1. 前言
April Tags 是一种视觉标签(类似 QR 码),用于通过相机进行定位和识别。它们通常用于计算机视觉任务中,帮助机器人识别和定位自己在物理空间中的位置,或者识别和追踪特定对象。
前提条件
-
启用 ROS 桥接:确保已经启用了 ROS 桥接插件。
-
完成"相机与变换树以及里程计"教程:已掌握相机数据、变换树以及里程计相关知识。
-
安装 apriltag-ros 包 :需要安装用于 April Tag 检测的 ROS 包。
执行以下命令来安装
apriltag-ros:sudo apt-get install ros-$ROS_DISTRO-apriltag-ros -
确保已经完成工作空间的
source操作。
2. 检测 April Tags
-
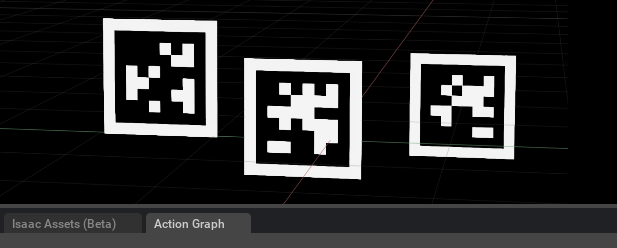
打开 April Tag 示例 :在 Isaac Sim 中,进入 Isaac Examples → ROS → April Tag。这时视口中会显示出三个 April Tags。
-
查看 Stage Tree 和打开 Action Graph:
-
打开 Stage Tree,找到场景中的相关对象。
-
右键点击目标对象,然后选择 Open Graph 。此时,Action Graph 将打开,其中应该已自动设置 ROS 时钟发布器、TF 发布器和相机助手节点(用于初始化
camera_info和rgb图像发布器)。
-
-
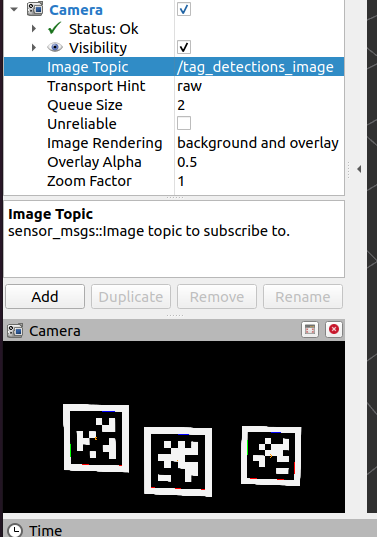
开始仿真 :点击 Play 按钮,开始向 ROS 发布数据。此时,April Tags 的数据会通过 ROS 被传输,你可以在 RViz 或其他 ROS 工具中查看检测到的标签。
在一个新的已 source ROS 环境的终端中,运行以下命令启动 AprilTag 检测节点:
roslaunch isaac_tutorials apriltag_continuous_detection.launch这将启动一个 ROS 节点,持续检测场景中的 AprilTags。节点会从相机图像中提取标签信息并准备好进行后续处理。
在另一个已 source ROS 环境的终端中,运行以下命令来启动 RViz,并加载 AprilTag 的配置文件,以便可视化检测到的标签:
rviz -d <noetic_ws>/src/isaac_tutorials/rviz/apriltag_config.rviz选项指定了 RViz 使用的配置文件。该配置文件包括显示相机图像和标记位置的设置。启动后,你应该能在 RViz 中看到从相机捕获的图像,以及检测到的 AprilTags 及其位置信息。
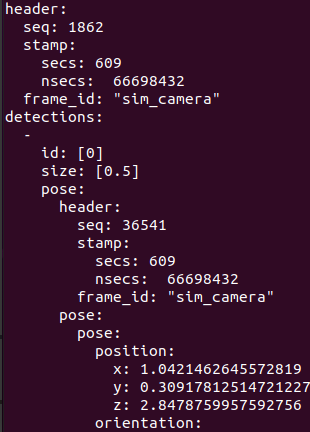
为了查看检测到的原始标签数据,可以运行以下命令,订阅并打印 /tag_detections 话题:
rostopic echo /tag_detections这将显示检测到的 AprilTag 数据,包括标签的 ID、位置、姿态等信息,通常以 geometry_msgs/PoseStamped 消息格式呈现。
3. 给相机添加噪声
学习目标
在本示例中,我们将:
-
简要介绍如何为传感器图像添加增强(augmentation)。
-
发布带有噪声的图像数据。
1. 在一个终端中,运行以下命令来启动带有噪声增强的相机脚本:
./python.sh standalone_examples/api/omni.isaac.ros_bridge/camera_noise.py当场景加载完成后,你应该会看到视口中的一个仓库场景,它会逆时针旋转。
2. 启动 RViz 并查看图像数据
在一个新的终端中,source ROS 环境并运行 RViz:
3. 在 RViz 中添加图像显示窗口
-
在 RViz 窗口的左下角点击 Add,打开弹出的窗口。
-
在 By display type 选项卡下选择 Image ,然后点击 OK。
此时,RViz 窗口中会出现一个新的图像显示窗口,并且在 Display 菜单中会有一个标记为 Image 的菜单项。你可以将该图像窗口拖动到一个合适的位置。
4.配置图像显示话题
展开 Image 菜单,并将 Image Topic 设置为 /rgb_augmented。这时,你应该能在 RViz 中看到 Isaac Sim 中稍微带噪声的图像版本。

5. 代码解释
1. 设置相机路径
首先,我们设置一个相机在我们想要捕获数据的渲染产品上。可以使用 API 来设置视口中的相机,或者使用更底层的 API,直接操作渲染产品的 prim(这会直接影响渲染设置)。这两种方法都可以达到相同的目的。为了演示,我们使用 set_camera_prim_path,因为我们已经在处理渲染产品的路径。
python
# 获取当前视口的渲染产品路径
render_product_path = get_active_viewport().get_render_product_path()
# 使用渲染产品路径设置相机路径
set_camera_prim_path(render_product_path, CAMERA_STAGE_PATH)2. 定义图像增强
在传感器中有几种方式来定义增强(augmentation)。增强可以通过不同的方式实现,常见的有:
-
C++ OmniGraph 节点
-
Python OmniGraph 节点
-
omni.warp核心 -
numpy核心
接下来,我们用 numpy 和 omni.warp 核心来定义一个简单的噪声函数。为了简化,这里没有做颜色值的越界检查。
GPU 噪声核心(使用 omni.warp)
python
# GPU 噪声核,用于生成高斯噪声
@wp.kernel
def image_gaussian_noise_warp(
