大纲
1.对动态代理接口的方法进行调用时的入口
2.动态代理基于Invoker执行RPC调用
3.服务发现获取目标服务实例集群Invokers
4.DynamicDirectory进行服务发现的流程
5.构造DubboInvoker并建立网络连接的过程
6.LoadBalance的负载均衡机制
7.Dubbo进行RPC调用时的异步执行过程
8.Dubbo进行RPC调用后会如何等待响应
9.NettyServer会如何调用本地代码
10.Dubbo的分层架构原理
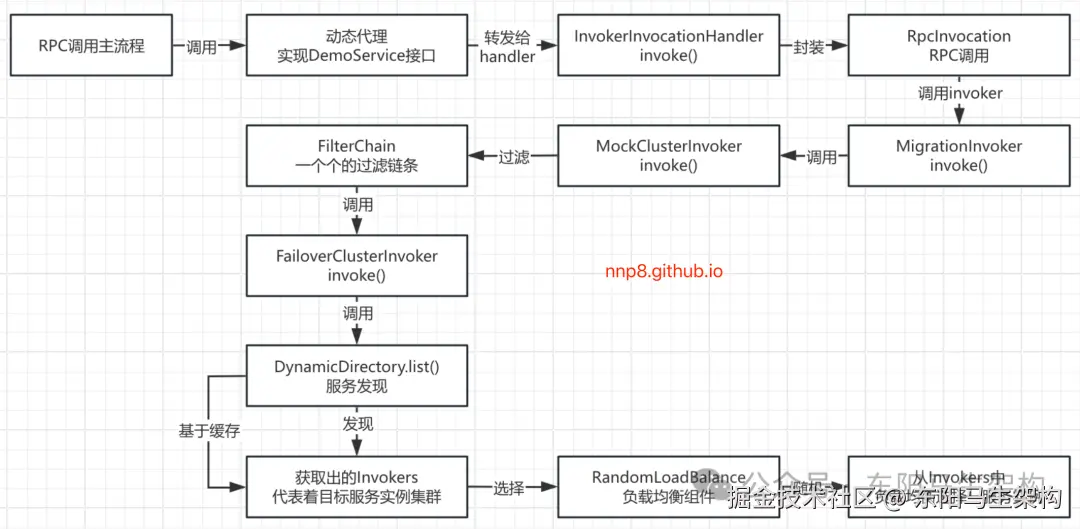
6.LoadBalance的负载均衡机制
处理负载均衡的入口是AbstractClusterInvoker的initLoadBalance()方法。
arduino
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke()
//-> MigrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> MockClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractCluster.ClusterFilterInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> ConsumerContextFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> FutureFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> MonitorFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> RouterSnapshotFilter.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()具体如下:
scss
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractLoadBalance.select()
//-> RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()
//如果要对一个目标服务实例进行RPC调用,那么负责调用的这个组件就可以叫做Invoker
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//检测当前Invoker是否已销毁
checkWhetherDestroyed();
InvocationProfilerUtils.enterDetailProfiler(invocation, () -> "Router route.");
//下面会根据invocation信息列出所有的Invoker
//也就是通过DynamicDirectory.list()方法进行服务发现
//由于通过Directory获取Invoker对象列表
//通过了解RegistryDirectory可知,其中已经调用了Router进行过滤
//从而可以知道有哪些服务实例、有哪些Invoker
//由于一个服务实例会对应一个Invoker,所以目标服务实例集群已变成invokers了
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
InvocationProfilerUtils.releaseDetailProfiler(invocation);
//通过SPI加载LoadBalance实例,也就是在这里选择出对应的负载均衡策略
//比如下面默认会获取到一个RandomLoadBalance
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
InvocationProfilerUtils.enterDetailProfiler(invocation, () -> "Cluster " + this.getClass().getName() + " invoke.");
try {
//调用由子类实现的抽象方法doInvoke()
//下面会由子类FailoverClusterInvoker执行doInvoke()方法
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
} finally {
InvocationProfilerUtils.releaseDetailProfiler(invocation);
}
}
//Init LoadBalance.
//if invokers is not empty, init from the first invoke's url and invocation
//if invokes is empty, init a default LoadBalance(RandomLoadBalance)
protected LoadBalance initLoadBalance(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
ApplicationModel applicationModel = ScopeModelUtil.getApplicationModel(invocation.getModuleModel());
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(invokers)) {
//通过SPI获取负载均衡组件
return applicationModel.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(
invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(
RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation), LOADBALANCE_KEY, DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE
)
);
} else {
return applicationModel.getExtensionLoader(LoadBalance.class).getExtension(DEFAULT_LOADBALANCE);
}
}
...
}
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
...
//该方法会找出一个Invoker
//把invocation交给多个Invokers里的一个去发起RPC调用
//其中会根据传入的loadbalance来实现负载均衡
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
//下面先做一个引用赋值
List<Invoker<T>> copyInvokers = invokers;
//检查Invokers
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
//从RPC调用里提取一个method方法名称,从而确定需要调用的是哪个方法
String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//计算最多调用次数;因为Failover策略是,如果发现调用不成功会进行重试,但默认会最多调用3次来让调用成功
int len = calculateInvokeTimes(methodName);
//retry loop.
RpcException le = null;//last exception.
//构建了一个跟invokers数量相等的一个list
List<Invoker<T>> invoked = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(copyInvokers.size());//invoked invokers.
//基于计算出的调用次数,构建一个set;如果调用次数为3,那么意味着最多会调用3个provider服务实例
Set<String> providers = new HashSet<String>(len);
//对len次数进行循环
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
//Reselect before retry to avoid a change of candidate `invokers`.
//NOTE: if `invokers` changed, then `invoked` also lose accuracy.
