监控系统负载
系统负载介绍
系统负载平均值:Linux内核以活动请求数 的指数移动平均值来表示。
- 活动请求数 不仅包含运行中进程 ,还包含等待IO的进程,对应于R和D。等待IO包括处于睡眠等待预期磁盘和网络响应的任务。
- 指数移动平均值是一个数学公式,可以平滑趋势数据的高值和低值,更加准确地表示一段时间内系统负载,并确定系统负载是随着时间增加还是减少。
- 根据所有CPU活动请求数,每5秒计算一次Load Average 。通过汇总这些值,可以得到最近1分钟,5分钟和15分钟内的指数移动平均值。
- 一些UNIX系统仅考虑CPU使用率 或运行队列长度。Linux中负载平均值中还包含了对IO的考量,遇到负载平均值很高但CPU活动很低时,检查磁盘和网络活动。
- Linux将各个物理CPU核心和微处理器超线程计为独立执行单元。每个独立的执行单元拥有独立的请求队列。
查看系统负载
bash
# 查看CPU
[furongwang@localhost ~]$ lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 2
On-line CPU(s) list: 0,1
Thread(s) per core: 1
Core(s) per socket: 1
座: 2
NUMA 节点: 1
厂商 ID: GenuineIntel
CPU 系列: 6
型号: 142
型号名称: Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-8250U CPU @ 1.60GHz
步进: 10
CPU MHz: 1800.002
BogoMIPS: 3600.00
......
# 查看负载
[furongwang@localhost ~]$ uptime
14:10:01 up 4:27, 3 users, load average: 0.08, 0.03, 0.05
# 给系统加负载
[furongwang@localhost ~]$ md5sum /dev/zero &
[1] 6703
[furongwang@localhost ~]$ md5sum /dev/zero &
[2] 6712
# 等30秒左右
[furongwang@localhost ~]$ uptime
14:12:54 up 4:30, 3 users, load average: 1.24, 0.37, 0.16负载解读
示例:4核心的CPU
-
负载为: 2.92 4.48 5.20
-
每个cpu负载为:0.73(2.92/4) 1.12(4.48/4) 1.30(5.20/4)
比较理想的值为 75% 左右。
top 命令
作用:动态查看进程信息,包括不同状态任务数量,CPU消耗和内存消耗。
bash
[root@localhost ~]# top
top - 14:21:09 up 4:38, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.15, 0
Tasks: 190 total, 1 running, 189 sleeping, 0 stopped, 0 z
%Cpu(s): 0.0 us, 0.2 sy, 0.0 ni, 99.8 id, 0.0 wa, 0.0 hi,
KiB Mem : 1862996 total, 467632 free, 471112 used, 92425
KiB Swap: 2097148 total, 2097148 free, 0 used. 120692
PID USER PR NI VIRT RES SHR S %CPU %MEM
6582 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.3 0.0
6756 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.3 0.0
1 root 20 0 191256 4276 2616 S 0.0 0.2
2 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
4 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
6 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
7 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
8 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
9 root 20 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
