贪心算法
贪心的本质是:选择每一阶段的局部最优,从而达到全局最优
做题的时候,只要想清楚 局部最优 是什么,如果推导出全局最优,其实就够了。
买卖股票的最佳实际
思路:如果第i天卖出股票,则最大利润为(该天的股价-前面天数中最小的股价),然后与已知的最大利润比较,如果大于则更新当前最大利润的值

java
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
// 初始化最大利润为0,最低价格为第一个价格
int maxProfit = 0;
int minPrice = 100000;
// 遍历价格数组
for (int price : prices) {
// 更新最低价格
minPrice = Math.min(minPrice, price);
// 更新最大利润
maxProfit = Math.max(maxProfit, price - minPrice);
}
return maxProfit;
}
}跳跃游戏

java
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int maxReach = 0; // 记录能到达的最远索引
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前位置 i 已经超出最大可达范围,则说明无法继续前进
if (i > maxReach) {
return false;
}
// 更新最大可达范围
maxReach = Math.max(maxReach, i + nums[i]);
// 如果最大可达范围已经超过或等于最后一个索引,则返回 true
if (maxReach >= n - 1) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}跳跃游戏Ⅱ
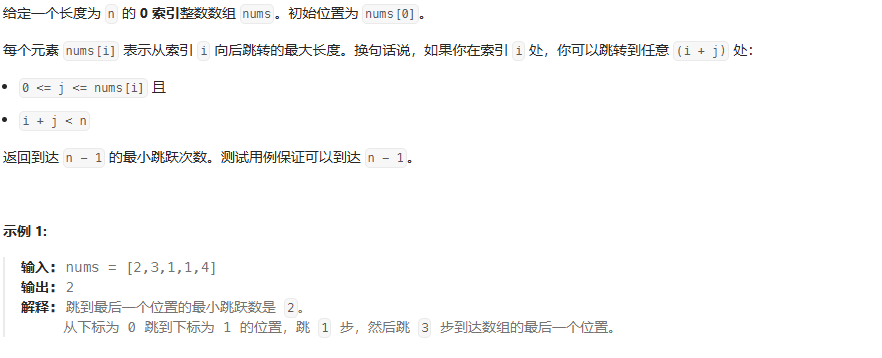
java
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int maxReach = 0;
int current = 0;
int jumps = 0;
if( nums.length == 1) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
maxReach=Math.max(i+nums[i],maxReach);
if(i == current){
jumps++;
current = maxReach;
if(current >= nums.length-1){
return jumps;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}划分字母区间

java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String S) {
char[] s = S.toCharArray();
int n = s.length;
int[] last = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
last[s[i] - 'a'] = i; // 每个字母最后出现的下标
}
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 0, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
end = Math.max(end, last[s[i] - 'a']); // 更新当前区间右端点的最大值
if (end == i) { // 当前区间合并完毕
ans.add(end - start + 1); // 区间长度加入答案
start = i + 1; // 下一个区间的左端点
}
}
return ans;
}
}矩阵
堆
数组中第K个最大元素

java
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] buckets = new int[20001];
int n = nums.length;
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
buckets[nums[i]+10000]++;
}
for(int i = 20000;i>=0;i--){
k = k - buckets[i];
if(k <= 0){
return i-10000;
}
}
return 0;
}
}栈
有效括号

java
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
//特殊情况
if(s.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
//创建栈,字符类型
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(c == '('){
stack.push(')');
}
else if(c == '{'){
stack.push('}');
}
else if(c=='['){
stack.push(']');
}
// 要先判断是否为空,再判断出栈
else if(stack.empty() || c!=stack.pop()){
return false;
}
}
if(stack.empty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}每日温度
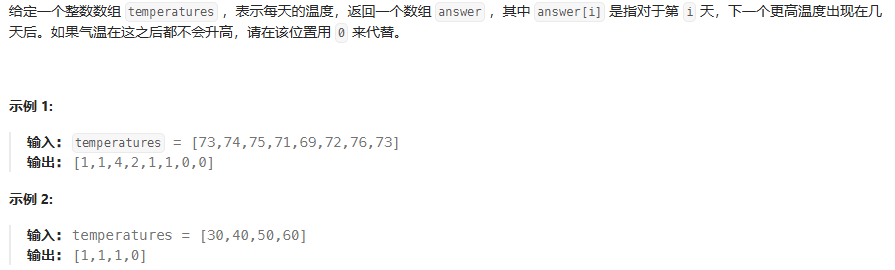
java
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.length;
int[] result = new int[n];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>(); // 单调递减栈,存索引
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 如果当前温度比栈顶索引的温度高,则计算等待天数
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
int prevIndex = stack.pop();
result[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex;
}
// 当前索引入栈
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}