data_in: wp.array(dtype=wp.uint8, ndim=3), # 输入数据(图像)
data_out: wp.array(dtype=wp.uint8, ndim=3), # 输出数据(带噪声的图像)
seed: int, # 随机种子
sigma: float = 25.0, # 噪声强度(标准差)
):
i, j = wp.tid()
state = wp.rand_init(seed, wp.tid())
# 为每个像素通道添加高斯噪声
data_out[i, j, 0] = wp.uint8(wp.int32(data_in[i, j, 0]) + wp.int32(sigma * wp.randn(state)))
data_out[i, j, 1] = wp.uint8(wp.int32(data_in[i, j, 1]) + wp.int32(sigma * wp.randn(state)))
data_out[i, j, 2] = wp.uint8(wp.int32(data_in[i, j, 2]) + wp.int32(sigma * wp.randn(state)))CPU 噪声核心(使用 numpy):
python
# CPU 噪声核,用于生成高斯噪声
def image_gaussian_noise_np(data_in: np.ndarray, seed: int, sigma: float = 25.0):
np.random.seed(seed)
# 通过 numpy 为输入图像添加高斯噪声
return data_in + sigma * np.random.randn(*data_in.shape)3. 定义图像增强操作
我们使用 rep.Augmentation.from_function() 来定义一个图像增强操作。在这个例子中,我们增强的是图像的输出,将 IsaacConvertRGBAToRGB 注释器的结果(将 RGBA 转换为 RGB)与噪声增强结合起来。
python
# 获取 RGB 数据的渲染变量名
rv_rgb = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar(sd.SensorType.Rgb.name)
# 获取 RGBA 到 RGB 的转换注释器
rgba_to_rgb_annotator = f"{rv_rgb}IsaacConvertRGBAToRGB"
# 注册新的增强注释器,添加噪声
rep.annotators.register(
name="rgb_gaussian_noise", # 增强的名称
annotator=rep.annotators.augment_compose(
source_annotator=rgba_to_rgb_annotator, # 使用已有的 RGBA 到 RGB 转换注释器
augmentations=[rep.Augmentation.from_function(image_gaussian_noise_warp, seed=1234, sigma=25)], # 使用噪声增强
),
)Augmentation.from_function():
-
这是用来从函数创建一个增强操作的方式,
image_gaussian_noise_warp或image_gaussian_noise_np就是传递的增强函数。 -
seed参数用于初始化随机数生成器,以确保噪声可以重复生成。它还与节点标识符结合,生成唯一的种子值。
4. 使用增强注释器并将其附加到 ROS 发布器
最终,我们替换现有的 IsaacConvertRGBAToRGB 注释器,使用新的带噪声的 rgb_gaussian_noise 注释器。然后,我们初始化 ROS 发布器并将其附加到渲染产品路径上,以开始捕获并发布数据。
python
# 替换现有的 IsaacConvertRGBAToRGB 注释器,使用带噪声的 rgb_gaussian_noise 注释器
writer = rep.writers.get(f"{rv_rgb}" + "ROS1PublishImage")
writer.annotators[0] = "rgb_gaussian_noise"
writer.initialize(topicName="rgb_augmented", frameId="sim_camera")
writer.attach([render_product_path]) # 附加到渲染产品路径4. 发布相机数据
为了开始本教程,我们首先设置一个包含 omni.isaac.sensor.Camera 对象的环境。运行以下代码会加载一个简单的仓库环境,并在场景中放置一个相机。
运行以下脚本:
python
import carb
from isaacsim import SimulationApp
import sys
BACKGROUND_STAGE_PATH = "/background"
BACKGROUND_USD_PATH = "/Isaac/Environments/Simple_Warehouse/warehouse_with_forklifts.usd"
CONFIG = {"renderer": "RayTracedLighting", "headless": False}
simulation_app = SimulationApp(CONFIG)
import omni
import numpy as np
import omni.graph.core as og
import omni.replicator.core as rep
import omni.syntheticdata._syntheticdata as sd
from omni.isaac.core import SimulationContext
