Flowable BPMN:智能流程自动化技术全面指南
文章目录
- [Flowable BPMN:智能流程自动化技术全面指南](#Flowable BPMN:智能流程自动化技术全面指南)
-
- [Flowable BPMN基础概念与核心架构](#Flowable BPMN基础概念与核心架构)
- 主要功能特性深度解析
-
- [BPMN 2.0标准支持](#BPMN 2.0标准支持)
- 异步执行和性能优化
- [Spring Boot无缝集成](#Spring Boot无缝集成)
- BPMN流程定义与实战示例
-
- 创建请假流程
- [Spring Boot集成实现](#Spring Boot集成实现)
- 实际应用场景与最佳实践
- 快速上手指南
- [使用Flowable BPMN的核心优势](#使用Flowable BPMN的核心优势)
- 系统集成能力详解
- 企业级实施最佳实践
- 最新发展趋势:AI驱动的智能流程
- 结语:构建智能化的流程自动化平台
Flowable是一个轻量级、开源的Java业务流程引擎,完全支持BPMN 2.0标准,并在2025年推出了革命性的AI智能体功能,将传统流程自动化提升到智能自动化新高度。作为Activiti原班人马打造的新一代流程引擎,Flowable不仅性能卓越、功能全面,还通过多引擎架构支持BPMN、CMMN(案例管理)、DMN(决策管理)等多种标准,特别适合需要构建复杂业务流程自动化的企业级应用。本文将从基础概念到高级实践,全面介绍Flowable BPMN技术栈,帮助开发者快速掌握这一强大的流程自动化平台。
Flowable BPMN基础概念与核心架构
Flowable诞生于2016年10月,由Activiti的核心开发团队创建。作为一个Apache 2.0许可的开源项目,Flowable在继承Activiti优秀特性的基础上,进行了大量架构优化和功能增强。
什么是BPMN和流程引擎
**BPMN(Business Process Model and Notation)**是一种业务流程建模和标记的国际标准,提供了一套图形化的符号来描述业务流程。流程引擎则是执行这些BPMN模型的运行时环境。Flowable作为BPMN引擎,能够:
- 解析和执行BPMN 2.0 XML格式的流程定义
- 管理流程实例的生命周期
- 处理用户任务分配和完成
- 支持复杂的流程控制逻辑(条件、并行、循环等)
- 提供流程历史数据查询和分析
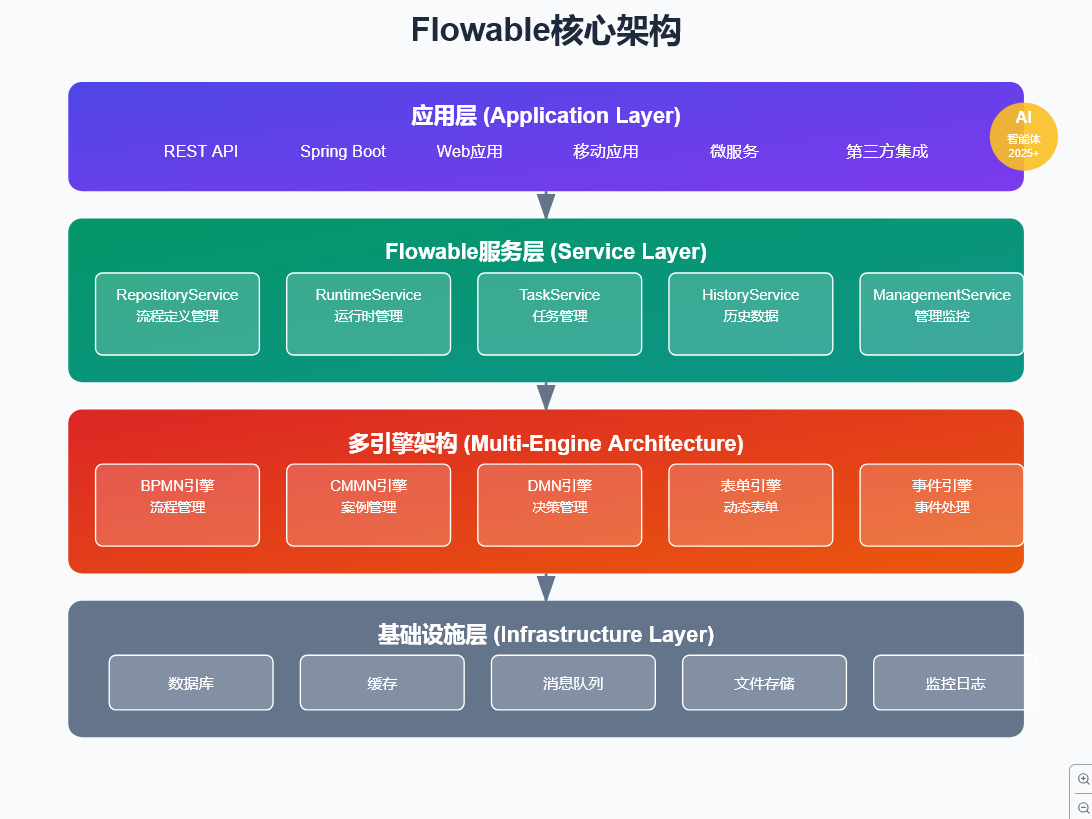
Flowable核心架构组件
Flowable采用服务导向架构,主要包含以下核心服务:
java
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngineConfiguration
.createStandaloneProcessEngineConfiguration()
.buildProcessEngine();
// 核心服务组件
RepositoryService repositoryService = processEngine.getRepositoryService(); // 流程定义管理
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService(); // 流程实例运行时管理
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService(); // 用户任务管理
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService(); // 历史数据查询
ManagementService managementService = processEngine.getManagementService(); // 管理和监控多引擎架构是Flowable的一大特色,除了核心的BPMN引擎外,还包括:
- CMMN引擎:处理案例管理,适合非结构化的知识工作
- DMN引擎:执行决策表,实现业务规则管理
- 事件注册引擎:支持事件驱动的流程编排
- 表单引擎:动态表单管理
- 内容引擎:文档和内容管理
下图展示了Flowable的完整架构分层:
主要功能特性深度解析
BPMN 2.0标准支持
Flowable提供了完整的BPMN 2.0标准实现,支持所有主要的BPMN元素:
- 事件类型:开始事件、结束事件、边界事件、中间捕获事件
- 活动类型:用户任务、服务任务、脚本任务、调用活动
- 网关类型:排他网关、并行网关、包容网关、事件网关
- 流程结构:子流程、事件子流程、事务子流程
- 高级特性:补偿、多实例、条件表达式
异步执行和性能优化
Flowable内置了高性能的异步执行器,支持:
- 全局锁机制保证分布式环境下的任务不重复执行
- 可配置的线程池大小和队列容量
- 批量处理优化数据库操作
- 瞬时变量减少数据库存储压力
性能基准测试显示,Flowable 6.3.0+版本在某些场景下吞吐量提升达100%,特别是在高并发和复杂流程场景下表现优异。
Spring Boot无缝集成
Flowable提供了完善的Spring Boot Starter,实现自动配置:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>7.0.0</version>
