这是一个基于ONNX Runtime的YOLOv8目标检测项目,支持CPU和GPU加速,使用Qt框架构建图形化界面。
摄像头实时画面识别
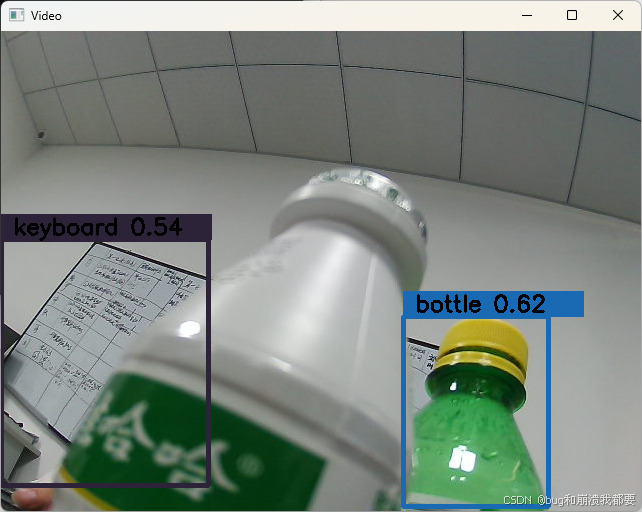
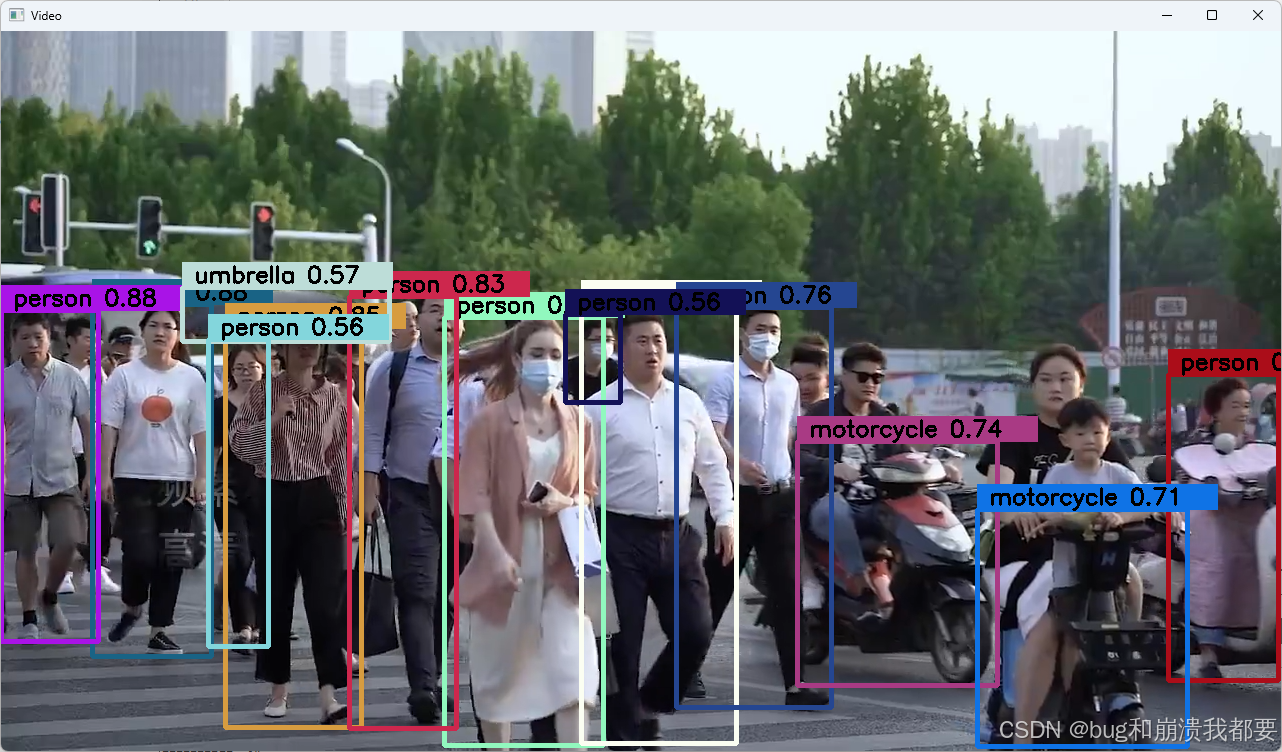
视频文件识别,能正常识别目标:红绿灯,人,公交,巴士,摩托车 等

YOLOv8推理引擎 核心检测算法实现
ONNX Runtime 1.20.1 - 支持CPU和GPU两个版本
OpenCV 4.5.4 - 图像处理和计算机视觉
tl-expected- 错误处理库
cpp
QT += core gui widgets
CONFIG += c++17 console
CONFIG += WIN_MSVC
#CONFIG += LINUX_X86
CONFIG += CPU
#CONFIG += GPU
##############WIN_MSVC###############
CONFIG(WIN_MSVC){
DESTDIR = ./bin_win/
#opecv
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\opencv454\include
CONFIG(debug,debug|release): LIBS += $$PWD\ThirdParty\opencv454\x64\vc16\lib\opencv_world454d.lib
CONFIG(release,debug|release): LIBS += $$PWD\ThirdParty\opencv454\x64\vc16\lib\opencv_world454.lib
#onnxruntime
CONFIG(CPU){
DEFINES += CPU
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-1.20.1\include
LIBS += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-1.20.1\lib\onnxruntime.lib
}
CONFIG(GPU){
DEFINES += GPU
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-1.20.1\include
LIBS += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-1.20.1\lib\onnxruntime.lib
}
}
##############LINUX_X86###############
CONFIG(LINUX_X86){
DESTDIR = ./bin_linux/
#opecv
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\opencv454\include
LIBS += -lopencv_core -lopencv_highgui -lopencv_imgcodecs -lopencv_imgproc -lopencv_video -lopencv_videoio -lopencv_calib3d
#onnxruntime
CONFIG(CPU){
DEFINES += CPU
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-1.20.1\include
LIBS += -lonnxruntime
}
CONFIG(GPU){
DEFINES += GPU
INCLUDEPATH += $$PWD\ThirdParty\onnxruntime-win-x64-gpu-1.20.1\include
LIBS += -lonnxruntime
}
}
######################################
SOURCES += \
inference.cpp \
main.cpp \
mainwindow.cpp
HEADERS += \
inference.h \
mainwindow.h \
tl-expected.hpp
FORMS += \
mainwindow.ui
MOC_DIR = tmp/moc
RCC_DIR = tmp/rcc
UI_DIR = tmp/ui
OBJECTS_DIR = tmp/obj
cpp
#include "inference.h"
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <codecvt> // macos必须,否则提示String2WString函数报错
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
std::vector<std::string> YoloV8::st_classes_;
tl::expected<bool, std::string> YoloV8::create_session(const std::string &model_path)
{
// 检查模型文件是否存在
if (!fs::exists(model_path)) return tl::unexpected("模型文件不存在!");
// 创建Ort环境
env_ = Ort::Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING, "Yolo");
Ort::SessionOptions session_options;
// 添加CUDA执行提供程序
#ifdef GPU
OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(session_options, 0);
#endif
// 设置图优化级别
session_options.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(GraphOptimizationLevel::ORT_ENABLE_ALL);
// 设置线程数
session_options.SetIntraOpNumThreads(5);
// 设置日志级别
session_options.SetLogSeverityLevel(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_WARNING);
// 创建会话
std::wstring model_path_w = String2WString(model_path);
session_ = Ort::Session(env_, model_path_w.c_str(), session_options);
