【iOS】 消息流程探索
文章目录
cache的结构
在这之前在类与对象中讲述了一个cache类型,这个类其实就是用来查找方法的.首先我们要认识cache这种存储的到底是什么东西:
objc
struct cache_t {
private:
explicit_atomic<uintptr_t> _bucketsAndMaybeMask;
union {
struct {
explicit_atomic<mask_t> _maybeMask;
#if __LP64__
uint16_t _flags;
#endif
uint16_t _occupied;
};
explicit_atomic<preopt_cache_t *> _originalPreoptCache;
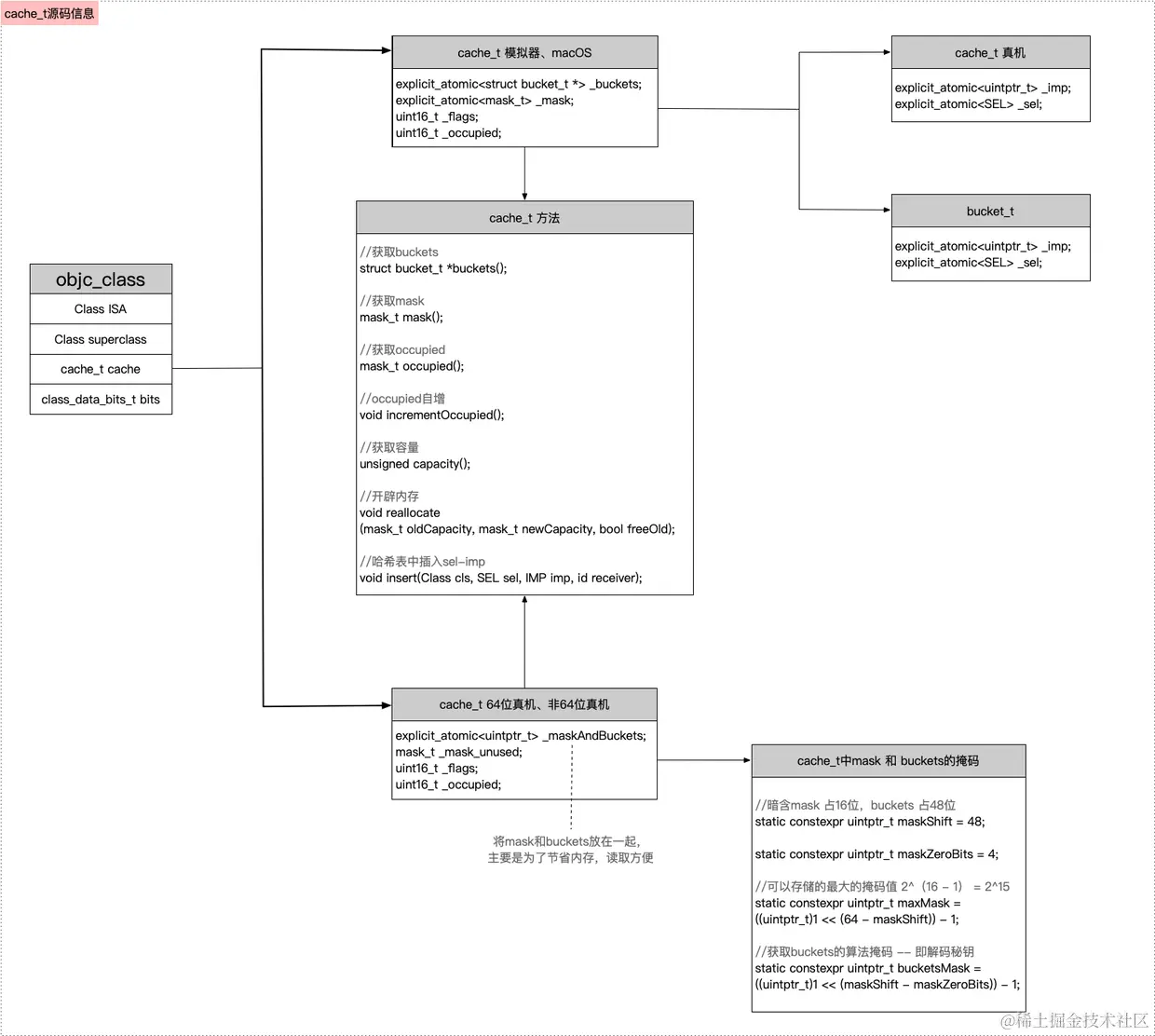
};查看cache_t的源码,发现分成了3个架构的处理,其中真机的架构中,mask和bucket是写在一起,目的是为了优化,可以通过各自的掩码来获取相应的数据.
CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_OUTLINED表示运行的环境模拟器或者macOSCACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16表示运行环境是64位的真机CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4表示运行环境是非64位 的真机

下面这里的这张图片展示cache_t的内容
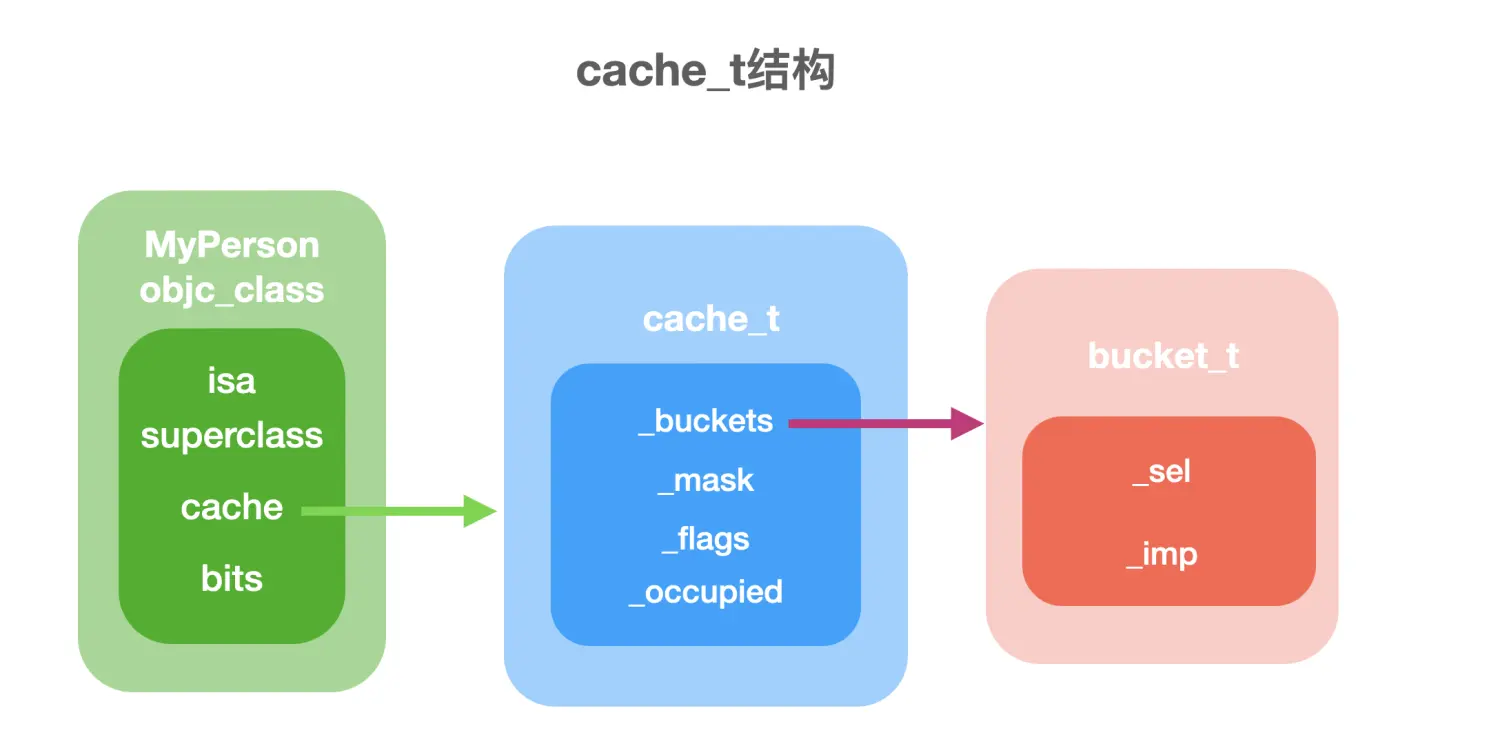
这里我们再看一下这个bucket这个结构体,不同的区别在于sel和imp的顺序不同
objc
struct bucket_t {
private:
// IMP-first is better for arm64e ptrauth and no worse for arm64.