</dependency>配置文件示例(application.properties):
properties
# 数据库配置
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/flowable?characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=flowable
spring.datasource.password=flowable
# Flowable配置
flowable.database-schema-update=true
flowable.history-level=audit
flowable.async-executor-activate=trueBPMN流程定义与实战示例
创建请假流程
让我们通过一个完整的请假流程示例来理解Flowable的实际应用。下图展示了一个典型的请假申请BPMN流程:
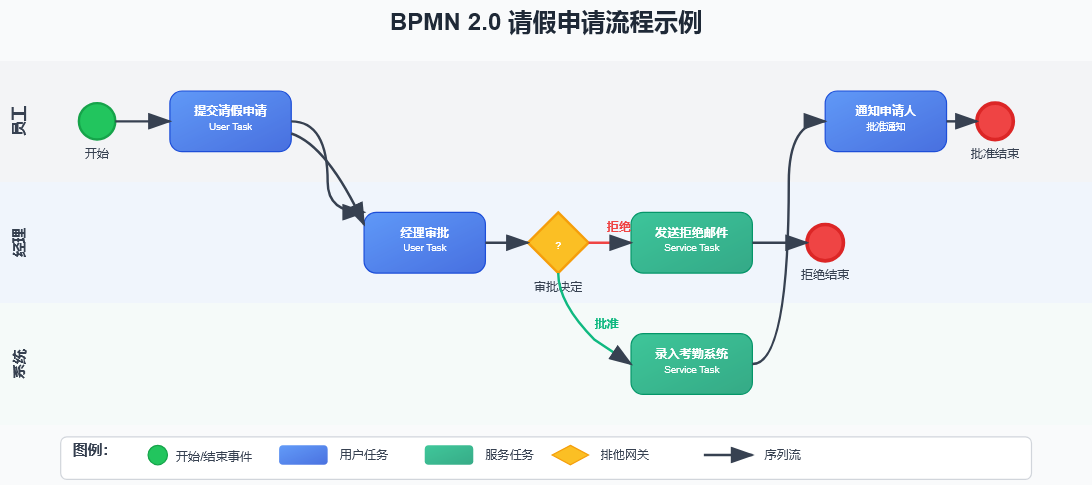
BPMN流程定义(holiday-request.bpmn20.xml):
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<definitions xmlns="http://www.omg.org/spec/BPMN/20100524/MODEL"
xmlns:flowable="http://flowable.org/bpmn"
targetNamespace="http://www.flowable.org/processdef">
<process id="holidayRequest" name="请假申请流程" isExecutable="true">
<startEvent id="startEvent" name="开始"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="startEvent" targetRef="approveTask"/>
<userTask id="approveTask" name="经理审批"
flowable:candidateGroups="managers"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="approveTask" targetRef="decision"/>
<exclusiveGateway id="decision" name="审批决定"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="decision" targetRef="externalSystemCall">
<conditionExpression>${approved}</conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="decision" targetRef="sendRejectionMail">
<conditionExpression>${!approved}</conditionExpression>
</sequenceFlow>
<serviceTask id="externalSystemCall" name="录入考勤系统"
flowable:class="com.example.CallExternalSystemDelegate"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="externalSystemCall" targetRef="holidayApprovedTask"/>
<userTask id="holidayApprovedTask" name="通知申请人"
flowable:assignee="${employee}"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="holidayApprovedTask" targetRef="approveEnd"/>
<serviceTask id="sendRejectionMail" name="发送拒绝邮件"
flowable:class="com.example.SendRejectionMail"/>
<sequenceFlow sourceRef="sendRejectionMail" targetRef="rejectEnd"/>
<endEvent id="approveEnd" name="批准结束"/>
<endEvent id="rejectEnd" name="拒绝结束"/>
</process>
</definitions>Spring Boot集成实现
服务层实现:
java
@Service
@Transactional
public class HolidayService {
@Autowired
private RuntimeService runtimeService;
@Autowired