from omni.isaac.core.utils import stage, extensions, nucleus
from omni.isaac.sensor import Camera
import omni.isaac.core.utils.numpy.rotations as rot_utils
from omni.isaac.core.utils.prims import is_prim_path_valid
from omni.isaac.core_nodes.scripts.utils import set_target_prims
# 启用 ROS 桥接扩展
extensions.enable_extension("omni.isaac.ros_bridge")
simulation_app.update()
# 检查 rosmaster 节点是否正在运行
import rosgraph
if not rosgraph.is_master_online():
carb.log_error("Please run roscore before executing this script")
simulation_app.close()
exit()
simulation_context = SimulationContext(stage_units_in_meters=1.0)
# 查找 Isaac Sim 资产文件夹并加载环境和机器人场景
assets_root_path = nucleus.get_assets_root_path()
if assets_root_path is None:
carb.log_error("Could not find Isaac Sim assets folder")
simulation_app.close()
sys.exit()
# 加载环境
stage.add_reference_to_stage(assets_root_path + BACKGROUND_USD_PATH, BACKGROUND_STAGE_PATH)
###### 相机辅助函数 ########
# 这里应该粘贴教程中的函数
def publish_camera_tf(camera: Camera):
camera_prim = camera.prim_path
if not is_prim_path_valid(camera_prim):
raise ValueError(f"Camera path '{camera_prim}' is invalid.")
try:
# Generate the camera_frame_id. OmniActionGraph will use the last part of
# the full camera prim path as the frame name, so we will extract it here
# and use it for the pointcloud frame_id.
camera_frame_id=camera_prim.split("/")[-1]
# Generate an action graph associated with camera TF publishing.
ros_camera_graph_path = "/CameraTFActionGraph"
# If a camera graph is not found, create a new one.
if not is_prim_path_valid(ros_camera_graph_path):
(ros_camera_graph, _, _, _) = og.Controller.edit(
{
"graph_path": ros_camera_graph_path,
"evaluator_name": "execution",
"pipeline_stage": og.GraphPipelineStage.GRAPH_PIPELINE_STAGE_SIMULATION,
},
{
og.Controller.Keys.CREATE_NODES: [
("OnTick", "omni.graph.action.OnTick"),
("IsaacClock", "omni.isaac.core_nodes.IsaacReadSimulationTime"),
("RosPublisher", "omni.isaac.ros_bridge.ROS1PublishClock"),
],
og.Controller.Keys.CONNECT: [
("OnTick.outputs:tick", "RosPublisher.inputs:execIn"),
("IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime", "RosPublisher.inputs:timeStamp"),
]
}
)
# Generate 2 nodes associated with each camera: TF from world to ROS camera convention, and world frame.
og.Controller.edit(
ros_camera_graph_path,
{
og.Controller.Keys.CREATE_NODES: [
("PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id, "omni.isaac.ros_bridge.ROS1PublishTransformTree"),
("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world", "omni.isaac.ros_bridge.ROS1PublishRawTransformTree"),
