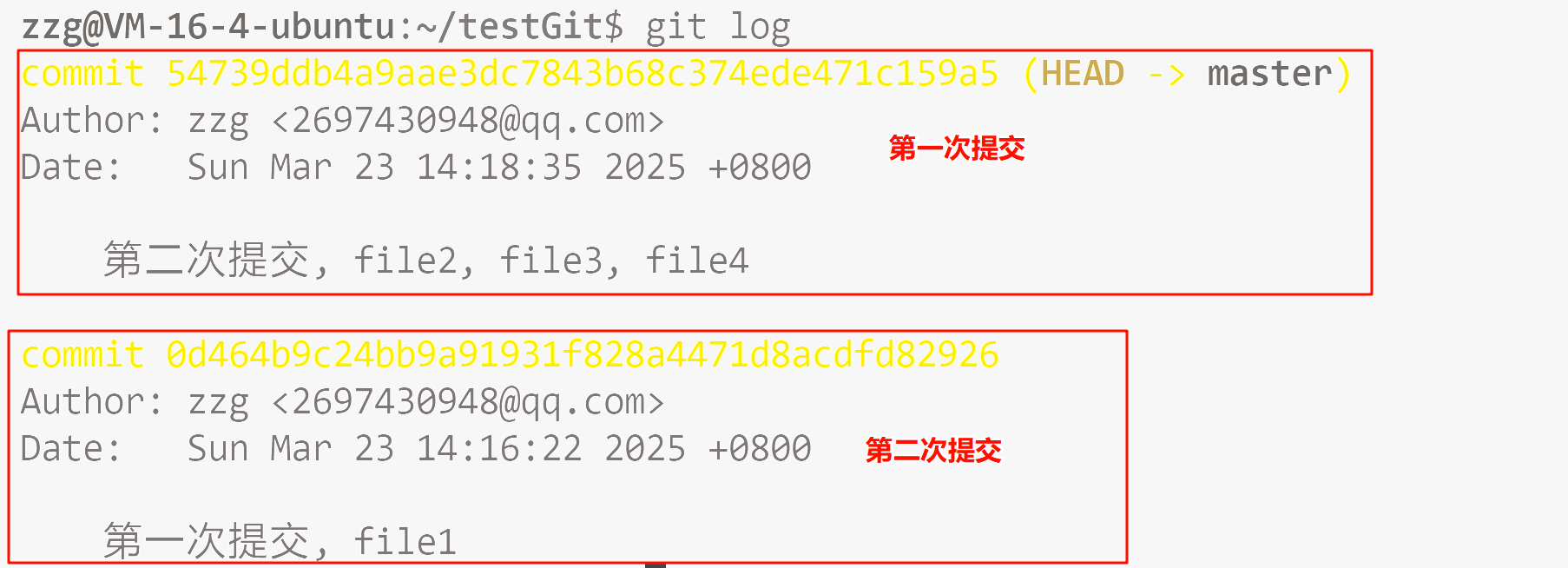
git log 打印日志(从近到远, 以每次 commit 为单位进行打印).

6. 查看第一次 commit 后, .git 的变化
-
新增了 index

-
查看 head 指针, 该指针指向 rets/heads/master.

我们再查看一下rets/heads/master是个什么东西:

这个实际上是在我们.git仓库下的一个对象:

-
查看 git 对象仓库里面的内容, 不能用 git

我们可以用 git cat-file filename 来进行查看:

-
这个 tree 是啥呢? 是一个 commit 时候我们暂存区的目录结构. 打印一下看看:

打印出来了 4 行提示, 有 file1, 有 file2, file3, 和 file4.
我们来查看一下file1和file2中的内容:

-
所以 git 仓库是通过对象来记录修改记录的!
tree 存放的内容.
你的理解基本正确。在 Git 中,commit 提交时,会将 暂存区(索引区)的内容 生成一个 tree 对象,这个 tree 记录了本次提交对应的 目录结构、文件列表、文件权限 等信息。
具体来说:
- 暂存区的作用 :用户通过
git add将文件添加到暂存区,暂存区保存了即将提交的内容。 - tree 的生成 :执行
git commit时,Git 会基于暂存区的内容生成tree对象,它像一个"目录快照",记录提交时刻的文件组织形式(包括文件、子目录及其对应哈希值)。
因此,tree 确实是 commit 时暂存区内容所对应的目录结构记录,它是 Git 实现版本管理的核心数据结构之一。
7. git 修改文件
首先先说一个修改的定义: 修改包括新增, 删除, 修改文件内容
之后, 我们的 git 是管理文件修改的, 而非文件本身
下面进行操作演示:
让我们将 file1.txt 文件进行一次修改:
此时,仓库中的readme和我们工作区的readme是不同的,如何查看当前仓库的状态呢?git 状态呢?git
status****命令用于查看在你上次提交之后是否有对文件进行再次修改。 
我们发现, 上面提示我们在暂存区没有修改, 但是在工作区有个修改是 ReadMe 文件. 那修改了啥内容呢? 我们不清楚, 因此需要查询一下:
**git diff[file]**命令用来显示暂存区和工作区文件的差异,显示的格式正是unix通用的diff 格式。也可以使用 **git diff HEAD -- [file]**命令来查看版本库(这里的版本库指的是暂存区)和工作区文件的区别。