//到i>0时,表示的是第一次调用失败,要开始进行重试了
if (i > 0) {
//检查当前服务实例是否被销毁
checkWhetherDestroyed();
//此时要调用DynamicDirectory进行一次invokers列表刷新
//因为第一次调用都失败了,所以有可能invokers列表出现了变化,因而需要刷新一下invokers列表
copyInvokers = list(invocation);
//check again
//再次check一下invokers是否为空
checkInvokers(copyInvokers, invocation);
}
//1.下面会调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法
//select()方法会选择一个Invoker出来,具体逻辑是:
//首先尝试用负载均衡算法去选
//如果选出的Invoker是选过的或者不可用的,那么就直接reselect
//也就是对选过的找一个可用的,对选不出的直接挑选下一个
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
invoked.add(invoker);
RpcContext.getServiceContext().setInvokers((List) invoked);
boolean success = false;
try {
//2.调用AbstractClusterInvoker的invokeWithContext()方法
//基于该Invoker发起RPC调用,并拿到一个result
Result result = invokeWithContext(invoker, invocation);
if (le != null && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("...");
}
success = true;
return result;
} catch (RpcException e) {
//如果本次RPC调用失败了,那么就会有异常抛出来
if (e.isBiz()) {
throw e;
}
le = e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
le = new RpcException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
if (!success) {
//下面会把出现RPC调用异常的进行设置,把本次调用失败的invoker地址添加到providers
providers.add(invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
}
}
//如果最后抛出如下这个异常,则说明本次RPC调用彻底失败了
throw new RpcException("...");
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
//第一个参数是此次使用的LoadBalance实现
//第二个参数Invocation是此次服务调用的上下文信息
//第三个参数是待选择的Invoker集合
//第四个参数用来记录负载均衡已经选出来、尝试过的Invoker集合
protected Invoker<T> select(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
//invokers不能为空,为空的话就直接返回
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
}
//获取调用方法名,调用的方法名称处理逻辑是:
//如果RPC调用是null,则method方法名就是一个空字符串,否则就是RPC调用里的方法名称
String methodName = invocation == null ? StringUtils.EMPTY_STRING : invocation.getMethodName();
//下面会获取sticky的配置,其中sticky表示粘滞连接
//所谓粘滞连接是指Consumer会尽可能的调用同一个Provider节点,除非这个Provider无法提供服务
//invokers代表了服务集群地址,首先会根据invokers获取第一个invoker
//然后拿到这个invoker的URL,接着去获取URL中对应的sticky,其默认值是false
boolean sticky = invokers.get(0).getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, CLUSTER_STICKY_KEY, DEFAULT_CLUSTER_STICKY);
//ignore overloaded method
//检测invokers列表是否包含stickyInvoker
//如果不包含则说明stickyInvoker代表的服务提供者挂了,此时需要将其置空
if (stickyInvoker != null && !invokers.contains(stickyInvoker)) {
stickyInvoker = null;
}
//ignore concurrency problem
//如果开启了粘滞连接特性,则需要先判断这个Provider节点是否已经重试过了
//下面的判断前半部分表示粘滞连接,后半部分表示stickyInvoker未重试过
if (sticky && stickyInvoker != null && (selected == null || !selected.contains(stickyInvoker))) {
//检测当前stickyInvoker是否可用,如果可用,直接返回stickyInvoker
if (availableCheck && stickyInvoker.isAvailable()) {
return stickyInvoker;
}
}
//执行到这里,说明前面的stickyInvoker为空,或者不可用
//这里会继续调用doSelect选择新的Invoker对象
//也就是基于LoadBalance去进行负载均衡选择一个Invoker出来
Invoker<T> invoker = doSelect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected);
//是否开启粘滞,更新stickyInvoker为选择出来的invoker
//sticky表示粘滞连接(粘滞调用)
//所谓粘滞连接(粘滞调用)是指Consumer会尽可能的调用同一个Provider节点,除非这个Provider无法提供服务
//也就是把一个Consumer端和一个Provider端粘在一起
if (sticky) {
stickyInvoker = invoker;
}
return invoker;
}
private Invoker<T> doSelect(LoadBalance loadbalance, Invocation invocation, List<Invoker<T>> invokers, List<Invoker<T>> selected) throws RpcException {
//判断是否需要进行负载均衡,Invoker集合为空,直接返回null
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
return null;
}
//只有一个Invoker对象,直接返回即可
//如果invokers的数量就1个,那么目标Provider服务实例就一个
//所以直接返回invokers里的第一个即可
if (invokers.size() == 1) {
Invoker<T> tInvoker = invokers.get(0);
checkShouldInvalidateInvoker(tInvoker);
return tInvoker;
}
//通过LoadBalance实现选择Invoker对象
//即基于负载均衡的策略和算法选择出一个Invoker
Invoker<T> invoker = loadbalance.select(invokers, getUrl(), invocation);
//Invoke是否已经尝试调用过但是失败了
boolean isSelected = selected != null && selected.contains(invoker);
//Invoker是否不可用
boolean isUnavailable = availableCheck && !invoker.isAvailable() && getUrl() != null;
if (isUnavailable) {
invalidateInvoker(invoker);
}
//如果LoadBalance选出的Invoker对象,已经尝试请求过了或不可用,则需要调用reselect()方法进行重选
if (isSelected || isUnavailable) {
try {
//调用reselect()方法重选
Invoker<T> rInvoker = reselect(loadbalance, invocation, invokers, selected, availableCheck);
if (rInvoker != null) {
//如果重选的Invoker对象不为空,则直接返回这个rInvoker
invoker = rInvoker;
} else {
//Check the index of current selected invoker, if it's not the last one, choose the one at index+1.
//如果选来选去都是空,那么对当前Invoker就直接选择它的下一个invoker即可
int index = invokers.indexOf(invoker);
try {
//Avoid collision
//如果重选的Invoker对象为空,则返回该Invoker的下一个Invoker对象
invoker = invokers.get((index + 1) % invokers.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn(e.getMessage() + " may because invokers list dynamic change, ignore.", e);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.error("cluster reselect fail reason is :" + t.getMessage() + " if can not solve, you can set cluster.availablecheck=false in url", t);
}
}
return invoker;
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractLoadBalance implements LoadBalance {
...
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(invokers)) {
//Invoker集合为空,直接返回null
return null;
}
//Invoker集合只包含一个Invoker,则直接返回该Invoker对象
if (invokers.size() == 1) {
return invokers.get(0);
}
//Invoker集合包含多个Invoker对象时,交给doSelect()方法处理
//交给doSelect()方法是个抽象方法,留给子类具体实现
return doSelect(invokers, url, invocation);
}
protected abstract <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation);
...
}
public class RandomLoadBalance extends AbstractLoadBalance {
public static final String NAME = "random";
//Select one invoker between a list using a random criteria
@Override
protected <T> Invoker<T> doSelect(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) {
//先拿到目标服务实例集群的invokers数量
int length = invokers.size();
if (!needWeightLoadBalance(invokers, invocation)) {
//基于一个随机的类,通过其nextInt()方法拿到invokers数量范围之内的机器对应的invoker
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
//什么是权重?
//对于权重越高的invoker它被调用的几率会越高一些
//而这里随机负载均衡的invokers它们被调用到的机会/几率是相同的
//Every invoker has the same weight?
boolean sameWeight = true;
//the maxWeight of every invokers, the minWeight = 0 or the maxWeight of the last invoker
//计算每个Invoker对象对应的权重,并填充到weights[]数组中
int[] weights = new int[length];
//The sum of weights
int totalWeight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
//计算每个Invoker的权重,以及总权重totalWeight
int weight = getWeight(invokers.get(i), invocation);
//Sum
totalWeight += weight;
//save for later use
weights[i] = totalWeight;
//检测每个Provider的权重是否相同
if (sameWeight && totalWeight != weight * (i + 1)) {
sameWeight = false;
}
}
//各个Invoker权重值不相等时,计算随机数落在哪个区间上
if (totalWeight > 0 && !sameWeight) {
//If (not every invoker has the same weight & at least one invoker's weight>0), select randomly based on totalWeight.
//随机获取一个[0, totalWeight) 区间内的数字
int offset = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(totalWeight);
//Return a invoker based on the random value.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (offset < weights[i]) {
return invokers.get(i);
}
}
}
//If all invokers have the same weight value or totalWeight=0, return evenly.
//各个Invoker权重值相同时,随机返回一个Invoker即可
return invokers.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(length));
}
private <T> boolean needWeightLoadBalance(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, Invocation invocation) {
Invoker invoker = invokers.get(0);
URL invokerUrl = invoker.getUrl();
if (invoker instanceof ClusterInvoker) {
invokerUrl = ((ClusterInvoker<?>) invoker).getRegistryUrl();
}
// Multiple registry scenario, load balance among multiple registries.
if (REGISTRY_SERVICE_REFERENCE_PATH.equals(invokerUrl.getServiceInterface())) {
String weight = invokerUrl.getParameter(WEIGHT_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(weight)) {
return true;
}
} else {
String weight = invokerUrl.getMethodParameter(invocation.getMethodName(), WEIGHT_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(weight)) {
return true;
} else {
String timeStamp = invoker.getUrl().getParameter(TIMESTAMP_KEY);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(timeStamp)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
...
