案例
前置条件:
在 resources 目录下有 hello/hello.properties 文件,文件内容如下:
java
hello=nihao案例一:
在 HelloController 类中通过 @PropertySource 注解引用 properties 文件的内容,然后就可以通过 @Value 注解引用这个配置文件中的 hello 这个 key 了。
java
@PropertySource({"classpath:hello/hello.properties"})
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return hello;
}
}案例一执行的结果是返回 nihao 这个字符串。
案例二:
在 AnotherController 类中通过 @PropertySource 注解引用 properties 文件的内容,在 HelloController 中仍然可以通过 @Value 注解引用这个配置文件中的 hello 这个 key 。
java
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return hello;
}
}
@RestController
@PropertySource({"classpath:hello/hello.properties"})
public class AnotherController {
// 省略代码
}案例二返回的结果和案例一一致,这说明了只需要一个 Bean 通过 @PropertySource 注解引用了 properties 配置文件后,其它的 Bean 无需再使用@PropertySource 注解引用即可通过 @Value 注入其中的值。
案例三:
java
@Getter
@Setter
public class TestBean {
private String attributeA;
private String attributeB;
}
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("AttributeA = " + testBean.getAttributeA());
System.out.println("AttributeB = " + testBean.getAttributeB());
return hello;
}
}
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:testBean/testBean.properties"/>
<bean id="testBean" class="com.test.TestBean">
<property name="attributeA" value="${valueA}"/>
<property name="attributeB" value="${valueB}"/>
<!-- 省略其它配置 -->
</bean>
</beans>testBean.properties 配置文件中的值如下:
java
valueA=testA
valueB=testB案例三执行的结果是 testBean 中的属性被正确替换为了 testBean.properties 配置文件中的值。
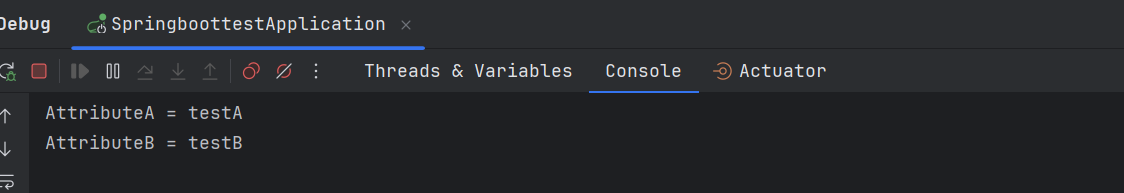
案例四:
在 hello.properties 文件中增加 attributeA 配置项,其它和案例三保持一致:
java
valueA=anotherTestA案例四执行的结果是 testBean 中的 attributeA 属性被替换为了 hello.properties 中的值,attributeB 中的属性被替换为了 testBean.properties 中的值。
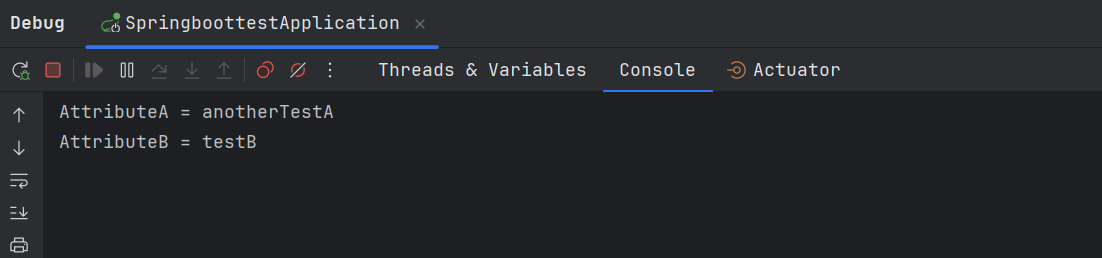
源码分析
@PropertySource注解
在 Spring 中提供了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,它提供了一个方法可以注册额外的 Bean 定义。代码如下:
java
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}Spring 中提供了 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 做为实现类,在它的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 通过 ConfigurationClassParser 去将 @Configuration 等注解修饰的类解析成 Bean 定义并注册。
而在 ConfigurationClassParser 中的 doProcessConfigurationClass() 方法会解析所有 @PropertySource 注解的配置信息,然后根据配置的路径加载对应路径下的配置文件,然后注册到 Environment 中。代码如下:
java
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass,
Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class,
PropertySources.class, true)) {
if (this.propertySourceRegistry != null) {
this.propertySourceRegistry.processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
}在 PropertySourceRegistry 的 processPropertySource() 方法中获取到注解配置的文件的位置,然后又委托给了 PropertySourceProcessor 处理。代码如下:
java
void processPropertySource(AnnotationAttributes propertySource) throws IOException {
String name = propertySource.getString("name");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
name = null;
}
String encoding = propertySource.getString("encoding");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(encoding)) {
encoding = null;
}
// 获取到注解中配置的配置文件的位置
String[] locations = propertySource.getStringArray("value");
Assert.isTrue(locations.length > 0, "At least one @PropertySource(value) location is required");
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = propertySource.getBoolean("ignoreResourceNotFound");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClass = propertySource.getClass("factory");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClassToUse =
(factoryClass != PropertySourceFactory.class ? factoryClass : null);
PropertySourceDescriptor descriptor = new PropertySourceDescriptor(Arrays.asList(locations),
ignoreResourceNotFound, name, factoryClassToUse, encoding);
//
this.propertySourceProcessor.processPropertySource(descriptor);
this.descriptors.add(descriptor);
}在 PropertySourceProcessor 的 processPropertySource() 方法中遍历每个配置文件位置加载配置文件,然后添加到 Environment 的 propertySources 中。代码如下:
java
public void processPropertySource(PropertySourceDescriptor descriptor) throws IOException {
String name = descriptor.name();
String encoding = descriptor.encoding();
List<String> locations = descriptor.locations();
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = descriptor.ignoreResourceNotFound();
PropertySourceFactory factory = (descriptor.propertySourceFactory() != null ?