// SEL-first is better for armv7* and i386 and x86_64.
#if __arm64__ //不同的架构有不同的结果arm64 真机
explicit_atomic<uintptr_t> _imp;
explicit_atomic<SEL> _sel;
#else //非真机
explicit_atomic<SEL> _sel;
explicit_atomic<uintptr_t> _imp;
#endifcache中缓存的是sel-imp
cache中插入一个新缓存的方法
这里看一下这里的insert方法
objc
void cache_t::insert(SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
// Never cache before +initialize is done
if (slowpath(!cls()->isInitialized())) {
return;
}
if (isConstantOptimizedCache()) {
_objc_fatal("cache_t::insert() called with a preoptimized cache for %s",
cls()->nameForLogging());
}
#if DEBUG_TASK_THREADS
return _collecting_in_critical();
#else
#if CONFIG_USE_CACHE_LOCK
mutex_locker_t lock(cacheUpdateLock);
#endif
ASSERT(sel != 0 && cls()->isInitialized());
// Use the cache as-is if until we exceed our expected fill ratio.
mask_t newOccupied = occupied() + 1; // 第一次insert的时候occupied()即_occupied会是0,newOccupied会是1
// capacity的值就是buckets的长度
unsigned oldCapacity = capacity(), capacity = oldCapacity;
// 如果cache为空,则分配 arm64下长度为2 x86_64下长度为4的buckets,reallocate里无需释放老buckets
if (slowpath(isConstantEmptyCache())) {
// Cache is read-only. Replace it.
// 给容量附上初始值,x86_64为4,arm64为2
if (!capacity) capacity = INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, /* freeOld */false);
}
// 在arm64下,缓存的大小 <= buckets长度的7/8 不扩容
// 在x86_64下,缓存的大小 <= buckets长度的3/4 不扩容
else if (fastpath(newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= cache_fill_ratio(capacity))) {
// Cache is less than 3/4 or 7/8 full. Use it as-is.
}
#if CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION // 只有arm64才需要走这个判断
// 在arm64下,buckets的长度 < = 8 时,不扩容
else if (capacity <= FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE && newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= capacity) {
// Allow 100% cache utilization for small buckets. Use it as-is.
}
#endif
else { // 除却上面的逻辑,就是扩容逻辑了
// 对当前容量的2倍扩容,并且如果扩容后容量大小 大于 一个最大阈值,则设置为这个最大值
capacity = capacity ? capacity * 2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if (capacity > MAX_CACHE_SIZE) {
capacity = MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
}
// 创建新的扩容后的buckets,释放旧的bukets
reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, true);
}
bucket_t *b = buckets(); // 获取buckets数组指针
mask_t m = capacity - 1; // m是buckets的长度-1
mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m);// 通过hash计算出要插入的方法在buckets上的起始位置(begin不会超过buckets的长度-1)
mask_t i = begin;
// Scan for the first unused slot and insert there.
// There is guaranteed to be an empty slot.
do {
if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) { // 当前hash计算出来的buckets在i的位置它有没有值,如果没有值就去存方法
incrementOccupied();
b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(b, sel, imp, cls());
return;
}
if (b[i].sel() == sel) { // 当前hash计算出来的buckets在i的位置sel有值,并且这个值等于要存储的sel,说明该方法已有缓存
// The entry was added to the cache by some other thread
// before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock.
return;
}
} while (fastpath((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin)); // 如果计算出来的起始位置i存在hash冲突的话,就通过cache_next去改变i的值(增大i)
bad_cache(receiver, (SEL)sel);
#endif // !DEBUG_TASK_THREADS
}这里总结一下他的一个主要逻辑:
- 保证线程安全,保证类已经初始化成功,保证不是预编译的只读cache
- 判读是否需要扩容,先获取自己当前已经缓存了多少个方法
- 第一次插入的时候需要初始化缓存
- 判断是否需要扩容,扩容到对应的方法(超过对应的比值就开始更新大小,保证)
- 找到哈希插入的一个位置
- 插入方法,如果在之前已经插入过就不用继续插入了,如果冲突了就处理冲突逻辑问题
- 如果插入失败就进入异常处理
这里注意如果超出了最大的缓存大小,就把新的缓存全部替换原先的一个旧缓存,也就是旧方法中的所有的缓存全被清除了
处理扩容
首先获取到buckets数组指针,得到buckets最大的下标 m,并且通过cache_hash函数计算出要缓存的方法在buckets中的起始位置;(可以把buckets看做是hash表)
让后通过一个hash函数来处理它的一个下标值:
objc
static inline mask_t cache_hash(SEL sel, mask_t mask)
{
uintptr_t value = (uintptr_t)sel;// 把SEL转化成unsigned long类型,一个很大的数字
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
value ^= value >> 7;
#endif
// value是一串很大的数,去&上 buckets长度-1
// 一个很大的数 & 一个小的数 得到的结果最大值是 这个小的数
return (mask_t)(value & mask);
}cache_hash保证起始位置一定在buckets最大下标里。
这里可能会出现一个哈希冲突:
然后进入一个处理哈希冲突的函数,来处理这里的一个起始位置:
objc
#if CACHE_END_MARKER
static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) {
return (i+1) & mask;
}
#elif __arm64__
static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) {
return i ? i-1 : mask;
}
#else
#error unexpected configuration
#endif然后判断他的一个位置有没有值去储存方法,然后判断计算出来的其实位置有没有相同的一个sel则说明由缓存
为什么缓存的方法不是连续的,因为这里的buckets的起始位置是hash算出来的,所以不一定是连续的
处理扩容
a.首先如果缓存为空的话,就给
buckets分配初始化的长度(x86_64为4,arm为2)并且创建一个buckets;b.在arm64框架下,缓存的大小 <= buckets长度的7/8,并且buckets长度<=8没装满8,不扩容,在x86_64下,缓存的大小 <= buckets长度的3/4 ,不扩容。
c.除却b的逻辑,就是扩容逻辑:对当前容量的
2倍扩容,并且如果扩容后容量大小 >MAX_CACHE_SIZE,则设置为MAX_CACHE_SIZE;计算出扩容大小后,以这个容量去创建新的buckets,和释放旧的buckets。
这里注意一个点扩容后会先创建新的buckets,然后释放旧的buckets,那么以前的缓存的方法就全部没有了
认识runtime
runtime称作运行是,它区别于编译时
- 运行时是代码跑起来,被装到内存中的一个过程,如果此时出错,则程序会崩溃,是一个动态阶段
- 编译时是源代码翻译成机器能识别的代码的过程,主要是对语言进一个最基本的检查报错,即词法分析,语法分析等,是一个静态状态
runtime的使用有以下三个方式,这三种实现方式于编译层和底层的关系如图所示:
- 通过OC代码,例如
[person sayNB] - 通过NSObject方法,例如
isKindOfClass - 通过
Runtime API,例如class_getInstanceSize
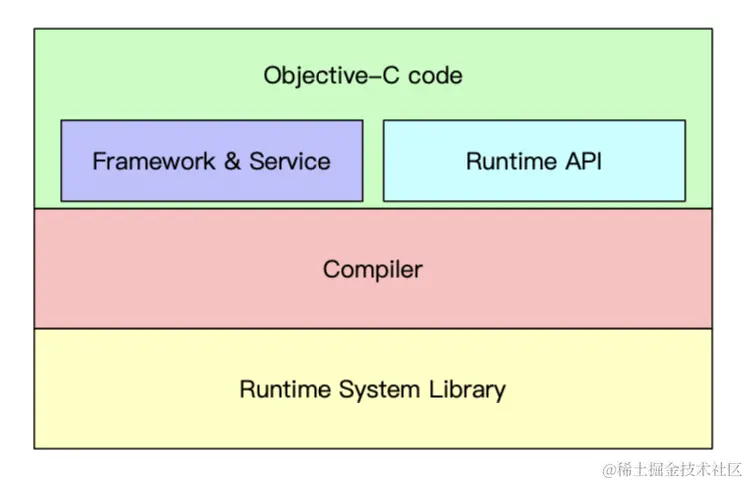
这里的compiler是我们了解的一个编译器,即LLVM,例如OC的alloc对应底层的objc_alloc,runtime system libarary也就是底层库
三个动态特点
动态类型
OC中的对象是动态类型的,这意味着我们呢可以在运行的时候发送信息给对象,对象可以根据接受到的类型执行方法.与静态语言类型不同,静态类型在编译是就必须要确定引用那种对象,而动态类型就更加泛化.
