题⽬描述
输⼊⼀个矩阵,按照从外向⾥以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每⼀个数字,例如,如果输⼊如下4 X 4 矩阵:

则依次打印出数字 1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10 .
思路及解答
边界收缩法(推荐)
我们使⽤的是不断缩⼩矩阵上,下,左,右四个边界的⽅法。⾸先定义⼀个up (上边界为0 ), down (下边界为matrix.length - 1 ), left (左边界为0 ), right (右边界为matrix[0].length - 1 )。
从第⼀个⾏第⼀个开始打印,向左边界遍历到右边界,之后将上边界加上1 (因为已经遍历完成上边界⼀⾏),判断上边界加上⼀之后是否⼤于下边界,如果是则调出。
之后执⾏类型操作,从上到下,从右到左,从下到上。
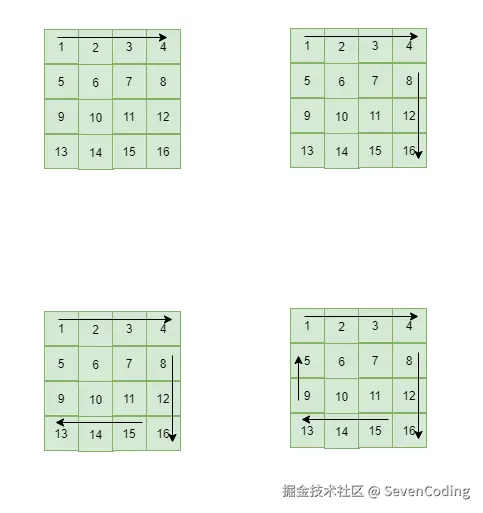
具体思路如下:
- 定义四个边界:上(up)、下(down)、左(left)、右(right)
- 按照顺时针方向遍历当前层:
- 从左到右遍历上边界
- 从上到下遍历右边界
- 从右到左遍历下边界
- 从下到上遍历左边界
- 遍历完一层后,收缩边界进入下一层
java
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> results = new ArrayList();
if (matrix != null && matrix.length > 0) {
int left = 0;
int right = matrix[0].length - 1;
int up = 0;
int down = matrix.length - 1;
int i;
while (true) {
for (i = left; i <= right; i++) {
results.add(matrix[up][i]);
}
if ((++up) > down) {
break;
}
for (i = up; i <= down; i++) {
results.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
if (--right < left) {
break;
}
for(i=right;i>=left;i--){
results.add(matrix[down][i]);
}
if(--down<up){
break;
}
for(i=down;i>=up;i--){
results.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
if(++left>right){
break;
}
}
}
return results;
}
}注意: (++up) > down 代表 up=up+1;up>dowm 两个语句。
- 时间复杂度:O(mn),每个元素被访问一次
- 空间复杂度:O(1),除了输出结果外只使用了固定数量的变量
方向模拟法
模拟顺时针移动的路径,按照右→下→左→上的方向顺序遍历:
- 定义四个方向向量表示移动方向
- 使用一个二维数组记录已访问的位置
- 当遇到边界或已访问的位置时,顺时针旋转方向
java
public List<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return result;
int rows = matrix.length, cols = matrix[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rows][cols];
int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
int directionIndex = 0;
int row = 0, col = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows * cols; i++) {
result.add(matrix[row][col]);
visited[row][col] = true;
int nextRow = row + directions[directionIndex][0];
int nextCol = col + directions[directionIndex][1];
if (nextRow < 0 || nextRow >= rows || nextCol < 0 || nextCol >= cols
|| visited[nextRow][nextCol]) {
directionIndex = (directionIndex + 1) % 4;
}
row += directions[directionIndex][0];
col += directions[directionIndex][1];
}
return result;
}- 时间复杂度:O(mn)
- 空间复杂度:O(mn),需要额外的visited数组
递归分解法
将矩阵分解为外层和内层,递归处理:
- 遍历当前矩阵的最外层
- 将剩余部分作为新矩阵递归处理
- 递归终止条件:矩阵为空或只剩一行/一列
java
public List<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return result;
spiralHelper(matrix, 0, matrix.length - 1, 0, matrix[0].length - 1, result);
return result;
}
private void spiralHelper(int[][] matrix, int top, int bottom, int left, int right, List<Integer> result) {
if (left > right || top > bottom) return;
// 遍历上边
for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) {
result.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
// 遍历右边
for (int i = top + 1; i <= bottom; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
if (top < bottom && left < right) { // 防止单行或单列
// 遍历下边
for (int i = right - 1; i >= left; i--) {
result.add(matrix[bottom][i]);
}
// 遍历左边
for (int i = bottom - 1; i > top; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
}
// 递归处理内层
spiralHelper(matrix, top + 1, bottom - 1, left + 1, right - 1, result);
}- 时间复杂度:O(mn)
- 空间复杂度:O(min(m,n)),递归栈的深度