instantiateClass(descriptor.propertySourceFactory()) : defaultPropertySourceFactory);
for (String location : locations) { // 遍历每个配置文件位置加载配置文件
try {
String resolvedLocation = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
for (Resource resource : this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(resolvedLocation)) {
addPropertySource(factory.createPropertySource(name, new EncodedResource(resource, encoding)));
}
} catch (RuntimeException | IOException ex) {
// 省略点
}
}
}
private void addPropertySource(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
String name = propertySource.getName();
MutablePropertySources propertySources = this.environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.propertySourceNames.contains(name)) {
// 省略代码
}
if (this.propertySourceNames.isEmpty()) {
propertySources.addLast(propertySource);
}
else {
String lastAdded = this.propertySourceNames.get(this.propertySourceNames.size() - 1);
// 添加到 propertySources 中
propertySources.addBefore(lastAdded, propertySource);
}
this.propertySourceNames.add(name);
}在 AbstractApplicationContext 中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法中,会先判断是否有注册 EmbeddedValueResolver,如果没有再注册,如果有的话就不注册了,这里和 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 联动起来了。代码如下:
java
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
而 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,它的 postProcessBeanFactory() 方法中,首先以 environment 对象构建一个 PropertySource 对象,添加到 propertySources 中;然后根据它自己配置的 location (即前面在xml中配置的 )构建一个 PropertySource 对象,添加到 propertySources 中,默认添加在尾部,这个对于解释场景四很重要 。最后基于 propertySources 构建了一个 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 对象去调用 processProperties() 方法。
java
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (this.propertySources == null) {
this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
if (this.environment != null) {
PropertyResolver propertyResolver = this.environment;
// If the ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders flag is set to true, we have to create a
// local PropertyResolver to enforce that setting, since the Environment is most
// likely not configured with ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders set to true.
// See https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues/27947
if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders &&
(this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment configurableEnvironment)) {
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver resolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(configurableEnvironment.getPropertySources());
resolver.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(true);
propertyResolver = resolver;
}
// 将environment构建为一个PropertySource对象
PropertyResolver propertyResolverToUse = propertyResolver;
this.propertySources.addLast(
new PropertySource<>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String key) {
return propertyResolverToUse.getProperty(key);
}
}
);
}
try {
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) {
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else { // 默认情况下是将配置加入到最后
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
processProperties(beanFactory, createPropertyResolver(this.propertySources));
this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources;
}在 processProperties() 方法中通过 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 对象又构造了一个 StringValueResolver 对象,然后调用了 doProcessProperties() 方法。代码如下:
java
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);
propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);
propertyResolver.setEscapeCharacter(this.escapeCharacter);
// 构造了一个StringValueResolver对象
StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {
String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?
propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :
propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));
if (this.trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved);
};
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}在 doProcessProperties() 方法中又通过 StringValueResolver 对象构造了一个 BeanDefinitionVisitor 对象,然后调用它的 visitBeanDefinition() 实现了对 Bean 定义中属性引用的解析。然后调用 BeanFactory 的 addEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法把 StringValueResolver 对象设置给了 BeanFactory,这里就和前面的AbstractApplicationContext 中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法呼应起来了,这里设置了值,那边就不设置了,这里没有设置,那边就会设置。
java
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
// 构造BeanDefinitionVisitor对象
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
// Check that we're not parsing our own bean definition,
// to avoid failing on unresolvable placeholders in properties file locations.
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
// 对Bean定义中引用的配置进行解析
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
// Resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well.
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
// Resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes.
// 添加到BeanFactory中
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}在之前的文章Spring 中 @Value 注解实现原理中介绍了在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的 resolveEmbeddedValue() 方法中实现了对 @Value 注解的解析,这里实际上就是调用的上面设置的 StringValueResolver 对象的 resolveStringValue() 方法来实现的。
java
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
}
return result;
}案例解答
对于案例二: 在解析 Bean 定义的时候会把所有 @PropertySource 注解定义配置文件解析到 Environment 集中保存起来,然后在解析 @Value 注解值的时候统一从这个集中的地方去查找。因此只需要有一个类通过 @PropertySource 注解引用这个配置即可。
对于案例三: 实际上是依赖实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,它的 postProcessBeanFactory() 方法中实现了在 Bean 真正创建之前,对 Bean 定义中引用属性的解析。
对于案例四: 在默认的情况下解析依赖的配置文件是所有 @PropertySource 引用的配置文件加上 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 的 location 属性引用的配置文件,且 @PropertySource 引用的配置文件在它的 location 属性引用的配置文件前面,查找的时候是按照顺序查找的。@PropertySource 引用的配置文件中定义了相同的 key,则直接会获取值返回,不会再继续往后查找了,所以就出现了案例四中 hello.properties 配置文件中的相同配置项覆盖了 testBean.properties 配置文件中的配置项。t
同时 Spring 提供了一个配置项 local-override,当设置为 true 时,才会使用testBean.properties 配置覆盖hello.properties 配置。覆盖的原理就是把配置加到最前面。代码如下:
xml
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:testBean.properties" local-override="true" />
java
try {
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) { // 设置为true的时候将配置加入到最前面
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else { // 默认情况下是将配置加入到最后
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}