10 root 0 -20 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
11 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
12 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
13 root rt 0 0 0 0 S 0.0 0.0
# 内容实时刷新%Cpu列解读:
- us,用户进程消耗CPU的时间
- sy,系统进程消耗CPU的时间
- wa,CPU用于等待IO进程的时间
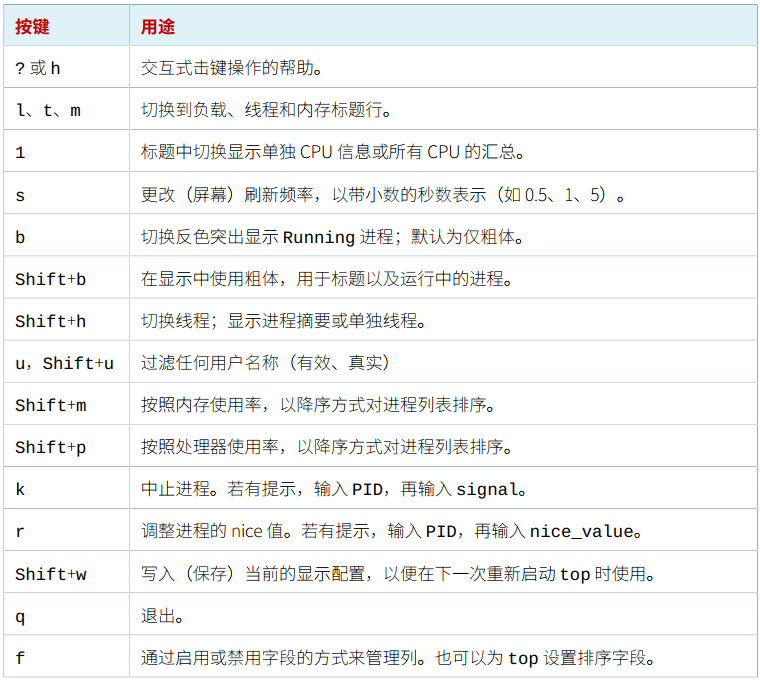
top命令快捷键
常用的命令:数字1,P,M,k,q,h。
free命令
作用:可以显示当前系统未使用的和已使用的内存数目,还可以显示被内核使用的内存缓冲区。
bash
[root@localhost ~]# free --help
Usage:
free [options]
Options:
-b, --bytes show output in bytes
-k, --kilo show output in kilobytes
-m, --mega show output in megabytes
-g, --giga show output in gigabytes
--tera show output in terabytes
--peta show output in petabytes
-h, --human show human-readable output
--si use powers of 1000 not 1024
-l, --lohi show detailed low and high memory statistics
-t, --total show total for RAM + swap
-s N, --seconds N repeat printing every N seconds
-c N, --count N repeat printing N times, then exit
-w, --wide wide output
--help display this help and exit
-V, --version output version information and exit
For more details see free(1).sar命令
sar(System Activity Reporter)是 Linux 系统中用于收集和报告系统活动信息的命令。它是 sysstat 包的一部分,能够实时和历史地显示 CPU 负载、内存使用、I/O 设备使用等统计信息。
bash
[root@localhost ~]# sar --help
用法: sar [ 选项 ] [ <时间间隔> [ <次数> ] ]
Options are:
[ -A ] [ -B ] [ -b ] [ -C ] [ -d ] [ -F [ MOUNT ] ] [ -H ] [ -h ] [ -p ] [ -q ] [ -R ]
[ -r ] [ -S ] [ -t ] [ -u [ ALL ] ] [ -V ] [ -v ] [ -W ] [ -w ] [ -y ]
[ -I { <int> [,...] | SUM | ALL | XALL } ] [ -P { <cpu> [,...] | ALL } ]
[ -m { <keyword> [,...] | ALL } ] [ -n { <keyword> [,...] | ALL } ]
[ -j { ID | LABEL | PATH | UUID | ... } ]
[ -f [ <filename> ] | -o [ <filename> ] | -[0-9]+ ]
[ -i <interval> ] [ -s [ <hh:mm:ss> ] ] [ -e [ <hh:mm:ss> ] ]stress 工具
Linux 中的 stress 工具用于对系统进行压力测试,可模拟 CPU、内存、I/O 和磁盘等资源的高负载状态。通过指定参数(如 -c 压 CPU、-m 压内存)可创建负载,帮助发现系统在压力下的稳定性问题,常用于性能调优或硬件验证。
bash
# 安装
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y stress
# 帮助信息
[root@localhost ~]# stress --help
`stress' imposes certain types of compute stress on your system
Usage: stress [OPTION [ARG]] ...