之后, 我们再把这次修改提交到版本库(暂存区)中.

git add之后,就没有看到上面no changes added to commit (use "gita dd" and/or "git commit -a" )的消息了。不过他提示我们暂存区和 master 中有区别, 接下来让我们继续git commit即可:

小结:
git status**-> 用来查看工作区 与 暂存区, 暂存区 与 master 分支哪些文件发生了修改**
git diff**-> 命令用来显示暂存区和工作区文件的内容差异**
8. 版本回退
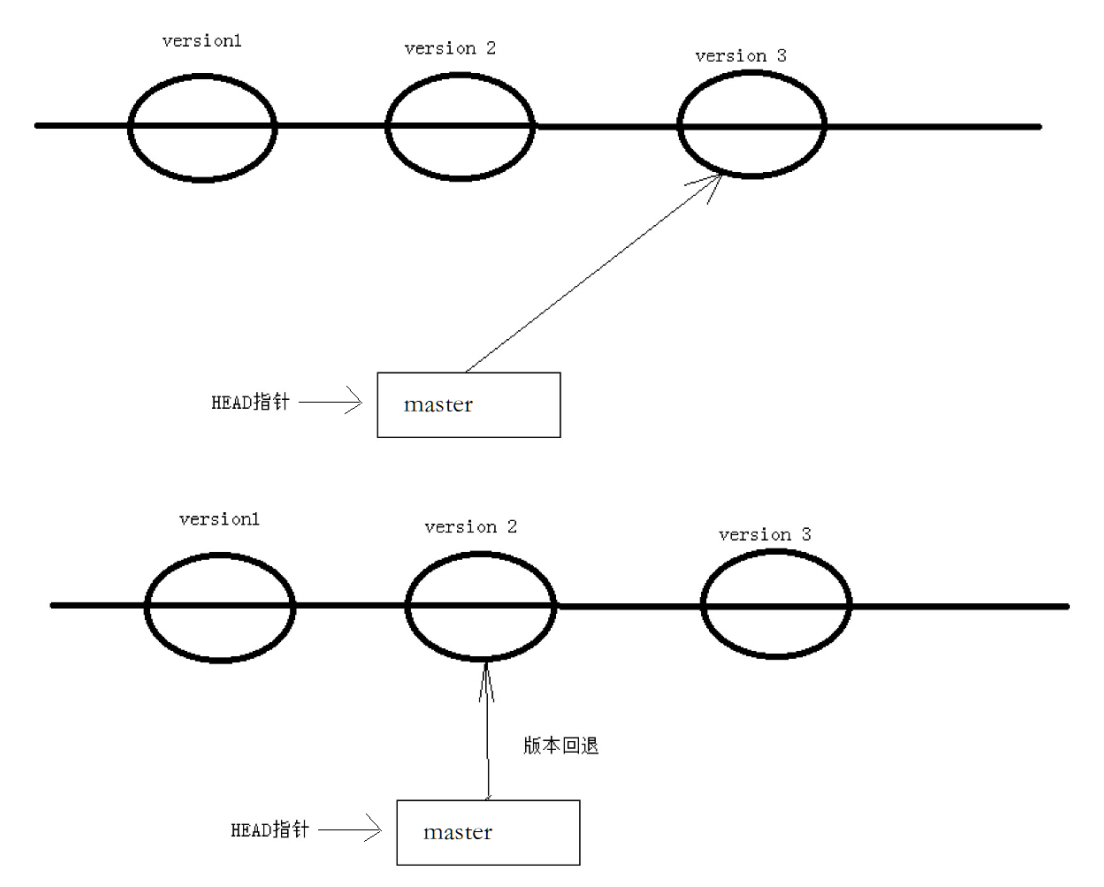
之前我们也提到过,gt能够管理文件的历史版本,这也是版本控制器重要的能力。如果有一天你发现之前前的工作做的出现了很大的问题,需要在某个特定的历史版本重新开始,这个时候,就需要版本回退的功能了。
执行gitreset命令用于回退版本,可以指定退回某一次提交的版本。要解释一下"回退"本质是要将版本库中的内容进行回退,工作区或暂存区是否回退由命令参数决定。
git reset****命令语法格式为: git reset [--soft | --mixed | --hard] [HEAD]
- --mixed
-
- 为默认选项,使用时可以不用带该参数。该参数将暂存区的内容退回到指定提交版本内容,工作区文件保持不变。
- --soft
-
- 参数对于工作区和暂存区的内容都不变,只是将版本库回退到某个指定版本。
- --hard
-
- 参数将暂存区与工作区都退回到指定版本。 切记工作区有未提交的代码时不要用这个命令,因为工作区会回滚,你没有提交的代码就再也找不回来了,所以使用该参数前一定要慎重 。
- HEAD****说明:
-
- 可直接写成 commit id**,表示指定退回的版本**
- HEAD****表示当前版本
- **HEAD^**上一个版本
- **HEAD^^**上上一个版本
- 以此类推...
- 可以使用 ~数字****表示:
-
-
- HEAD~0****表示当前版本
- HEAD~1****上一个版本
- HEAD^2****上上一个版本
- 以此类推...
-
操作演示详解
为了方便测试回退功能, 我们下面先提交三个版本, 然后进行回退操作:
- 第一次修改提交
-
-
查看ReadMe文件内容:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
-
-
-
添加ReadMe文件到暂存区:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git add ReadMe
-
-
-
提交修改:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git commit -m"add version1"
[master cff9d1e] add version1
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
-
- 第二次修改提交
-
-
再次查看ReadMe文件内容:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
-
-
-
添加ReadMe文件到暂存区:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git add ReadMe
-
-
-
提交修改:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git commit -m"add version2"
[master d95c13f] add version2
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
-
- 第三次修改提交
-
-
再次查看ReadMe文件内容:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
-
-
-
添加ReadMe文件到暂存区:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git add ReadMe
-
-
-
提交修改:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git commit -m"add version3"
[master d95c13f] add version3
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
-
- 查看历史提交记录
-
-
使用 git log****查看提交记录:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git log --pretty=oneline # 打印日志
d95c13ffc87a855a25a3d04e22abfc7d2e31383 (HEAD -> master) add version3
14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd add version2
cff9d1e01933318156f8c7d356a78c9e949ae6b7 add version1
-
现在,如果我们在提交完version3后,发现version3编写错误,想回退到version2,重新基于version2开始编写。由于我们在这里希望的是将工作区的内容也回退到version 2版本,所以需要用到--hard参数,示例如下:
- 执行
git reset命令
-
-
使用
--hard参数将工作区回退到version2版本:hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git reset --hard 14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd
-
-
-
此时
HEAD指向add version2:HEAD is now at 14c12c3 add version2
-
- 查看
ReadMe文件内容
-
-
查看
ReadMe文件,发现内容已经回退到version2:hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
-
- 查看提交日志
-
-
使用
git log查看提交日志,发现HEAD指向version2:hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git log --pretty=oneline