objc
id someObject = [[NSString alloc] initWithString:@"Hello world"];
someObject = [[NSDate alloc] init];动态绑定
动态绑定是指方法调用可以在运行时解析,而不是在编译的时候,这一位之OC对象在运行时决定要执行对象的哪一个方法,而不是在编译的时候.这种机制是通过消息传递实现的,使得你可以在程序运行期间改变对象的调用方法.
动态语言
OC能被称为动态语言的一个核心点就是消息转发机制 ,消息转发机制允许开发者截取并处理未被对象识别的消息。
探索方法的本质
这里我们看一下编译后的方法和编译前的方法:
objc
CJLPerson *person = [CJLPerson alloc];
[person sayHello];
[person sayBye];
[person sayNB];
[person sayMaster];
//clang编译后的底层实现
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayHello"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayBye"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayNB"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)person, sel_registerName("sayMaster"));通过上面的代码我们可以看出,方法的本质是objc_msgSend消息发送
这里我们看一下这个objc_msgSend()的两个参数:(结构体, sel)
SEL
首先apple官方公示的SEL
objc
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;SEL一个不透明的类型,代表方法的选择子.定义如下:
objc
// GNU OC 中的 objc_selector
struct objc_selector {
void *sel_id;
const char *sel_types;
}; SEL其实就是一个选择器,告诉编译器当前我们想要调用哪一个方法?
在运行时,方法选择器用来表示方法的名字。一个方法选择器就是一个C字符串,在OC的运行时被注册。编译器生成选择器在类加载时由运行时自动映射。
可以在运行时添加新的选择器,并使用sel_registerName函数检索现有的选择器。

这里OC会在便宜的时候根据方法名生成唯一一个区分的ID,这个ID是SEL类型的,只要方法名字相同,SEL返回的就相同
在Runtime中维护了一个SEL的表,这个表按NSSet来存储,只要相同的SEL就会被看作是同一个方法并被加载到表中,因此OC中要尽量避免方法重载
IMP
指向方法实现的首地址的指针,从这里可以看出它的一个定义
objc
#if !OBJC_OLD_DISPATCH_PROTOTYPES
typedef void (*IMP)(void /* id, SEL, ... */ );
#else
typedef id _Nullable (*IMP)(id _Nonnull, SEL _Nonnull, ...);
#endifIMP的数据类型是指针,指向方法实现开始的位置
Method
不透明的类型,表示类中定义的方法:
objc
/// An opaque type that represents a method in a class definition.
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method {
SEL _Nonnull method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //表示方法名的字符串
char * _Nullable method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //char* 类型的,表示方法的类型,包含返回值和参数的类型
IMP _Nonnull method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE; //IMP类型,指向方法实现地址的指针
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;这里可以看出Method是一个结构体类型指针.
Method操作函数如下
objc
方法操作主要有以下函数:
BOOL class_addMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types); // 添加方法
Method class_getInstanceMethod(Class cls, SEL name); // 获取实例方法
Method class_getClassMethod(Class cls, SEL name); // 获取类方法
Method *class_copyMethodList(Class cls, unsigned int *outCount); // 获取所有方法的数组
// 替代方法的实现
IMP class_replaceMethod(Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types);
// 交换两个方法的实现
method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2)小结
SEL方法选择器,实际上就是一个字符串的名字,编译器生成选择器在类加载时由运行时自动映射。可以理解为书的一个标题
IMP指向方法实现首地址的指针,理解为书的页码
Method是一个结构体,包含上述两者,同时包含char*表示函数的类型(包含返回值和参数类型),理解为书哪一章节的具体内容
SEL、IMP、Method之间的关系
当向对象发送消息时,调用SEL在对象的类以及父类方法列表中进行查找Method,因为Method结构体中包含IMP指针,因此一旦找到对应的Method就直接调用IMP去实现方法
子类调用父类的方法
定义子类和父类
首先我们先定义两个类,一个类继承自另一个类.
objc
- (void)sayBye {
NSLog(@"%@ say: %s", [self class], __func__);
NSLog(@"%@ say: %s", [super class], __func__);
}
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_rb_0ts7dvhs3zg9fc6kk2nvtlr00000gn_T_CJLPerson_d760c5_mi_2, ((Class (*)(__rw_objc_super *, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSendSuper)((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("CJLPerson"))}, sel_registerName("class")), __func__);这里的打印结果是:

这里我们可能会非常疑惑,为什么这里的super class打印出来的还是我们的CJLTeacher
这里我们将上面的这个代码重新编译成C
这里我们可以看到第二条的super变成了objc_msgSendSuper
苹果官方文档对其方法解释为:
当遇到方法调用时,编译器会生成对以下函数之一的调用:objc_msgSend、objc_msgSend_stret、objc_msgSendSuper或objc_msgSendSuper_stret。发送到对象超类的消息(使用super关键字)使用objc_msgSendSuper发送;其他消息使用objc_msgSend发送。使用objc_msgSendSuper_stret和objc_msgSend_stret发送以数据结构作为返回值的方法。
这里我们可以重新认识一下objc_super数据结构的指针.传递值.标识消息发送到上下问,包括要接受消息的类的实例和要开始搜索方法发的实现
objc
((__rw_objc_super){(id)self, (id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("CJLPerson"))}方法的接受和查找不一定是同一个人,方法的接受者是self,方法的查找是在super中去查找的.
super只是关键字,结构体中的super_class 等于父类,代表从父类对象开始查找;不代表接收者receiver是父类对象;
objc_msgSendSuper的区别在于找方法的初始位置不一样。
objc_msgSend快速查找流程分析CacheLookup
在objc-838中查找有关于objc_msgSend的源码实现,这里注意这里的一个源码实现是通过我们的汇编去实现的:
采用汇编的优点:
- 速度更快,直接使用参数,免去类大量参数拷贝的开销
- 在函数和全局变量前面都会加下划线防止符号冲突
objc
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
cmp p0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check
// 判断是否为空,也就是判断接受者是否存在,其中p0是objc_msgSend的第一个参数-消息接收者receiver
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
//---- le小于 --支持taggedpointer(小对象类型)的流程
b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative)
#else
// p0为空的时候直接返回空,也就是接受者为nil的时候消息不会被做一个处理
b.eq LReturnZero
#endif
//取出isa指针
ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa
//---- 在64位架构下通过 p16 = isa(p13) & ISA_MASK,拿出shiftcls信息,得到class信息,获得isa中的一个类信息
GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13, 1, x0 // p16 = class
LGetIsaDone:
// calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached
//如果有isa.走到cacheLookup方法面也就我们这里的核心部分快速查找流程
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend, __objc_msgSend_uncached
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
LNilOrTagged:
//等于空返回空
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
GetTaggedClass
b LGetIsaDone
// SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
#endif
LReturnZero:
// x0 is already zero
mov x1, #0
movi d0, #0
movi d1, #0
movi d2, #0
movi d3, #0
ret
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend这里主要由一下几个步骤
- 判断
objc_msgSend方法的第一个参数receiver是否为空- 如果支持
tagged pointer就跳转到LNilOrTaggedLNilOrTagged- 如果小对象为空,就直接返回空
- 不为空,则处理小对象的一个isa
- 如果不是小队血,
receiver不为空- 从
recever中间取出isa存入p13寄存器 - 通过
GetClassFromIsa_p16中,arm64架构下通过isa & ISA_MASK获取shiftcls位域的类信息,即class
- 从
- 如果支持
这里获取类信息的汇编代码就不看了,我们直接进入正题:快速查找的函数实现部分:
objc
.macro CacheLookup Mode, Function, MissLabelDynamic, MissLabelConstant
//
// Restart protocol:
//
// As soon as we're past the LLookupStart\Function label we may have
// loaded an invalid cache pointer or mask.