Ort::AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
// 获取输入节点名称
size_t input_count = session_.GetInputCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < input_count; i++)
input_node_names_.emplace_back(session_.GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
// 获取输出节点名称
size_t output_count = session_.GetOutputCount();
for (size_t i = 0; i < output_count; i++)
output_node_names_.emplace_back(session_.GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
// 创建运行选项
options_ = Ort::RunOptions{nullptr};
return true;
}
// 对输入的图像进行预处理
tl::expected<cv::Mat, std::string> YoloV8::pre_process(cv::Mat &img, cv::Size img_size)
{
// 如果输入的图像为空,则返回一个错误信息
if (img.empty())
{
return tl::unexpected("图片为空");
}
// 获取输入图像的宽度和高度的最大值
int max_side = std::max(img.cols, img.rows);
// 计算输入图像的缩放比例
resize_scales_ = max_side / static_cast<float>(img_size.width);
// 创建一个与输入图像大小相同的空白图像,填充值为114, 114, 114
cv::Mat tmp(max_side, max_side, CV_8UC3, cv::Scalar(114, 114, 114));
// 将输入图像复制到空白图像中
img.copyTo(tmp(cv::Rect(0, 0, img.cols, img.rows)));
// 将空白图像转换为深度学习模型所需的输入格式
cv::Mat res = cv::dnn::blobFromImage(tmp, 1.0 / 255.0, img_size, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), true, false, CV_32F);
// 返回转换后的图像
return res;
}
std::vector<DlResult> YoloV8::post_process(std::vector<Ort::Value> &outputs, float conf_threshold, float iou_threshold)
{
// 定义一个存储结果的向量
std::vector<DlResult> vec_results;
// 获取输出的类型信息
Ort::TypeInfo type_info = outputs.front().GetTypeInfo();
// 获取输出的张量类型和形状信息
auto tensor_info = type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
// 获取输出的形状
std::vector<int64_t> output_node_dims = tensor_info.GetShape();
// 获取输出的数据
auto output = outputs.front().GetTensorMutableData<float>(); // 8400
// 输出的形状是 [1, 84, 8400]
int stride_num = output_node_dims[2]; // 8400
int signal_result_num = output_node_dims[1]; // 84
// 定义存储类别、置信度和框的向量
std::vector<int> class_ids;
std::vector<float> confidences;
std::vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
// 为存储类别、置信度和框的向量预留空间
class_ids.reserve(stride_num / 8);
confidences.reserve(stride_num / 8);
boxes.reserve(stride_num / 8);
// 将输出的数据转换为矩阵
cv::Mat raw_data = cv::Mat(signal_result_num, stride_num, CV_32F, output).t();
// 获取矩阵的指针
float *data = raw_data.ptr<float>(0);
// 遍历每个输出
for (int i = 0; i < stride_num; ++i)
{
// 找到置信度最高的类别
auto max_it = std::max_element(data + 4, data + 80); // std::max_element返回指向最大元素的迭代器
float max_class_socre = *max_it;
int max_idx = std::distance(data + 4, max_it);
// 如果置信度大于阈值,则存储类别、置信度和框
if (max_class_socre > conf_threshold)
{
confidences.push_back(max_class_socre);
class_ids.push_back(max_idx);
float x = data[0];
float y = data[1];
float w = data[2];
float h = data[3];
// 计算框的位置和大小
int left = int((x - 0.5 * w) * resize_scales_);
int top = int((y - 0.5 * h) * resize_scales_);
int width = int(w * resize_scales_);
int height = int(h * resize_scales_);
// 存储框
boxes.emplace_back(left, top, width, height);
}
// 移动到下一个输出
data += signal_result_num;
}
// 进行非极大值抑制