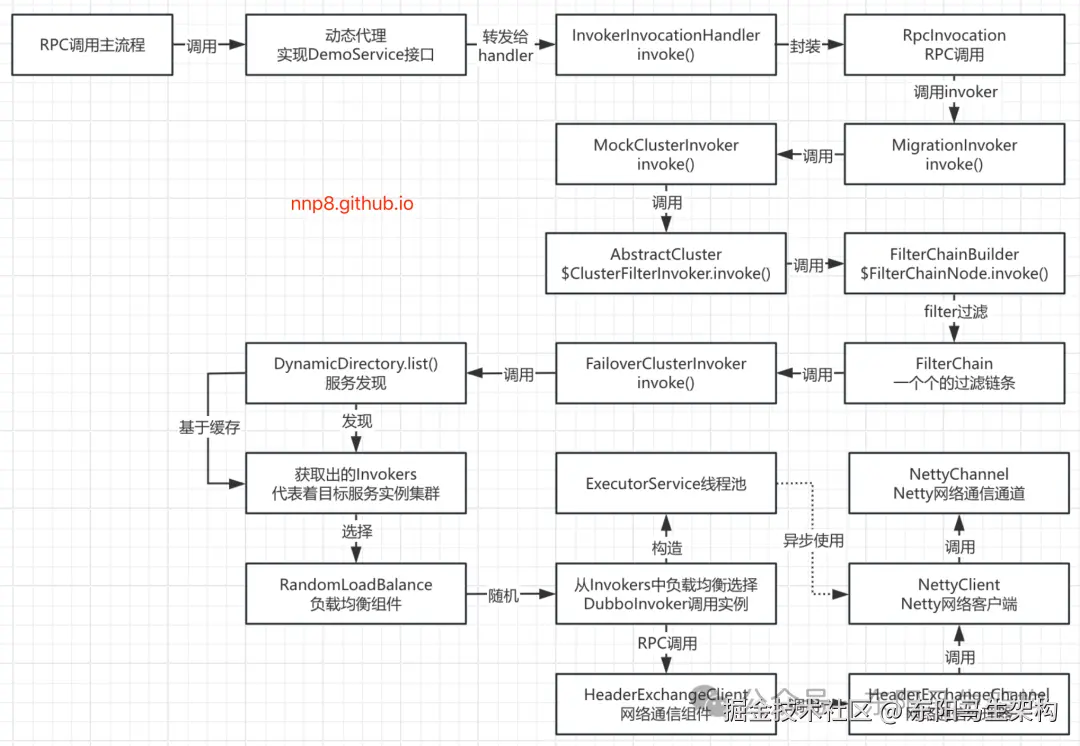
}通过负载均衡机制选出一个Invoker之后,就可以在FailoverClusterInvoker的doInvoke()方法中,通过FailoverClusterInvoker父类AbstractClusterInvoker的invokeWithContext()方法去执行Invoker的invoke()方法进行RPC调用。
java
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invokeWithContext()
//-> ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.invoke()
public class FailoverClusterInvoker<T> extends AbstractClusterInvoker<T> {
...
//该方法会找一个Invoker,把invocation交给多个Invokers里的一个去发起RPC调用
public Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation, final List<Invoker<T>> invokers, LoadBalance loadbalance) throws RpcException {
...
//1.下面会调用AbstractClusterInvoker的select()方法
//select()方法会选择一个Invoker出来,具体逻辑是:
//首先尝试用负载均衡算法去选
//如果选出的Invoker是选过的或者不可用的,那么就直接reselect
//也就是对选过的找一个可用的,对选不出的直接挑选下一个
Invoker<T> invoker = select(loadbalance, invocation, copyInvokers, invoked);
...
//2.调用AbstractClusterInvoker的invokeWithContext()方法
//基于该Invoker发起RPC调用,并拿到一个result
Result result = invokeWithContext(invoker, invocation);
...
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
...
protected Result invokeWithContext(Invoker<T> invoker, Invocation invocation) {
setContext(invoker);
Result result;
try {
if (ProfilerSwitch.isEnableSimpleProfiler()) {
InvocationProfilerUtils.enterProfiler(invocation, "Invoker invoke. Target Address: " + invoker.getUrl().getAddress());
}
//下面会调用ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke()方法
result = invoker.invoke(invocation);
} finally {
clearContext(invoker);
InvocationProfilerUtils.releaseSimpleProfiler(invocation);
}
return result;
}
...
}
public class ListenerInvokerWrapper<T> implements Invoker<T> {
//这是一个DubboInvoker
private final Invoker<T> invoker;
...
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//下面会调用DubboInvoker的父类AbstractInvoker.invoke()方法
return invoker.invoke(invocation);
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
...
//首先将传入的Invocation转换为RpcInvocation
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
//prepare rpc invocation
prepareInvocation(invocation);
//do invoke rpc invocation and return async result
//RPC调用返回的结果是异步的:async
AsyncRpcResult asyncResult = doInvokeAndReturn(invocation);
//wait rpc result if sync
//默认情况下发起的RPC请求是异步化操作
//但如果需要同步的话,那么是可以在这里等待同步的结果
waitForResultIfSync(asyncResult, invocation);
return asyncResult;
}
private AsyncRpcResult doInvokeAndReturn(RpcInvocation invocation) {
...
//调用子类实现的doInvoke()方法
//比如DubboInvoker的doInvoke()方法
asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult) doInvoke(invocation);
...
}
protected abstract Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
...
}7.Dubbo进行RPC调用时的异步执行过程
在AbstractInvoker的invoke()方法中,会通过调用AbstractInvoker的doInvokeAndReturn()方法来开始异步执行RPC调用。
arduino
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke() [invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()]
//...
//-> AbstractInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.doInvokeAndReturn()
//-> DubboInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.getCallbackExecutor()
//-> 配合线程池使用currentClient.request()发起RPC请求
//-> ReferenceCountExchangeClient.request()
//-> HeaderExchangeClient.request()
//-> HeaderExchangeChannel.request()
//-> DefaultFuture.newFuture()
//-> NettyClient.send() => AbstractPeer.send() => AbstractClient.send()
//-> NettyChannel.send() => channel.writeAndFlush()
scss
public abstract class AbstractInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
...
//首先将传入的Invocation转换为RpcInvocation
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
//prepare rpc invocation
prepareInvocation(invocation);
//do invoke rpc invocation and return async result,RPC调用返回的结果是异步的:async
AsyncRpcResult asyncResult = doInvokeAndReturn(invocation);
//wait rpc result if sync
//默认情况下发起的RPC请求是异步化操作,但如果需要同步的话,那么是可以在这里等待同步的结果
waitForResultIfSync(asyncResult, invocation);
return asyncResult;
}
private AsyncRpcResult doInvokeAndReturn(RpcInvocation invocation) {
...
//调用子类实现的doInvoke()方法
//比如DubboInvoker的doInvoke()方法
asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult) doInvoke(invocation);
...
}
protected abstract Result doInvoke(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
protected ExecutorService getCallbackExecutor(URL url, Invocation inv) {
//首先通过SPI机制拿到ExecutorRepository------线程池存储组件
//Dubbo会把内部所有的线程池都存放在该线程池存储组件里,或者要创建新的线程池也是通过它
//model组件体系,其实就是封装了dubbo内部所有的公共的组件体系,可以用设计模式来形容
//model组件设计思想就是门面模式,Model(本身是没有意义的) -> 门面,它封装了很多的组件如SPI、service数据、配置、Repository组件、BeanFactory
//model就成为了一个门面,在整个dubbo框架里,如果要用到一些公共组件,就直接找model去获取就可以了
if (InvokeMode.SYNC == RpcUtils.getInvokeMode(getUrl(), inv)) {
return new ThreadlessExecutor();
}
return url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel()
.getExtensionLoader(ExecutorRepository.class)
.getDefaultExtension()
.getExecutor(url);
}
...