14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd (HEAD -> master) add version2
cff9d1e01933318156f8c7d356a78c9e949ae6b7 add version1
-
文中还提到,惊奇地发现ReadMe文件的内容已经回退到version2,并且HEAD也指向了version2。
不过, 我突然又想回去了, 那有机会回去吗? 如果你执行的 git 操作比较少的话, 是有机会回去的, 但是如果在此基础上你又执行了大量的 git 操作, 就很难回到之前的版本了. 因为我们上面完全没有执行任何操作, 所以可以回去的, 如何回去看下面演示即可.
以下是提取的代码和文字:
到这里一般回退功能就演示完了,但现在如果我后悔了,想再回到version3怎么办?我们可以继续使用git reset命令,回退到version 3版本,但我们必须要拿到version 3的commit id去指定回退的版本。
但我们看到了git log并不能打印出version 3的commit id,运气好的话我们可以从终端上去找找之前的记录,运气不好的话commit id已经被我们搞丢了=。=
Git还提供了一个git reflog命令能补救一下,该命令用来记录本地的每一次操作。
代码部分:
-
使用
git reflog查看操作记录:hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git reflog
14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to 14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd
d95c13ffc87a855a25a3d04e22abfc7d2e31383 HEAD@{1}: commit: add version3
14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{2}: commit: add version2
cff9d1e01933318156f8c7d356a78c9e949ae6b7 HEAD@{3}: commit: add version1
94da6950d27e26230368b22f1ffc4bbf761b5b00 HEAD@{4}: commit: add Modify ReadMe file
23807c5693698cd868c4fb264997ca575756eed HEAD@{5}: commit: add 3 files
c61428926f38534d4ec6dde9044150be6c1abc6c HEAD@{6}: commit (initial): commit my first file -
回退到
version3:回退到v3
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git reset --hard d95c13f
HEAD is now at d95c13f add version3 -
查看工作区:
查看工作区
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3 -
查看
log:查看log
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git log --pretty=oneline
d95c13ffc87a855a25a3d04e22abfc7d2e31383 (HEAD -> master) add version3
14c12c32464d6ead7159f5c24e786ce450c89ddd add version2
cff9d1e01933318156f8c7d356a78c9e949ae6b7 add version1
git 为什么版本更换非常快? 几乎不需要时间? 这与他的设计结构有关, 因为 git 是记录的是修改本身, 而非文件本身:
9. 撤销修改
9.1. 情况一:没有add,也没有commit
命令: git checkout -- [file]
情景举例
# 向ReadMe中新增一行代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Nothing to commit, working tree clean
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ vim ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
This piece of code is like shit #新增代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: ReadMe
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
# 直接删除代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ vim ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean幸亏我们工作效率不高,才写了一行代码就发现不行了,要是你写了3天,一直都没有提交,该怎么删掉呢?你自己都忘了自己新增过哪些,有同学说,我可以git diff xxx一下,看看差别在哪啊,那你肯定又要花3天时间删代码了,并且很大的概率还会改错。一周过去了,你怎么向你的老板交代呢?
Git其实还为我们提供了更好的方式,我们可以使用git checkout -- [file]命令让工作区的文件回到最近一次add或commit时的状态。要注意git checkout -- [file]命令中的--很重要,切记不要省略,一旦省略,该命令就变为其他意思了,后面我们再说。示例如下:
# 向ReadMe中新增一行代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ vim ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
This piece of code is like shit #新增代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: ReadMe
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
