6.1.2 哈希表简单实现¶
我们先考虑最简单的情况,仅用一个数组来实现哈希表 。在哈希表中,我们将数组中的每个空位称为++桶(bucket)++ ,每个桶可存储一个键值对。因此,查询操作就是找到 key 对应的桶,并在桶中获取 value 。
那么,如何基于 key 定位对应的桶呢?这是通过++哈希函数(hash function)++ 实现的。哈希函数的作用是将一个较大的输入空间映射到一个较小的输出空间。在哈希表中,输入空间是所有 key ,输出空间是所有桶(数组索引)。换句话说,输入一个 key ,我们可以通过哈希函数得到该 key 对应的键值对在数组中的存储位置。
输入一个 key ,哈希函数的计算过程分为以下两步。
-
通过某种哈希算法
hash()计算得到哈希值。 -
将哈希值对桶数量(数组长度)
capacity取模,从而获取该key对应的数组索引index。index = hash(key) % capacity
随后,我们就可以利用 index 在哈希表中访问对应的桶,从而获取 value 。
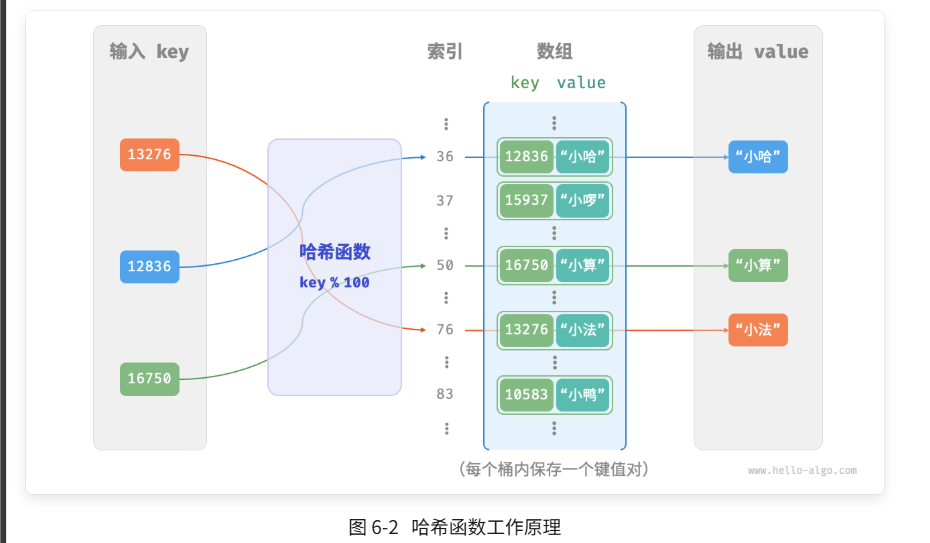
设数组长度 capacity = 100、哈希算法 hash(key) = key ,易得哈希函数为 key % 100 。图 6-2 以 key 学号和 value 姓名为例,展示了哈希函数的工作原理。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
/*
6.1.2 哈希表简单实现
我们先考虑最简单的情况,仅用一个数组来实现哈希表。在哈希表中,我们将数组中的每个空位称为桶(bucket),每个桶可存储一个键值对。因此,查询操作就是找到 key 对应的桶,并在桶中获取 value 。
那么,如何基于 key 定位对应的桶呢?这是通过哈希函数(hash function)实现的。哈希函数的作用是将一个较大的输入空间映射到一个较小的输出空间。在哈希表中,输入空间是所有 key ,输出空间是所有桶(数组索引)。换句话说,输入一个 key ,我们可以通过哈希函数得到该 key 对应的键值对在数组中的存储位置。
输入一个 key ,哈希函数的计算过程分为以下两步。
通过某种哈希算法 hash() 计算得到哈希值。
将哈希值对桶数量(数组长度)capacity 取模,从而获取该 key 对应的数组索引 index 。
index = hash(key) % capacity
随后,我们就可以利用 index 在哈希表中访问对应的桶,从而获取 value 。
设数组长度 capacity = 100、哈希算法 hash(key) = key ,易得哈希函数为 key % 100 。
*/
/* 键值对 */
struct Pair {
public:
int key;
string val;
Pair(int key, string val) {
this->key = key;
this->val = val;
}
};
/* 基于数组实现的哈希表 */
class ArrayHashMap {
private:
vector<Pair*> buckets;
public:
// 构造函数,初始化100个桶为空指针
ArrayHashMap() {
buckets = vector<Pair*>(100, nullptr);
}
// 析构函数,释放所有动态分配的Pair对象
~ArrayHashMap() {
for (auto& pair : buckets) {
delete pair;
}
buckets.clear();
}
// 哈希函数:取key模100(桶数)
int hashFunc(int key) {
return key % buckets.size();
}
// 查询操作,返回对应值或空字符串
string get(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
Pair* pair = buckets[index];
if (pair == nullptr || pair->key != key) {
// 可能发生哈希冲突,需匹配key
return "";
}
return pair->val;
}
// 添加或更新操作
void put(int key, const string& val) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