}
public class DubboInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
//ExchangeClient底层封装的就是NettyClient
private final ExchangeClient[] clients;
private final Set<Invoker<?>> invokers;
...
public DubboInvoker(Class<T> serviceType, URL url, ExchangeClient[] clients, Set<Invoker<?>> invokers) {
super(serviceType, url, new String[]{INTERFACE_KEY, GROUP_KEY, TOKEN_KEY});
//DubboProtocol的protocolBindingRefer()方法在构建DubboInvoker时
//会先通过DubboProtocol的getClients()方法获取ReferenceCountExchangeClient
//然后再将这些ReferenceCountExchangeClient传入这里去构建DubboInvoker
this.clients = clients;
this.invokers = invokers;
...
}
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation inv = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
//此次调用的方法名称
final String methodName = RpcUtils.getMethodName(invocation);
//向Invocation中添加附加信息
//这里将URL的path和version添加到附加信息中
inv.setAttachment(PATH_KEY, getUrl().getPath());
inv.setAttachment(VERSION_KEY, version);
//ExchangeClient和Exchange都是跟网络相关的
ExchangeClient currentClient;
if (clients.length == 1) {
//选择一个ExchangeClient实例
currentClient = clients[0];
} else {
//如果有多个用于网络通信的Client,就会逐个去使用,这会是一个循环使用的过程
currentClient = clients[index.getAndIncrement() % clients.length];
}
try {
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
//根据调用的方法名称和配置计算此次调用的超时时间,默认是1秒
int timeout = calculateTimeout(invocation, methodName);
invocation.setAttachment(TIMEOUT_KEY, timeout);
if (isOneway) {
//不需要关注返回值的请求
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
} else {
//需要关注返回值的请求
//1.获取处理响应的线程池
//下面会调用AbstractInvoker的getCallbackExecutor()方法
//对于同步请求,会使用ThreadlessExecutor
//对于异步请求,则会使用共享的线程池
ExecutorService executor = getCallbackExecutor(getUrl(), inv);
//2.发起网络请求
//currentClient.request()会使用上面选出的ExchangeClient执行request()方法将请求发送出去
//下面其实会调用ReferenceCountExchangeClient的request()方法
//thenApply()会将AppResponse封装成AsyncRpcResult返回
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture =
currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor).thenApply(obj -> (AppResponse) obj);
//3.处理请求的响应结果
//save for 2.6.x compatibility, for example, TraceFilter in Zipkin uses com.alibaba.xxx.FutureAdapter
FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture);
AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv);
result.setExecutor(executor);
//要想拿到AppResponse结果,就需要基于CompletableFuture进行同步等待
//只要Provider返回响应结果,就必然会写入到CompletableFuture里
//此时就可以通过CompletableFuture取出AppResponse结果了
//比如InvocationUtil的invoke()方法在执行"invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()"时
//就会调用AsyncRpcResult的recreate()方法来获取Provider返回的响应结果
//也就是会调用到CompletableFuture的get()方法获取Provider返回的响应结果
return result;
}
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
...
}
}
...
}
public class AsyncRpcResult implements Result {
private CompletableFuture<AppResponse> responseFuture;
private Invocation invocation;
private final boolean async;
private Executor executor;
private RpcContext.RestoreContext storedContext;
...
public AsyncRpcResult(CompletableFuture<AppResponse> future, Invocation invocation) {
this.responseFuture = future;
this.invocation = invocation;
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
if ((rpcInvocation.get(PROVIDER_ASYNC_KEY) != null || InvokeMode.SYNC != rpcInvocation.getInvokeMode()) && !future.isDone()) {
async = true;
this.storedContext = RpcContext.clearAndStoreContext();
} else {
async = false;
}
}
@Override
public Object recreate() throws Throwable {
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = (RpcInvocation) invocation;
//对InvokeMode模式进行判断
if (InvokeMode.FUTURE == rpcInvocation.getInvokeMode()) {
//如果模式为FUTURE,则表示支持异步化,所以返回的就是一个future对象
//而这个future异步对象代表的就是一个异步化结果,此时可能有结果了也可能没有结果,这需要自己去获取
return RpcContext.getClientAttachment().getFuture();
} else if (InvokeMode.ASYNC == rpcInvocation.getInvokeMode()) {
//如果模式是ASYNC,则创建默认结果返回
return createDefaultValue(invocation).recreate();
}
//如果模式SYNC
return getAppResponse().recreate();
}
public Result getAppResponse() {
try {
//DubboInvoker.doInvoke()方法返回的AsyncRpcResult会封装一个CompletableFuture进去
//这里首先会做一个判断
//如果CompletableFuture的isDone()方法返回true,则表示已经完成请求并拿到了响应
//响应结果会通过HeaderExchangeHandler.received()被放到CompletableFuture里面
if (responseFuture.isDone()) {//检测responseFuture是否已完成
//从CompletableFuture进行阻塞式循环获取AppResponse并进行返回
return responseFuture.get();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//This should not happen in normal request process;
logger.error("Got exception when trying to fetch the underlying result from AsyncRpcResult.");
throw new RpcException(e);
}
//根据调用方法的返回值,生成默认值
return createDefaultValue(invocation);
}
@Override
public Result get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
if (executor != null && executor instanceof ThreadlessExecutor) {
//针对ThreadlessExecutor的特殊处理,这里调用waitAndDrain()等待响应
ThreadlessExecutor threadlessExecutor = (ThreadlessExecutor) executor;
threadlessExecutor.waitAndDrain();
}
//非ThreadlessExecutor线程池的场景中
//则直接调用Future(最底层是DefaultFuture)的get()方法阻塞
return responseFuture.get();
}
@Override
public Result get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (executor != null && executor instanceof ThreadlessExecutor) {
//针对ThreadlessExecutor的特殊处理,这里调用waitAndDrain()等待响应
ThreadlessExecutor threadlessExecutor = (ThreadlessExecutor) executor;
threadlessExecutor.waitAndDrain();
}
//非ThreadlessExecutor线程池的场景中
//则直接调用Future(最底层是DefaultFuture)的get()方法阻塞
return responseFuture.get(timeout, unit);
}
...
}
java
final class ReferenceCountExchangeClient implements ExchangeClient {
private ExchangeClient client;
...
//ReferenceCountExchangeClient的构入口是DubboProtocol的initClient()方法
public ReferenceCountExchangeClient(ExchangeClient client, String codec) {
this.client = client;
this.referenceCount.incrementAndGet();
this.url = client.getUrl();
}
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
//下面会调用HeaderExchangeClient.request()方法
return client.request(request, timeout, executor);
}
...
}
public class HeaderExchangeClient implements ExchangeClient {
...
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
//下面会调用HeaderExchangeChannel.request()
return channel.request(request, timeout, executor);
}
...
}
final class HeaderExchangeChannel implements ExchangeChannel {
...
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
...