//
// When task_restartable_ranges_synchronize() is called,
// (or when a signal hits us) before we're past LLookupEnd\Function,
// then our PC will be reset to LLookupRecover\Function which forcefully
// jumps to the cache-miss codepath which have the following
// requirements:
//
// GETIMP:
// The cache-miss is just returning NULL (setting x0 to 0)
//
// NORMAL and LOOKUP:
// - x0 contains the receiver
// - x1 contains the selector
// - x16 contains the isa
// - other registers are set as per calling conventions
//
//保存原始的isa
mov x15, x16 // stash the original isa
//把 isa 保存到 x15,因为后续可能修改 x16(比如走 fallback 重新查找)
LLookupStart\Function:
// p1 = SEL, p16 = isa
#if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16_BIG_ADDRS
//ldr表示将一个值存入到p10寄存器中
//x16表示p16寄存器存储的值,当前是Class
//#数值表示一个值,这里的CACHE经过全局搜索发现是2倍的指针地址,也就是16个字节
//#define CACHE (2 * __SIZEOF_POINTER__)
//经计算,p10就是cache
ldr p10, [x16, #CACHE] // p10 = mask|buckets
lsr p11, p10, #48 // p11 = mask
and p10, p10, #0xffffffffffff // p10 = buckets
and w12, w1, w11 // x12 = _cmd & mask
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16
ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE] // p11 = mask|buckets
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
tbnz p11, #0, LLookupPreopt\Function
and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets
#else
and p10, p11, #0x0000fffffffffffe // p10 = buckets
tbnz p11, #0, LLookupPreopt\Function
#endif
eor p12, p1, p1, LSR #7
and p12, p12, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = (_cmd ^ (_cmd >> 7)) & mask
#else
and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets
and p12, p1, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = _cmd & mask
#endif // CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4
ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE] // p11 = mask|buckets
and p10, p11, #~0xf // p10 = buckets
and p11, p11, #0xf // p11 = maskShift
mov p12, #0xffff
lsr p11, p12, p11 // p11 = mask = 0xffff >> p11
and p12, p1, p11 // x12 = _cmd & mask
#else
#error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64.
#endif // 上面的内容其实就是从类对象中读取cache,cache里面有mask和bucker两部分内容,这里是根据选择器来算出它可能在哪一个bucker里面
add p13, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) // 定位到第一个桶中
// p13 = buckets + ((_cmd & mask) << (1+PTRSHIFT))
// do {
1: ldp p17, p9, [x13], #-BUCKET_SIZE // {imp, sel} = *bucket--
cmp p9, p1 // if (sel != _cmd) {
b.ne 3f // scan more
// } else {
2: CacheHit \Mode // hit: call or return imp // 找到了相关的缓存内容
// }
3: cbz p9, \MissLabelDynamic // if (sel == 0) goto Miss;
cmp p13, p10 // } while (bucket >= buckets)
b.hs 1b // 循环查找桶
// wrap-around:
// p10 = first bucket
// p11 = mask (and maybe other bits on LP64)
// p12 = _cmd & mask
//
// A full cache can happen with CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION.
// So stop when we circle back to the first probed bucket
// rather than when hitting the first bucket again.
//
// Note that we might probe the initial bucket twice
// when the first probed slot is the last entry.
#if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16_BIG_ADDRS
add p13, p10, w11, UXTW #(1+PTRSHIFT)
// p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16
add p13, p10, p11, LSR #(48 - (1+PTRSHIFT))
// p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
// see comment about maskZeroBits
#elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4
add p13, p10, p11, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)
// p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT)
#else
#error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64.
#endif
add p12, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)
// p12 = first probed bucket
// do {
4: ldp p17, p9, [x13], #-BUCKET_SIZE // {imp, sel} = *bucket--
cmp p9, p1 // if (sel == _cmd)
b.eq 2b // goto hit
cmp p9, #0 // } while (sel != 0 &&
ccmp p13, p12, #0, ne // bucket > first_probed)
b.hi 4b
//避免出现一个死循环
LLookupEnd\Function:
LLookupRecover\Function:
b \MissLabelDynamic//如果没找到就跳转的miss处理
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
#if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE != CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16
#error config unsupported
#endif
LLookupPreopt\Function: // 支持 Preoptimized Caches
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
and p10, p11, #0x007ffffffffffffe // p10 = buckets
autdb x10, x16 // auth as early as possible
#endif
// x12 = (_cmd - first_shared_cache_sel)
adrp x9, _MagicSelRef@PAGE
ldr p9, [x9, _MagicSelRef@PAGEOFF]
sub p12, p1, p9
// w9 = ((_cmd - first_shared_cache_sel) >> hash_shift & hash_mask)
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
// bits 63..60 of x11 are the number of bits in hash_mask
// bits 59..55 of x11 is hash_shift
lsr x17, x11, #55 // w17 = (hash_shift, ...)
lsr w9, w12, w17 // >>= shift
lsr x17, x11, #60 // w17 = mask_bits
mov x11, #0x7fff
lsr x11, x11, x17 // p11 = mask (0x7fff >> mask_bits)
and x9, x9, x11 // &= mask
#else
// bits 63..53 of x11 is hash_mask
// bits 52..48 of x11 is hash_shift
lsr x17, x11, #48 // w17 = (hash_shift, hash_mask)
lsr w9, w12, w17 // >>= shift
and x9, x9, x11, LSR #53 // &= mask
#endif
// sel_offs is 26 bits because it needs to address a 64 MB buffer (~ 20 MB as of writing)
// keep the remaining 38 bits for the IMP offset, which may need to reach
// across the shared cache. This offset needs to be shifted << 2. We did this
// to give it even more reach, given the alignment of source (the class data)
// and destination (the IMP)
ldr x17, [x10, x9, LSL #3] // x17 == (sel_offs << 38) | imp_offs
cmp x12, x17, LSR #38
.if \Mode == GETIMP
b.ne \MissLabelConstant // cache miss
sbfiz x17, x17, #2, #38 // imp_offs = combined_imp_and_sel[0..37] << 2
sub x0, x16, x17 // imp = isa - imp_offs
SignAsImp x0
ret
.else
b.ne 5f // cache miss
sbfiz x17, x17, #2, #38 // imp_offs = combined_imp_and_sel[0..37] << 2
sub x17, x16, x17 // imp = isa - imp_offs
.if \Mode == NORMAL
br x17
.elseif \Mode == LOOKUP
orr x16, x16, #3 // for instrumentation, note that we hit a constant cache
SignAsImp x17
ret
.else
.abort unhandled mode \Mode
.endif
5: ldursw x9, [x10, #-8] // offset -8 is the fallback offset
add x16, x16, x9 // compute the fallback isa
b LLookupStart\Function // lookup again with a new isa
.endif
#endif // CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
.endmacro这个方法方法中通过类对象
小结
- 检查消息接受者
receiver是否存在,为nil则不做任何处理 - 通过
receiver的isa指针来找到对应的一个class对象 - 找到
class类对象进行内存平移,找到cache - 从
cache中获得buckets - 从
bucket对比参数sel,看在缓存有没有同名方法 - 如果
bucket中有对应的sel->cacheHit->直接调用imp - 如果
bucket中没有对应的sel那么就直接进入慢速查找
消息发送会先通过缓存进行查找方法实现,如果在缓存中没有找到方法实现,就会进入慢速查找过程,去类的方法列表以及父类链中进行循环查找
慢速查找lookUpImpOrForward
我们在上面讲过如果这个方法没有在缓存中保存过,这样就会进入__objc_msgSend_uncached函数
objc
NEVER_INLINE
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
//定义的消息转发,imp初始化为空
const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
IMP imp = nil;
Class curClass;
//curClass保存当前正在查找的类
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) {
// The first message sent to a class is often +new or +alloc, or +self
// which goes through objc_opt_* or various optimized entry points.