# 恢复到上一次add或commit
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git checkout -- ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version39.2. 情况二:已经add,但没有commit
add 之后保存到了暂存区, 如何撤销呢?
我们下面来举个例子:
# 向ReadMe中新增一行代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ vim ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
This piece of code is like shit #新增代码
# add 存入暂存区
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git add ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: ReadMe让我们来回忆一下学过的`git reset`回退命令,该命令如果使用`--mixed`参数,可以将暂存区的内容退回到指定的版本内容,但工作区文件保持不变。那我们就可以回退下暂存区的内容了!!!
以下是提取的代码和文字:
# --mixed是默认参数,使用时可以省略
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git reset HEAD ReadMe
Unstaged changes after reset:
M ReadMe
# 用 git status 查看一下,发现现在暂存区是干净的,工作区有修改。
# 查看状态
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: ReadMe
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")还记得如何丢弃工作区的代码吗?
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git checkout -- ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version39.3. 已经 add 并且也已经 commit 了
不要担心,我们可以`git reset --hard HEAD^`回退到上一个版本!不过,这是有条件的,就是你还没有把自己的本地版本库推送到远程。还记得Git是分布式版本控制系统吗?我们后面会讲到远程版本库,一旦你推送到远程版本库,你就真的惨了......
# 向ReadMe中新增一行代码
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ vim ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version3
This piece of code is like shit #新增代码
# 提交
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git add ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git commit -m"test quash"
[master 5f71ae1] test quash
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
# 回退
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git reset --hard HEAD^
HEAD is now at 144a3f8 add file
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ cat ReadMe
hello bit
hello git
hello world
hello version1
hello version2
hello version310. 删除文件

git 中,删除也是一个修改操作,我们实战一下,如果要删除file5文件,怎么搞呢?如果你这样做故了:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ ls
file1 file2 file3 file4 file5 ReadMe
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ rm file5但这样直接删除是没有用的,反而徒增烦恼,git status命令会立刻告诉你哪些文件被删除了:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: file5
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")此时,工作区和版本库就不一致了,要删文件,目前除了要删工作区的文件,还要清除版本库的文件。
一般走到这里,有两种可能:
- 确实要从版本库中删除该文件
- 不小心删错了
对第二种情况,很明显误删,需要使用git来进行恢复,很简单,我们刚学过(删除也是修改):
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git checkout -- file5
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ ls
file1 file2 file3 file4 file5 ReadMe对于第一种情况,很明显是没有删完,我们只删除了工作区的文件。这时就需要使用git rm将文件从暂存区和工作区中删除,并且commit:
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git rm file5
rm 'file5'
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
deleted: file5
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git commit -m"deleted file5"
[master 5476bde] deleted file5
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 file5
hyb@139-159-150-152:~/gitcode$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean现在,文件就从版本库中被删除了。