//为什么Dubbo中要设计出来Exchange这一层
//官方的解释是Exchange这一层会负责同步转异步
//也就是进行Request/Response网络请求响应模型的封装
//当Consumer端最终发送请求时,最终会执行到这里
//这里首先会构建一个Request,把RpcInvocation对象封装为Request对象
//也就是把一个业务语义的对象RpcInvocation,封装为网络通信里的请求响应模型里的Request对象
//因此从这一步开始,会进入网络通信的范围,引入Request这些概念,便是多年架构经验设计出来的
//如果直接将RpcInvocation交给Netty框架去进行处理,那么就不太符合网络通信的请求响应模型了
//然后会创建future,并调用channel.send()进行请求发送,而这又涉及了同步转异步的过程
//也就是最后会直接返回一个future,如果需要同步等待响应,那么可以调用future.get()方法进行阻塞
//create request.
Request req = new Request();
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
//双向请求,表示请求过去了还得返回对应的响应
req.setTwoWay(true);
//这个request就是我们的RpcInvocation
req.setData(request);
//创建完一个future后,调用方后续在收到响应结果时会再来进行处理
//所以返回的异步future结果,与发送请求是脱离开来的
//下面会将NettyClient、request、timeout、线程池executor,封装成一个future
DefaultFuture future = DefaultFuture.newFuture(channel, req, timeout, executor);
//正常情况下,一般不会有超时问题
try {
//下面会调用NettyClient的send()方法
//也就是调用AbstractPeer.send()方法,因为NettyClient没有覆盖其父类的send()方法
//AbstractClient.send()又会调用NettyChannel.send()方法
//NettyChannel.send()又会调用Netty底层的channel的writeAndFlush()方法
//会同步发起请求,但默认不会等待请求完成了才返回
channel.send(req);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
future.cancel();
throw e;
}
return future;
}
...
}
public class DefaultFuture extends CompletableFuture<Object> {
private final Channel channel;
private final Request request;
private final Long id;
private final int timeout;
//请求ID和DefaultFuture的映射关系
private static final Map<Long, DefaultFuture> FUTURES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//请求ID和Channel的映射关系
private static final Map<Long, Channel> CHANNELS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private static final GlobalResourceInitializer<Timer> TIME_OUT_TIMER =
new GlobalResourceInitializer<>(
() -> new HashedWheelTimer(new NamedThreadFactory("dubbo-future-timeout", true), 30, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS),
DefaultFuture::destroy
);
...
private DefaultFuture(Channel channel, Request request, int timeout) {
this.channel = channel;
this.request = request;
this.id = request.getId();
this.timeout = timeout > 0 ? timeout : channel.getUrl().getPositiveParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
//put into waiting map.
FUTURES.put(id, this);
CHANNELS.put(id, channel);
}
public static DefaultFuture newFuture(Channel channel, Request request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) {
//1.根据channel、request、timeout创建DefaultFuture对象
//然后设置其线程池为executor,该过程只是简单的赋值操作
final DefaultFuture future = new DefaultFuture(channel, request, timeout);
future.setExecutor(executor);
//ThreadlessExecutor needs to hold the waiting future in case of circuit return.
if (executor instanceof ThreadlessExecutor) {
((ThreadlessExecutor) executor).setWaitingFuture(future);
}
//2.timeout check
timeoutCheck(future);
return future;
}
//利用TIME_OUT_TIMER时间轮启动一个定时任务进行task超时检查
private static void timeoutCheck(DefaultFuture future) {
TimeoutCheckTask task = new TimeoutCheckTask(future.getId());
future.timeoutCheckTask = TIME_OUT_TIMER.get().newTimeout(task, future.getTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
...
}
public class NettyClient extends AbstractClient {
...
...
}
public abstract class AbstractPeer implements Endpoint, ChannelHandler {
...
public void send(Object message) throws RemotingException {
//false表示不会同步等待发送完毕后才返回
//从入参为false可知,NettyChannel发送数据时,默认就是异步化的
//比如下面会调用AbstractClient.send()
send(message, url.getParameter(Constants.SENT_KEY, false));
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractClient extends AbstractEndpoint implements Client {
private final Lock connectLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final boolean needReconnect;
protected volatile ExecutorService executor;
...
public AbstractClient(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
//调用父类的构造方法
super(url, handler);
//解析URL,初始化needReconnect值
needReconnect = url.getParameter(Constants.SEND_RECONNECT_KEY, true);
//解析URL,初始化executor线程池
initExecutor(url);
try {
//初始化底层的NIO库的相关组件
doOpen();
} catch (Throwable t) {
close();
throw new RemotingException("...");
}
try {
//connect创建底层连接
connect();
} catch (Throwable t) {
close();
throw new RemotingException("...");
}
}
private void initExecutor(URL url) {
ExecutorRepository executorRepository = url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel()
.getExtensionLoader(ExecutorRepository.class).getDefaultExtension();
url = url.addParameter(THREAD_NAME_KEY, CLIENT_THREAD_POOL_NAME)
.addParameterIfAbsent(THREADPOOL_KEY, DEFAULT_CLIENT_THREADPOOL);
executor = executorRepository.createExecutorIfAbsent(url);
}
@Override
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
if (needReconnect && !isConnected()) {
connect();
}
//比如下面会获取到NettyChannel
Channel channel = getChannel();
if (channel == null || !channel.isConnected()) {
throw new RemotingException(this, "message can not send, because channel is closed . url:" + getUrl());
}
//比如下面会调用NettyChannel.send()
//因为NettyClient的doConnect()方法建立连接时会拿到一个Channel
//然后将这个Channel赋值到NettyClient的channel属性中
channel.send(message, sent);
}
protected void connect() throws RemotingException {
connectLock.lock();
try {
doConnect();
} finally {
connectLock.unlock();
}
}
...
}
final class NettyChannel extends AbstractChannel {
...
public void send(Object message, boolean sent) throws RemotingException {
...
//下面这行代码的channel是一个NioSocketChannel
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(message);
if (sent) {
//wait timeout ms
timeout = getUrl().getPositiveParameter(TIMEOUT_KEY, DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
success = future.await(timeout);
}
...
}
...
}8.Dubbo进行RPC调用后会如何等待响应
AbstractInvoker的waitForResultIfSync()方法是等待响应的入口。
java
//-> InvokerInvocationHandler.invoke()
//-> InvocationUtil.invoke() [invoker.invoke(rpcInvocation).recreate()]
//...
//-> MigrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> MockClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractCluster.ClusterFilterInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CallbackRegistrationInvoker.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> ConsumerContextFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> FutureFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> MonitorFilter.invoke()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.CopyOfFilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> RouterSnapshotFilter.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.initLoadBalance()
//-> FailoverClusterInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.select()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.doSelect()
//-> AbstractLoadBalance.select()
//-> RandomLoadBalance.doSelect()
//-> AbstractClusterInvoker.invokeWithContext()
//-> ListenerInvokerWrapper.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.invoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.doInvokeAndReturn()
//-> DubboInvoker.doInvoke()
//-> AbstractInvoker.waitForResultIfSync()
//-> AsyncRpcResult.get()
public abstract class AbstractInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation inv) throws RpcException {
...
//首先将传入的Invocation转换为RpcInvocation
RpcInvocation invocation = (RpcInvocation) inv;
//prepare rpc invocation
prepareInvocation(invocation);
//do invoke rpc invocation and return async result,RPC调用返回的结果是异步的:async
AsyncRpcResult asyncResult = doInvokeAndReturn(invocation);
//wait rpc result if sync
//默认情况下发起的RPC请求是异步化操作,但如果需要同步的话,那么是可以在这里等待同步的结果
waitForResultIfSync(asyncResult, invocation);
return asyncResult;
}
private AsyncRpcResult doInvokeAndReturn(RpcInvocation invocation) {
...
//调用子类实现的doInvoke()方法
//比如DubboInvoker的doInvoke()方法
asyncResult = (AsyncRpcResult) doInvoke(invocation);
...