//
// However, the class isn't realized/initialized yet at this point,
// and the optimized entry points fall down through objc_msgSend,
// which ends up here.
//
// We really want to avoid caching these, as it can cause IMP caches
// to be made with a single entry forever.
//
// Note that this check is racy as several threads might try to
// message a given class for the first time at the same time,
// in which case we might cache anyway.
behavior |= LOOKUP_NOCACHE;
}//判断类有没有初始化过,如果cls还没有初始化完成,那么给behavior加一个禁止缓存
// runtimeLock is held during isRealized and isInitialized checking
// to prevent races against concurrent realization.
// runtimeLock is held during method search to make
// method-lookup + cache-fill atomic with respect to method addition.
// Otherwise, a category could be added but ignored indefinitely because
// the cache was re-filled with the old value after the cache flush on
// behalf of the category.
runtimeLock.lock();//加锁,保证线程安全
// We don't want people to be able to craft a binary blob that looks like
// a class but really isn't one and do a CFI attack.
//
// To make these harder we want to make sure this is a class that was
// either built into the binary or legitimately registered through
// objc_duplicateClass, objc_initializeClassPair or objc_allocateClassPair.
checkIsKnownClass(cls);
//确定当前类的一个继承链关系
cls = realizeAndInitializeIfNeeded_locked(inst, cls, behavior & LOOKUP_INITIALIZE);
//确保这个类是realized + initialized状态
// runtimeLock may have been dropped but is now locked again
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
curClass = cls;
// The code used to lookup the class's cache again right after
// we take the lock but for the vast majority of the cases
// evidence shows this is a miss most of the time, hence a time loss.
//
// The only codepath calling into this without having performed some
// kind of cache lookup is class_getInstanceMethod().
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) { // 进入查找循环
if (curClass->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) { //尝试查找方法
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
//如果是常量优化缓存
//再一次尝试从cache中查找imp
//目的防止多线程操作的时候,刚好调用函数缓存进来了
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) goto done_unlock;
curClass = curClass->cache.preoptFallbackClass();
#endif
} else {
// curClass method list.
method_t *meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
imp = meth->imp(false);
goto done;
}
if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil)) { //如果当前类没有,再往父类去找
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = forward_imp;
break;
}
}
// Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain.
if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) { // 限制循环次数
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// Superclass cache.
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); // 从父类的cache中去找,看能不能捡到imp
if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
if (fastpath(imp)) {
// Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class.
goto done;
}
}
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) { //第二次进入后, 在第一次的时候behavior就被取反了,所以第二次进入的时候就不会进入了,因此动态解析的过程其实是一个执行一次的单例操作.
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior); //没找到,走methodresolver
}
done:
if (fastpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0)) {
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
while (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) {
cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass();
}
#endif
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass); //找到imp去缓存它
}
done_unlock:
runtimeLock.unlock(); // 解锁并且返回
if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp)) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
}这里主要分成以下几个步骤:
- 检查类是否被初始化,是否是一个已知的关系,确定继承关系.
- 进入了循环查找方法的一个逻辑,从本类的
method查找imp(查找的方式是getMethodNoSuper_nolock)- 从本类的
method list查找imp - 从本类父类的
cache中查找imp - 从本类父类的
method list中查找imp - 若上面的环节有任何一个环节查找到了
imp,跳出循环先缓存方法到cache中 - 知道查找到
nil,指定imp为消息转发,跳出循环
- 从本类的
- 跳出循环后的逻辑,如果找到了
imp,就会把imp缓存到本类cache里(log_and_fill_cache):(注意这里不管是本类还是本类的父类找到了imp,都会缓存到本类中去)
现在我们来看一下在类和父类继承链中查找imp是怎么样的一个逻辑
objc
static method_t *
getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
// fixme nil cls?
// fixme nil sel?
auto const methods = cls->data()->methods();
for (auto mlists = methods.beginLists(),
end = methods.endLists();
mlists != end;
++mlists)
{
// <rdar://problem/46904873> getMethodNoSuper_nolock is the hottest
// caller of search_method_list, inlining it turns
// getMethodNoSuper_nolock into a frame-less function and eliminates
// any store from this codepath.
method_t *m = search_method_list_inline(*mlists, sel); // 这里是查找方法的函数
if (m) return m;
}
return nil;
}
search_method_list_inline(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel) // 这里面是查找函数的一个具体实现
{
int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp();
int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->isExpectedSize();
if (fastpath(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize)) {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist); // 有序查找,也就是采用二分查找的方式
} else {
// Linear search of unsorted method list
if (auto *m = findMethodInUnsortedMethodList(sel, mlist)) // 无序查找,也就是采用遍历的方式
return m;
}
#if DEBUG
// sanity-check negative results
if (mlist->isFixedUp()) {
for (auto& meth : *mlist) {
if (meth.name() == sel) {
_objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not");
}
}
}
#endif
return nil;
}这里我们主要理解一下有关于二分查找这个函数的一个逻辑:
getMethodNoSuper_nolock方法:二分查找方法列表
objc
ALWAYS_INLINE static method_t *
findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t *list)
{
if (list->isSmallList()) {
if (CONFIG_SHARED_CACHE_RELATIVE_DIRECT_SELECTORS && objc::inSharedCache((uintptr_t)list)) {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(key, list, [](method_t &m) { return m.getSmallNameAsSEL(); });
} else {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(key, list, [](method_t &m) { return m.getSmallNameAsSELRef(); });
}
} else {
return findMethodInSortedMethodList(key, list, [](method_t &m) { return m.big().name; });
}
}
ALWAYS_INLINE static method_t *
findMethodInSortedMethodList(SEL key, const method_list_t *list, const getNameFunc &getName)
{
ASSERT(list);
auto first = list->begin();
auto base = first;
decltype(first) probe;
uintptr_t keyValue = (uintptr_t)key;
uint32_t count;
for (count = list->count; count != 0; count >>= 1) {
probe = base + (count >> 1);//从首地址+下标 --> 移动到中间位置(count >> 1 右移1位即 count/2 = 4)
uintptr_t probeValue = (uintptr_t)getName(probe);
//如果查找的key的keyValue等于中间位置,就直接返回
if (keyValue == probeValue) {
// `probe` is a match.
// Rewind looking for the *first* occurrence of this value.
// This is required for correct category overrides.
while (probe > first && keyValue == (uintptr_t)getName((probe - 1))) {
//排除分类重名方法(方法的存储是先存储类方法,在存储分类---按照先进后出的原则,分类方法最先出,而我们要取的类方法,所以需要先排除分类方法)
probe--;
}
return &*probe;
}
//如果keyValue大于probeValue 就往中间位置的右边进行一个查找
if (keyValue > probeValue) {
base = probe + 1;
count--;
}
}
return nil;
}这里处理向前查找方法列表的第一个类方法可能不是那么好理解,这里我们看下面这个图:

这里我们可以发现这个类会存储所有实例方法,然后按照顺序查找的内容,所以我们直接根据二分算法按顺序查找这部分内容,找到第一方法就可以退出了.