private TaskService taskService;
@Autowired
private RepositoryService repositoryService;
// 提交请假申请
public String submitRequest(String employeeName, Integer days, String reason) {
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("employee", employeeName);
variables.put("nrOfHolidays", days);
variables.put("description", reason);
ProcessInstance processInstance =
runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("holidayRequest", variables);
return processInstance.getId();
}
// 获取待审批任务
public List<HolidayTask> getManagerTasks() {
List<Task> tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.taskCandidateGroup("managers")
.list();
return tasks.stream()
.map(this::convertToHolidayTask)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
// 完成审批
public void completeApproval(String taskId, boolean approved, String comments) {
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("approved", approved);
variables.put("comments", comments);
taskService.complete(taskId, variables);
}
private HolidayTask convertToHolidayTask(Task task) {
Map<String, Object> processVariables =
taskService.getVariables(task.getId());
return new HolidayTask(
task.getId(),
task.getName(),
(String) processVariables.get("employee"),
(Integer) processVariables.get("nrOfHolidays"),
(String) processVariables.get("description")
);
}
}REST控制器:
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/holiday")
public class HolidayController {
@Autowired
private HolidayService holidayService;
@PostMapping("/request")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> submitRequest(
@RequestBody HolidayRequest request) {
String processId = holidayService.submitRequest(
request.getEmployeeName(),
request.getDays(),
request.getReason()
);
Map<String, String> response = new HashMap<>();
response.put("processId", processId);
response.put("message", "请假申请已提交");
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
@GetMapping("/tasks")
public List<HolidayTask> getManagerTasks() {
return holidayService.getManagerTasks();
}
@PostMapping("/approve/{taskId}")
public ResponseEntity<String> approveRequest(
@PathVariable String taskId,
@RequestBody ApprovalRequest approval) {
holidayService.completeApproval(
taskId,
approval.isApproved(),
approval.getComments()
);
return ResponseEntity.ok("审批完成");
}