}
private void waitForResultIfSync(AsyncRpcResult asyncResult, RpcInvocation invocation) {
...
Object timeout = invocation.getObjectAttachmentWithoutConvert(TIMEOUT_KEY);
if (timeout instanceof Integer) {
asyncResult.get((Integer) timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
asyncResult.get(Integer.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
...
}
...
}
public class AsyncRpcResult implements Result {
private CompletableFuture<AppResponse> responseFuture;
...
public Result get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
if (executor != null && executor instanceof ThreadlessExecutor) {
//针对ThreadlessExecutor的特殊处理,这里调用waitAndDrain()等待响应
ThreadlessExecutor threadlessExecutor = (ThreadlessExecutor) executor;
threadlessExecutor.waitAndDrain();
}
//非ThreadlessExecutor线程池的场景中,则直接调用Future(最底层是DefaultFuture)的get()方法阻塞
return responseFuture.get();
}
...
}9.NettyServer会如何调用本地代码
Consumer端发送过来的RPC请求,会由Provider端的NettyServer进行处理。
bash
//-> NettyServer
//-> NettyServerHandler.channelRead()
//-> NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel() [读取请求,获取到NettyChannel]
//-> AbstractPeer.received()
//-> MultiMessageHandler.received()
//-> HeartbeatHandler.received()
//-> AllChannelHandler.received()
//-> WrappedChannelHandler.getPreferredExecutorService() [获取线程池]
//-> new ChannelEventRunnable()
//-> AllChannelHandler.received()#executor.execute() [提交一个异步任务给线程池进行处理]
//-> ChannelEventRunnable.run() [启动任务处理请求]
//-> DecodeHandler.received()
//-> HeaderExchangeHandler.received()
//-> HeaderExchangeHandler.handleRequest() [对请求进行处理]
//-> DubboProtocol.requestHandler.reply()
//-> FilterChainBuilder.FilterChainNode.invoke()
//-> AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke() [在FilterChain中最终会跑到AbstractProxyInvoker.invke()]
//-> JavassistProxyFactory.getInvoker().doInvoke()
//-> 目标实现类方法
java
public class NettyServer extends AbstractServer {
private EventLoopGroup bossGroup;
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
private Map<String, Channel> channels;
private io.netty.channel.Channel channel;
private final int serverShutdownTimeoutMills;
//NettyServer在构建的过程中,会构建和打开真正的网络服务器
//这里是基于netty4技术去实现了网络服务器构建和打开的,一旦打开后,Netty Server就开始监听指定的端口号
//当发现有请求过来就可以去进行处理,也就是通过ProxyInvoker去调用本地实现类的目标方法
//入参handler其实就是DubboProtocol中的requestHandler
//入参handler会先被HeartbeatHandler装饰,再被MultiMessageHandler装饰,再被其他修饰等等
public NettyServer(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException {
//you can customize name and type of client thread pool by THREAD_NAME_KEY and THREAD_POOL_KEY in CommonConstants.
//the handler will be wrapped: MultiMessageHandler -> HeartbeatHandler -> handler
super(ExecutorUtil.setThreadName(url, SERVER_THREAD_POOL_NAME), ChannelHandlers.wrap(handler, url));
//read config before destroy
serverShutdownTimeoutMills = ConfigurationUtils.getServerShutdownTimeout(getUrl().getOrDefaultModuleModel());
}
//Init and start netty server
@Override
protected void doOpen() throws Throwable {
//创建ServerBootstrap
bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//EventLoop,也可以理解为网络服务器,它会监听一个本地的端口号
//外部系统针对本地服务器端口号发起连接、通信、网络事件时,监听的端口号就会不停的产生网络事件
//EventLoop网络服务器,还会不停轮询监听到的网络事件
//boss的意思是负责监听端口号是否有外部系统的连接请求,它是一个EventLoopGroup线程池
//如果发现了网络事件,就需要进行请求处理,可以通过workerGroup里的多个线程进行并发处理
//创建boss EventLoopGroup,线程数是1
bossGroup = createBossGroup();
//创建worker EventLoopGroup,线程数是CPU核数 + 1,但最多不会超过32个线程
workerGroup = createWorkerGroup();
//创建NettyServerHandler
//它是一个Netty中的ChannelHandler实现,不是Dubbo Remoting层的ChannelHandler接口的实现
final NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler = createNettyServerHandler();
//获取当前NettyServer创建的所有Channel
//channels集合中的Channel不是Netty中的Channel对象,而是Dubbo Remoting层的Channel对象
channels = nettyServerHandler.getChannels();
//初始化ServerBootstrap,指定boss和worker EventLoopGroup
initServerBootstrap(nettyServerHandler);
//绑定指定的地址和端口
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.bind(getBindAddress());
//等待bind操作完成
channelFuture.syncUninterruptibly();
channel = channelFuture.channel();
}
protected EventLoopGroup createBossGroup() {
return NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup(1, EVENT_LOOP_BOSS_POOL_NAME);
}
protected EventLoopGroup createWorkerGroup() {
return NettyEventLoopFactory.eventLoopGroup(
getUrl().getPositiveParameter(IO_THREADS_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_IO_THREADS),
EVENT_LOOP_WORKER_POOL_NAME
);
}
//NettyServer本身就是一个handler,它的顶级父类实现了ChannelHandler接口
//这个方法会将NettyServer自己作为参数传入NettyServerHandler之中
protected NettyServerHandler createNettyServerHandler() {
return new NettyServerHandler(getUrl(), this);
}
protected void initServerBootstrap(NettyServerHandler nettyServerHandler) {
boolean keepalive = getUrl().getParameter(KEEP_ALIVE_KEY, Boolean.FALSE);
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NettyEventLoopFactory.serverSocketChannelClass())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, Boolean.TRUE)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, keepalive)
.childOption(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//连接空闲超时时间
int idleTimeout = UrlUtils.getIdleTimeout(getUrl());
//NettyCodecAdapter中会创建Decoder和Encoder
NettyCodecAdapter adapter = new NettyCodecAdapter(getCodec(), getUrl(), NettyServer.this);
if (getUrl().getParameter(SSL_ENABLED_KEY, false)) {
ch.pipeline().addLast("negotiation", new SslServerTlsHandler(getUrl()));
}
ch.pipeline()
//注册Decoder和Encoder
.addLast("decoder", adapter.getDecoder())
.addLast("encoder", adapter.getEncoder())
//注册IdleStateHandler
.addLast("server-idle-handler", new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, idleTimeout, MILLISECONDS))
//注册NettyServerHandler
.addLast("handler", nettyServerHandler);
}
});
}
}
public class ChannelHandlers {
private static ChannelHandlers INSTANCE = new ChannelHandlers();
protected ChannelHandlers() {
}
public static ChannelHandler wrap(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
return ChannelHandlers.getInstance().wrapInternal(handler, url);
}
protected static ChannelHandlers getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
static void setTestingChannelHandlers(ChannelHandlers instance) {
INSTANCE = instance;
}
//MultiMessageHandler -> HeartbeatHandler -> AllChannelHandler -> DecodeHandler -> HeaderExchangeHandler -> DubboProtocol的requestHandler
//其中AllChannelHandler是由下面代码通过SPI获取到的自适应实现类AllDispatcher的dispatch()方法返回的
protected ChannelHandler wrapInternal(ChannelHandler handler, URL url) {
return new MultiMessageHandler(new HeartbeatHandler(url.getOrDefaultFrameworkModel().getExtensionLoader(Dispatcher.class)
.getAdaptiveExtension().dispatch(handler, url)));
}
}
public class NettyServerHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
private final URL url;
private final ChannelHandler handler;
...
