Task
Write a shader that draws the full screen rhombus.
编写一个绘制全屏菱形的着色器
Requirements
The shader should avoid using branching or conditional statements in its code, and instead rely on the
absandstepfunctions to determine the color of each pixel.
着色器应避免在其代码中使用分支或条件语句,而是依赖abs和step函数来确定每个像素的颜色。
Theory
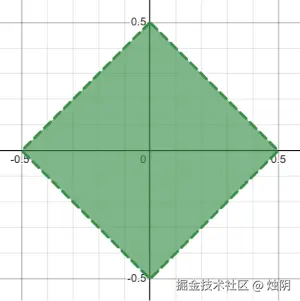
曼哈顿距离:菱形的数学本质
我们通过abs将所有象限的坐标折叠到第一象限,折叠后坐标的 x 和 y 分量相加:
glsl
float d = abs_st.x + abs_st.y;
// 或者写成 float d = abs(st.x) + abs(st.y);这个 d 值代表什么?它在数学上有一个响亮的名字:曼哈顿距离(Manhattan Distance) ,也叫 L1 范数。它表示从原点 (0,0) 到点 (x,y) 只允许沿着坐标轴方向移动所需的最短距离。
现在,我们来分析这个 d 值:
- 在画布中心
(0,0),d = 0。 - 随着点向外移动,
d值线性增加。 - 所有满足
abs(st.x) + abs(st.y) = C(C为常数)的点,构成了一个等值线。
当 C = 0.5 时,这条等值线正好是连接 (0.5, 0), (0, 0.5), (-0.5, 0), (0, -0.5) 四个点的正菱形!
其它:
- 正方形 (L∞ 范数/切比雪夫距离):
d = max(abs(st.x), abs(st.y));- 圆形 (L2 范数/欧几里得距离):
d = length(st);或d = sqrt(st.x*st.x + st.y*st.y);
Answer
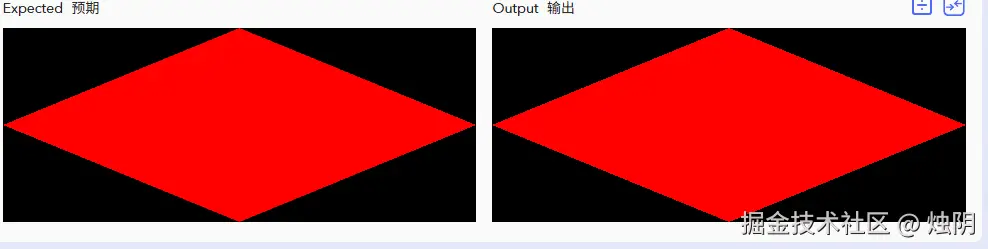
glsl
uniform vec2 iResolution;
void main() {
vec2 uv = gl_FragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy;
uv -= 0.5; // 坐标中心化 将坐标从 [0, 1] 映射到 [-0.5, 0.5]
float t = abs(uv.x) + abs(uv.y);
t = 1.0 - step(0.5, t);
gl_FragColor = vec4(t, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}效果
练习
最后
如果你觉得这篇文章有用,记得点赞、关注、收藏,学Shader更轻松!!