}实际应用场景与最佳实践
典型应用场景
Flowable在以下场景中表现出色:
1. 审批工作流
- 采购审批:基于金额阈值的多级审批
- 文档审批:合同、政策文档的审核流程
- 财务审批:报销、付款申请流程
2. 业务流程自动化
- 客户开户:身份验证、账户创建、欢迎邮件
- 订单处理:从下单到发货的全流程管理
- 保险理赔:复杂的多方参与案例处理
3. 微服务编排
- 分布式事务协调
- 服务间的复杂交互管理
- 补偿机制和错误处理
生产环境最佳实践
数据库配置优化:
- 使用生产级数据库(PostgreSQL、MySQL推荐)
- 配置合适的连接池大小
- 对于SQL Server,启用"Read Committed Snapshot"隔离级别
- 定期清理历史数据,保持性能
流程设计原则:
- 保持流程简洁清晰,避免过度复杂
- 使用有意义的活动和变量命名
- 实现完善的错误处理机制
- 考虑长时间运行流程的状态持久化
性能调优建议:
java
@Configuration
public class FlowableConfig {
@Bean
public ProcessEngineConfigurationConfigurer processEngineConfigurationConfigurer() {
return engineConfiguration -> {
// 异步执行器配置
engineConfiguration.setAsyncExecutorActivate(true);
engineConfiguration.setAsyncExecutorCorePoolSize(10);
engineConfiguration.setAsyncExecutorMaxPoolSize(50);
// 历史级别配置
engineConfiguration.setHistoryLevel(HistoryLevel.AUDIT);
// ID生成器配置(高并发场景)
engineConfiguration.setIdGenerator(new StrongUuidGenerator());
};
}
}快速上手指南
环境准备
系统要求:
- Flowable 7.x:需要Java 17+
- Flowable 6.x:支持Java 8+
- 数据库:H2(开发)、MySQL/PostgreSQL(生产)
Maven项目配置
创建Spring Boot项目并添加依赖:
xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- Flowable Spring Boot Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>7.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- REST API支持 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flowable</groupId>
<artifactId>flowable-spring-boot-starter-rest</artifactId>
<version>7.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>项目结构组织
推荐的项目结构:
src/main/
├── java/
│ └── com/example/flowable/
│ ├── FlowableApplication.java
│ ├── config/
│ │ └── FlowableConfig.java
│ ├── service/
│ │ └── ProcessService.java
│ ├── controller/
│ │ └── ProcessController.java
│ └── delegate/
│ └── ServiceTaskDelegate.java
└── resources/
├── processes/ # BPMN文件自动部署
│ └── my-process.bpmn20.xml
├── cases/ # CMMN文件
├── dmn/ # DMN文件
└── application.yml第一个流程示例
简单审批流程:
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class FlowableApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FlowableApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner init(final RepositoryService repositoryService,
final RuntimeService runtimeService,
final TaskService taskService) {
return args -> {
// 查看已部署的流程定义
System.out.println("流程定义数量: " +
repositoryService.createProcessDefinitionQuery().count());