//NettyServer会将自己作为参数传入NettyServerHandler的构造函数之中
public NettyServerHandler(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
}
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null");
}
this.url = url;
this.handler = handler;
}
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
//下面会调用AbstractPeer.received()方法
handler.received(channel, msg);
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractPeer implements Endpoint, ChannelHandler {
...
public void received(Channel ch, Object msg) throws RemotingException {
if (closed) {
return;
}
//这里的handler会被如下handler先后装饰
//MultiMessageHandler -> HeartbeatHandler -> AllChannelHandler -> DecodeHandler -> HeaderExchangeHandler -> DubboProtocol的requestHandler
//下面会调用MultiMessageHandler.received()方法
handler.received(ch, msg);
}
...
}
scala
public class MultiMessageHandler extends AbstractChannelHandlerDelegate {
...
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
...
//下面会执行HeartbeatHandler.received()方法
handler.received(channel, message);
}
...
}
public class HeartbeatHandler extends AbstractChannelHandlerDelegate {
...
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
//记录最近的读写事件时间戳
setReadTimestamp(channel);
if (isHeartbeatRequest(message)) {
//收到心跳请求
Request req = (Request) message;
if (req.isTwoWay()) {
//返回心跳响应,注意,携带请求的ID
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
res.setEvent(HEARTBEAT_EVENT);
channel.send(res);
...
}
return;
}
...
//下面会执行AllChannelHandler.received()方法
handler.received(channel, message);
}
...
}
public class AllChannelHandler extends WrappedChannelHandler {
...
@Override
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
//通过父类WrappedChannelHandler的方法获取线程池
ExecutorService executor = getPreferredExecutorService(message);
try {
//将消息封装成ChannelEventRunnable任务,提交到线程池中执行
executor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message));
} catch (Throwable t) {
//如果线程池满了,请求会被拒绝,这里会根据请求配置决定是否返回一个说明性的响应
if (message instanceof Request && t instanceof RejectedExecutionException){
sendFeedback(channel, (Request) message, t);
return;
}
throw new ExecutionException(message, channel, getClass() + " error when process received event .", t);
}
}
...
}
public class WrappedChannelHandler implements ChannelHandlerDelegate {
...
public ExecutorService getPreferredExecutorService(Object msg) {
if (msg instanceof Response) {
Response response = (Response) msg;
//获取请求关联的DefaultFuture
DefaultFuture responseFuture = DefaultFuture.getFuture(response.getId());
if (responseFuture == null) {
return getSharedExecutorService();
} else {
//如果请求关联了线程池,则会获取相关的线程来处理响应
ExecutorService executor = responseFuture.getExecutor();
if (executor == null || executor.isShutdown()) {
executor = getSharedExecutorService();
}
return executor;
}
} else {
//返回共享线程池
return getSharedExecutorService();
}
}
public ExecutorService getSharedExecutorService() {
if (url.getApplicationModel() == null || url.getApplicationModel().isDestroyed()) {
return GlobalResourcesRepository.getGlobalExecutorService();
}
ApplicationModel applicationModel = url.getOrDefaultApplicationModel();
//ExecutorRepository主要是负责来获取线程池的,ExecutorRepository是一个存储线程池的组件
//下面会通过ExtensionLoader,基于SPI扩展机制,去获取具体扩展实现类对象
ExecutorRepository executorRepository = applicationModel.getExtensionLoader(ExecutorRepository.class).getDefaultExtension();
//传入一个url,从url里提取一些参数出来,然后根据url参数来决定会获取到什么样的线程池
ExecutorService executor = executorRepository.getExecutor(url);
if (executor == null) {
//创建和构建线程池
executor = executorRepository.createExecutorIfAbsent(url);
}
return executor;
}
...
}
public class ChannelEventRunnable implements Runnable {
...
public void run() {
...
//接收到了请求
//比如会调用DecodeHandler.received()方法
handler.received(channel, message);
...
}
...
}
public class DecodeHandler extends AbstractChannelHandlerDelegate {
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
if (message instanceof Decodeable) {
decode(message);
}
if (message instanceof Request) {
decode(((Request) message).getData());
}
if (message instanceof Response) {
decode(((Response) message).getResult());
}
//比如会调用HeaderExchangeHandler.received()
handler.received(channel, message);
}
...
}
public class HeaderExchangeHandler implements ChannelHandlerDelegate {
...
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
//收到Request请求
if (message instanceof Request) {
//handle request.
Request request = (Request) message;
if (request.isEvent()) {
//事件类型的请求
handlerEvent(channel, request);
} else {
//非事件的请求
if (request.isTwoWay()) {//twoway
//下面会对请求进行处理
handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request);
} else {//oneway
handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData());
}
}
...
}
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException {
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
//请求解码失败
if (req.isBroken()) {
Object data = req.getData();
String msg;
if (data == null) {
msg = null;
} else if (data instanceof Throwable) {
msg = StringUtils.toString((Throwable) data);
} else {
msg = data.toString();
}
res.setErrorMessage("Fail to decode request due to: " + msg);
res.setStatus(Response.BAD_REQUEST);
//将异常响应返回给对端
channel.send(res);
return;
}
//find handler by message class.
Object msg = req.getData();
try {
//交给上层实现的ExchangeHandler进行请求处理,比如DubboProtocol的requestHandler
CompletionStage<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg);
future.whenComplete((appResult, t) -> {
//处理结束后的回调
try {
if (t == null) {//返回正常响应
res.setStatus(Response.OK);
res.setResult(appResult);
} else {//处理过程发生异常,设置异常信息和错误码
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
}
//发送响应
channel.send(res);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + e);
}
});
} catch (Throwable e) {
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e));
channel.send(res);
}
}
...
}
public class DubboProtocol extends AbstractProtocol {
...
private final ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() {
public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
...
//将客户端发过来的message转换为Invocation对象
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
//获取此次调用Invoker对象
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
...
//Provider服务端会在下面执行真正的本地实现类的调用
//比如下面会调用到FilterChainBuilder.FilterChainNode.invoke()方法
Result result = invoker.invoke(inv);
//返回结果
return result.thenApply(Function.identity());
}
...
};
...
}
public interface FilterChainBuilder {
class FilterChainNode<T, TYPE extends Invoker<T>, FILTER extends BaseFilter> implements Invoker<T> {
...
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
...
//比如Consumer端处理时下面会调用ConsumerContextFilter的invoke()方法
//Provider端处理时下面会最终调用AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke()方法
asyncResult = filter.invoke(nextNode, invocation);
...
}
}
...
}
public abstract class AbstractProxyInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
...
//当Netty Server接受到了请求后,经过解析就会知道是要调用什么
//然后会把解析出来的数据放入Invocation中
//于是可以通过AbstractProxyInvoker的invoke()方法来进行调用
@Override
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
//执行doInvoke()方法,调用业务实现
Object value = doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments());
}
...
}
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
...
