Java锁这样用,从单机到分布式一步到位
单机锁已经不够用了?分布式系统中如何保证数据安全?今天我们来聊聊从单机锁到分布式锁的完整解决方案,最后用一个注解就能搞定所有锁的问题!
为什么需要锁?
在多线程或多进程环境中,多个操作同时访问同一资源时可能出现数据不一致的问题。锁就是用来保证同一时间只有一个操作能访问共享资源。
锁的作用:
- 保证数据一致性
- 防止并发冲突
- 确保操作的原子性
简单理解: 就像厕所门上的锁,同一时间只能有一个人使用,其他人必须等待。
单机锁的局限性
synchronized关键字
Java最简单的锁机制。
java
public class CounterService {
private int count = 0;
public synchronized void increment() {
count++;
}
public synchronized int getCount() {
return count;
}
}ReentrantLock可重入锁
更灵活的锁机制。
java
public class CounterService {
private int count = 0;
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void increment() {
lock.lock();
try {
count++;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}单机锁的问题:
- 只能在单个JVM内生效
- 多个服务实例之间无法互斥
- 分布式环境下失效
分布式环境的挑战
当应用部署在多台服务器上时,单机锁就不够用了。
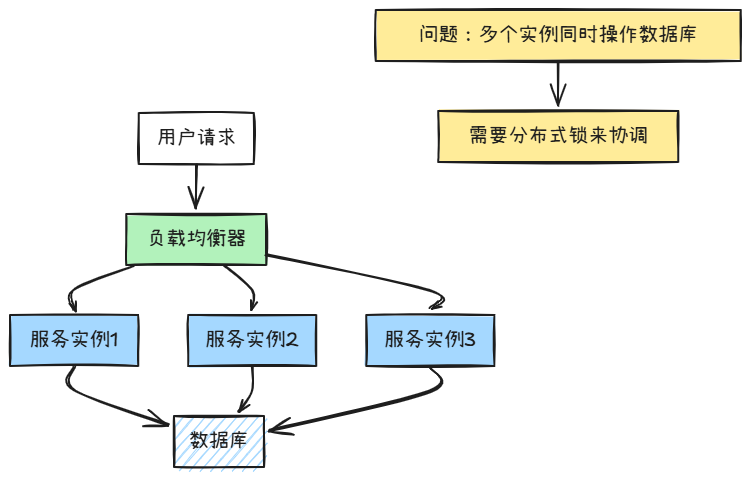
分布式环境下的问题:
- 多个服务实例可能同时执行相同操作
- 库存扣减、订单生成等场景容易出现数据不一致
- 需要跨JVM的锁机制
基于Redis的分布式锁
简单的Redis分布式锁
使用Redis的SET命令实现。
java
@Component
public class SimpleRedisLock {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
public boolean tryLock(String key, String value, long expireTime) {
Boolean result = redisTemplate.opsForValue()
.setIfAbsent(key, value, expireTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return Boolean.TRUE.equals(result);
}
public void releaseLock(String key, String value) {
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then " +
"return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
redisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript<>(script, Long.class),
Arrays.asList(key), value);
}
}使用示例
java
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private SimpleRedisLock redisLock;
public void createOrder(Long userId) {
String lockKey = "order:user:" + userId;
String lockValue = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
if (redisLock.tryLock(lockKey, lockValue, 30)) {
try {
// 执行订单创建逻辑
doCreateOrder(userId);
} finally {
redisLock.releaseLock(lockKey, lockValue);
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("获取锁失败,请稍后重试");
}
}
private void doCreateOrder(Long userId) {
// 具体的订单创建逻辑
}
}基于Redisson的分布式锁
Redisson提供了更完善的分布式锁实现。
引入依赖
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.20.1</version>
</dependency>配置Redisson
java
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://localhost:6379")
.setDatabase(0);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}使用Redisson锁
java
@Service
public class OrderService {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
public void createOrder(Long userId) {
String lockKey = "order:user:" + userId;
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
try {
if (lock.tryLock(10, 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
// 执行订单创建逻辑
doCreateOrder(userId);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("获取锁失败,请稍后重试");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException("获取锁被中断");
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}Redisson的优势:
- 自动续期机制
- 可重入锁支持
- 公平锁、读写锁等多种锁类型
- 异常处理更完善
注解式分布式锁工具
手动加锁解锁容易出错,我们可以通过注解来简化使用。
自定义锁注解
java
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface DistributedLock {
String key() default "";
long waitTime() default 10;
long leaseTime() default 30;
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.SECONDS;
String errorMessage() default "获取锁失败,请稍后重试";
}AOP切面实现
java
@Aspect
@Component
public class DistributedLockAspect {
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Around("@annotation(distributedLock)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, DistributedLock distributedLock) throws Throwable {