// 启动流程实例
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("applicant", "张三");
variables.put("amount", 5000);
ProcessInstance processInstance = runtimeService
.startProcessInstanceByKey("expenseApproval", variables);
System.out.println("流程实例ID: " + processInstance.getId());
// 查询并完成任务
List<Task> tasks = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processInstanceId(processInstance.getId())
.list();
for (Task task : tasks) {
System.out.println("待处理任务: " + task.getName());
// 完成任务
taskService.complete(task.getId());
}
};
}
}使用Flowable BPMN的核心优势
技术优势
1. 标准合规性
Flowable完全遵循BPMN 2.0国际标准,确保流程定义的可移植性和互操作性。这意味着在Flowable中设计的流程可以轻松迁移到其他支持BPMN的平台。
2. 高性能架构
- 优化的数据库访问层,减少网络往返
- 智能的异步执行机制
- 支持流程实例迁移,无需停机更新
- 批量操作优化,提升大规模处理性能
3. 灵活的部署方式
- 嵌入式:直接集成到Java应用中
- 独立服务:通过REST API提供服务
- 容器化:Docker和Kubernetes原生支持
- 云部署:支持各种云平台部署
业务价值
提升效率:自动化重复性工作,减少人工操作错误,加快业务流程执行速度。
增强合规性:所有流程执行都有完整的审计跟踪,满足合规要求。
改善协作:清晰的流程定义促进跨部门协作,减少沟通成本。
敏捷响应:快速调整流程以适应业务变化,支持持续改进。
系统集成能力详解
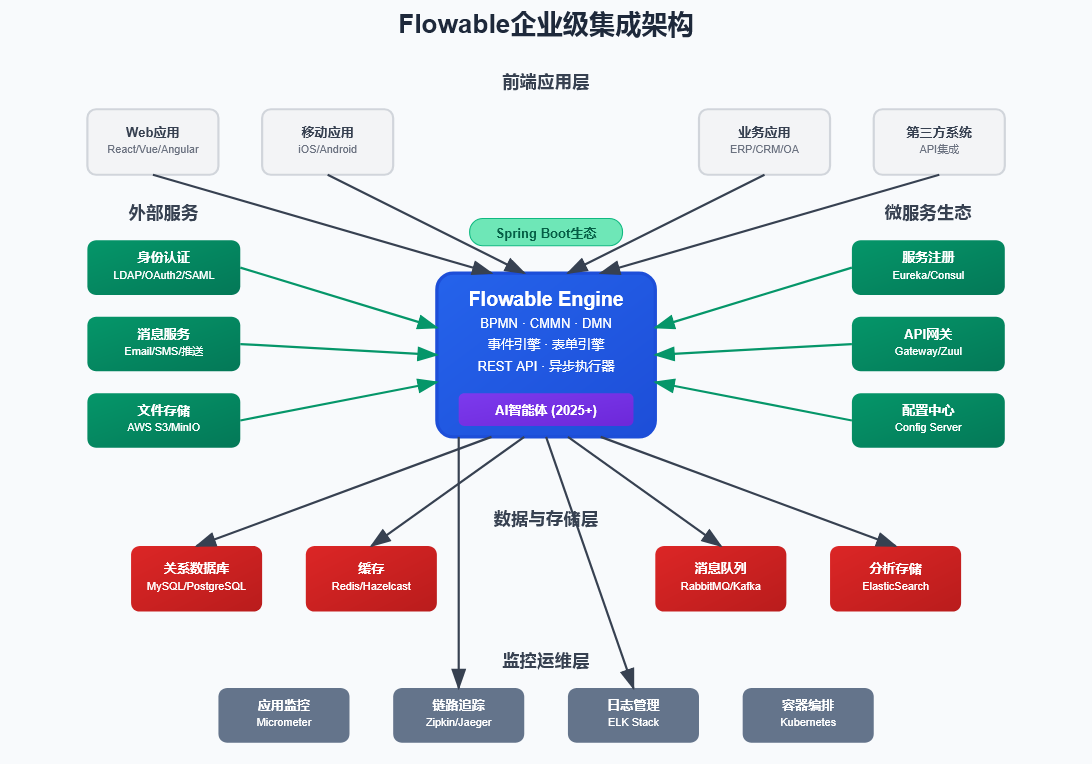
REST API集成
Flowable提供了完整的REST API,几乎覆盖所有Java API功能:
bash
# 启动流程实例
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/flowable-rest/service/runtime/process-instances \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u rest-admin:test \
-d '{
"processDefinitionKey": "holidayRequest",
"variables": [
{"name": "employee", "value": "张三"},
{"name": "nrOfHolidays", "value": 5}
]
}'
# 查询任务
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/flowable-rest/service/query/tasks \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-u rest-admin:test \
-d '{"candidateGroup": "managers"}'消息队列集成
Flowable事件注册引擎支持多种消息队列:
Kafka集成配置:
yaml
flowable:
eventregistry:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: flowable-consumer-group
producer:
retries: 3事件订阅示例:
java
@Component
public class OrderEventListener {
@EventListener
@Async
public void handleOrderCreated(FlowableEvent event) {
if ("order-created".equals(event.getType())) {
// 触发订单处理流程
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
variables.put("orderId", event.getData().get("orderId"));
variables.put("customerId", event.getData().get("customerId"));
runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey("orderProcess", variables);
}
}
}外部系统集成
HTTP任务配置:
xml
<serviceTask id="callRestApi" name="调用外部API">