@Override
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException {
try {
//下面会通过Wrapper创建一个包装类对象
//该对象是动态构建出来的,它属于Wrapper的一个子类,里面会拼接一个关键的方法invokeMethod(),拼接代码由Javassist动态生成
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
//下面会创建一个实现了AbstractProxyInvoker的匿名内部类
//其doInvoker()方法会直接委托给Wrapper对象的invokeMethod()方法
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
//当AbstractProxyInvoker.invoke()方法被调用时,便会执行到这里
//这里会通过类似于JDK反射的技术,调用本地实现类如DemoServiceImpl.sayHello()
//这个wrapper对象是由javassist技术动态生成的,已经对本地实现类进行包装
//这个动态生成的wrapper对象会通过javassist技术自己特有的方法
//在invokerMethod()方法被调用时执行本地实现类的目标方法
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
} catch (Throwable fromJavassist) {
//使用JDK的反射去调用本地,这时没有动态生成的Wrapper类了
Invoker<T> invoker = jdkProxyFactory.getInvoker(proxy, type, url);
return invoker;
}
}
...
}10.Dubbo的分层架构原理
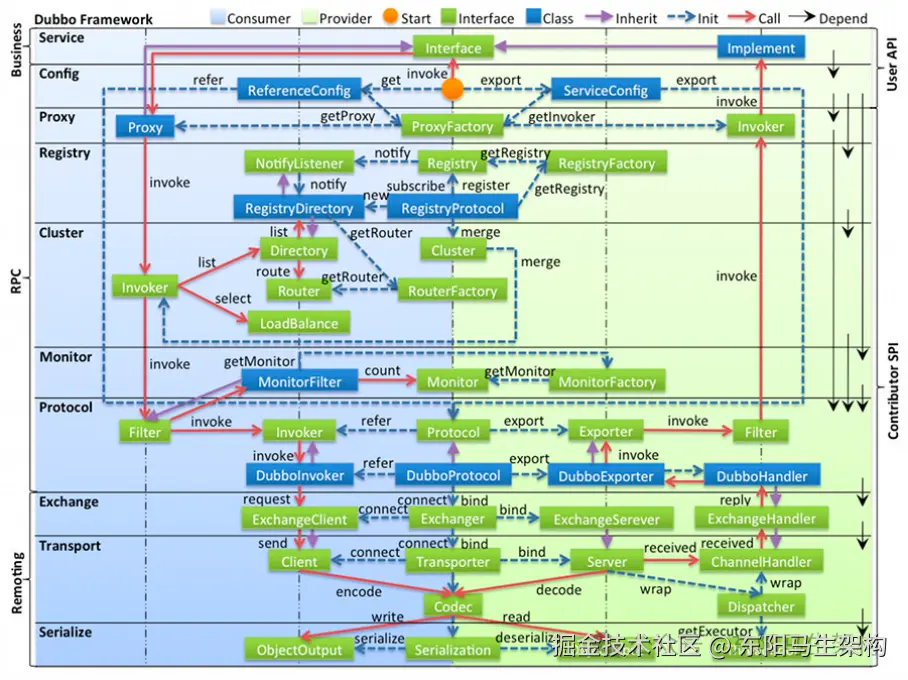
(1)架构图说明
(2)各层简单介绍
(3)各层关系说明
(1)架构图说明
说明一: 左边淡蓝色背景的为服务消费方使用的接口,右边淡绿色背景的为服务提供方使用的接口,位于中轴线上的为双方都用到的接口。
说明二: 图中从下至上分为十层,各层均为单向依赖,右边的黑色箭头代表层之间的依赖关系。每一层都可以剥离上层被复用,其中Service和Config层为API,其它各层均为SPI。
说明三: 图中绿色小块的为扩展接口,蓝色小块为实现类,图中只显示用于关联各层的实现类。
说明四: 图中蓝色虚线为初始化过程,即启动时组装链,红色实线为方法调用过程,即运行时调用链。紫色三角箭头为继承,可以把子类看作父类的同一个节点,线上的文字为调用的方法。
(2)各层简单介绍
rust
服务 -> 配置 -> 代理 -> 注册 ->
路由 -> 监控 -> 调用 ->
交换 -> 传输 -> 序列化
服配代注 路监调 交传序一.Service服务接口层
与实际业务逻辑相关的,根据服务提供方和服务消费方的业务,设计对应的接口和实现。
arduino
//Interface
//Implement二.Config配置层
对外配置接口,以ServiceConfig、ReferenceConfig为中心,可以直接new配置类,也可以通过spring解析配置生成配置类。
arduino
//ReferenceConfig
//ServiceConfig三.Proxy服务代理层
服务接口透明代理,生成服务的客户端Stub和服务器端Skeleton,以ServiceProxy为中心,扩展接口为ProxyFactory。
arduino
//Proxy
//ProxyFactory
//Invoker四.Registry注册中心层
封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务URL为中心,扩展接口为RegistryFactory、Registry、RegistryService。
arduino
//NotifyListener
//Registry
//RegistryFactory
//RegistryDirectory
//RegistryProtocol五.Cluster路由层
封装多个提供者的路由及负载均衡,并桥接注册中心。以Invoker为中心,扩展接口为Cluster、Directory、Router、LoadBalance。
arduino
//Invoker
//Directory
//LoadBalance
//Cluster
//Router
//RouterFactory六.Monitor监控层
RPC调用次数和调用时间监控,以Statistics为中心,扩展接口为MonitorFactory、Monitor、MonitorService。
arduino
//MonitorFilter
//Monitor
//MonitorFactory七.Protocol远程调用层
封装RPC调用,以Invocation、Result为中心,扩展接口为Protocol、Invoker、Exporter。
arduino
//Filter
//Invoker
//DubboInvoker
//Protocol
//DubboProtocol
//Exporter
//DubboExporter
//DubboHandler八.Exchange信息交换层
封装请求响应模式,同步转异步。以Request、Response为中心,扩展接口为Exchanger、ExchangeChannel、ExchangeClient、ExchangeServer。
arduino
//ExchangeClient
//Exchanger
//ExchangeServer
//ExchangeHandler九.Transport传输层
抽象Mina和Netty为统一接口,以message为中心,扩展接口为Channel、Transporter、Client、Server、Codec。
arduino
//Client
//Transporter
//Server
//ChannelHandler
//Codec
//Dispatcher十.Serialize数据序列化层
可复用的一些工具,扩展接口为Serialization、ObjectInput、ObjectOutput、ThreadPool。
arduino
//ObjectOutput
//Serialization
//ObjectInput
//ThreadPool(3)各层关系说明
说明一: 在RPC中,Protocol是核心层。也就是只要有Protocol+Invoker+Exporter就可以完成非透明的RPC调用,然后在Invoker的主过程上Filter拦截点。
说明二: 图中的Consumer和Provider是抽象概念,只是为了更直观呈现哪些类属于客户端和服务器端。不用Client和Server的原因是Dubbo使用Provider、Consumer、Registry、Monitor划分逻辑拓扑节点,保持概念统一。
说明三: 图中Cluster是外围概念,所以Cluster的目的是将多个Invoker伪装成一个Invoker。这样其他人只要关注Protocol层Invoker即可,Cluster的有无对其他层都不会造成影响,因为只有一个提供者时无需Cluster。
说明四: Proxy层封装了所有接口的透明化代理,而在其他层都以Invoker为中心。只有到了暴露给用户使用时,才用Proxy将Invoker转成接口,或将接口实现转成Invoker。也就是去掉Proxy层RPC是可以运行的,只是不那么透明,不那么看起来像调本地服务一样调远程服务。
说明五: Remoting实现是Dubbo协议的实现,如果选择RMI协议则整个Remoting都不会用上。Remoting内部再划分为Transport传输层和Exchange信息交换层。Transport层只负责单向消息传输,是对Mina、Netty、Grizzly的抽象,它也可以扩展UDP传输。Exchange层是在传输层之上封装了Request-Response语义。
说明六: Registry和Monitor实际上不算一层而是一个独立的节点,只是为了全局概览,用层的方式画在一起。