-?, --help show this help statement
--version show version statement
-v, --verbose be verbose
-q, --quiet be quiet
-n, --dry-run show what would have been done
-t, --timeout N timeout after N seconds
--backoff N wait factor of N microseconds before work starts
-c, --cpu N spawn N workers spinning on sqrt()
-i, --io N spawn N workers spinning on sync()
-m, --vm N spawn N workers spinning on malloc()/free()
--vm-bytes B malloc B bytes per vm worker (default is 256MB)
--vm-stride B touch a byte every B bytes (default is 4096)
--vm-hang N sleep N secs before free (default none, 0 is inf)
--vm-keep redirty memory instead of freeing and reallocating
-d, --hdd N spawn N workers spinning on write()/unlink()
--hdd-bytes B write B bytes per hdd worker (default is 1GB)
Example: stress --cpu 8 --io 4 --vm 2 --vm-bytes 128M --timeout 10s
Note: Numbers may be suffixed with s,m,h,d,y (time) or B,K,M,G (size).压力测试-CPU
bash
# 消耗2个CPU
[root@localhost ~]# stress -c 2
stress: info: [6944] dispatching hogs: 2 cpu, 0 io, 0 vm, 0 hdd
# top监控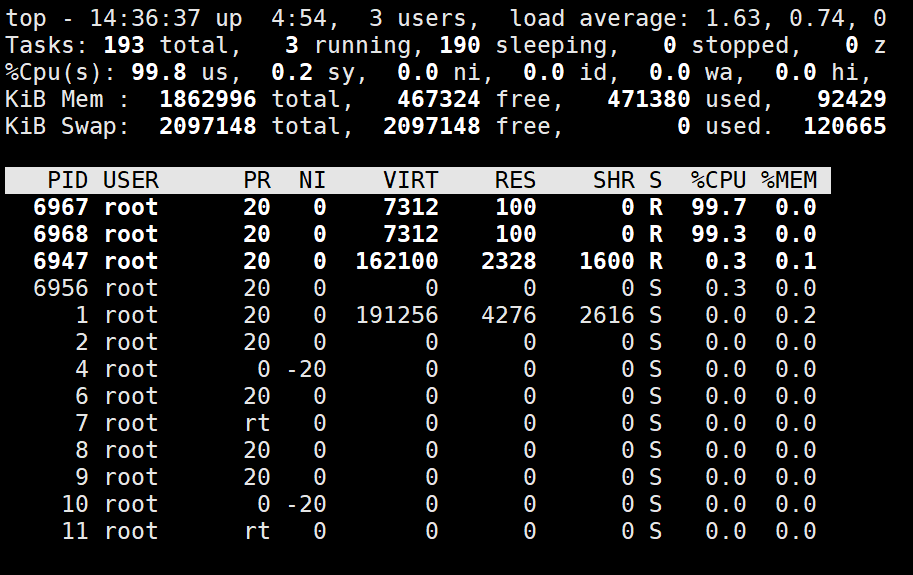
可以发现CPU被大幅占用。
压力测试-内存
bash
# 消耗前内存
[root@localhost ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 459 457 16 902 1179
Swap: 2047 0 2047
# 消耗1G内存
[root@localhost ~]# stress -m 1 --vm-bytes 1G
stress: info: [6994] dispatching hogs: 0 cpu, 0 io, 1 vm, 0 hdd
# 消耗后内存
[root@localhost ~]# free -m
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 1819 1413 136 15 268 230
Swap: 2047 1 2046压力测试-磁盘
bash
# 消耗磁盘IO
[root@localhost ~]# stress -d 1 --hdd-bytes 2G
stress: info: [7034] dispatching hogs: 0 cpu, 0 io, 0 vm, 1 hdd
# 监视活动状态百分比,%util
[root@localhost ~]# sar -dp 5
......
14时42分56秒 DEV tps rd_sec/s wr_sec/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await svctm %util
14时43分01秒 sr0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
14时43分01秒 sda 81.00 57.60 80283.00 991.86 149.24 1754.75 12.35 100.00
14时43分01秒 centos-root 81.20 57.60 78669.60 969.55 151.56 1761.56 12.32 100.00
14时43分01秒 centos-swap 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
14时43分01秒 centos-home 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
14时43分01秒 DEV tps rd_sec/s wr_sec/s avgrq-sz avgqu-sz await svctm %util
14时43分06秒 sr0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
14时43分06秒 sda 98.40 1177.60 93824.80 965.47 130.20 1312.11 10.06 99.00
14时43分06秒 centos-root 94.80 1179.20 91136.00 973.79 132.13 1396.08 10.44 99.00
14时43分06秒 centos-swap 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
14时43分06秒 centos-home 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
......网络测试
bash
# 传输一个大文件
[root@localhost ~]# wget http://192.168.43.100/%E7%B3%BB%E7%BB%9F%E9%95%9C%E5%83%8F/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-2207-02.iso
# 监控带宽
[root@localhost ~]# sar -n DEV 1(此处结果可自行尝试)