<extensionElements>
<flowable:field name="requestMethod">
<flowable:string>POST</flowable:string>
</flowable:field>
<flowable:field name="requestUrl">
<flowable:expression>
https://api.example.com/orders/${orderId}/confirm
</flowable:expression>
</flowable:field>
<flowable:field name="requestHeaders">
<flowable:string>
Content-Type: application/json
Authorization: Bearer ${authToken}
</flowable:string>
</flowable:field>
</extensionElements>
</serviceTask>企业级实施最佳实践
流程治理
版本管理策略:
- 使用语义化版本号管理流程定义
- 实施流程发布审批机制
- 保留历史版本用于回滚
- 使用流程实例迁移功能平滑升级
监控和运维:
java
@Component
public class ProcessMonitor {
@Autowired
private ManagementService managementService;
@Autowired
private HistoryService historyService;
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 60000)
public void monitorProcesses() {
// 监控活跃流程实例
long activeInstances = runtimeService.createProcessInstanceQuery()
.active()
.count();
// 监控异步作业
long pendingJobs = managementService.createJobQuery()
.count();
// 监控死信作业
long deadletterJobs = managementService.createDeadLetterJobQuery()
.count();
// 发送监控指标
metricsService.send("flowable.active.instances", activeInstances);
metricsService.send("flowable.pending.jobs", pendingJobs);
metricsService.send("flowable.deadletter.jobs", deadletterJobs);
}
}安全性考虑
身份认证和授权:
java
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeHttpRequests(authz -> authz
.requestMatchers("/api/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.requestMatchers("/api/process/**").hasRole("USER")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.httpBasic()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public IdmIdentityService idmIdentityService() {
// 集成企业身份管理系统
return new CustomIdmIdentityService();
}
}高可用部署架构
集群部署配置:
yaml
flowable:
async-executor:
activate: true
core-pool-size: 10
max-pool-size: 50
keep-alive-time: 5000
# 数据库配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://mysql-cluster:3306/flowable?useSSL=false
username: flowable
password: ${DB_PASSWORD}
# 集群配置
process:
async:
executor:
default-async-job-acquire-wait-time: 5000
default-timer-job-acquire-wait-time: 5000最新发展趋势:AI驱动的智能流程
Flowable 2025.1革命性AI功能
Flowable最新版本引入了四种AI智能体类型,将传统BPM提升到智能自动化新境界:
1. 工具型智能体(Utility Agent)
- 数据增强和情感分析
- 文本分类和实体识别
- 自动数据转换和验证
2. 文档智能体(Document Agent)
- 非结构化文档处理(发票、合同、护照)