std::vector<int> nms_result;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, conf_threshold, iou_threshold, nms_result);
// 将结果存储到向量中
for (int i = 0; i < nms_result.size(); ++i)
{
int idx = nms_result[i];
DlResult result;
result.class_id = class_ids[idx];
result.confidence = confidences[idx];
result.box = boxes[idx];
vec_results.push_back(result);
}
// 返回结果
return vec_results;
}
// 定义一个函数,用于将Ort::AllocatedStringPtr类型的向量转换为const char*类型的向量
std::vector<const char *> YoloV8::get_name_data(std::vector<Ort::AllocatedStringPtr> &names)
{
// 定义一个const char*类型的向量,用于存储转换后的数据
std::vector<const char *> res;
// 遍历names向量中的每一个元素
for (const auto &name : names)
{
// 将每一个元素转换为const char*类型,并添加到res向量中
res.push_back(name.get());
}
// 返回转换后的向量
return res;
}
tl::expected<std::vector<DlResult>, std::string> YoloV8::run_session(cv::Mat &img, cv::Size input_size, float confidence_threshold, float iou_threshold)
{
// 预处理图像
auto ex_img = pre_process(img, input_size);
// 如果预处理失败,返回错误信息
if (!ex_img)
{
return tl::unexpected(ex_img.error());
}
// 定义输入张量的形状
std::vector<int64_t> input_shape = {1, 3, input_size.height, input_size.width};
// 创建输入张量
Ort::Value input_tensor = Ort::Value::CreateTensor<float>(
Ort::MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU), ex_img.value().ptr<float>(0), 3 * input_size.height * input_size.width, input_shape.data(), input_shape.size());
// 运行会话
auto output_tensor = session_.Run(options_, get_name_data(input_node_names_).data(), &input_tensor, input_node_names_.size(), get_name_data(output_node_names_).data(),
output_node_names_.size());
// 后处理输出张量
auto outputs = post_process(output_tensor, confidence_threshold, iou_threshold);
// 返回后处理结果
return outputs;
}
void YoloV8::draw_boxes(cv::Mat &img, std::vector<DlResult> &results)
{
if (st_classes_.size() == 0)
return;
for (auto &re : results)
{
cv::RNG rng(cv::getTickCount());
cv::Scalar color(rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256), rng.uniform(0, 256));
cv::rectangle(img, re.box, color, 3);
float confidence = floor(100 * re.confidence) / 100;
std::string label = st_classes_[re.class_id] + " " +
std::to_string(confidence).substr(0, std::to_string(confidence).size() - 4);
cv::rectangle(
img,
cv::Point(re.box.x, re.box.y - 25),
cv::Point(re.box.x + label.length() * 15, re.box.y),
color,
cv::FILLED);
cv::putText(
img,
label,
cv::Point(re.box.x, re.box.y - 5),
cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.75,
cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0),
2);
}
}主要功能特性
-
**CPU推理**: 使用标准ONNX Runtime
-
**GPU推理**: 支持CUDA加速
- 完整的检测流水线
**预处理** (`pre_process`)
-
图像尺寸调整到640x640
-
Letterbox填充保持宽高比
-
像素值归一化
**推理** (`run_session`)
-
ONNX模型前向推理
-
批量处理支持
**后处理** (`post_process`)
-
非极大值抑制(NMS)
-
置信度过滤
-
边界框坐标转换
- 可视化功能
-
检测框绘制
-
类别标签显示
-
置信度分数展示
内存管理
-
使用ONNX Runtime的内存分配器
-
智能指针管理资源生命周期
-
避免内存泄漏
性能优化
-
支持GPU加速推理
-
批量处理能力
-
高效的图像预处理pipeline
适用场景
这个项目特别适合:
-
**实时目标检测应用**
-
**工业质检系统**
-
**监控分析系统**
-
**教学和研究项目**
项目提供了完整的从模型加载到结果可视化的端到端解决方案,是学习和部署YOLOv8模型的优秀起点。