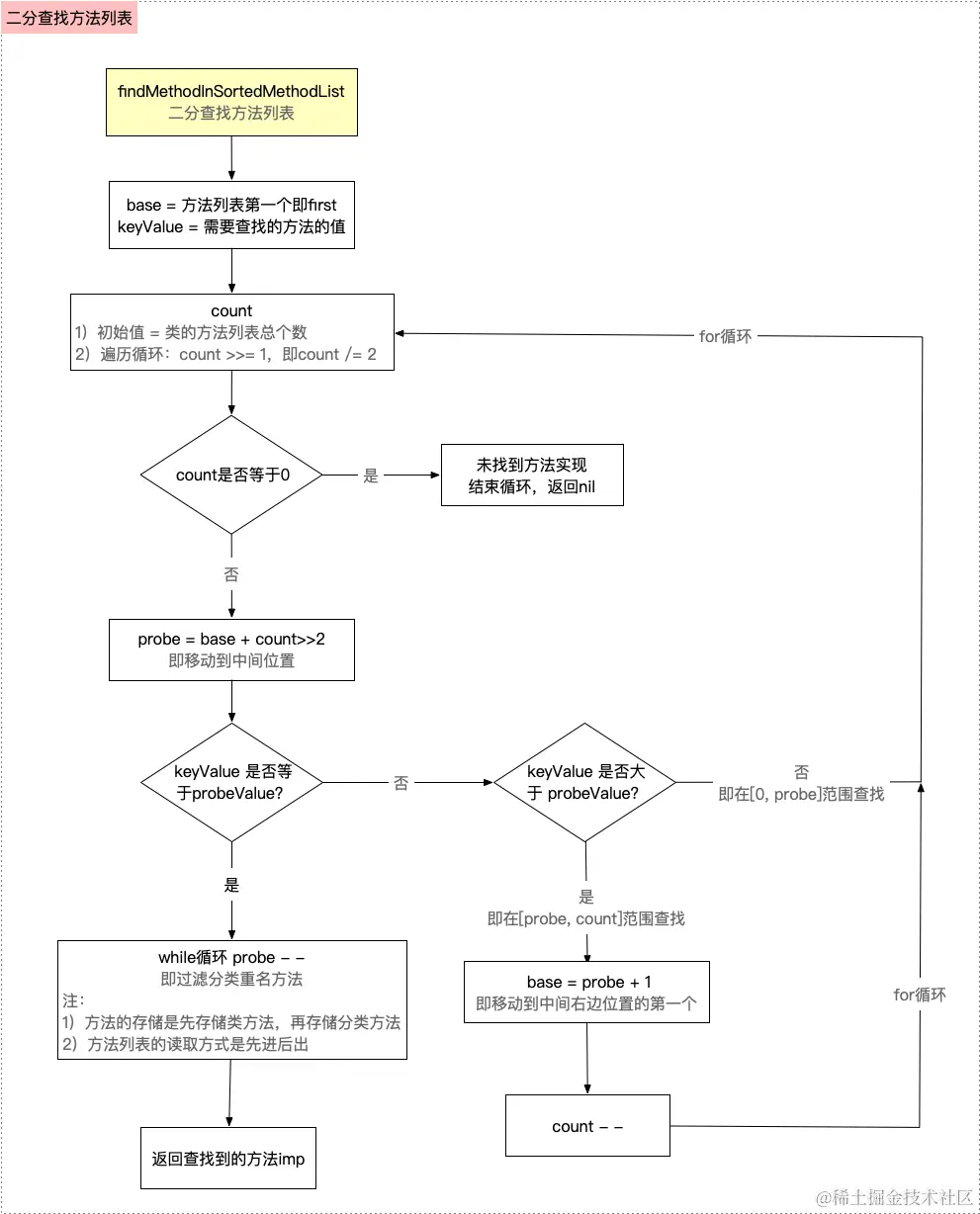
小结
总结消息发送慢速查找
imp(c/c++):
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)1.从本类的
method list(二分查找/遍历查找)查找imp2.从本类的父类的
cache查找imp(汇编)3.从本类的父类的
method list(二分查找/遍历查找)查找imp...继承链遍历...(父类->...->根父类)里找
cache和method list的imp4.若上面环节有任何一个环节查找到了
imp,跳出循环,缓存方法到本类的cache,并返回imp(不管是在父类找到还是在本类找到,都存储到本类的缓存)5.直到查找到
nil,指定imp为消息转发,跳出循环,执行动态方法解析resolveMethod_locked
动态方法决议
前面在提到方法转发流程的时候,我们如果在前两次方法中都没有找到对应的方法,apple官方给了程序员补救的一个方法,也就是在动态方法决议 或者是消息转发(快速转发和慢速转发) 这两个地方进一个保底操作,如果这两个方法都没有处理的话,就会直接出现一个方法未实现的崩溃报错
这里我们主要介绍一下动态方法决议这个内容:
在慢速查找流程没有找到方法实现的时候,源码如下:
objc
static NEVER_INLINE IMP
resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
runtimeLock.assertLocked();
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
runtimeLock.unlock();
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls)) {
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
}
// chances are that calling the resolver have populated the cache
// so attempt using it
return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
//最后返回的都是在缓存中查找是否有对应的一个方法实现
}
IMP lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
return _lookUpImpTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
static IMP _lookUpImpTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) {
// see comment in lookUpImpOrForward
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
IMP imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp != NULL) goto done;
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
if (fastpath(cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true))) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(), sel);
}
#endif
if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) {
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
done:
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) { // 这里进入消息转发流程类
return nil;
}
return imp;
}
//上面这个方法是_lookUpImpTryCache方法:主要作用是在方法缓存中查找给定的类和选择器(sel)对应的方法实现(IMP)。如果找到了,就直接返回这个方法实现。如果没有找到,就会调用 lookUpImpOrForward 函数,进一步查找方法实现或者进入消息转发(forwarding)流程。步骤如下:
-
如果是类,执行实例方法的动态决议方法
resolveInstanceMethod如果是元类,执行类方法的动态决议方法
resolveClassMethod,如果在元类中没有找到或者未空,则在元类的实例方法的动态决议方法resolveInstanceMethod(因为类反复该在元类中是实例方法),所以还需要查找元类中实例方法的动态决议. -
如果动态方法决议中,将其指向了其他方法,则要继续查找对应的一个
imp,就是慢速查找流程
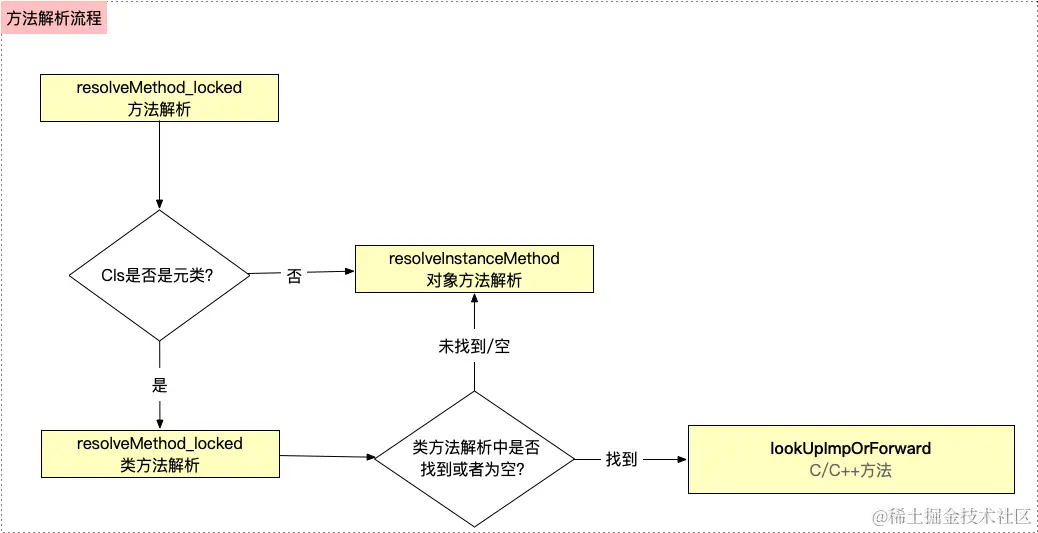
实例方法
针对实例方法调用,在快速-慢速查找均没有找到实例方法的实现,我们有一次挽救的机会,也就是看这部分代码
objc
static void resolveInstanceMethod(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked(); //检查运行时锁状态
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
SEL resolve_sel = @selector(resolveInstanceMethod:); //定义动态解析方法的选择器
// lookUpImpOrNilTryCache 会去元类继承链里找是否有resolveInstacenMethod的imp,如果本类中没有实现它,最终找到NSObject的根元类的系统默认实现
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(cls, resolve_sel, cls->ISA(/*authenticated*/true))) { // 检查类是否实现解析方法
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
}
// 给类对象主动发送resolveInstanceMethod消息(调用类对象里resolveInstacenMethod的imp,调用后会加入到类对象的cache里)
//总结一下上面这几行代码的一个流程:
//先从元类的继承链中去找imp,如果本类实现了这个方法,那么就可以在这个类的元类中找到imp
//如果本类里没有实现它,则可以在最终的根元类的NSObject中找到默认声明的imp
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(cls, resolve_sel, sel);
//第二个部分,主动发送resolveInstanceMethod消息给类对象
//绑定sel+imp
//先到本类的cache找到resolveInstanceMethod
//再到本类的元类继承链中找resolveInstanceMethod的imp
//如果本类中没有实现就会调用NSObject默认实现,调用这个imp缓存到cache中
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls);
//和第一个部分的流程大致一致,但是更换了一下参数.可以理解为从前面已经主动发送过消息了,所以类对象的cache中肯定是缓存了imp,这里就直接返回前面缓存的一个imp
if (resolved && PrintResolving) {
if (imp) {
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] "
"dynamically resolved to %p",
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp);
}
else {
// Method resolver didn't add anything?