- 智能信息提取
- 多语言文档理解
3. 知识智能体(Knowledge Agent)
- 企业知识库集成
- RAG(检索增强生成)支持
- 上下文感知问答
4. 编排智能体(Orchestrator Agent)
- 智能案例和工作流协调
- 动态决策制定
- 自主客户沟通
AI集成示例
java
@Component
public class AIEnhancedProcess {
@Autowired
private FlowableAIService aiService;
// 使用AI智能体处理文档
public void processInvoiceWithAI(String processInstanceId, byte[] invoiceData) {
// 创建文档智能体任务
AIAgentTask documentTask = AIAgentTask.builder()
.agentType(AgentType.DOCUMENT)
.inputData(invoiceData)
.extractionFields(Arrays.asList(
"invoiceNumber", "totalAmount", "vendorName", "dueDate"
))
.build();
// 执行AI处理
AIAgentResult result = aiService.executeAgent(documentTask);
// 将提取的数据设置为流程变量
Map<String, Object> extractedData = result.getExtractedData();
runtimeService.setVariables(processInstanceId, extractedData);
}
// 使用知识智能体回答问题
public String answerProcessQuestion(String question, String processInstanceId) {
AIAgentTask knowledgeTask = AIAgentTask.builder()
.agentType(AgentType.KNOWLEDGE)
.question(question)
.context(getProcessContext(processInstanceId))
.build();
AIAgentResult result = aiService.executeAgent(knowledgeTask);
return result.getAnswer();
}
}云原生和容器化趋势
Docker部署示例:
dockerfile
FROM openjdk:17-jdk-slim
VOLUME /tmp
COPY target/flowable-app.jar app.jar
ENTRYPOINT ["java","-jar","/app.jar"]Kubernetes部署配置:
yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: flowable-engine
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: flowable
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: flowable
spec:
containers:
- name: flowable
image: flowable/flowable-rest:7.0.0
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_URL
value: jdbc:postgresql://postgres:5432/flowable
- name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_USERNAME
value: flowable
- name: SPRING_DATASOURCE_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: db-secret
key: password结语:构建智能化的流程自动化平台
Flowable BPMN已经从传统的流程引擎演进为综合性的智能自动化平台。通过结合BPMN标准流程管理、CMMN案例管理、DMN决策管理,以及最新的AI智能体能力,Flowable为企业提供了完整的业务流程自动化解决方案。
关键要点总结:
- 技术选型优势:完全开源、标准合规、高性能、易集成
- 架构灵活性:支持嵌入式、独立部署、云原生等多种部署方式
- 开发友好性:优秀的Spring Boot集成、完整的REST API、丰富的文档
- 企业级特性:生产级的可靠性、可扩展性和安全性
- 创新能力:AI智能体集成开启智能流程自动化新篇章
无论是构建简单的审批工作流,还是复杂的跨系统业务流程编排,Flowable都提供了强大而灵活的技术支撑。随着AI技术的深度集成,Flowable正在帮助企业从传统的流程自动化迈向智能化的业务流程管理新时代。对于正在寻求现代化流程管理解决方案的技术团队,Flowable无疑是一个值得深入研究和应用的优秀选择。