// 如果桶为空,直接插入
if (buckets[index] == nullptr) {
buckets[index] = new Pair(key, val);
}
else {
// 如果桶已有元素,判断key是否相同
if (buckets[index]->key == key) {
// 更新值
buckets[index]->val = val;
}
else {
// 发生哈希碰撞, 简单冲突策略:覆盖(替换现有元素)
delete buckets[index]; // 删除旧的
buckets[index] = new Pair(key, val);
}
}
}
// 删除操作
void remove(int key) {
int index = hashFunc(key);
if (buckets[index] != nullptr && buckets[index]->key == key) {
delete buckets[index];
buckets[index] = nullptr;
}
}
// 获取所有的Key-Value对(只返回非空槽)
vector<Pair*> pairSet() {
vector<Pair*> res;
for (auto& pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
res.push_back(pair);
}
}
return res;
}
// 获取所有的Key
vector<int> keySet() {
vector<int> keys;
for (auto& pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
keys.push_back(pair->key);
}
}
return keys;
}
// 获取所有的值
vector<string> valueSet() {
vector<string> values;
for (auto& pair : buckets) {
if (pair != nullptr) {
values.push_back(pair->val);
}
}
return values;
}
// 打印哈希表内容
void print() {
for (auto& kv : pairSet()) {
cout << kv->key << " -> " << kv->val << endl;
}
}
};
/* 简单测试例子 */
int main() {
ArrayHashMap map;
// 添加
map.put(1, "Apple");
map.put(2, "Banana");
map.put(102, "Orange"); // 102和2可能冲突
// 打印
map.print();
// 获取
cout << "Key 1: " << map.get(1) << endl;
cout << "Key 2: " << map.get(2) << endl;
cout << "Key 102: " << map.get(102) << endl;
// 更新
map.put(2, "Grape");
cout << "After update:" << endl;
map.print();
// 删除
map.remove(1);
cout << "After deleting key 1:" << endl;
map.print();
system("pause");
return 0;
}6.1.3 哈希冲突与扩容
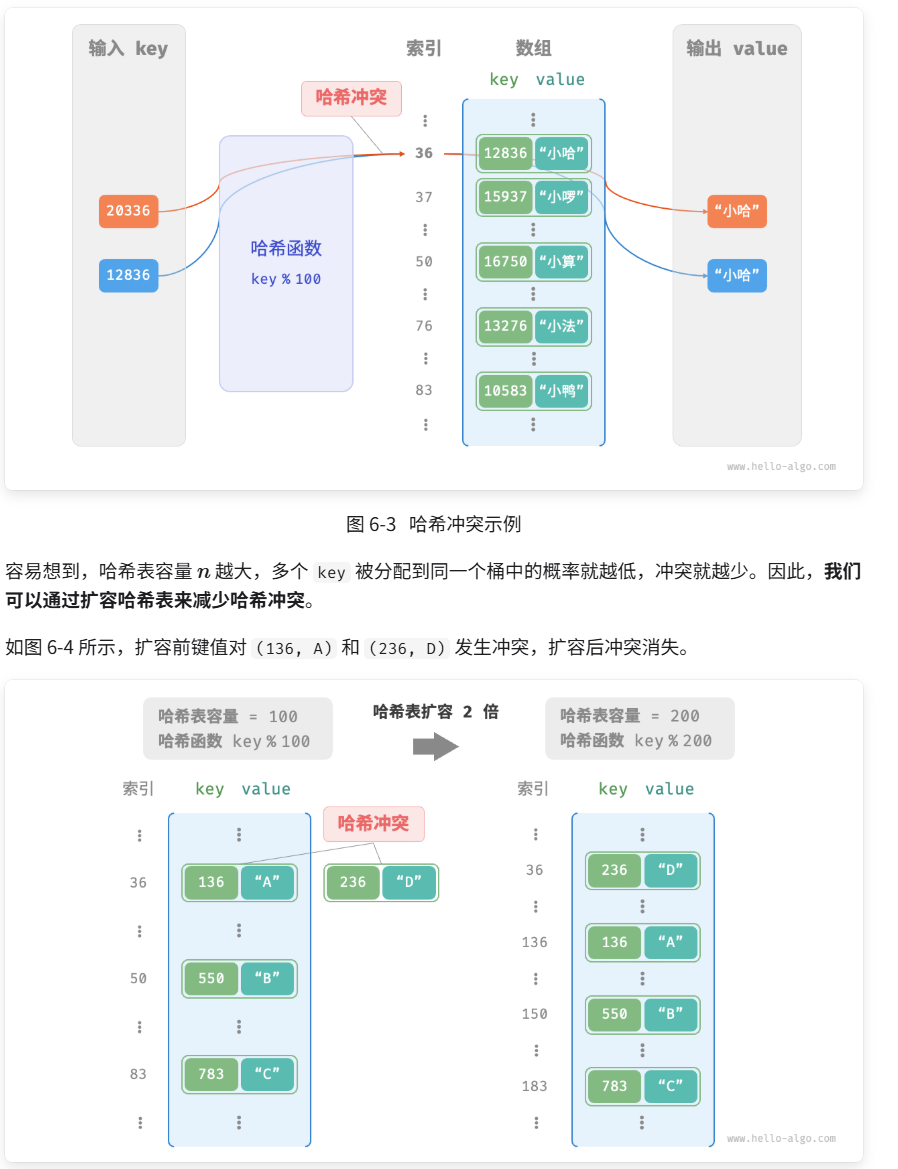
从本质上看,哈希函数的作用是将所有 key 构成的输入空间映射到数组所有索引构成的输出空间,而输入空间往往远大于输出空间。因此,理论上一定存在"多个输入对应相同输出"的情况。
对于上述示例中的哈希函数,当输入的 key 后两位相同时,哈希函数的输出结果也相同。例如,查询学号为 12836 和 20336 的两个学生时,我们得到:
12836 % 100 = 36
20336 % 100 = 36如图 6-3 所示,两个学号指向了同一个姓名,这显然是不对的。我们将这种多个输入对应同一输出的情况称为++哈希冲突(hash collision)++ 。