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveInstanceMethod:%s] returned YES"
", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found",
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel),
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel));
}
}
}这里它多次调用了这个函数lookUpImpOrNilTryCache,所以我们简单看一下这个函数的逻辑:
objc
IMP lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
return _lookUpImpTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior | LOOKUP_NIL); //
}
static IMP _lookUpImpTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
runtimeLock.assertUnlocked();
if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) {
// see comment in lookUpImpOrForward
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
//元类里面cache里面找imp,肯定没找到
IMP imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp != NULL) goto done;
#if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES
if (fastpath(cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true))) {
imp = cache_getImp(cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(), sel);
}
#endif
if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) {
return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior); // 执行慢速查找,也就是经过动态查找还是没有找到这个sel,但是第二次进入之后看上去会产生循环,但是实际上因为behavior位被取反了,导致它肯定不会再次进入动态方法解析流程了,
}
done:
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
return nil;
}
return imp;
}流程小结:
主要分成一下几个步骤:
-
给类对象主动发送resolveInstanceMethod消息(调用类对象里resolveInstacenMethod的imp,调用后会加入到类对象的cache里
-
先从元类的继承链中去找imp, 如果本类实现了这个方法,那么就可以在这个类的元类中找到imp,
-
如果本类里没有实现它,则可以在最终的根元类的NSObject中找到默认声明的imp
-
-
第二个部分,主动发送resolveInstanceMethod消息给类对象
- 绑定sel+imp
- 先到本类的cache找到resolveInstanceMethod
- 再到本类的元类继承链中找resolveInstanceMethod的imp
- 如果本类中没有实现就会调用NSObject默认实现,调用这个imp缓存到cache中
-
和第一个部分的流程大致一致,但是更换了一下参数.可以理解为从前面已经主动发送过消息了,所以类对象的cache中肯定是缓存了imp,这里就直接返回前面缓存的一个imp
类方法
这里先看一下类方法的一个源码流程:
objc
static void resolveClassMethod(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
lockdebug::assert_unlocked(&runtimeLock);
ASSERT(cls->isRealized());
ASSERT(cls->isMetaClass());
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, @selector(resolveClassMethod:), cls)) {
// Resolver not implemented.
return;
}
// 处理元类,nonmeta赋值成类对象
Class nonmeta;
{
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
nonmeta = getMaybeUnrealizedNonMetaClass(cls, inst);
// +initialize path should have realized nonmeta already
if (!nonmeta->isRealized()) {
_objc_fatal("nonmeta class %s (%p) unexpectedly not realized",
nonmeta->nameForLogging(), nonmeta);
}
}
//给类对象发送resloveClassMethod消息,绑定sel和imp指针
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend;
bool resolved = msg(nonmeta, @selector(resolveClassMethod:), sel);
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveClassMethod adds to self->ISA() a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls);
if (resolved && PrintResolving) {
if (imp) {
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: method %c[%s %s] "
"dynamically resolved to %p",
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel), imp);
}
else {
// Method resolver didn't add anything?
_objc_inform("RESOLVE: +[%s resolveClassMethod:%s] returned YES"
", but no new implementation of %c[%s %s] was found",
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel),
cls->isMetaClass() ? '+' : '-',
cls->nameForLogging(), sel_getName(sel));
}
}
}流程小结:
- 会从元类的继承链里找
resolveClassMethod的imp;- 如果本类里实现了
+(Bool)resolveClassMethod方法,则在元类里能找到imp; - 如果本类里没有实现它,则最终在根元类
NSObject里找imp,因为NSObject类里默认声明了+(Bool)resolveClassMethod方法实现。
- 如果本类里实现了
- 获得这个类的元类,进入这个
getMaybeUnrealizedNonMetaClass方法里面,将这个nonmeta赋值成类对象 - 主动发送
resolveClassMethod,不管是在那一个层级找到的都会把它赋值到我们的本类的一个cache中 - 获取之前发送的一个imp.
- 这个
resolveClassMethod不生效之后,再去在元类中查找那个实例方法resolveInstanceMethod(因为类方法在元类中是以实例方法的样式来存储的)
崩溃修改
所以我们在这里可以实现一个保底机制
objc
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
//ISA_MASK 0x00007ffffffffff8ULL
CJLPerson *person = [CJLPerson alloc];
CJLTeacher* teacher = [CJLTeacher alloc];
[teacher sayBye];
struct objc_super lgsuper;
lgsuper.receiver = teacher;
lgsuper.super_class = [CJLPerson class];
//((void (*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSendSuper)(&lgsuper, @selector(sayBye));
//((void (*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(person, @selector(sayNB));
// Class pClass = [CJLPerson class];
// [person sayHello];
// [person sayBye];
NSLog(@"123");
[person sayNB];
[person sayHello];
// [person sayMaster];
}
return 0;
}
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
NSLog(@"%@, 保底机制", NSStringFromSelector(sel));
// if (sel == @selector(sayHello)) {
// IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self, @selector(sayNB));
// Method sayMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(sayNB));
// const char* type = method_getTypeEncoding(sayMethod);
// return class_addMethod(self, sel, imp, type);
// }
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}动态方法添加函数:
这里讲一下我们这里的一个动态方法添加的函数class_addMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name, IMP _Nonnull imp, const char * _Nullable types) :
cls给哪一个类对象添加方法nameSEL类型给哪一个方法名添加方法实现imp方法具体实现,也就是给对应的一个方法添加给定的方法名- types 就是表示返回值和参数类型的子符串
这个可以给类对象添加一个方法.