],
og.Controller.Keys.SET_VALUES: [
("PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:topicName", "/tf"),
# Note if topic_name is changed to something else besides "/tf",
# it will not be captured by the ROS tf broadcaster.
("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:topicName", "/tf"),
("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:parentFrameId", camera_frame_id),
("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:childFrameId", camera_frame_id+"_world"),
# Static transform from ROS camera convention to world (+Z up, +X forward) convention:
("PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:rotation", [0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5]),
],
og.Controller.Keys.CONNECT: [
(ros_camera_graph_path+"/OnTick.outputs:tick",
"PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:execIn"),
(ros_camera_graph_path+"/OnTick.outputs:tick",
"PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:execIn"),
(ros_camera_graph_path+"/IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime",
"PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id+".inputs:timeStamp"),
(ros_camera_graph_path+"/IsaacClock.outputs:simulationTime",
"PublishRawTF_"+camera_frame_id+"_world.inputs:timeStamp"),
],
},
)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
# Add target prims for the USD pose. All other frames are static.
set_target_prims(
primPath=ros_camera_graph_path+"/PublishTF_"+camera_frame_id,
inputName="inputs:targetPrims",
targetPrimPaths=[camera_prim],
)
return
def publish_camera_info(camera: Camera, freq):
# The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name.
render_product = camera._render_product_path
step_size = int(60/freq)
topic_name = camera.name+"_camera_info"
queue_size = 1
node_namespace = ""
frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing.
stereo_offset = [0.0, 0.0]
writer = rep.writers.get("ROS1PublishCameraInfo")
writer.initialize(
frameId=frame_id,
nodeNamespace=node_namespace,
queueSize=queue_size,
topicName=topic_name,
stereoOffset=stereo_offset,
)
writer.attach([render_product])
gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path(
"PostProcessDispatch" + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product
)
# Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate
og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size)
return
def publish_pointcloud_from_depth(camera: Camera, freq):
# The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name.
render_product = camera._render_product_path
step_size = int(60/freq)
topic_name = camera.name+"_pointcloud" # Set topic name to the camera's name
queue_size = 1
node_namespace = ""
frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing.
# Note, this pointcloud publisher will simply convert the Depth image to a pointcloud using the Camera intrinsics.
# This pointcloud generation method does not support semantic labelled objects.
rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar(
sd.SensorType.DistanceToImagePlane.name
)
writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS1PublishPointCloud")
writer.initialize(
frameId=frame_id,
nodeNamespace=node_namespace,
queueSize=queue_size,
topicName=topic_name
)
writer.attach([render_product])
# Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate
gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path(
rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product
)
og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size)
return
def publish_depth(camera: Camera, freq):
# The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name.
render_product = camera._render_product_path
step_size = int(60/freq)
topic_name = camera.name+"_depth"
queue_size = 1
node_namespace = ""
frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing.
rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar(
sd.SensorType.DistanceToImagePlane.name
)
writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS1PublishImage")
writer.initialize(
frameId=frame_id,
nodeNamespace=node_namespace,
queueSize=queue_size,
topicName=topic_name
)
writer.attach([render_product])
# Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate
gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path(
rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product
)
og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size)
return
def publish_rgb(camera: Camera, freq):
# The following code will link the camera's render product and publish the data to the specified topic name.
render_product = camera._render_product_path
step_size = int(60/freq)
topic_name = camera.name+"_rgb"
queue_size = 1
node_namespace = ""
frame_id = camera.prim_path.split("/")[-1] # This matches what the TF tree is publishing.
rv = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData.convert_sensor_type_to_rendervar(sd.SensorType.Rgb.name)
writer = rep.writers.get(rv + "ROS1PublishImage")
writer.initialize(
frameId=frame_id,
nodeNamespace=node_namespace,
queueSize=queue_size,
topicName=topic_name
)
writer.attach([render_product])
# Set step input of the Isaac Simulation Gate nodes upstream of ROS publishers to control their execution rate
gate_path = omni.syntheticdata.SyntheticData._get_node_path(
rv + "IsaacSimulationGate", render_product
)
og.Controller.attribute(gate_path + ".inputs:step").set(step_size)
return
###################################################################
# 创建相机实例。注意,Camera 类接受位置和方向的世界轴约定。
camera = Camera(
prim_path="/World/floating_camera",
position=np.array([-3.11, -1.87, 1.0]),
frequency=20,
resolution=(256, 256),
orientation=rot_utils.euler_angles_to_quats(np.array([0, 0, 0]), degrees=True),
)
camera.initialize()
simulation_app.update()
camera.initialize()
############### 调用相机发布函数 ###############
# 调用发布器函数。
# 确保你已经粘贴了上面定义的辅助函数,并取消注释以下行再运行。
approx_freq = 30
publish_camera_tf(camera)
publish_camera_info(camera, approx_freq)
publish_rgb(camera, approx_freq)
publish_depth(camera, approx_freq)
publish_pointcloud_from_depth(camera, approx_freq)
####################################################################
# 初始化物理引擎
simulation_context.initialize_physics()
# 开始仿真
simulation_context.play()
while simulation_app.is_running():
simulation_context.step(render=True)
simulation_context.stop()
simulation_app.close()