String lockKey = generateLockKey(joinPoint, distributedLock.key());
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(lockKey);
try {
boolean acquired = lock.tryLock(
distributedLock.waitTime(),
distributedLock.leaseTime(),
distributedLock.timeUnit()
);
if (!acquired) {
throw new RuntimeException(distributedLock.errorMessage());
}
return joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException("获取锁被中断");
} finally {
if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
private String generateLockKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, String key) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(key)) {
return parseKey(key, joinPoint);
}
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
return className + ":" + methodName;
}
private String parseKey(String key, ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
if (key.contains("#")) {
// 支持SpEL表达式解析参数
return parseSpEL(key, joinPoint);
}
return key;
}
private String parseSpEL(String key, ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
// SpEL表达式解析实现
// 这里简化处理,实际项目中可以使用Spring的SpEL解析器
return key.replace("#userId", String.valueOf(joinPoint.getArgs()[0]));
}
}使用注解式分布式锁
java
@Service
public class OrderService {
@DistributedLock(key = "order:user:#userId", waitTime = 5, leaseTime = 30)
public void createOrder(Long userId) {
// 方法执行时自动加锁
doCreateOrder(userId);
// 方法执行完成后自动释放锁
}
@DistributedLock(key = "inventory:product:#productId")
public void decreaseInventory(Long productId, Integer quantity) {
// 库存扣减逻辑
doDecreaseInventory(productId, quantity);
}
private void doCreateOrder(Long userId) {
// 具体的订单创建逻辑
}
private void doDecreaseInventory(Long productId, Integer quantity) {
// 具体的库存扣减逻辑
}
}分布式锁的注意事项
1. 锁超时时间设置
锁的超时时间要根据业务执行时间合理设置。
java
// 根据业务复杂度设置合适的超时时间
@DistributedLock(key = "complex:task:#taskId", leaseTime = 60) // 复杂任务60秒
public void executeComplexTask(String taskId) {
// 复杂业务逻辑
}
@DistributedLock(key = "simple:task:#taskId", leaseTime = 10) // 简单任务10秒
public void executeSimpleTask(String taskId) {
// 简单业务逻辑
}2. 锁的粒度控制
锁的粒度要合适,既要保证安全性,又要避免性能问题。
java
// 细粒度锁 - 针对具体用户
@DistributedLock(key = "user:operation:#userId")
public void userOperation(Long userId) {
// 只锁定特定用户的操作
}
// 粗粒度锁 - 全局锁(慎用)
@DistributedLock(key = "global:operation")
public void globalOperation() {
// 全局操作,会影响所有用户
}3. 异常处理
确保在异常情况下锁能正确释放。
java
@DistributedLock(key = "order:#orderId", errorMessage = "订单正在处理中,请勿重复操作")
public void processOrder(Long orderId) {
try {
// 业务逻辑
doProcessOrder(orderId);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 记录日志
log.error("订单处理失败: {}", orderId, e);
throw e; // 重新抛出异常,确保事务回滚
}
// 锁会在方法结束时自动释放
}性能优化建议
1. 连接池配置
java
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer()
.setAddress("redis://localhost:6379")
.setConnectionPoolSize(50) // 连接池大小
.setConnectionMinimumIdleSize(10); // 最小空闲连接
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}2. 锁等待策略
java
// 快速失败策略
@DistributedLock(key = "quick:#id", waitTime = 0)
public void quickOperation(String id) {
// 不等待,立即返回
}
// 适度等待策略
@DistributedLock(key = "normal:#id", waitTime = 3)
public void normalOperation(String id) {
// 等待3秒
}总结
Java锁的演进过程:
单机锁:
- synchronized、ReentrantLock
- 只能在单个JVM内使用
分布式锁:
- 基于Redis实现
- 支持跨JVM协调
注解式分布式锁:
- 使用简单,一个注解搞定
- 减少重复代码,降低出错概率
选择建议:
- 单机应用:使用synchronized或ReentrantLock
- 分布式应用:使用Redisson分布式锁
- 追求简洁:使用注解式分布式锁
掌握这套锁的升级方案,让你的应用在任何环境下都能保证数据安全!
如果这篇文章对你有帮助,请不要忘记:
- 👍 点赞支持一下
- 🔔 关注我,获取更多Java技术干货
- ⭐ 推荐给你的朋友同事
关注微信公众号【划水的程序猿】,专注于Java技术分享。让我们一起在技术的海洋中成长!