这里打印出来的结果是下面这张图:

这里为什么会打印两次呢:
- 第一次的打印是在查找当前这个方法的时候会进入一个
动态方法决议 - 第二次打印的原因是进入类慢速转发流程中调用
NSObject(NSObject) methodSignatureForSelector:会再次进入一个转发流程
正确的处理方式如下:
objc
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel {
NSLog(@"%@, 保底机制", NSStringFromSelector(sel));
if (sel == @selector(sayHello)) {
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self, @selector(sayNB)); // 获得该类的一个方法选择器的实现
Method sayMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(sayNB));
const char* type = method_getTypeEncoding(sayMethod);
return class_addMethod(self, sel, imp, type);
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}这样子就起到了一个保底的效果:

优化
上面的这种方式是单独在每个类中重写,有没有更好的,一劳永逸的方法呢?其实通过方法慢速查找流程可以发现其查找路径有两条
- 实例方法:
类 -- 父类 -- 根类 -- nil - 类方法:
元类 -- 根元类 -- 根类 -- nil
这里不管怎么我们都会进入NSObject中进行一个查找,所以我们是否可以将上面的两个方法整合到一起呢?答案是可以的,我们呢可以将实力方法和类方法的都写在根类的分类中:
objc
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(say666)) {
NSLog(@"%@ 来了", NSStringFromSelector(sel));
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self, @selector(sayMaster));
Method sayMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(sayMaster));
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(sayMethod);
return class_addMethod(self, sel, imp, type);
}else if (sel == @selector(sayNB)) {
NSLog(@"%@ 来了", NSStringFromSelector(sel));
IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson"), @selector(lgClassMethod));
Method lgClassMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson"), @selector(lgClassMethod));
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(lgClassMethod);
return class_addMethod(objc_getMetaClass("LGPerson"), sel, imp, type);
}
return NO;
}这种方式的实现,正好与源码中针对类方法的处理逻辑是一致的,即完美阐述为什么调用了类方法动态方法决议,还要调用对象方法动态方法决议,其根本原因还是类方法在元类中的实例方法。
当然,上面这种写法还是会有其他的问题,比如系统方法也会被更改,针对这一点,是可以优化的,即我们可以针对自定义类中方法统一方法名的前缀,根据前缀来判断是否是自定义方法,然后统一处理自定义方法,例如可以在崩溃前pop到首页,主要是用于app线上防崩溃的处理,提升用户的体验。
动态方法解析小结:
- 首先慢速查找失败进入动态方法解析.动态方法解析
- 根据不同类别进入我们的一个实例动态方法解析或者是类动态方法解析(只会执行一次)
- 然后进入在实例动态方法解析里面在给类对象主动发送这个消息,如果类中找不到就依次向上寻找,找不到再次进入我们的慢速查找,但是此时不会在循环回来了,而是进入消息转发了
_objc_msgForward_impcache
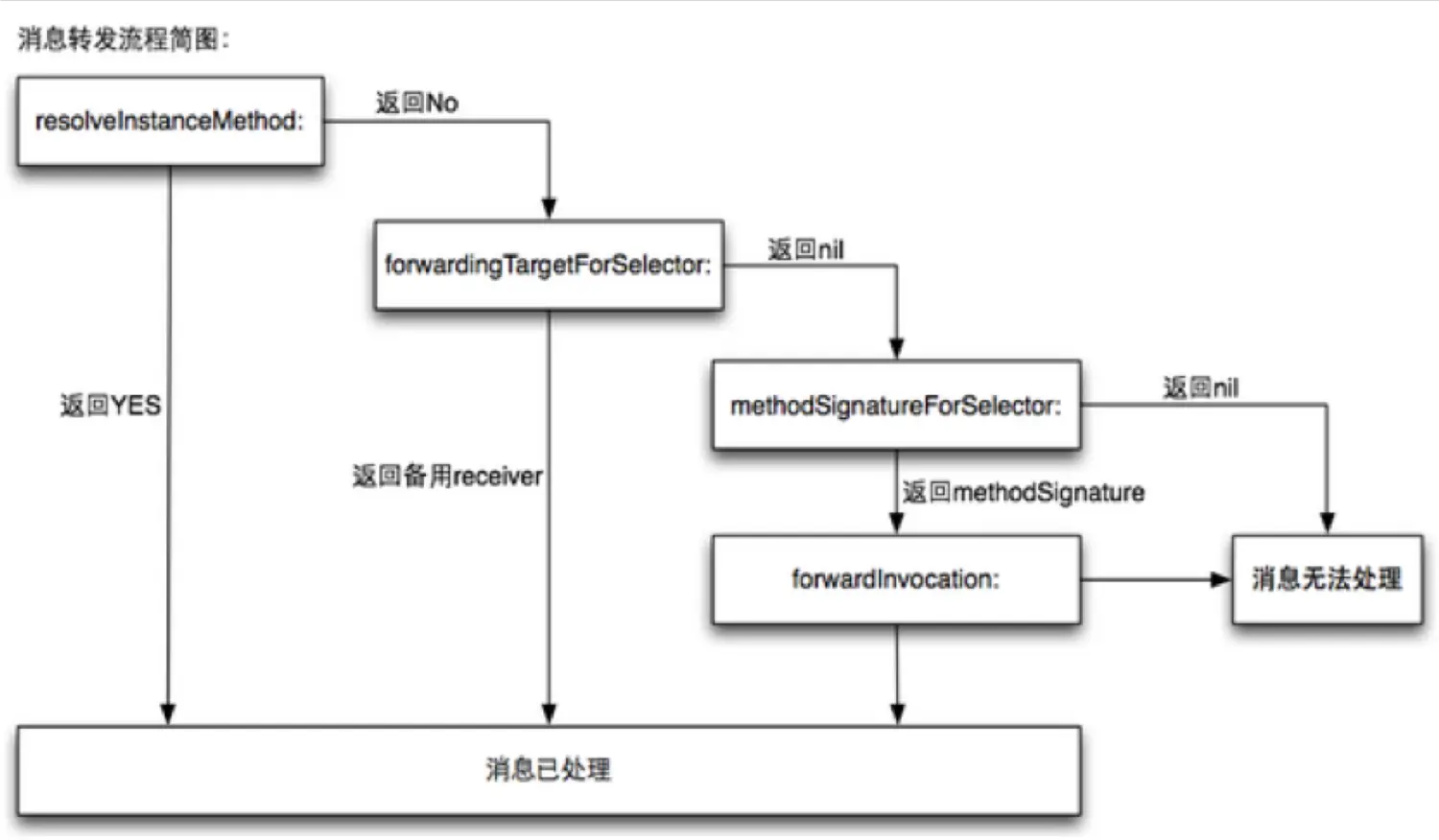
消息转发
快速转发forwardingTargetForSelector
我们先要知道他是在那里进入一个快速转发流程的:
objc
if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) { // 这里进入消息转发流程类
return nil;
} imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache在这个函数中进入消息转发流程
它对应这个方法,其他就是底层的东西了:
objc
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector {
if (aSelector == @selector(sayHello)) {
return [CJLTeacher new]; // 返回其他类中实现过这个方法的方法.
}
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}这样就可以让class1的方法转发到class2中
慢速转发(methodSignatureForSelector 和 forwardInvocation)
针对第二次机会即快速转发中还是没有找到,则进入最后的一次挽救机会,即在LGPerson中重写methodSignatureForSelector,如下所示
objc
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSLog(@"%s - %@",__func__,NSStringFromSelector(aSelector));
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:"]; // v@表示void类型
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
NSLog(@"%s - %@",__func__,anInvocation);
}
//这两个方法要一起出现的,不能缺省下面一个, 也不能血沉过下面那个样式
//- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
//[super forwardInvocation:anInvocation];
//NSLog(@"%s - %@",__func__,anInvocation);
//}- 第一个函数我们需要给他这个这个未知的方法签名一个合适的的值,否则会抛出一个异常
- 如果上一步获取到了方法签名,那么运行时系统就会创建一个 NSInvocation 对象,并调用 forwardInvocation: 方法。在这个方法中,你可以自定义消息的处理方式。例如,你可以将这个消息转发给另一个对象,或者你可以决定忽略这个消息。
消息流程小结
- 对于对象方法来说,即在
类中查找其慢速查找的父亲链是类--父类--根类--nil - 对于类方法来说,查找的链是
元链--根元类--根类--nil - 如果快速查找,慢速查找都没有找到方法是小安,则尝试动态方法决议
- 如果动态方法决议还没有找到,就进行一个消息转发
防止系统崩溃的三根稻草:
- 动态方法解析
- 快速转发
- 慢速转发
OC方法调用的本质就是消息发送,消息发送就是SEL-IMP的查找过程.
最后以两张思维导图结尾:

参考博客:
iOS-底层原理 14:消息流程分析之 动态方法决议 & 消息转发